What is arrhythmia? Causes and treatment of arrhythmia at home
Arrhythmia is a violation of the frequency, rhythm and/or sequence of contractions of the heart. The term combines heartbeat disturbances that are different in their causes, clinical manifestations and consequences: increased heart rate (> 100 beats/min, tachycardia); slowing (<60 beats/min, bradycardia); irregularity (extrasystole).
To understand what cardiac arrhythmia is and why it occurs, you need to understand what natural mechanisms continuously maintain the heart rhythm throughout life.
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia
In practically healthy people, arrhythmia can occur due to overheating, being in a stuffy room, overeating, and also as a result of taking certain medications.
There is a high risk of this disease in patients suffering from diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. In women, arrhythmia is often detected during menopause and pregnancy, which is a temporary condition.
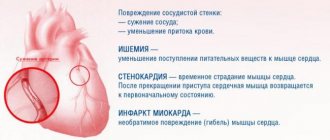
Much more serious causes are heart diseases: myocarditis, coronary disease, heart defects, myocardial infarction, malignant neoplasms. In these cases, arrhythmia is an indicator to which the doctor must pay close attention in order to prescribe the correct timely treatment.
Classification
In medicine, there are several types of arrhythmias - each of them has different symptoms and course, so it is necessary to diagnose not just the arrhythmia, but also its specific type - the choice of therapeutic therapy will depend on the results.
- Sinus arrhythmia. Most often diagnosed in childhood and adolescence, it is characterized by an abnormal alternation of heart beats. With this type of disorder in question, no specific treatment is required, the patient’s condition is not disturbed, and the normal rhythm of the heartbeat can be quickly restored by simply holding the breath for a few seconds.
- Sinus tachycardia is diagnosed if the heart rate exceeds 90 beats/min, of course, for no apparent reason (running, exercise, excitement). Typically, with such tachycardia, the heart rate does not exceed 160 beats per minute under calm conditions, and only during intense exercise can it reach up to 200 beats. It is caused by many factors associated with pathological processes in the body, therefore the treatment of such tachycardia is aimed at the underlying disease;
- Sinus bradycardia. This type of arrhythmia is manifested by a decrease in heart rate - in a patient this figure may be less than 55 beats per minute.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia, similar to extrasystole, developing suddenly and also suddenly stopping, is characterized by a regular, strict rhythm, although the contraction frequency can reach 240 beats/min (atrial) or pronounced changes in hemodynamics (ventricular);
- Flickering arrhythmia. Doctors characterize this type of arrhythmia as fluttering in the chest - the heart begins to contract faster (up to 150 beats per minute), then even faster (up to 300 beats per minute), the atria do not contract completely, and the ventricles do so irregularly.
Ventricular flutter and fibrillation are considered the most life-threatening manifestations of arrhythmia. This usually occurs against the background of heart pathologies, electric shock, or taking certain medications.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
Manifestations of rhythm changes can either be completely invisible to the patient, or have quite noticeable signs:
- sensations of heartbeats, interruptions;
- increased or slowed heart rate;
- feeling of a sinking heart;
- When blood flow is impaired, dizziness occurs and there may be episodes of loss of consciousness.
Rhythm disturbances can be permanent or occur in the form of paroxysms. In this case, an attack of arrhythmia occurs unexpectedly and also suddenly stops.
Prevention of complications
Rhythm disturbances are dangerous due to the possibility of blood clots forming and breaking off. The most unfavorable in this regard is atrial fibrillation.
To avoid thromboembolic complications, the following drugs are used:
- Anticoagulants (reduce blood clotting):
- with a direct mechanism of action (heparin and heparinoids);
- with indirect (hydroxycoumarin and phenylindanedione derivatives).
- Antiplatelet agents (reduce the ability of platelets to stick together):
- acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin), Clofibrate, Anturan, Dipyridamole.
The drug regimen is selected by the attending physician based on the number of risk factors present in the patient.
Clinical signs of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation, is the most common disorder, characterized by an increase in heart rate up to 600 beats per minute.
It can be constant, persistent and paroxysmal. The most common symptoms of atrial fibrillation include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, discomfort or stabbing pain in the heart area, increased sweating, increased urination and muscle weakness. Patients complain of a feeling of unreasonable fear, a state of panic, and dizziness and fainting are often observed.
Symptoms of extrasystole
Extrasystole is a heart rhythm disorder characterized by the occurrence of one or more extraordinary contractions of the heart muscle. The most characteristic symptoms of the disease include strong heartbeats, a short stop and a subsequent noticeable shock.
Patients often complain of chest pain, lack of air, feelings of fear and causeless anxiety, and increased sweating. Depending on the location of the source of excitation, extrasystolic heart rhythm disturbances are atrial, ventricular and atrioventricular (atrioventricular).
How to stop arrhythmia
Some types of arrhythmias (ventricular and atrial extrasystole) may not be treated at all if the number of extrasystoles per day is small. But in most cases, arrhythmia still needs to be treated. For this purpose, there are special antiarrhythmic drugs that a cardiologist can select for you. In case of severe cases of some types of arrhythmias, it will be necessary to prescribe droppers or treatment with electric current - electric pulse therapy. In the most difficult cases, surgical intervention is performed. Folk remedies for arrhythmia should not be used; treatment should be trusted exclusively to a cardiologist. It is very important to monitor the dynamics of the disease and adjust therapy in a timely manner.
Symptoms of sinus bradycardia
This type of arrhythmia is characterized by a heart rate not exceeding 60 beats per minute. Most often, bradycardia develops against the background of organic heart damage. Heart rhythm disturbances (heart rate below 40 beats per minute) are accompanied by weakness, sticky cold sweat, pain in the heart area, dizziness, instability of blood pressure, possible short-term loss or confusion, impaired memory and concentration, short-term visual disturbances.
The most dangerous condition with bradycardia is convulsions (Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attacks), lasting about a minute. In the absence of timely medical assistance, the attack can drag on and lead to respiratory arrest.
Symptoms of paroxysmal tachycardia
Paroxysmal tachycardia is a pathological condition accompanied by paroxysms (attacks of palpitations) with a heart rate of 140-220 beats per minute. A suddenly developing and also suddenly subsiding disturbance of heart pulsation, characterized by a preserved regular rhythm, can have a different duration (from several seconds to several days).
Depending on the location of the source of excitation, paroxysmal tachycardia is divided into 3 forms: atrial, ventricular and atrioventricular. Attacks of arrhythmia are accompanied by dizziness, a feeling of numbness and compression in the chest, in the heart area, and tinnitus. Some patients may experience neurological symptoms (weakening of voluntary movements (hemiparesis), speech impairment). Also characteristic signs of paroxysmal tachycardia include a slight increase in body temperature, nausea, accumulation of gases in the intestines, and increased sweating.
After an attack, the patient develops polyuria (excretion of large amounts of low-density urine). With long-term supraventricular arrhythmia, a drop in blood pressure is observed, severe weakness develops, and fainting is possible.
General rules for first aid
The rules for providing first aid for the treatment of paroxysm of atrial fibrillation are carried out differently depending on several characteristics of the attack:
- blood pressure level;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- duration of the attack;
- heart rate;
- primary or repeated paroxysm.
Depending on this, emergency doctors either try to restore sinus rhythm or reduce the heart rate, while simultaneously preventing the formation of blood clots. For this purpose, medications are used, and, if necessary and conditions exist, electropulse therapy is used.
What you can and cannot do at home during an attack
If an attack of irregular heartbeat develops, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Before the medical team arrives, you can:
- give the patient a semi-sitting position;
- unbutton tight clothes;
- provide fresh air access to the room;
- invite the patient to breathe with his stomach, wipe his face with a handkerchief dipped in cold water;
- give 20 - 30 drops of Corvalol in half a glass of water;
- prepare for the arrival of the team: organize its meeting, prepare medical documents, previous ECGs, think about transporting the patient to the ambulance (such a need may arise, but the duties of the ambulance personnel do not include carrying the patient);
- reassure the patient, tell him to call the doctors.
When detecting an attack of MA before the arrival of the ambulance, you cannot:
- Arrhythmia attack: methods for restoring heart rhythm at home
- give the patient medications before the ambulance arrives, including nitroglycerin;
- massage the eyeballs or the area of the carotid arteries;
- waste time measuring blood pressure without preparing for the arrival of medical personnel;
- collect things for hospitalization (this will be the time while the doctor examines the patient, relieves the attack, etc.; hospitalization is not always required);
- worry and panic.
How to stop an attack of MA on your own (a pill in your pocket)
Some patients whose diagnosis of “paroxysmal atrial fibrillation” has been established for a long time, and attacks occur less than once a month, can learn to independently stop such paroxysms. This tactic is called “pill in the pocket.”
It is used in intellectually intact patients who can adequately assess their condition. The “pill in your pocket” strategy should not be used if the next attack of arrhythmia caused any new symptoms:
- chest pain;
- dizziness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- facial asymmetry and so on.
In such cases, you should not stop the paroxysm on your own, since these symptoms may be a sign of the development of a heart attack or stroke.
If paroxysmal fibrillation proceeds as usual, the patient can take the drug propanorm at a dosage of 450–600 mg.
The patient should consult his cardiologist in advance about in what cases and in what dose to take this medicine. It is better if the first dose of propanorm is taken in a hospital, under the supervision of medical professionals.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of suspected arrhythmia need to be carefully checked. Alarming signs include not only rapid heartbeat, but also sudden cardiac arrest, pressure changes, weakness, alternating with drowsiness.
If you experience the above symptoms, it is time to see a doctor and undergo a full diagnosis. You should contact a cardiologist - first of all, he will begin to check the thyroid gland and identify possible heart diseases.
Many methods have been developed to diagnose arrhythmia. An electrocardiogram must be recorded - it can be short or long. Sometimes doctors provoke an arrhythmia to record readings and more accurately determine the source of the problem. Thus, diagnostics are divided into passive and active. Passive techniques include:
| Echocardiography | An ultrasonic sensor is used here. The doctor receives an image of the heart chambers, observes the movement of the valves and walls, and specifies their sizes. |
| Electrocardiography | Electrodes are attached to the patient's chest, arms and legs. The duration of the contraction phases of the heart muscle is studied and the intervals are recorded. |
| Daily ECG monitoring | This diagnosis is also called the Holter method. The patient carries a portable recorder with him at all times. This happens within 24 hours. Doctors receive information about heartbeats during sleep, rest and activity. |
In some cases, passive research is not enough. Then doctors induce arrhythmia by artificial means. Several standard tests have been developed for this purpose. Here they are:
- exercise stress;
- mapping;
- electrophysiological study;
- Tilt table test.
Prevention
Simple but effective methods will help prevent an attack of atrial fibrillation.
The patient is advised to reconsider his diet. It is important to exclude from the menu all foods and drinks that can change the functionality of the heart muscle. If you have cardiac diseases, you should not drink alcohol in any form; it is recommended to avoid coffee, strong tea, dark chocolate, and cocoa.
Products that are beneficial for cardiac activity are nuts, bananas, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, tomatoes, pumpkin pulp, cabbage of all varieties, boiled beets, etc. In addition, to reduce the risk of developing atrial fibrillation, advice from traditional medicine and aromatherapy is useful.
Folk recipes
- Tea with hawthorn . In 1/2 tbsp. Brew a handful of hawthorn berries with water. Boil the broth and leave to brew for 2 hours. Take 1 tbsp of tea. spoon up to 4 times/day for a course of 1 month.
- Tea from lily of the valley flowers . In 1 tbsp. Brew 2 tbsp of water. lily of the valley spoons. After preparation, the broth should sit for 1 hour, then strain the liquid and divide into 3 equal parts. The decoction is taken three times a day (one serving). To prevent an attack of atrial fibrillation, take the decoction daily for 2 weeks.
Aromatherapy
Aromatic oils will help prevent the development of heart disease:
- pine trees;
- thyme;
- anise;
- carnations;
- cinnamon;
- mint;
- lemon balm;
- sage
Essential oils are used in special aroma lamps . If they are not there, then you can put a couple of drops of the selected aromatic oil on a handkerchief and inhale the beneficial vapors for 10-15 minutes.
Important! Aromatherapy can be used as a preventive measure only after consultation with the attending physician. Aromatherapy is not recommended for people suffering from high blood pressure.
Why is arrhythmia dangerous?
If we are talking about sinus tachycardia or bradycardia, the patient most often experiences severe discomfort during unexpected attacks: dizziness, rapid or slow heartbeat, nausea, fear. There is also general weakness and malaise.
These symptoms seriously affect your well-being, but are not life-threatening, and with the right regimen and treatment lead to complete recovery. Paroxysmal arrhythmia, which disrupts blood circulation and is an indicator of the presence of heart disease, requires a more serious attitude. Extrasystole can be deadly and indicate myocardial infarction or other serious pathologies.
Treatment of arrhythmia
Effective treatment of disorders of proper excitability and conduction in the heart requires not only an individual approach taking into account the existing pathology, but also a comprehensive examination for a targeted impact on the underlying cause of the disease.
The worst way to treat arrhythmias is considered to be advice from friends, because antiarrhythmic drugs require individual selection, which depends on the form of arrhythmia, the patient’s body’s response to treatment measures, the presence of concomitant diseases and simply one’s own sensitivity to the drug. One thing suits one, another suits another, so only a specialist in these matters can prescribe or advise.
However, some medications should still be considered, since patients follow new products and are very interested in their pharmacological effects.
- In case of overwhelming bradycardia, implantation of a pacemaker will be the most effective. It is recommended in cases where there are signs of AV block or heart rate drops below 40 times per minute. If the reduction in contractions is not so significant, then treatment is limited to medications.
- With atrial fibrillation, it is possible to prescribe medications during attacks, but if it is permanent, then drug therapy is required on an ongoing basis. Among the drugs, the most effective are novocainamide, quinidine, cordarone, propanorm, potassium preparations, and sedatives. In some cases, electrical cardioversion may be performed. It is most effective in the first 48 hours from the moment the flicker develops and can be medicinal or electrical. In both cases, it is aimed at coordinating the contractions of the ventricles and atria in the correct rhythm. At a later date, attempts to normalize heart function may be less effective due to the development of thrombus formation in the vessels and inevitable stroke.
As for respiratory arrhythmia, it does not require special treatment, and in the case of sinus tachycardia not associated with the act of breathing, treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that caused this pathology.
How to relieve an attack of arrhythmia?
Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels are the most common reasons for providing emergency medical care. Typically, resuscitation measures are carried out for myocardial infarction and other acute conditions, but a contraction rhythm disorder can be no less dangerous. In order to understand how to relieve an attack of arrhythmia, you need to know the features of the course of the disease. Additionally, not all cases require treatment. A consultation with a cardiologist will help you find out all the aspects of treating a pathology such as cardiac arrhythmia: how to relieve an attack, and whether surgery is needed.
Arrhythmia Information
Disorders of the heart, characterized by an irregular heartbeat rhythm, are called arrhythmia. In the medical literature, different forms of the disease are distinguished depending on the clinical picture and cause of occurrence. The most common forms include tachycardia and bradycardia. The disease is primarily dangerous due to hemodynamic disturbances and the risk of severe complications. The most dangerous complication of arrhythmia is ischemic stroke.
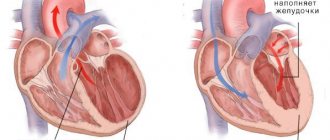
Being the most active muscular organ, the heart continuously contracts and delivers oxygen along with nutrients to all tissues. Developed external and internal forms of regulation ensure the constancy of hemodynamics. An electrical impulse that causes contraction of muscle fibers occurs in the sinus node of the upper parts of the heart and spreads through secondary nodes to all parts of the myocardium. A slight delay in the transmission of the signal from the atria to the ventricles allows the chambers of the heart to fill with blood before contracting. Thus, the special rhythm of the heart is set by the sinus node. External nervous and humoral influences can only temporarily change the rhythm.
8
24/7
Main forms of arrhythmia:
- Fibrillation is the occurrence of frequent and chaotic contractions of the atria or ventricles myocardium. In the most dangerous form of the disease, ventricular fibrillation, the heart rate can reach 600 beats per minute. A common complication of atrial fibrillation is cardiac arrest.
- Tachycardia is the occurrence of rapid heartbeat (more than 100 beats per minute).
- Bradycardia is the occurrence of too rare myocardial contractions (no more than 60 beats per minute).
- Flutter is a disorder of the rhythm of contractions of the atria or ventricles, characterized by rapid and inconsistent heartbeats. It is also a common complication of heart surgery.
- Extrasystole is the occurrence of an additional contraction immediately after systole. Normally, there is a short rest interval between contractions, during which the chambers of the heart fill with blood.
Clarifying the form of myocardial rhythm disturbance is important in order to understand how to relieve an attack of arrhythmia. Treatment of primary pathology of the cardiovascular system is often required.
Causes and risk factors
The mechanism of development of arrhythmia is in many ways similar to other heart diseases. This may be a consequence of abnormal development of the organ in the prenatal period, an infectious disease or injury. In addition, rhythm disorder may be a complication of the primary disease.
Main reasons:
- Damage to the conductive elements of the heart during ischemia and myocardial infarction.
- Disturbance of the heart valves.
- Consequences of heart surgery.
- Toxic myocardial damage.
- Nervous regulation disorders.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Imbalance of electrolytes in the blood.
- Abuse of caffeine and alcoholic beverages.
- Addiction.
- Breathing disorder during sleep.
- Thickening of the myocardium and enlargement of the heart parts against the background of high loads.
There are also risk factors that can increase the likelihood of arrhythmia. The main factors include:
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle.
- High blood pressure.
- Diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis of heart vessels.
- Panic attacks.
- Lung diseases.
- Poor nutrition.
- Old age.
It should be borne in mind that the listed risk factors are common to many cardiovascular pathologies, so heart attack prevention is also a measure to prevent arrhythmia.
An important feature is the origin of the rhythm disorder. A person's heart may begin to beat faster due to physical activity. In this case, the natural form of tachycardia is due to the adaptation of the heart to the high needs of muscle tissue. Pathological tachycardia occurs at rest and does not meet the current requirements of the body.
8
24/7
Symptoms
The disease usually manifests itself during attacks. The rest of the time, the cardiovascular system can operate as usual. That is why the intensity of symptoms largely depends on the frequency of attacks. Some patients do not even notice rare interruptions in the functioning of the heart, while others constantly suffer from insufficient blood circulation. Knowing the characteristics of the course of the disease is important in order to find out how to relieve an attack of arrhythmia at a specific moment.
Possible symptoms:
- Substernal pain.
- Sensation of pulsation in the temple area.
- Dyspnea.
- Dizziness and nausea.
- Brief loss of consciousness.
- Increased sweating.
- Anxiety.
The asymptomatic course of the disease is typical mainly for children and adolescents. The presence of other chronic heart pathologies may aggravate symptoms.
Diagnostic methods
The main way to identify heart rhythm disorders is instrumental diagnosis. Before prescribing therapeutic and diagnostic procedures, the doctor will find out complaints, examine the medical history for previous diseases and risk factors, and also conduct a physical examination. Auscultation of the heart, study of the pulse and tonometry are methods of primary diagnosis. However, outside of attacks, heart function may not be impaired, so additional methods are always required.
Additional diagnostics:
- Electrocardiography is a study of the bioelectrical activity of the heart. To obtain a cardiogram, a special device and electrodes are used that are attached to the patient’s body. Cardiography results indicate a delay in impulse conduction and other disorders of the conduction system.
- Echocardiography – methods of visualizing the heart using ultrasound equipment. A special sensor sends high-frequency sound waves to the myocardial area and forms an image of the organ on the monitor using reflected waves. The method is effective for assessing the severity of the condition and finding the cause of rhythm disturbances.
- Holter monitoring is a long-term study of heart function using a portable cardiogram recording device. During the examination, the patient goes about his normal activities and presses a button on the device if symptoms occur.
- Stress test is a method of recording a cardiogram during physical activity. To stimulate increased heart function, exercise equipment and special medications are used. This procedure is useful if the patient experiences an arrhythmia attack only during exercise.
- Study of heart vessels using angiography. Based on the results, one can judge whether they are blocked or narrowed.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones, minerals and heart attack indicator enzymes.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging - scanning the heart and blood vessels to detect the source of the rhythm disorder.
Only a comprehensive diagnosis will help figure out how to relieve an arrhythmia attack in a particular patient. Screening methods are important if there are other heart diseases that can cause arrhythmia.
How to quickly relieve an attack of arrhythmia?
After receiving the results of the examination and making a final diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe medication or surgical treatment. The treatment regimen depends on the form of the rhythm disorder, the frequency of exacerbations and other factors. As a rule, drug therapy is justified for uncomplicated disease.
Medication prescriptions:
- Direct antiarrhythmic drugs as symptomatic treatment.
- Glycosides, beta blockers and other drugs that affect the myocardial conduction system.
- Anticoagulants for blood thinning and stroke prevention.
If the initial prescriptions do not help, you need to make an appointment with your doctor again. The cardiologist can change the dosage and explain how to relieve an arrhythmia attack. In case of fibrillation, resuscitation measures aimed at quickly correcting the rhythm may be required.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery is often a more reliable method of rhythm correction. This method of treatment is indicated for severe arrhythmia and ineffectiveness of drug therapy. Depending on the type of pathology, the following methods of surgical correction may be prescribed:
- Radiofrequency catheter ablation is the removal of the affected area in the myocardium using an electric current. This is a fairly simple and safe procedure that does not require open surgery.
- Implantation of devices that normalize heart rhythm during an exacerbation of the disease. A patient with a pacemaker does not need to think about how to relieve an arrhythmia attack.
- Surgery of structural pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
When the first symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Early diagnosis allows for great success. A specialized specialist will be able to explain all the features of such a condition as atrial fibrillation: how to relieve an attack, and what treatment options exist.
8
24/7
How to treat cardiac arrhythmia at home?
You can try to treat arrhythmia at home, but remember that arrhythmia and arrhythmia are different. In some forms, even drug treatment does not respond, but in simple cases, the power of plants may help.
- It is highly advisable to start treating arrhythmia at home with nutrition and daily routine. As with any other cardiac pathology, the patient is prescribed diet No. 10, excluding fatty, fried, pickled, spicy, and salty foods. Meals should be fractional, since a significant portion of food taken at large intervals can itself provoke arrhythmia (food load). Indulging in strong coffee and teas, and even more so, drinks containing alcohol, will not lead to good either; they can become sources of rhythm disruption.
- Infuse 1 tbsp. dried calendula flowers in half a liter of boiling water for an hour. Take half a glass of infusion half an hour before meals three times a day. It is useful to consume up to 20 drops of alcohol tincture on a piece of sugar 2 hours after meals.
- Crush three glasses of viburnum berries and place in a three-liter jar. Pour boiling water to the top, close the lid and place the jar in a warm place. After a few hours, strain and add honey to taste. Store in a cellar or refrigerator. Drink 1/3 cup half an hour before meals for thirty days. It is most effective to treat cardiac arrhythmia in three courses, taking weekly breaks.
- Heart arrhythmia is treated with dill seeds. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a third of a glass of seeds and leave for 15-20 minutes. Take 1/3 cup half an hour before meals.
- Hawthorn tincture, purchased at a pharmacy, is taken 30 drops before meals.
- Brew 20-30 hawthorn berries with a glass of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes. Drink throughout the day, dividing into equal portions.
- Brew 1 tsp. dried hawthorn flowers or leaves with a glass of boiling water, leave for two hours, strain. Take 50 ml half an hour before meals.
- Grind turnips, 2 tbsp. Brew a glass of boiling water, simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes. Leave for half an hour, strain. Take half a glass half an hour before breakfast and lunch. Then prepare a fresh decoction.
- Wash 5 lemons, cut, remove seeds, mince. Add 30 crushed apricot kernels, 300 g of honey. Mix thoroughly and wait at room temperature for 8-10 hours. Keep refrigerated. Take 1 tbsp. after breakfast and dinner.
- If sleep is disturbed and you cannot fall asleep, you can prepare the following composition. Mix lemon balm leaves and valerian roots, taken in equal parts, with three parts of yarrow herb. Pour the resulting mixture with 250 ml of cold water and leave for 3-4 hours, simmer for a quarter of an hour in a water bath, strain. Treat yourself with the resulting decoction, taking a few sips every day.
- Brew a glass of boiling water with 4 calendula flowers and 1 tsp. mint tea, insist. Take with honey four times a day.
It’s great if, with the help of folk remedies, arrhythmia is forgotten, but if it still continues to bother you, then with this problem you need to go straight to the doctor to find out its origin, the degree of danger and choose treatment.
conclusions
Paroxysm of arrhythmia occurs with the active use of compensatory capabilities.
This happens with physical or emotional overload, exacerbation of the disease. You can relieve an attack of arrhythmia at home by ensuring complete rest, sometimes using light sedatives. For sinus tachycardia, vagal tests will be effective, while ventricular fibrillation requires resuscitation measures. The diagnosis of arrhythmia is confirmed by an electrocardiogram.
Disruption of blood flow can lead to the formation of a clot in the heart cavity (detected by ultrasound), its rupture and thromboembolic complications. For prevention, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (Warfarin, Xarelto, Dabigatran) are used as continuous medications.