Sports are an integral part of a healthy part of the population. Regular exercise allows you to strengthen your body, become more resilient, and emotionally balanced. But when a heart rhythm disturbance occurs, the question immediately arises: is it possible to play sports with cardiac arrhythmia?
Sports are an integral part of a healthy part of the population. Regular exercise allows you to strengthen your body, become more resilient, and emotionally balanced. But when a heart rhythm disturbance occurs, the question immediately arises: is it possible to play sports with cardiac arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is a disease of the cardiovascular system in which the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions changes. The causes of arrhythmia may be organic heart damage and non-cardiac pathological conditions.
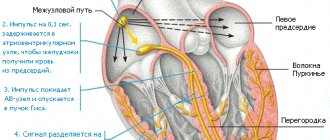
In a normal state, a person has a sinus rhythm and a heart rate in the range of 60-90 times per minute (adult norm).
Rhythm disturbances can be expressed in various forms. There is a classification of arrhythmias, according to which the most unfavorable are fibrillation, fluttering, flickering, and heart blockades of 3 and 4 degrees. Accordingly, answer the question “Is it possible to play sports with arrhythmia?” It will only work out when the form of cardiac dysfunction is precisely established. Video Doctor Sport “Heartbeat and Arrhythmias”
Is sport good for arrhythmia?
During an attack of arrhythmia, when you feel palpitations, discomfort in the heart area, and autonomic disorders appear (increased sweating, pale or red skin, a feeling of heat in the body), it is important to maintain complete rest. The heart needs to return to normal and it is advisable not to delay this, otherwise every day the prognosis of the condition worsens. Therefore, in the so-called acute period of the disease, the answer to the question “Is it possible to run with arrhythmia?” unequivocal - no.
If the heartbeat is not detected, a person feels completely healthy, then, on the contrary, one should try to strengthen the heart with the help of properly selected sports activities. During moderate physical activity, blood supply to the entire body and the heart in particular improves. The organ receives more oxygen and nutrients, which means metabolism is more active, and cardiomyocytes can contract fully.
On the contrary, some forms of arrhythmia can be cured by exercise. They are called functional and are often associated with a disorder of the nervous system. If the latter is strengthened by well-chosen physical training, then you will not have to worry about whether you can play sports if you have arrhythmia or not.
How to exercise correctly if you have arrhythmia?
First of all, classes should be held with pleasure, without any irritation or self-persuasion. Only a good mood together with your favorite sports exercise can have a positive effect on the cardiovascular system.
Important points that all patients with cardiac arrhythmia and who want to know whether it is possible to play sports with this disease should know:
- Moderation. Arrhythmia often manifests itself as an increase in heart rate. Increased physical activity can only complicate the condition, so it is important to start any training with light exercises and gradually increase their intensity, without reaching the most complex and difficult ones.
- Regularity. Sports bring results only with regular, systematic training. Long breaks in training set the athlete back and it is necessary to start all over again.
- Control. During training, it is very important to monitor your well-being. No one else, except the athlete himself, who has been diagnosed with arrhythmia, will be able to know whether the heart normally perceives the load or whether the intensity needs to be reduced. In some cases, you may need to consult with your doctor several times before you can find the right pace for your exercise.
Following the recommendations presented will allow you to play sports for the benefit of your heart and not worry about sinus arrhythmia, but is it possible to play sports? Moderation, regularity, control - and everything will be fine.
Video How not to lose your HEART when training in the Gym?
Not sports, but health-improving physical education!
Patients with arrhythmia should not at all take a comfortable place on the sofa and give up on themselves: light, targeted exercise will always benefit them. The most important thing is to follow simple rules:
- do not overexert yourself, no matter what set of exercises the patient performs;
- select the degree of load depending on your condition and after consultation with your doctor;
- lead an active lifestyle if you have decided to give up targeted physical exercise;
- do not look at the “laurels of Olympic champions” and live an ordinary life.
Which sport is suitable for patients with arrhythmia?
In case of cardiovascular diseases, it is better to pay attention to gentle sports that do not involve heavy physical exertion. In particular, the following sports activities in sports sections may be suitable:
- swimming;
- badminton;
- tennis;
- gymnastics;
- Pilates.
If you don’t want to attend group training, then you can exercise on an exercise bike at home, ride a bike, hike in the summer, and ski in the winter.
It is important to constantly remember that the load should be increased systematically, after preliminary consultation with your doctor.
Doctors' opinion
Numerous studies have confirmed a direct connection between the occurrence of atrial fibrillation and how intensely a person exercised. The most common type of disease, atrial fibrillation, has recently been diagnosed more and more often in young people who spend a lot of time in the gym. Although, according to generally accepted opinion, it is the “prerogative” of elderly people, patients with heart defects and arterial hypertension.
This suggests that with cardiac arrhythmia, prolonged physical activity can be life-threatening. Moreover, patients with such a diagnosis will probably be banned from professional sports by a cardiologist.
Can a child play sports with arrhythmia?
Adults can independently observe and control whether certain exercises can be performed or not. It's not so simple with children. A child's body is much more sensitive and less resilient. Yesterday's training, which did not cause any complications, today can provoke an attack. Therefore, children who are diagnosed with arrhythmia should first of all be carefully monitored by their parents or their caregivers.
Some forms of rhythm disturbance do not cause noticeable clinical manifestations. Sinus arrhythmia is often detected in a child and the question of whether it is possible to play sports practically does not arise. This condition is considered by many doctors to be physiological and does not require special treatment.
It is important to know those manifestations in which it is impossible to train, even if you really want to or are pressed for preparation for any competition.
Contraindications to sports are:
- loss of consciousness or dizziness;
- discomfort or pain in the heart area;
- irritability appeared for no reason;
- palpitations, pronounced pulsation of blood vessels;
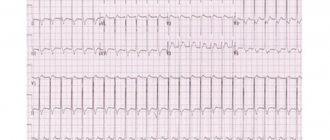
- an attack of atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation is determined.
Such signs cannot be ignored and considered a manifestation of the weak. The body thus suggests that it is time to moderate the load or change the sport altogether. In some cases, you have to be content with breathing exercises and quiet walks before the heart recovers and you can perform more intense exercises. In any case, you should consult a cardiologist and follow his recommendations.
Sports heart in children
Natalya Vladimirovna Tereshchenko, a doctor of ultrasound and functional diagnostics at the Edkarik polyclinic, talks about the “athletic heart” in children.
The heart of an athlete is somewhat different from the heart of a person who does not bother with constant intense physical activity. Already from the first months of training, the heart muscle adapts to the stress, which is manifested, in particular, by moderate bradycardia (slowing the heart rate).
Under the influence of properly organized systematic muscle exercises and sports, changes occur in the human cardiovascular system that increase its functional level and the physical performance of the body. Due to the fact that sports have become “younger”, the problem of the sports heart is now facing pediatricians. Recently, the number of cases of myocardial dystrophy (disorders of cardiac muscle nutrition) in children involved in sports has increased. This may be due to an increase in the volume and intensity of training loads without taking into account the individual characteristics of the child. Often young athletes end up in a cardiology hospital with irreversible consequences of myocardial dystrophy. Meanwhile, timely correction of exercise, nutrition and daily routine may well prevent the development of pathological changes in the heart.
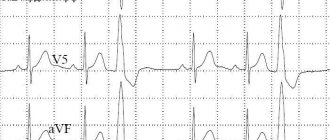
For the purpose of prevention, children involved in sports must undergo examinations such as ECG (electrocardiography) and ECHO-CG (echocardiography or ultrasound of the heart) - once a year and, if necessary, be examined by a cardiologist.
Please note that very often, even with existing changes during examinations, children do not complain. Because the compensatory capabilities of the child’s body are very great. An electrocardiogram (ECG) in children often reveals sinus arrhythmia as a feature of childhood.
The position of the electrical axis of the heart is most often normal, but it is often vertical or horizontal (depending on the height and shape of the chest). Some children may experience migration of the pacemaker source within the atria and atrioventricular node. Many children under 12 years of age experience changes characteristic of partial blockade of the right bundle branch (conduction disturbance along the right bundle branch). When performing Doppler echocardiography (Decho-CG or ultrasound of the heart) in children involved in sports, a moderate expansion of the left ventricular cavity without signs of overload and hypertrophy can be detected. Some children experience prolapse of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve (Mitral Valve Prolapse) within the first degree (up to 4-5-6 mm) with signs of physiological regurgitation and this is not a reason to stop playing sports.
Most often, children who do not experience any discomfort during and after training and competitions are allowed to continue sports activities at the same level. For children who show signs of autonomic dysfunction during medical examinations and who present complaints, it is recommended to reduce physical activity by 2 times in terms of volume and duration of training, establish a rational daily routine and nutrition, and prescribe multivitamin complexes with microelements. Restoration of autonomic functions in children usually occurs within 3 months, less often - within 6 months. The transition from the physiological state of the cardiovascular system in athletes to the pathological one, which is referred to as the “pathological sports heart,” occurs gradually. At this phase of the functional restructuring of the body, which should be regarded as a “state on the verge of failure of compensation,” athletes achieve the highest sports results.
Thus, children involved in sports should be under constant supervision of a pediatrician and cardiologist. It is very important not to miss the so-called borderline state of the cardiovascular system, which can later develop into a pathological sports heart and myocardial dystrophy due to myocardial overstrain. With timely and adequate therapy, complete restoration of the function of the heart and blood vessels is possible.
And most importantly, a growing child’s body has its own physiological characteristics, which are also reflected in the conclusions of the examinations performed. And what sometimes requires treatment in an adult, in a child is most often a variant of the age norm and simply requires monitoring over time without the use of medications. Therefore, come with your child to our specialized children's clinic, where doctors have precise knowledge about the functional age characteristics of childhood and will explain to you in detail the results obtained after the examinations.
What is the opinion of cardiologists?
If the patient has sinus arrhythmia, then the question of whether it is possible to play sports does not arise at all. Classes are conducted at a rhythm suitable for normal conditions. With other forms of arrhythmia it is somewhat more difficult, especially with paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the pulse and well-being should be carefully monitored. If an athlete takes a reasonable approach to performing certain exercises, then he will be able to perform even complex ones with success and without harm to his health.
4.12 Aug. rating ( 82 % score) – 8 votes – ratings
What health indicators need to be closely monitored?
At the time when a person has made a decision and is ready to engage in Nordic walking or running, before starting training, I recommend conducting a cardio-respiratory test with gas analysis. This is very important for three reasons.
Firstly, this test is extremely sensitive in diagnostic terms and allows you to identify various pathologies, including hidden ones.
Secondly, if a person is overweight, then conducting this test will give a clear understanding of what heart rate zone he needs to exercise in in order to lose weight as effectively as possible.
And the third reason is that the cardiorespiratory test reveals the threshold of anaerobic metabolism. That is, the limit when the load becomes excessive for a person with a certain cardiac pathology. Knowing this threshold, we individually approach the pulse limits and say what the target pulse range is for the patient. His personal “green zone” is, for example, 140-150 beats per minute. But for a person who has suffered a myocardial infarction and is overweight, the target zone is in the region of 110-120 units.
Photo: unsplash.com/@alvarordesign
This test makes it possible to individually select loads and make running safe.
Be attentive to your blood pressure and pulse. If after 2-4 months of training, blood pressure begins to decrease excessively, this is a reason to reconsider the amount of therapy. If your pulse has decreased beyond measure and has become 47-48 (less than 50) beats per minute or, conversely, you begin to see an irregular pulse more often, a rhythm disturbance, you should definitely consult a cardiologist. The doctor will look at the medications you are taking and make recommendations on the intensity and type of exercise you practice.