This is what atrial fibrillation is called in translation from Latin. This is one of the forms of heart rhythm disturbances, which is based on a disorder of the atria. Atrial fibrillation is a fairly widespread disease these days.
We talk about the features of this cardiac pathology with Elena Gennadievna Nikulina, a cardiologist at the regional cardiac clinic.
— TV presenter of a popular health program Elena Malysheva called atrial fibrillation a deadly disease. Why?
— Elena Malysheva outlined a very important problem in one general phrase, but, in my opinion, she exaggerated the colors somewhat. If our patients (and there are many thousands of them in the region, and citizens with coronary heart disease account for approximately 10-14 percent of cases of atrial fibrillation) are told that atrial fibrillation is a deadly disease, imagine how many people will consider themselves hopelessly ill. But this is absolutely not true.
Yes, atrial fibrillation is associated with an abnormal heart rhythm. This is caused by the fact that the chambers of the heart contract incorrectly, while blood is not released to the periphery to other organs in full. The blood supply to the heart is disrupted. There are many complications of atrial fibrillation, but today’s medicine is able to treat, correct and prevent both the pathology itself and its complications, so patients with atrial fibrillation live for many, many years. And it, like some others, becomes fatal only when nothing is done to treat the disease.
— Can atrial fibrillation lead to a stroke?
- Yes maybe. Among all thromboembolic complications, this is the most common - strokes account for 91% of all types of thromboembolism. Unfortunately, such strokes can be extensive and lead to serious consequences. But, I repeat, provided that the patient is not observed by a cardiologist and does not carry out therapeutic measures. Brain stroke and myocardial infarction occur because atrial fibrillation causes improper emptying of the heart chambers. There is stagnation of blood, and where there is stagnation, the ability to form blood clots increases. And these blood clots can shoot, including into the vessels of the brain or coronary arteries. With timely and correct treatment, patients with atrial fibrillation live a long time. Recommended regimens usually include two- or three-component drugs, including anticoagulants, that is, blood thinners, and together they all affect the various phases of thrombus formation.
— Why does such arrhythmia occur?
— There are many reasons for the occurrence of atrial fibrillation. The fact is that with this pathology, the normal (that is, sinus) heart rhythm is disrupted and the heart can no longer effectively pump out blood. The atria, instead of working synchronously, only randomly twitch, flutter, and flicker. The ventricles also contract irregularly and more frequently. Erratic contraction of the atria and ventricles is called atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation.
With age, it is diagnosed more and more often: if at 40-50 years of age, atrial fibrillation occurs in approximately 1% of the population, then among people over 60 years of age - in 5%, and after 80 years of age, about 10% of the population already suffers from it. This is due to the fact that in old age, hardening of the walls of the heart and coronary arteries is observed, and coronary heart disease (CHD) develops. Ischemia, as well as its complications - myocardial infarction, often causes atrial fibrillation.
But the most common cause of atrial fibrillation in older people is arterial hypertension. Increased pressure causes stretching of the chambers of the heart and atria, which leads to rhythm disturbances. As well as acquired and congenital heart defects. There are other reasons too. For example, increased thyroid function (thyrotoxicosis) or alcohol abuse. The influence of heredity is noted. But there is no generally accepted theory that would explain the mechanism of development of atrial fibrillation.
— What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
- They can be very diverse. Some patients do not feel any discomfort, and their rhythm disturbance is detected by the results of an electrocardiogram (ECG) only by chance. And for others, in addition to frequent irregular contractions, when the pulse can reach 200 beats per minute, shortness of breath, causeless fatigue, weakness, even fainting appear. There may be dizziness, a feeling of anxiety, restlessness, chest pain, a sharp decrease in blood pressure and other unpleasant symptoms. Atrial fibrillation can appear in attacks, and then they speak of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. But atrial fibrillation can also be idiopathic, that is, of unknown origin.
In any case, with atrial fibrillation, the risk of ischemic stroke increases 7 times!
— Is this disease acquired or could it be congenital?
— Congenital atrial fibrillation, as a rule, does not occur; it is an acquired pathology. It mainly manifests itself in people after forty years of age; the incidence of coronary heart disease and hypertension peaks at this age.
- Who is more susceptible - men or women?
- Same.
— Is there prevention?
— This is treatment of the underlying disease, and the most important prevention, if you have been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, you need to prevent its complications: fight thromboembolic complications
It is also extremely important to take care of the prevention of those diseases that provoke the development of atrial fibrillation. And above all, as we have already said, arterial hypertension and coronary heart disease. Of course, alcohol abuse should not be allowed.
* * *
Treatment of heart rhythm disorders
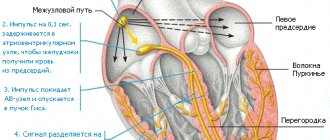
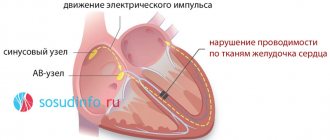
Our heart supplies the entire body with blood, delivering nutrients to every cell. Periodically contracting, the heart moves blood flow through the vessels, and these contractions occur due to electrical impulses appearing directly in the heart.
In a healthy person, such impulses occur at specific time intervals. When this electrical system malfunctions, the heart contracts irregularly. It is this disorder of the heart rhythm that is called arrhythmia. methods for cardiac arrhythmias are different and largely depend on its type (cause of occurrence).
This deviation can occur for various reasons, but there are cases when it is not possible to determine the root cause of the heart rhythm disturbance. In addition, the manifestation of arrhythmia may be a symptom of another disease or be considered as a separate type of disease.
Sometimes a person does not even realize that he has a heart rhythm disorder, i.e. the disease does not manifest itself in any way or these manifestations are minimal. But in most cases, the patient feels the occurrence of arrhythmia. Symptoms may include a rapid or slow heartbeat, along with a feeling of fatigue, sudden weakness, shallow breathing and chest pain.
When the arrhythmia continues for several hours or additional complications appear, you need to urgently seek medical help. In any case, a trip to the cardiology department will not hurt.
Methods for treating heart rhythm disorders
Treatment of heart rhythm disorders and methods for detecting them are constantly being improved.
To identify the causes of arrhythmia, the doctor will order an ECG (electrocardiogram). It is also necessary to do an ECG-atropine test, when you are injected into a vein with atropine, which changes the regulation of heart rhythm. An ECG during exercise and an ultrasound of the heart may also be prescribed.
Treatment of heart rhythm disorders is carried out in different ways. Your doctor may simply prescribe certain medications to normalize your rhythm if your arrhythmia is not associated with another cardiovascular disease.
In case of serious anatomical abnormalities of the conduction system, surgical procedures (implantation of a cardiac cardioverter-defibrillator) are necessary. It happens that treatment of cardiac arrhythmia is simply not necessary, because it may go away on its own over time. All studies and treatment process are discussed with the doctor.
New information about arrhythmia is constantly emerging. Therefore, detection and treatment of heart rhythm disorders has become more accessible, and the use of timely measures improves the quality and length of life.
Arrhythmia attacks can be prevented if you know that they occur during increased solar activity (magnetic storms). During this time, try to follow the recommendations of doctors and carry the medicine with you.
Please do not self-medicate!
Remember, only a doctor can determine the diagnosis and correctly prescribe treatment.
How to treat atrial fibrillation
There are 2 generally accepted treatment strategies for patients with symptoms of atrial fibrillation. The first is the restoration and maintenance of normal sinus rhythm of the heart. The second is a decrease in the frequency of contractions of the ventricles of the heart, that is, atrial fibrillation remains, but becomes less intense (within 80–100 beats per minute), and the patient does not feel it.
1. Camm AJ, Kirchhof P., Gregory YH at al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2010 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation-executive summary // Eur. Heart J. – 2010. – Vol. 31. – P. 2369-2429.
Numerous clinical studies have shown that the strategic goal of maintaining sinus rhythm does not provide advantages over a hands-off approach during AF other than attempts to limit (control) the ventricular rate of the heart. Tighter heart rate control also had no additional effect.
It turns out that with proper treatment, diet and proper physical training with the symptoms of atrial fibrillation, you can live happily ever after? This is almost true, if not for the high risk of stroke.
2. Hylek EM, Go AS, Chang Y., et al. Effect of intensity of oral anticoagulation on stroke severity and mortality in atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2003; 349:1019–1026.
Research results indicate that only antithrombotic therapy (one of the most optimal methods of blood thinning) causes a decrease in mortality associated with atrial fibrillation.
What to drink to thin your blood?
To prevent stroke, anticoagulant blood thinners are prescribed. They are indicated for almost 90% of patients with signs of atrial fibrillation, regardless of the stage of the disease. However, anticoagulants should be taken with caution: if used incorrectly, they can reduce blood clotting and provoke bleeding. Anticoagulant therapy should be accompanied by careful monitoring of the blood coagulation system using INR determination. This stops many people from taking anticoagulants for a long time.
Rice. 1. Insufficient frequency of warfarin prescription
As an additional therapy, in addition to medications, in the early stages of the disease or with mild symptoms, on the recommendation of a doctor, treatment of atrial fibrillation with folk remedies can be used, which helps thin the blood and strengthens the heart. Basically, folk treatment is herbal medicine: a decoction of hawthorn or viburnum berries, an infusion of yarrow, a decoction of dill seeds.
So what do you need to thin your blood?
“The study results demonstrated that when treating atrial fibrillation, antithrombotic therapy alone was associated with a reduction in mortality.”
The decision on the advisability of eliminating atrial fibrillation should be made by the attending physician. This largely depends on the form of the arrhythmia, the cause of its occurrence, the disease against which it arose and on the effectiveness of the previously prescribed drug treatment for atrial fibrillation.
Figure 1. Warfarin reduces the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation (based on Hart et al., 2007)
Despite the fact that the paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation most often goes away on its own within a few hours or days, it is usually sought to be eliminated with the help of antiarrhythmic drugs.
If the paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation lasts more than 2 days, before eliminating it, it is necessary to carry out prophylaxis with drugs that reduce blood clotting. This is necessary to prevent the occurrence of thromboembolism at the time of restoration of normal sinus rhythm or in the first hours after elimination of the arrhythmia.
With a permanent form of atrial fibrillation, the attending physician can choose both tactics for eliminating atrial fibrillation and tactics for preserving it. In any case, this can only be done after long-term (3-4 weeks) use of drugs that reduce blood clotting. In addition, these drugs should be taken for at least 1 month after the permanent form of atrial fibrillation has been eliminated.
Heart is pounding
It is clear that with each heartbeat there is a sequential contraction of its parts - first the atria, and then the ventricles. Only such alternation ensures efficient functioning of the heart. With arrhythmia, which has received the wonderful name “atrial fibrillation,” one of the phases of the cardiac cycle is lost, and specifically, atrial contraction. Their muscle fibers lose the ability to work synchronously. As a result, the atria only twitch chaotically - flicker. As a result, the ventricles begin to contract irregularly.
Why does atrial fibrillation appear?
In young people, the cause of arrhythmia is often mitral valve prolapse, in other words, sagging, weakness of one of the valve leaflets between the left atrium and the left ventricle. This pathology usually occurs in secret and is detected by chance. Atrial fibrillation may be its first manifestation. But not only an unhealthy heart is the cause of arrhythmia. A variety of diseases can give it a start. And not just diseases.
Very often, an attack of atrial fibrillation is provoked by drinking more alcohol than usual. There is even such a concept - “cardiac arrhythmia of special days.” Any day you can expect the occurrence of arrhythmia in people with diseases of the thyroid gland (especially with its excess function) and some other hormonal disorders.
Arrhythmia often develops after surgery, a heart attack, or various stresses. Its development can be stimulated by rich food, constipation, tight clothing, insect bites, and certain medications. For example, taking diuretics for the purpose of losing weight often lands “your own doctor” in a hospital bed. There is a high risk of developing atrial fibrillation in people with diabetes, especially if diabetes is combined with obesity and high blood pressure. In general, doctors are not always able to find the cause of arrhythmia.
How to find out about the onset of the disease? It is indicated, for example, by palpitations, when the heart is pounding so much that it seems like it is about to jump out of the chest. There may be a feeling of interruptions in the heart. “It will knock, knock, and suddenly freeze” or “something will turn inside,” this is how patients describe their condition. But often the arrhythmia proceeds unnoticed. Only by feeling the pulse can you establish the irregularity of heart contractions. Often the disease is detected only during a clinical examination using an ECG. But it can be even worse: the first manifestations of the disease are burdens.
Why is atrial fibrillation generally unsafe?
It is often accompanied by tachycardia, in other words, an increase in heart rate. With all this, a colossal load falls on the heart. As a result, chest pain may appear - symptoms of angina pectoris or even myocardial infarction. Arrhythmia may reduce the efficiency of the heart. This will lead to another burden - cardiac failure. With all this, the person feels suffocated, it seems to him that there is not enough air.
Can arrhythmia go away on its own?
In principle, it can. But if the arrhythmia persists for several hours or complications appear, you must immediately seek medical help. In general, even if the arrhythmia disappears on its own, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor. Repeated rhythm disturbance can occur at any time and end catastrophically. Therefore, self-medication will not help enough.
As a good song says: “No matter how much you cure your heart with validol, there are still continuous interruptions.” The fact is that it is best to restore the normal rhythm on the first day from the onset of arrhythmia. It is possible to eliminate arrhythmia later than this period, but then additional preparation will be needed. For atrial fibrillation
Read similar things about medicine
Can arrhythmia go away on its own?
In principle, it can. But if the arrhythmia persists for several hours or complications arise, you should immediately seek medical help. However, even if the arrhythmia disappears on its own, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor. Repeated rhythm disturbance can occur at any time and end tragically. Therefore, self-medication will not help much.
As a good song says: “No matter how much you treat your heart with validol, there are still continuous interruptions.” The fact is that restoration of normal rhythm is best done on the first day from the onset of arrhythmia. It is possible to eliminate arrhythmia later than this period, but then additional preparation will be required. With atrial fibrillation, when the atria do not contract normally, the blood flow in them sharply slows down and therefore blood clots - thrombi - form. This occurs on the second day after the onset of arrhythmia. When the normal rhythm is restored and the atria begin to contract, fragments of blood clots can break off and clog the vessels of any organ. Usually blood clots float into the vessels of the brain. And this leads to a stroke.
That is why anyone who consults a doctor more than 24-48 hours after the onset of arrhythmia is prescribed drugs that slow down blood clotting. Only when the effect is obtained, and this is in about 1-2 weeks, is it possible to restore the rhythm.
Atrial fibrillation
Sometimes it happens that a person’s heart is pounding very, very hard in his chest, beating like a bird in cages. And sometimes it beats and then becomes silent for a while. From a medical point of view, this phenomenon is called cardiac arrhythmia, as a result of which the movements of the heart muscle are disrupted from the desired rhythm. There are different types of arrhythmia, but atrial fibrillation is especially common.
It has been established that each heartbeat represents a gradual contraction of the muscles of various parts. This begins with contraction of the atria, after which the muscles of the ventricles contract. Only this sequence represents the correct functioning of the heart. If a person suffers from an arrhythmia with the interesting name “atrial fibrillation,” then one stage of the sequence disappears, or rather, atrial contraction is not observed. The muscles of these parts of the heart gradually lose the ability to move coherently, so the atria make some chaotic contractions, as they say, flicker. This rhythm disturbance also causes a disruption in the cyclicity of ventricular contraction.
Causes of atrial fibrillation
A large number of causes have been identified that cause atrial fibrillation. First of all, we should mention all kinds of heart diseases, such as heart defects, heart failure, coronary heart disease, infectious heart damage and myocardial infarction.
Excessive alcohol consumption can also be considered a cause of atrial fibrillation. They even use such a concept as “holiday arrhythmia.” Regardless of the calendar, attacks of arrhythmia can occur in people suffering from thyroid diseases, in particular with its increased function, as well as other hormonal imbalances.
It is not uncommon for arrhythmia to occur in people who have suffered a stroke, stressful situations or surgery. Taking certain medications is also a risk factor in this case. There is an observation that when using diuretics for the purpose of weight loss, the self-medicating person is sent straight to hospital for treatment. There is a very high risk of developing arrhythmia in diabetics, especially if there are complications such as obesity with hypertension. There is also a genetic predisposition to the manifestation of atrial fibrillation, transmitted from parents to children. In fairness, it should be noted that very rarely doctors are able to accurately and reliably determine the causes of the disease.
It is very important to recognize the appearance of atrial fibrillation in time. Symptoms include unusual heartbeats, in which the heart feels like it’s about to burst out of the chest. Even the person himself feels a disturbance in the rhythm of the heartbeat. Most often, arrhythmia develops unnoticed by the patient. Only feeling the pulse can help determine the presence of an abnormal heart rhythm. Very often, atrial fibrillation is determined by the results of an examination performed in a hospital using an ECG. In the worst case, the presence of atrial fibrillation is revealed by the complications that appear.
The danger of this disease is that it is often accompanied by tachycardia, the so-called increase in the frequency of repetitions of the cardiac cycle. In such conditions, the heart experiences a very heavy load, which is dangerous for its health. This can lead to chest pain, which is a sign of a heart attack or angina. Arrhythmia leads to a deterioration in the efficiency of the heart, and as a result, heart failure.
Arrhythmia can be a temporary phenomenon as a reaction of the body to certain influences or stress. In this case, it may go away over time. However, if the arrhythmia persists for more than a few hours or if any complications occur, you should immediately contact a specialist. Even if the arrhythmia goes away without medical intervention, it is also necessary to consult a doctor. An attack of arrhythmia can recur at any time, and this can lead to health problems and can even become a threat to life. That is why you should not get carried away with self-medication.
Treatment of arrhythmia is most effective within the first 24 hours from its onset. It will be possible to get rid of arrhythmia later, but this will require additional preparatory measures. Atrial fibrillation is a cessation of contraction of the atrium muscles, as a result of which blood flows through them at a lower speed, forming blood clots, the so-called accumulations of clotted blood. Blood clots form already on the second day of arrhythmia manifestation. If normal heart rhythm is restored, the atrial muscles begin to work properly again, and some of the blood clots can penetrate the vessels of the internal organs and clog the lumen. Most often, blood clots penetrate the blood vessels of the brain, resulting in a possible stroke.
Due to this danger, if a patient seeks medical help after 24-48 hours from the onset of arrhythmia, it is necessary to take special medications that slow down the blood clotting process. It will be possible to resolve the issue of restoring heart rhythm only after the start of the action of the above-described drugs after approximately 1-2 weeks of taking them.
Heart rate restoration
Often, restoration of heart rhythm is carried out using special antiarrhythmic drugs. To obtain the effect, they should be used intravenously. In some cases, the patient can take medications in the form of tablets, which are pre-selected by the doctor to prevent an attack of atrial fibrillation. At the moment, no special indicators have been identified, the analysis of which would determine the dosage form that is more effective. During the treatment process, it becomes necessary to test different drugs in order to find the optimal solution for a particular patient.
In real life, there are also difficult situations when atrial fibrillation does not go away under the influence of medications, and a threat to the health and even life of the patient appears. Then there is a need to restore the heart rhythm with a special electrical cardioversion. The procedure involves putting the patient to sleep for a couple of minutes. At this time, at a certain stage of the cardiac cycle, an electric current is applied to the heart, as a result of which the heart rhythm is restored. This method of treatment is somewhat complicated and inconvenient, since the patient must be put into a sleepy state, and complex medical equipment is also required for the procedure. This measure can only be carried out in a hospital setting with the participation of highly qualified doctors. The advantage of the method is that restoration of heart rhythm can be seen in most patients, while medications help only 60-80 percent of patients. In addition to being effective, the electrical pulse method can also be considered safer for the human body, since medications often cause side effects. If they occur, you should wait some time for the substances to leave the body. Based on the advantages of cardioversion, special medical devices are manufactured, so-called cardioverters, which are implanted under the patient’s skin. These devices instantly detect the occurrence of atrial fibrillation and eliminate it. The use of these devices is currently not very widespread.
After the heart rhythm is restored, the patient should maintain it. It is necessary to identify the pathology of the body that led to the occurrence of arrhythmia and cure it. That is, it is necessary to exclude the manifestation of all causes and factors that lead to the appearance of atrial fibrillation. If arrhythmia occurs quite rarely, then therapeutic methods may not be used. However, in practice, it is often necessary to take medications to prevent atrial fibrillation from developing.
If attacks of arrhythmia are very frequent and occur in a very complex form, then the patient is offered surgical intervention for treatment.
Is prolonged atrial fibrillation dangerous?
Experts divide arrhythmia into two different types. The first type - paroxysmal arrhythmia - occurs in the form of separate attacks. The second type is constant arrhythmia, when the atrial muscles contract chaotically for several years. The permanent form of atrial fibrillation usually does not require procedures to restore normal heart rhythm, although it causes quite complex consequences, especially in the case of tachycardia. Special medications that calm the rhythms come to the aid of patients. If you are wondering about the dangers of constantly taking medications, then we can assure you that refusing treatment will lead to many more complications and harm the health of the body.
Assistant surgery
In Russia, about 2.5 million people suffer from atrial fibrillation. But people are used to taking it lightly. Like, so what if the heart beats out of rhythm. Meanwhile, this very common disease in the world can lead to very tragic consequences.
The Bakulev Center uses a surgical method for eliminating atrial fibrillation, which has no analogues in the world. The first unique operations, the methodology of which was completely developed at the center, were carried out here under the leadership of academician Leo Bockeria. The monitors show areas of the heart where arrhythmia originates. A catheter is inserted into the patient through a small incision, which, having reached dangerous places, acts on them, completely destroying the disease. True, this method is possible if the case is not complicated in any way.
In difficult situations, traditional surgical intervention is still used. The task is the same - to stop the arrhythmia. Surgeons say the procedure is more complicated than a heart transplant. The organ is isolated from the circulatory system, temporarily connecting the body to an artificial analogue, they operate, freezing the problem areas, and then return everything back. The success rate of such operations here is close to 100%.
The Bakulev Center is the only clinic in the world where both methods of treating atrial fibrillation are practiced at once. The patient's rehabilitation period is very short. On average, a week after surgery, the patient returns home completely healthy.
Types of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation occurs
- constant
- and paroxysmal.
In the first case, restoring the correct heart rhythm is quite difficult and doctors rarely do this. If such a decision is made, then after taking blood thinning drugs for three weeks, the patient is given anesthesia and an electrical shock is applied with a defibrillator, after which the heart rate returns to normal.
However, the results of this unsafe procedure are very short-lived. After all, if a person has created conditions for constant atrial fibrillation, then the heart can “break” again at any moment. Therefore, this treatment tactic is most often abandoned.
Causes of atrial fibrillation
“Unfortunately, the cause of atrial fibrillation can be almost any cardiovascular disease : coronary heart disease, previous myocardial infarction, acquired and congenital defects, hypertensive heart,” says cardiologist, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department of faculty therapy of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov Anton Rodionov .
Another reason is increased thyroid function (thyrotoxicosis). Excess thyroxine, the main thyroid hormone, can cause increased heart rate, rhythm disturbances, and increased blood pressure. Therefore, people, especially young people who suddenly develop atrial fibrillation, definitely need to have their thyroid gland examined, among other things. alcoholic libations can also “flicker . True, in such patients, if they stop drinking, everything returns to normal.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation
With atrial fibrillation, the heart contracts very quickly. It does not have time to properly fill with blood and deliver it to all organs. In addition, frequent irregular heartbeat itself is difficult for patients to tolerate. Therefore, with a permanent form of atrial fibrillation, the main treatment tactic is to reduce the heart rate with the help of medications. If it is possible to reduce the rhythm to 60-75 beats per minute, then, as a rule, patients live calmly with atrial fibrillation and feel almost the same as ordinary people.
atrial fibrillation
Many patients believe that the appearance of atrial fibrillation is a harbinger of a stroke. I can say that not always, but there is certainly a risk. The fact is that when there is no full contraction of the atria, blood circulation is disrupted. Somewhere the blood may stagnate and a blood clot will form. If it breaks away from the wall of the vessel and, together with the blood flow, enters the vessels of the brain, a stroke will develop.
Blood clots can clog the vessels of the heart, kidneys, spleen, and legs. To prevent this from happening, a person with persistent atrial fibrillation must take blood thinners, which prevent the formation of blood clots. But it must be borne in mind that taking such medications requires strict control.
With a small dose, the drug simply will not work. Exceeding the dose can cause bleeding and the same stroke. Therefore, it is very important to strictly monitor blood clotting indicators. For this purpose, there is a special blood test called “INR” (international normalized ratio), which must be done once every 1-2 months according to an individually selected doctor’s regimen.
Atrial fibrillation. Treatment
Even asymptomatic atrial fibrillation (or atrial fibrillation) should be detected promptly. Without treatment, attacks may become more frequent and increase the risk of stroke. Therefore, patients at risk need to be examined regularly.
We continue the conversation about atrial fibrillation with the deputy chief physician of the consultative and diagnostic center for organizational and methodological work, cardiologist Alexander Vladimirovich Emelyanov. Today we’ll talk about the treatment of atrial fibrillation.
What methods are used to treat this disease?
The goal of treatment for atrial fibrillation is to restore normal heart rhythm, regulate heart rhythm, and minimize the risk of stroke. The heart rhythm can be restored with antiarrhythmic drugs or electrical cardioversion.
Electrical cardioversion provides a type of cardiac reset through a targeted dose of electrical current, after which the heart can once again beat at its normal heart rate. Cardioversion is performed under general anesthesia. During and after electrical cardioversion, there is a high risk of blood clotting inside the heart. To prevent blood clots, patients receive anticoagulant medications.
If, before the procedure, the doctor suspects the presence of blood clots inside the heart that may have already developed due to atrial fibrillation, a transesophageal echocardiogram is performed before cardioversion. The doctor inserts a small ultrasound device into the esophagus and guides it close to the heart. If the doctor finds no blood clots, he or she may perform cardioversion on site. However, if blood clots are found, cardioversion should be delayed and the patient given medications to clear existing clots and prevent new ones from developing.
After cardioversion, antiarrhythmic drugs are used to prevent recurrence of atrial fibrillation. If an antiarrhythmic drug cannot permanently normalize the heart rhythm, radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFA) will be considered, which treats the cells responsible for the abnormal heart rhythm.
Catheter ablation is performed to isolate the areas causing atrial fibrillation from the rest of the heart. Typically these cells are found in the left atrium around the veins of the lung. To get there, the doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube into a large blood vessel in the groin and carefully guides it into the left atrium. The "bad tissue" is destroyed using heat (radiofrequency energy) or extreme cold (cryoablation). After the procedure, the patient receives anticoagulant medications to prevent blood clots.
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation often does not require treatment because it resolves spontaneously.
What can the patient do?
First of all, follow the prescriptions and recommendations of your cardiologist. In addition, you should reduce your risk factors by living a healthy lifestyle, eating a light and balanced diet, and exercising frequently but not too strenuously.
Alexander Vladimirovich, remind our readers what are the risk factors for atrial fibrillation?
One of the main risk factors for atrial fibrillation is age. High blood pressure, heart failure, heart enlargement (dilatation), valvular heart disease: mitral valve stenosis, valvular aortic stenosis also increase the risk of atrial fibrillation. In addition, diseases such as hyperthyroidism or diabetes mellitus, as well as excessive alcohol consumption, snoring during sleep and electrolyte imbalances affect the development of atrial fibrillation.
You can make an appointment with a cardiologist at the Consultative and Diagnostic Center of the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine of the Russian Ministry of Health by calling 8 (495) 790-71-72.