Carrying a baby? This is a difficult, but quite pleasant process of waiting for the birth of your beloved baby. When you are in an interesting position, your body undergoes enormous changes that can affect the health of the expectant mother. It happens that doctors or you yourself detect high blood pressure during pregnancy. Dangerous? Or, perhaps, there is no need to panic, because this is a completely normal process? We will look into this issue in our article.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous during pregnancy?
It is worth understanding that constant high blood pressure during pregnancy is a very alarming signal, because gestosis may develop, and you should not hesitate to contact a medical center or antenatal clinic. This is a very dangerous and insidious condition, which is accompanied by a disorder in the functioning of vital organs - the cardiovascular and circulatory systems. It is believed that gestosis occurs because the placenta tries to supply the fetus with everything necessary, regardless of the needs of the mother’s body, and it produces substances that promote the formation of microholes in the vessels, through which fluid and plasma protein enter the surrounding tissues and edema occurs. The most dangerous thing is when not only the legs or arms swell, but also the placenta itself, while the fetus suffers from a lack of oxygen.
In a situation where high blood pressure is not a symptom of gestosis, it is still impossible to ignore it, because changes in the vessels of the placenta and fetus still occur - they narrow. At the same time, blood circulation between mother and fetus decreases, this condition is called fetoplacental insufficiency. If the fetus lacks nutrients and oxygen, then its intrauterine formation is likely to be delayed.
It is also quite likely that with high blood pressure during pregnancy, premature placental abruption may occur - this is a very dangerous complication for the normal course of pregnancy, that is, hypertension can cause premature termination of pregnancy or premature birth.
High blood pressure during pregnancy in combination with protein in the urine can lead to preeclampsia - damage to the kidneys, blood vessels and brain, and further to eclampsia, the so-called convulsive syndrome, loss of consciousness, which is very dangerous for both mother and child.
Pregnancy and blood pressure
Blood pressure and pregnancy
Pregnancy is a period when the female body uses all its potential, all its reserves, to provide everything necessary for the full bearing of a child.
Blood pressure is one of the main parameters of the intensity of blood flow in the body. During the period of bearing a baby, a woman’s body is faced with the need to provide oxygen and nutrition not only to itself, but also to the unborn child. Changes in blood pressure during pregnancy become an indicator of disturbances in the functioning of the body that threaten the health of the woman and child, and can also complicate the course of childbirth.
When is blood pressure measured?
At every appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist in the antenatal clinic, the expectant mother's blood pressure must be measured. But visits to the doctor's office should not be limited. It is necessary to measure this indicator yourself in the morning and evening; in order for the results to be compared, they must be written down daily in a special notebook. Particular attention to their blood pressure should be paid to those women who have previously had pregnancy toxicosis, miscarriages, or missed pregnancies. Women with hypertension, excess body weight, neurocircular and vegetative-vascular dystonia, kidney, heart, and vascular diseases should be specially registered and have their blood pressure measured as often as recommended by the doctor.
Hourly blood pressure measurement in high-risk pregnant women is called 24-hour monitoring. It is done three times during the entire period of pregnancy. The first time - at the very beginning of pregnancy, to identify a woman’s tendency to hypertension, the second time - at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy, to identify a predisposition to gestosis or late toxicosis of pregnant women, the third time - before childbirth, to determine the degree of risk for the woman and the fetus , and also resolve the issue of the method of obstetrics.
If problems with blood pressure are detected in a pregnant woman, then it is necessary to visit a cardiologist and a therapist who can advise what needs to be done to solve the problem of blood pressure during pregnancy.
Types of tonometers
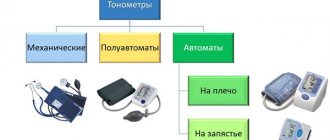
There are two types of tonometers (device for measuring blood pressure) - mechanical and electronic.
- Doctors use a mechanical tonometer. It gives the most accurate results. You can learn to use a mechanical tonometer at home. However, measuring your own blood pressure is very difficult, so if you want to use this type of blood pressure monitor, you will need an assistant.
- An electronic tonometer is easier to use. Simply put the cuff on your arm and press the button. The device itself will do the rest, and all you have to do is read the results on the electronic display. The electronic tonometer shows blood pressure and pulse, memorizing the indicators. There are blood pressure monitors whose cuff can be worn on the shoulder, on the wrist, and even on the finger. The most suitable device for home use is one whose cuff is placed on the shoulder. Wrist or finger devices can be used to measure blood pressure at work or while traveling.
Correct blood pressure measurement
You should not immediately panic because of high or low blood pressure during pregnancy; you need to make sure that the measurement is correct.
There are several important rules for correctly determining blood pressure:
- Before measuring, sit down and rest for a couple of minutes, think about something pleasant. Stress is one of the factors that causes short-term increases in blood pressure.
- Place the cuff on your bare arm or thin cloth. It must be selected according to size.
- Measure the pressure on both arms.
- Never round the numbers you get and write them down exactly.
- It is not recommended to determine blood pressure immediately after a meal or after physical activity.
Blood pressure during pregnancy: norm and deviations
Blood pressure is the force of blood flow on the wall of blood vessels. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and written as two numbers separated by a slash.
The first number shows the pressure value at the moment of maximum contraction of the heart (systolic blood pressure), and the second - at the moment of its complete relaxation (diastolic blood pressure). If blood pressure is normal, we can safely say that the mother’s cardiovascular system is doing its job, which means that all organs receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients brought by the blood flow.
Outside of pregnancy, blood pressure is considered normal in the range from 100/60 to 130/80 mmHg. Art. During pregnancy, the pressure may differ slightly from the original: if it is 10% lower or higher than usual, then such changes are still within normal limits. If the pressure is 15–20% or more lower or higher than usual, then we are dealing with arterial hypotension (low blood pressure) or arterial hypertension (high blood pressure). It is advisable for a woman to know her normal pressure level, which was before pregnancy, so that the doctor can draw the right conclusions.
1.1 What is the danger of changes in blood pressure
During pregnancy, nutrients and oxygen are constantly supplied to the fetus through the vascular network of the placenta, and waste products are constantly supplied back to the mother.
Such an exchange is possible only at an optimal level of pressure. A change in blood pressure in either direction can have adverse consequences.
With low blood pressure, transportation worsens and the amount of substances the child needs decreases, which can lead to fetal growth retardation syndrome. A significant increase in blood pressure can cause damage to microvessels, foci of hemorrhage are formed, which can lead to placental abruption. This is why it is so important to control your blood pressure during pregnancy and maintain it at an optimal level.
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy
The norms of blood pressure accepted in general medicine range from 100/60 to 120/80 mmHg. But during pregnancy, these indicators may change somewhat. Usually in the early stages (the entire 1st trimester and up to 20 weeks), these numbers decrease slightly, which is associated with changes in the hormonal levels of the whole body and the restructuring of metabolic processes.
Later, as the fetus grows and more intense blood flow forms to nourish it, the pressure may increase relative to “non-pregnant” indicators. Because of this, the average norm for expectant mothers lies in a wider range - from 105/60 to 139/89 mmHg.
Significant deviations from this range to a greater extent are called pregnancy hypertension, and to a lesser extent - hypotension.
Low blood pressure during pregnancy or hypotension
In the first months of pregnancy, the hormonal background of the expectant mother undergoes significant changes, works under heavy load, creating a favorable background for the development of the child, and these changes are often accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and hypotension.
1.1.1 Possible causes of hypotension
Sometimes it is impossible to determine the cause that provoked the appearance of such a disorder, but the following may play a role in its development:
- Hormonal changes;
- NCD of hypotonic type;
- Infectious diseases;
- Liver pathology;
- Taking certain medications;
- Peculiarities of a woman's emotionality.
Hypotension in pregnant women is often not perceived as a serious threat to the health and course of pregnancy. However, it can represent a serious pathogenic factor that provokes various pregnancy disorders:
- Abortion
- Fetal growth restriction
- Oxygen starvation of the baby
- Weakness of labor
- Possible bleeding after placenta separation
- Relaxation of the uterus after childbirth and repeated bleeding
1.1.2 Main symptoms of hypotension:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Headache
- Tinnitus
- Dyspnea
- Dizziness
- Increased fatigue
- Drowsiness
- Pale skin
- Increased sweating
- Loss of consciousness
1.1.3 How to increase blood pressure or what to do with low blood pressure
As a rule, women with low blood pressure are not hospitalized unless there is a risk to the child. Expectant mothers are observed by an obstetrician-gynecologist, a therapist and, if necessary, a cardiologist. Most often, the pressure normalizes in the third trimester.
Pregnant women should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Get at least 8 hours of sleep (9–10 hours is optimal) and rest during the day if possible.
- Spend more time outdoors (at least 2 hours a day).
- You should take food in small portions, but throughout the day.
- Moderate physical activity is recommended - do gymnastics for pregnant women; If possible, swim.
- Water procedures are useful - showers, douches, contrast foot baths, as well as massage; Physiotherapy (electric sleep, salt-pine and mineral baths) and acupuncture are successfully used for treatment.
- If necessary, doctors can prescribe drug therapy: usually pregnant women are prescribed herbal preparations that increase the tone of the autonomic nervous system, for example, eleutherococcus extracts, radiols, tinctures of lemongrass, aralia, zamanikha in combination with sedatives (valerian, motherwort), as well as caffeine-based medications .
If a pregnant woman loses consciousness due to a sharp drop in pressure, first of all she must be laid horizontally on her side and call an ambulance. Then open the door or window, unfasten the collar, and let the ammonia smell. You can massage the area between the nose and lip or work on the tips of your fingers.
High blood pressure during pregnancy or hypertension
Arterial hypertension is a disease characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure. Changes that occur in the body during pregnancy predispose to the development of hypertension and therefore pregnant women are at higher risk of developing hypertension than the general population. Arterial hypertension is a risk factor for various pregnancy complications and ranks second in the list of causes of maternal mortality. At the same time, the diagnosis and treatment of arterial hypertension in pregnant women requires a special approach.
If before pregnancy you noted that your blood pressure was higher than normal, took pills, and visited the appropriate doctors, be prepared that this problem will pop up now. Moreover, most likely it will manifest itself with greater force.
Remember: the situation is completely different now, you don’t need to take the same pills as before pregnancy.
Forms of arterial hypertension during pregnancy
Arterial hypertension of pregnancy is an increase in blood pressure during pregnancy. It is regarded as a persistent increase in systolic blood pressure above 140 mmHg. and diastolic blood pressure above 90 mmHg. in women with normal blood pressure before pregnancy. Women with such elevated blood pressure require close medical supervision.
There are several types of arterial hypertension during pregnancy:
- Chronic hypertension is characterized by the presence of high blood pressure before pregnancy and its persistence after pregnancy.
- Arterial hypertension of pregnancy is a persistent increase in blood pressure that develops after the 20th week of pregnancy, which disappears at the end of pregnancy.
- Preeclampsia/eclampsia is a severe disorder of the cardiovascular system and kidneys during pregnancy, which includes: hypertension and impaired renal function.
In pregnant women, arterial hypertension occurs with a frequency of 4-8%, which is a very high figure, especially if we take into account the young age of most expectant mothers. During pregnancy, a woman’s body adapts to new operating conditions, which include ensuring the vital activity and development of the fetus. The following changes occur in the body of a pregnant woman regarding the cardiovascular system:
- An increase in the volume of circulating blood and the appearance of the placental circulatory system is necessary to ensure the nutrition and development of the child. In pregnant women, the volume of circulating blood increases by 25-30%, which, in addition to providing nutrition for the child, allows women to lose some blood during childbirth, without significant damage to health.
- Increased heart rate.
- An increase in intra-abdominal pressure, an increase in the diaphragm and a change in the position of the heart in the chest due to a significant increase in the size of the uterus.
- Gradual weight gain in a pregnant woman.
Possible other causes of high blood pressure
- Physical exercise
- Drinking strong tea or coffee
- Chronic stress, fatigue, lack of sleep, emotional stress
- Smoking, alcohol abuse
- Unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins and minerals
- Obesity, overweight
- Multiple pregnancy
- Weak physical activity
- Thyroid diseases
- Adrenal diseases
- Diabetes
- Head, brain and spinal cord injuries
- Encephalitis
- Myelitis
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
- Renal dysfunction
- Hereditary predisposition
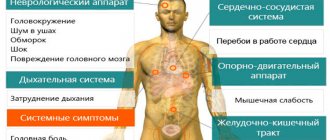
Main symptoms of hypertension:
- Headache
- Nausea, vomiting
- Dizziness, weakness, powerlessness
- Redness of the skin of the hands and face
- Noise or ringing in the ears
- Deterioration of vision
- Edema
- Protein excretion in urine
- Convulsions
High blood pressure can cause complications such as retinal detachment or retinal hemorrhage, which can lead to partial or complete loss of vision.
If blood pressure begins to increase in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, then we are probably dealing with a serious complication of pregnancy - gestosis.
Preeclampsia is a special condition that occurs only during pregnancy and ends with its completion. Manifestations of gestosis are varied, but the classic symptoms are:
- arterial hypertension
- swelling
- proteinuria (protein in urine)
With gestosis, microcirculation is disrupted in all vital organs: blood supply to the brain deteriorates, kidney failure develops, the blood becomes viscous, and the resulting microthrombi disrupt the functioning of all organs and systems. Particularly dangerous is such damage to the blood vessels of the placenta and brain. The most severe manifestation of gestosis is eclampsia - convulsive seizures ending in cerebral coma.
But gestosis often begins with a pathological increase in body weight. Expectant mothers often wonder why the doctor pays so much attention to weight. Well, just think, I added a couple of extra pounds.
But such an increase is due to fluid retention in the body, or so-called hidden edema.
And if treatment is not started in time, all manifestations of gestosis will not take long to appear. If there was an increase in blood pressure before pregnancy, then its successful course is possible only with good preparation and the correct selection of medications that lower blood pressure. For uncomplicated hypertension and a slight increase in blood pressure, only non-drug measures are sufficient.
More about gestosis
Treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension during pregnancy
Treatment of arterial hypertension during pregnancy is a complex and responsible task. Therefore, the basis of any type of treatment should be close cooperation between patient and doctor.
In the treatment of arterial hypertension in pregnant women, as well as in the treatment of arterial hypertension, the following methods are used: non-drug treatment and drug treatment.
Non-drug treatment, that is, treatment without drugs, is the most acceptable method of treating hypertension during pregnancy, since many drugs used in the treatment of this disease can be dangerous to the fetus.
What to do with blood pressure, how to reduce blood pressure during pregnancy
Non-drug treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension includes:
- Diet. The basic requirements for the diet of women suffering from hypertension are reducing the consumption of table salt, coffee, tea, and giving up bad habits. The permissible amount of salt per day for patients with hypertension is 5 grams, and the calculation must include not only the salt with which we season food, but also the salt contained in various food products.
- Physical activity. Moderate physical activity has a beneficial effect on the general condition of the body, promotes fat burning, normalizes metabolism, improves blood supply to internal organs and the fetus, increases muscle tone and helps to establish the correct position of the fetus in the uterus. For the treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension during pregnancy, daily physical activity in the form of gymnastics (preferably with an instructor), walking in the fresh air, and swimming are recommended.
- Maintaining normal body weight. The common expression that during pregnancy a woman “must eat for two” is not true. In fact, the “energy supplement” during pregnancy should not exceed 350 kcal. At the same time, maintaining a normal body weight during pregnancy is extremely important for maintaining the health of the pregnant woman herself and her child (obesity contributes to the development of hypertension and diabetes). The normal increase in body weight of a pregnant woman by the end of pregnancy should not exceed 12 kg.
Drug treatment of hypertension during pregnancy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist and only using safe drugs.
- With a single slight increase in blood pressure, treatment begins with the prescription of sedative natural drugs, for example: valerian, motherwort, novopassit and others. In combination with non-drug therapy, these measures are very effective.
- If there is a constant increase in blood pressure, the following drugs can usually be prescribed, but only after the recommendation of a doctor. The main drug or “drug of choice,” the most effective and safe, is Methyldopa (Dopegit), which can be used during pregnancy from early stages of pregnancy.
- A group of drugs that can be prescribed from the second trimester of pregnancy are calcium channel blockers: Verapamil, Nifedipine.
- For persistent hypertension, beta-blockers can be prescribed from the 2nd-3rd trimester; this group of drugs does not have a teratogenic effect.
While taking medications, monitoring of the intrauterine condition of the fetus is necessary.
If the pressure suddenly increases and you feel unwell, urgent hospitalization is necessary. Only in a hospital is full control over the condition of the child and mother and full therapy possible.
The delivery plan and referral to the maternity hospital for pregnant women with high blood pressure are drawn up in advance. If problems arise that cannot be corrected, a caesarean section is performed.
Follow your doctor's advice.
He is a professional, he knows what is best for you and your child! Tags: pregnancy
Some signs of high blood pressure during pregnancy
If the consultation reveals problems with pressure surges in a pregnant woman, then it is worth buying a tonometer to measure pressure. High blood pressure during pregnancy is accompanied by the following sensations: tinnitus, deterioration in health, nausea or even vomiting, the appearance of dark spots before the eyes, redness of the skin on the face and chest, weakness and dizziness, headache. However, it also happens that the increase in pressure is asymptomatic and this can only be determined by measuring blood pressure.
What does high blood pressure indicate in the 1st and 3rd trimester?
If in the early stages the pressure reaches 140/90, and such an increase is observed regularly, then we can talk about the presence of hypertension associated with the course of pregnancy itself and disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system.
Frequent high blood pressure in the 3rd trimester may indicate gestosis, which impairs blood flow and the functioning of individual organs. In the risk group, gynecologists include women who have infections, intoxication of the body, and nervous disorders.
Negative manifestations of high blood pressure:
- cardiac arrhythmia
- constant swelling
- vision problems
- constant weakness
- placental abruption
- rejection of the fetus by the female body (in addition to high blood pressure, increased protein in the urine and excessive weight gain are added).
Possible causes of high blood pressure during pregnancy
- Stress. The loads are so great that the body does not have time to readjust and reacts with an increase or surges in pressure.
- Lack of compensatory forces in the body - the heart, forced to pump blood for two, cannot cope with the increased volume of blood required for this.
- Hereditary factors. If blood relatives have problems with high blood pressure, there is a possibility of a similar problem occurring.
- Diabetes mellitus does not increase blood pressure, but serves as an additional unfavorable factor for its occurrence in the presence of other causes.
- Low physical activity, because a trained heart can cope with stress better.
- Smoking. Nicotine constricts blood vessels and, as a result, blood pressure increases.
- Excess weight and rapid weight gain. Therefore, doctors strictly monitor its increase weekly during pregnancy.
- Kidney pathologies. Pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis cause high blood pressure not only during pregnancy.
- Hormonal disorders - malfunctions of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands.
Hypertension during pregnancy: norms and deviations
Every woman should know her usual blood pressure (BP). For some it may be lower than 120/80, for others it may be slightly higher.
When visiting your leading gynecologist, your blood pressure is measured every time. Of course, such manipulations are not carried out without reason - excessively high blood pressure can signal an unfavorable condition for the patient and the fetus.
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy varies between 100/60-140/90. An increase in this indicator by 15% shows the following picture:
- blood vessels constrict
- there is excessive strain on the heart muscle
- the fetus stops growing due to lack of oxygen
- placental insufficiency may develop
- Cases of placental abruption in the early stages have been recorded.
How to lower blood pressure?
Self-medication during pregnancy is contraindicated.
Drugs that have helped someone close to you may have a negative impact on your health and the health of your baby. Therefore, all medications should be prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive examination. It is worth abandoning the independent choice of herbal medicines and dietary supplements. Pregnancy is a contraindication for taking most of them. They can enhance or slow down the effect of the medications you take, cause allergies and a number of other complications. In order for your blood pressure to remain normal, it is important to control your weight, exercise (of course, within reasonable limits and after consulting a doctor), eliminate foods that increase blood pressure (coffee, strong black tea, chocolate) from your diet, and give up bad habits. High blood pressure is a condition that can and should be dealt with, especially during pregnancy. To prevent the development of complications associated with hypertension, it is enough to control your blood pressure and follow simple doctor’s recommendations. And then you and your baby will be healthy. Tags:
- Pressure
- pregnancy
- complications
To leave a comment you must be an authorized user
Features of changes in blood pressure in the early stages
At the initial stage of bearing a child, systolic and diastolic pressure indicators practically do not change. Registration of deviations is observed a month after conception, when a change in hormonal levels occurs in the female body. In the first trimester, progesterone is produced in high concentrations. This is a hormone that ensures the safety of pregnancy. Progesterone also has an effect on blood vessels, helping to relax their lumen. During this period, the woman experiences a decrease in blood pressure, which is a physiologically based process.
A change in values can be observed as a result of toxicosis or gestosis, when the functioning of organs and its systems is disrupted due to adaptation to pregnancy. This condition is accompanied by characteristic symptoms. Pregnant women experience nausea, dizziness, increased heart rate and low blood pressure.
At the end of the first trimester, blood pressure levels begin to increase due to activation of the uteroplacental circulation.
Why does blood pressure change in pregnant women?
The body has to adapt to a special condition - pregnancy. A woman’s body weight gradually increases, and additional blood circulation is activated between the uterus and placenta. The functioning of the heart and blood vessels at this time is affected by:
- Changes in hormonal levels;
- An increasing volume of blood circulating in the body;
- Increased tone of the central nervous system;
- Changing the location of the diaphragm, which rises upward;
- Increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity;
- Displacement of the heart in the chest;
- Increased heart rate.
The body directs all its efforts to improve blood flow in the placenta and in the uterus, because this is necessary to provide the developing fetus with oxygen and nutrients. Under these circumstances, blood pressure changes.
Features of pressure fixation during pregnancy
It is better to take a manual device, since automatic ones tend to slightly distort the results. It is recommended to take measurements at the same time of day - this is due to the body’s biologically active clock and hormonal fluctuations. There are a number of rules that must be followed during daily blood pressure measurements.
You should not start the measurement procedure immediately after physical activity or exercise that leaves you feeling tired. Adrenaline is still produced in the blood, increasing blood pressure by 5–10 units. Even if a woman feels tense after a walk or washing the dishes, she needs to wait a quarter of an hour and only then take the blood pressure monitor.
Do not measure blood pressure after a hearty meal - the digestive system is activated and blood volume is redistributed. As a result, the numbers on the device will be incorrect. The measurement is carried out 30–40 minutes after eating food. Take measurements an hour after drinking coffee or strong tea.
Since normal blood pressure during pregnancy is individual, the expectant mother, starting from 13–14 weeks, should record tonometer readings daily
Take a sitting position during the procedure, do not talk, laugh or eat. The blood flow in the artery of the shoulder must be full; for this, the hand is placed on the table top. If the pressure is measured lying on your side, this will significantly distort the result. Take measurements on both arms in the first few days. Once it is determined on which hand the pressure is recorded higher, measure only on it.
If a woman does not have a history, she does not suffer from cardiovascular diseases and feels well, her blood pressure can be measured once a week. If there are problems, measurements must be taken daily and the resulting numbers recorded in a notebook - this will help the attending physician decide on the need for hospitalization and the prescription of antihypertensive drugs.
Gestational hypotension
Hypotension in an expectant mother can be recognized not only based on blood pressure readings. A pregnant woman with low blood pressure often feels lethargic and tired. She periodically experiences dizziness and fainting.
Symptoms of hypotension also include:
- headaches, weather sensitivity;
- drowsiness, depression;
- decreased ability to work, emotional instability;
- tinnitus, palpitations;
- feeling of lack of air, cold extremities;
- pale skin, sweating.
The situation is complicated if a woman has a history of vegetative-vascular dystonia, which is accompanied by a decrease in vascular tone, or anemia. With a poor diet and diet, a persistent decrease in blood pressure is also observed. Symptoms of hypotension often make themselves felt in the morning, which is why they are usually confused with signs of early toxicosis. Moderate manifestations of gestational hypotension in the early stages of pregnancy are not considered a pathology, and do not cause harm to the health of the expectant mother and baby.
With pronounced hypotension of gestation:
- In pregnant women, early toxicosis develops more often and is more severe;
- in the later stages, gestosis and preeclampsia can be observed - complications of pregnancy;
- in severe cases, miscarriage is possible;
- due to disruption of normal blood flow in the placenta, the mother develops placental insufficiency;
- when, due to placental insufficiency, the transport of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus is disrupted, the unborn baby experiences IUGR (intrauterine growth retardation);
- due to reduced uterine tone, difficulties arise with delivery, and doctors have to perform a caesarean section;
- After childbirth, a mother with low blood pressure may develop hypotensive bleeding.
Gestational hypotension occurs:
- physiological - does not require treatment;
- subcompensated (unstable) - treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis;
- decompensated (with hypotensive crises) - requires hospital treatment and constant monitoring.
Treatment methods for hypotension in pregnant women are non-drug and with the help of special medications. In cases of physiological and unstable hypotension, preference is usually given to non-drug therapy.
It includes:
- correction of the diet - inclusion of foods rich in B vitamins, proteins, iron;
- compliance with the drinking regime - increasing the daily volume of fluid consumed;
- proper sleep and rest, mandatory daily walks in the fresh air;
- moderate physical activity, morning exercises, physical therapy;
- massage, contrast shower, water aerobics;
- creating a favorable emotional background;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - nasal caffeine electrophoresis, calcium electrophoresis on the collar area, etc.;
- oxygen therapy - hyperbaric oxygenation sessions.
Medicines for the treatment of hypotension in pregnant women - Riboxin, Panangin, Fethanol, Isadrin, Pantocrin, tinctures of ginseng, eleutherococcus and Chinese magnolia vine, Apilak. They can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor and strictly in the indicated dosages. Many drugs that increase blood pressure also affect the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus.
If before conception a woman suffered from arterial hypotension and took any medications that maintain normal blood pressure levels, she must inform her doctor about this. Expectant mothers are prohibited from drinking some medications, and treatment for hypotension will need to be adjusted taking into account pregnancy.
The automatic pulse tonometer is convenient to use, but may produce errors in measurements
Pressure surges
If before you managed to get pregnant, there were no problems with the readings on the tonometer, then during the period of bearing a child you can encounter jumps in blood pressure levels: the pressure is either increased or decreased. Symptoms of hypotension are replaced by hypertensive manifestations, and all this within one day. Why does blood pressure fluctuate in pregnant women?
- small or, conversely, excessive amount of fluid consumed;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- change in the ratio of blood parameters;
- stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- ignoring walks in the fresh air.
You can correct blood pressure readings using acupuncture, breathing exercises, evening walks, swimming, taking tinctures of Eleutherococcus, ginseng, etc. All chosen methods should be discussed with your doctor.
While you are expecting a baby, it is better to avoid prolonged work at the computer, as this can also provoke pressure surges.
Blood pressure control is the key to the health of mother and child
Often problems with pressure do not manifest themselves until the situation becomes truly threatening. Sometimes pregnant women attribute the deterioration in their health to their “interesting situation” and hormonal changes and fatigue. But pressure surges during such a period can have quite serious causes and dangerous consequences.
The sooner such prerequisites are identified, the easier it will be to normalize the state of health. This is why pregnant women are advised to regularly monitor their blood pressure, especially since it is very easy to do this with modern home blood pressure monitors.
Where does high blood pressure come from?
High blood pressure can accompany a woman during pregnancy if she was previously diagnosed with hypertension. In this case, it is doubly important to monitor your condition and listen to all the doctor’s recommendations. You should not take the same medications that were prescribed before pregnancy, as they may affect the development of the fetus. There are medications that do not have side effects on the baby; your doctor will select them for you.
There are medications for blood pressure that do not have side effects on the baby; your doctor will select them for you.
You can also “acquire” high blood pressure as a result of constant stress, heredity, smoking, overweight or obesity, diabetes mellitus or other concomitant diseases of the kidneys, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland. In any case, consultation with a specialist is necessary to minimize the risk of developing hypertension while expecting a child. To do this, it is advisable at the stage of pregnancy planning to eliminate all provoking factors, cure concomitant diseases, and get rid of bad habits.
Third trimester
By 30 weeks, the volume of circulating blood reaches its maximum, and blood pressure gradually increases, most often without crossing the normal limit. Subsequently, the growth of circulating blood volume stops, the fundus of the uterus drops somewhat, the height of the diaphragm decreases, and the expectant mother feels better. Blood pressure levels out and returns to pre-pregnancy levels.
Special attention! From the 28th to the 32nd week, a woman’s cardiovascular system experiences the maximum load, so during this period the health of pregnant women with diseases of the cardiovascular system may worsen.