What is organic damage to the nervous system?
Organic damage to the central nervous system
- a pathological condition in which the brain does not function fully. The lesion can be congenital or appear due to trauma, stroke, infectious diseases of the brain, alcoholism and drug addiction.
Lesions are divided into grades 1-3. Stage 1 lesions are diagnosed in many people; they do not manifest themselves in any way and do not require treatment. Lesions of degrees 2 and 3 interfere with normal life and can provoke more dangerous diseases, so they need to be treated.
When is it time to go to the doctor?
Only a medical specialist can understand what is happening. If discomfort in the head, neck or upper back appears sporadically, for example, when the weather changes, and then disappears without a trace for a long time, there is usually no cause for concern. If you suspect a cold, headache from fatigue, physical or mental stress, just rest. But if you experience the following symptoms, you should definitely go to the doctor:
- previous head injuries with and without complications;
- feverish condition;
- blurred perception;
- muscle tension in the neck or back of the head;
- sudden painful shootings;
- loss of sensation in the arms or legs;
- convulsions;
- problems concentrating your eyes or thoughts;
- bulging of the fontanelle in the newborn period.
Even short-term loss of vision or hearing is also a serious reason for medical intervention.
How does organic damage to the nervous system manifest and what is dangerous?
When the central nervous system is damaged, the following symptoms are observed:
- fast fatiguability;
- impaired coordination, inability to perform simple movements and actions because of this;
- problems with hearing, vision;
- inability to concentrate on a task, the need to constantly be distracted;
- trouble sleeping, insomnia, nightmares or constant awakenings;
- urinary incontinence;
- decreased immunity, which often causes colds and other diseases.
Brain lesions are especially dangerous for children who are lagging behind in physical development and cannot study normally and communicate with peers. Also, lesions lead to oligophrenia, that is, mental retardation, and dementia - loss of skills and knowledge, and the inability to acquire new ones.
Clinical picture
At the initial stages, symptoms are invisible. However, as it progresses, extremely unpleasant signals may appear:
- convulsions or even epileptic seizures;
- loss of criticality towards one's actions;
- speech impairment;
- problems expressing thoughts;
- memory problems;
- deterioration of the psycho-emotional state - when depression develops, increased irritability is noted, and mood swings are noticeable;
- loss of empathy for other people and much more.
If such symptoms appear that should alert, if not the person himself, then his loved ones, you should contact a specialist to determine the cause of the problem. For example, they conduct a hardware examination - they often talk about MRI and CT diagnostics in order to accurately understand the areas of brain damage, volumes and other important factors. In addition, they may offer examination of cerebral vessels and other options. Next, a decision on therapy is made.
Advantages of treating central nervous system lesions in our clinic
- We accept adults and children
. We enroll adult patients and preschool children. We send young patients to a doctor who specializes in brain damage in children. - We treat children in the presence of parents
. If a child experiences fear or anxiety, we conduct a consultation in the presence of the parents. If necessary, we carry out further treatment in front of the parents to reduce stress for the child. - We select therapy individually
. We assess the degree of damage, the presence of concomitant diseases and disorders. We select treatment taking into account the patient’s age, general health, and response to previous therapy. - We warn you about the duration of treatment and possible results
. We will tell you how long the treatment can last, since organic lesions require long-term therapy. We predict how effective the therapy will be in a particular case, and discuss this with the patient.
To make an appointment with a doctor, call or use the feedback form. The administrator will call you back, answer questions and help you choose a convenient appointment time.
Why is it developing?
Naturally, many are interested in what are the reasons for the development of such degenerative processes. The risks of brain shrinkage and deterioration increase with older age. Triggers for atrophy are:
- renal failure;
- long-term increased intracranial pressure;
- alcohol abuse and taking illegal drugs;
- infections of the cerebral cortex, such as polio, encephalitis and others;
- traumatic brain injury;
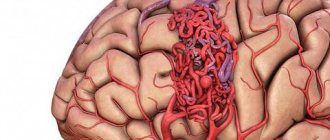
- vascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, aneurysms;
- metabolic failures;
- the presence of mental illness, in old age this may be Alzheimer's disease, as well as a neurodegenerative condition - Parkinson's disease.
- birth injuries, lack of B vitamins and folic acid;
- heredity.
Let go and don't forget. How the body saves memory when there is poor blood supply Read more
Treatment of cerebrospinal gravis
Since it is almost impossible to completely eliminate the immediate cause of cerebrovascular accident, one should strive to minimize the consequences of the brain catastrophe that has occurred by increasing the stability of nerve cells and replenishing their energy reserves.
For this purpose:
- nootropics and neuroprotectors (encephabol, noofen, actovegin);
- vascular (vinpocetine, sermion);
- vitamin complexes (milgamma, complivit).
Depending on the presence of certain manifestations, symptomatic therapy is prescribed - analgesics, sedatives, psychostimulants, antiemetics. But no medications will help if a person does not eliminate the factors that cause exacerbation of cerebrasthenic syndrome.
To prevent these factors it is necessary:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- take breaks while working;
- a full night's sleep;
- quitting smoking, alcohol, strong tea and coffee;
- take walks in the fresh air more often;
- alternate mental work with physical work.
Forecast for the development of the disease
The slow growth and subclinical course of benign neoplasms allow the disease to last up to 10-15 years. Malignant forms of tumors respond poorly to treatment. From the first symptoms it takes from a month to several years before death. Specific treatment alleviates symptoms and slightly prolongs the patient's life.
An MRI is necessary to diagnose a brain stem tumor. You can choose a clinic using our website. Registration for an appointment is free.
Diagnostics and differential diagnostics
Cerebral arthrosis is a disease for which diagnosis may require a detailed history of the patient.
The medical history is studied and the patient is interviewed about his living conditions and well-being.
But to make an accurate diagnosis, professionals send the patient to undergo the following diagnostic tests:
- CT head;
- diffuse optical tomography;
- MEG (measurement and visualization of magnetic fields);
- two-photon or single-photon emission tomography;
- MRI of the head.
And also in rare cases, differential diagnosis is possible. Having a patient's medical history, using a specially created computer program, a diagnosis can be made by exclusion. Based on the facts and symptoms that appear in the patient, the computer reduces the range of all possible diseases to one.
If it is impossible to carry out a complete diagnosis, a partial differential diagnosis can be made.
How to correctly identify the disease?
As soon as a preliminary history is collected, complaints are heard, first assumptions about a possible disease are made, a comprehensive diagnosis is prescribed, which includes the following procedures:
- Laboratory blood analysis.
- Radiography.
- Electroencephalography.
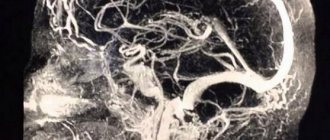
- Angiography.
- MRI of the brain.
- CT scan of the skull or cervical spine.
- MRI of soft tissues of the neck.
The most informative techniques are tomographic sessions. They give a complete picture of the existing changes in tissues and the root cause of the pathology. Even microscopic abnormalities, precancerous stages, and vascular abnormalities clearly appear on scans in one short procedure.
To undergo a full examination at a specialized tomography center, just contact our service, which works free of charge. Choose CT or MRI services, consider offers from different clinics in the city, compare options based on prices, equipment, ratings and other criteria. Here you can remotely consult on existing questions and sign up at your favorite institution with discounts from the service. Contact us, we will be happy to help you.
Huntington's chorea
This is a hereditary neurodegenerative disease in the middle and second half of life with a predominant lesion of the striatal system of the brain and less severe damage to other subcortical nuclei and the neocortex. The main manifestations of the disease are decreased intelligence, psychotic phenomena and choreic hyperkinesis.
Due to the fact that the latter sometimes does not develop even in the later stages, the process is also referred to as “Huntington’s disease”.
The prevalence of the disease reaches 4–8 people per 100 thousand population. Among patients in psychiatric hospitals it is 1%. The peak incidence rate occurs between 35 and 50 years of age. The disease lasts from 1 to 25 years.
In approximately half of the cases, the disease develops “due to a nervous defect” (Davidenkov, 1932) in the form of a personality disorder, mental underdevelopment and motor “moronism” (clumsiness, poor handwriting, etc.). The disease does not have a single development pattern. Choreic dementia is characterized by damage to the most complex forms of intellectual activity and uneven mental performance. Intellectual deficits are believed to be based on gross disturbances of attention and spasmodic loss of direction in the movement of thoughts. As intellectual impairments develop, they move closer to dementia.
Psychotic phenomena are recorded in 60% of patients. In Alzheimer's disease they occur in 43.5%, and in Pick's disease - in 11% of patients (Sternberg, 1967). In the early stages of Huntington's disease, predominantly psychogenic disorders are observed, including depression with apathy, hypochondria, or dysphoria. Paranoid psychoses with delusions of jealousy, persecution, and poisoning are relatively common. Later, paraphrenic states with delusions of grandeur, hallucinatory and hallucinatory-paranoid psychoses may develop. The most common hallucinations are tactile, visceral and fragmentary verbal. Choreic hyperkinesis is usually slow, low-amplitude, separated by large intervals; It is also typical that they include torsion and athetoid components and occur against a background of mild muscle hypotonia. Muscle strength decreases, eyelid ptosis and dysarthria occur.
There are abortive forms of Huntington's disease: a) neurological, with a predominance of akineto-hypertensive syndrome; usually begins early, b) with typical hyperkinesis and minimally expressed mental disorders, c) with minimal hyperkinetic and severe mental disorders, d) stationary forms, in which, despite extensive symptoms, the disease lasts for decades, so that patients die from intercurrent diseases. Most patients die in a state of mental insanity; in the terminal stage of the disease, hyperkinesis usually decreases or stops.
It has been established that predisposition to the disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and usually leads to atrophy of the striatum, and to a lesser extent, the cortex. Men get sick more often. Huntington described the disease in two brothers. In 12 families descended from them, 100 cases of the disease were described.
When treating patients, drugs that block dopamine receptors (phenothiazine derivatives, butyrophenones) or reduce the content of dopamine in tissues (reserpine, methyldopa) are used. Psychotic disorders are an indication for the use of aminazine, tizercin, propazine or teralen, and other antipsychotics. The results of therapy are usually disappointing. The prognosis of the disease is generally unfavorable.
How cerebral neurons die...
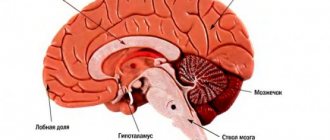
Cerebral atrophy affects the frontal areas of the brain (cortex and subcortex). It is this zone that is responsible for intellectual and mnestic functions and emotions. But this disease is classified into several types, which have different locations:
- Cortical atrophy . Here destruction occurs in the tissues of the cerebral cortex. And most often this appears during the aging process of nerve cells, but other pathological effects on the brain (BM) cannot be ruled out.
- Multisystem extinction . Characterized by damage to the cerebellum, brainstem trunk, and basal ganglia. Has a build-up effect.
- Diffuse mortality affects a variety of processes in opposite places. The disease begins its action in the cerebellum area, and then symptoms appear that are characteristic of other areas of the brain.
- Cerebellar death . Characterized by cerebellar disorders with additional pathological processes in other parts of the brain.
- Posterior cortical . Causes atrophy of neurons in the occipital and crown areas. Clusters of plaques and tangles of neurofibrillary tangles form, which contribute to death.