Rh factor is a specific protein found on the surface of red blood cells. Approximately 85% of the world's population has it, the remaining 15% do not. In the first case, Rh is positive, in the second - negative. The absence of this protein does not affect health or quality of life in any way.
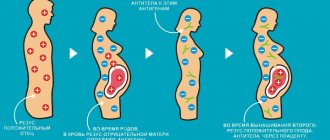
A negative Rh factor causes concern among doctors if a pregnant woman is Rh(-) and her partner is Rh(+). In this case, a conflict is possible between the body of the expectant mother and the red cells of the fetus.
What is Rh conflict
When the fetal red blood cells, which have a specific protein, come into contact with the mother’s blood, her immune system begins to produce antibodies against them in order to destroy them, since it mistakes them for foreign. When the red cells of the fetus are destroyed, a large amount of bilirubin is formed in its blood. The liver and kidneys do not have time to remove it, it accumulates and causes the skin to turn yellow. In addition, bilirubin can lead to problems with brain function. Due to the destruction of red blood cells, the production of new cells by the spleen and liver accelerates, but they cannot cope with their work. A decrease in the number of red cells leads to oxygen starvation of the fetus, and this can even result in its death.
Such incompatibility is possible only in one case, if the expectant mother has a negative Rh, and the father and fetus have a positive Rh.
Sources
- Ceniceros LC., Capitanio JP., Kinnally EL. Prenatal Relocation Stress Enhances Resilience Under Challenge in Infant Rhesus Macaques. // Front Behav Neurosci - 2021 - Vol15 - NNULL - p.641795; PMID:33854420
- Raguz MJ., Prce Z., Bjelanovic V., Bjelanovic I., Dzida S., Mabic M. 20 Years of Follow-up Alloimmunization and Hemolytic Disease in Newborn: Has Anything Changed in the Field Over the Years? // Klin Padiatr - 2021 - Vol232 - N6 - p.314-320; PMID:33063311
- Shirtcliff EA., Lubach GR., Mooney R., Beck RT., Fanning LK., Coe CL. Transgenerational propensities for infant birth weight reflect fetal growth history of the mother in rhesus monkeys. // Trends Dev Biol - 2021 - Vol12 - NNULL - p.55-65; PMID:32616989
- Deere JD., Chang WLW., Villalobos A., Schmidt KA., Deshpande A., Castillo LD., Fike J., Walter MR., Barry PA., Hartigan-O'Connor DJ. Neutralization of rhesus cytomegalovirus IL-10 reduces horizontal transmission and alters long-term immunity. // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA - 2021 - Vol116 - N26 - p.13036-13041; PMID:31189602
- Lee DS., Ruiz-Lambides AV., Higham JP. Higher offspring mortality with short interbirth intervals in free-ranging rhesus macaques. // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA - 2021 - Vol116 - N13 - p.6057-6062; PMID:30877247
- Aljuhaysh RM., El-Fetoh NMA., Alanazi MI., Albaqawi AS., Alanazi WM., Alanazi NS., Alanazi RM., Alanazi AM., Alnemer EM., Alenezi RA., Alabdullatif TK., Alanazi RA., Alanazi SS., Alsultan KS., Alanazi IM., Alsunayni DS. Maternal-fetal Rhesus (Rh) factor incompatibility in Arar, northern Saudi Arabia. // Electron Physician - 2021 - Vol9 - N12 - p.5908-5913; PMID:29560141
- Bishop CV., Stouffer RL., Takahashi DL., Mishler EC., Wilcox MC., Slayden OD., True CA. Chronic hyperandrogenemia and western-style diet beginning at puberty reduces fertility and increases metabolic dysfunction during pregnancy in young adult, female macaques. // Hum Reprod - 2021 - Vol33 - N4 - p.694-705; PMID:29401269
- Krendl C., Shaposhnikov D., Rishko V., Ori C., Ziegenhain C., Sass S., Simon L., Müller NS., Straub T., Brooks KE., Chavez SL., Enard W., Theis FJ ., Drukker M. GATA2/3-TFAP2A/C transcription factor network couples human pluripotent stem cell differentiation to trophectoderm with repression of pluripotency. // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA - 2021 - Vol114 - N45 - p.E9579-E9588; PMID:29078328
- Dettmer AM, Woodward RA, Suomi SJ. Reproductive consequences of a matrilineal overthrow in rhesus monkeys. // Am J Primatol - 2015 - Vol77 - N3 - p.346-52; PMID:25382028
- Dizik GM., Pavliuk RP. . // Klin Khir - 2011 - Vol - N9 - p.69-72; PMID:22168031
How do fetal red blood cells enter the mother's blood?
This is possible in the following cases:
- during blood transfusion;
- during termination of pregnancy;
- in case of miscarriage;
- during such medical procedures as puncture of amniotic fluid, taking blood from the umbilical cord, chorionic villus sampling and others;
- with placental abruption;
- during ectopic pregnancy.
When the blood of mother and fetus comes into contact, antibodies may begin to be produced. This process in medicine is called sensitization. Antibodies can freely cross the placenta, then enter the bloodstream of the unborn baby, after which the destruction of his red blood cells will begin. As a result, the fetus begins to become anemic, dropsy of the head occurs, and heart failure develops. This condition is called hemolytic disease of the fetus, which can lead to fetal death. This disease also occurs in newborns. At the same time, their bilirubin levels increase, and their skin turns yellow.
IVF and Rhesus conflict
IVF with a negative Rh factor is carried out in the same way as in women who have Rh antigens on the surface of their red blood cells. Only the pregnancy management tactics differ. There is a whole algorithm of recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Rh conflict, which are the same for both women who became pregnant using IVF and women who became pregnant naturally.
If the protocol uses donor sperm, then the woman is asked to choose a donor with a negative Rh factor to level out the risk of complications from the Rh conflict.
Probability of Rh conflict
First pregnancy
The production of antibodies in a woman depends on the type of pregnancy she has. The fact is that with the first, as a rule, the expectant mother with Rh (-) has no antibodies, unless she has previously received a transfusion of Rh-positive blood.
In a normal first pregnancy, a child born to a woman with negative Rh is born healthy and does not develop hemolytic disease. Even if fetal red cells enter the mother's blood, their number is small, and the woman's body produces very few antibodies. Even if they can penetrate the placenta into the fetal bloodstream, they will not cause anemia.
The baby's red blood cells can enter the mother's blood directly during childbirth, but this is not dangerous for either the child or the mother, and the newborn will not have hemolytic disease.
There is a risk of sensitization during a second pregnancy. It grows with each subsequent one. Thus, there is a possibility that hemolytic disease will develop.
Conflicting rhesus and conception
What should women with negative Rh blood factor keep in mind when planning pregnancy? Readers' questions are answered by a gynecologist at the Research Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology named after. BEFORE. Otta RAMS in St. Petersburg Marina Vladislavovna BONDARENKO.
We recommend that you read the article on our website: “Conceiving with a negative Rh factor”
What should women with negative Rh blood factor keep in mind when planning pregnancy? Readers' questions are answered by a gynecologist at the Research Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology named after. BEFORE. Otta RAMS in St. Petersburg Marina Vladislavovna BONDARENKO.
“I have negative Rh blood, and my husband is positive. Is Rh conflict a threat to our unborn child? “Lidiya K, Pyatigorsk
— A conflict can arise if the mother has a negative Rh factor, the father has a positive Rh factor, and the baby has inherited a positive Rh factor from his father. And if during pregnancy the fetal red blood cells enter the mother’s blood, then her immune system destroys them as “foreign”. Such exposure may occur during childbirth, abortion, or miscarriage. So women with negative Rhesus need to do an appropriate blood test before conception. And based on its results, engage in family planning.
If this is your first pregnancy, you should regularly check your blood for Rh antibodies. Standard deadlines have been developed for this. In the first half of pregnancy, antibody testing should be carried out once a month. In the second half - 2 times a month. After 36 weeks of pregnancy, antibodies in the blood are determined once a week, and immediately before childbirth - once every 3 days. This allows you to understand in time whether your unborn child is at risk of Rh conflict and take action.
“Is it possible to carry out some kind of prophylaxis during pregnancy to prevent Rh conflict from developing, and for what period? What affects the formation of antigen?”Natalia, Cherepovets
— Various complications during pregnancy can trigger the production of Rh antibodies. For example, placental abruption and any other violation of its integrity, gestosis, infections or abdominal injuries. In all these cases, fetal red blood cells can also enter the mother's blood and trigger a response from her immune system. Antibodies can appear if a woman has been transfused with Rh-incompatible blood in the past.
Increases the risk of a conflict situation and caesarean section. Even if antibodies are not detected in your blood, it is still worthwhile to prevent Rh conflict. This way you will protect yourself and your baby in case you want to become a mother again. It is carried out three times: at 10-12, 24-25 and 32-33 weeks of pregnancy. There are several drug regimens used for this purpose. The most effective combinations of ascorbic acid with glucose, sigetin, methionine, calcium gluconate, and rutin. Another regimen includes vitamin E, vitamin Bis and rutin. And at night it is recommended to take diphenhydramine.
“I heard that Rh conflict can lead to hemolytic disease in a child. What is this? “Anna Gromova, Arkhangelsk
— In hemolytic disease, bilirubin, a tissue poison, reaches the child through the blood. It disrupts the delivery of oxygen, damages the fetal brain, leads to hearing and speech impairment and turns the baby’s skin yellow. Such violations arise from which the child may die.
Currently, hemolytic disease can be diagnosed in utero. In particular, based on ultrasound examination. It shows an enlarged fetal liver, thickening of the placenta, and polyhydramnios. The diagnosis can be made by taking blood from the umbilical cord. It determines the level of bilirubin and hemoglobin in the fetus, which show how far the process has progressed. Bilirubin is also tested in amniotic fluid. The higher this indicator, the more severe the disease. The main method of treatment is intrauterine blood transfusion to the child. In this case, the “infected” blood is replaced with healthy one. Vitamins are an essential component of successful treatment.
“During the first pregnancy, no antibodies were found in the blood. I would like to become a mother two more times. How realistic is this? How many children can a woman with Rh incompatibility give birth to without risking their health? How often is it better to give birth? “G. Volkova, St. Petersburg
— There is no clear answer to the first two questions, because it is impossible to predict which parent’s Rh factor will be inherited by their next child. Only general patterns are known. During the first pregnancy, the level of Rh antibodies, if they appear, is usually not too high. This is due to the fact that the woman’s immune system encounters “foreign” cells for the first time.
In subsequent pregnancies, thanks to 'cellular memory', the woman's immune system produces antibodies much faster and in much larger quantities. This is why Rh-negative women are advised to avoid terminating their first pregnancy.
Keep in mind: once Rh antibodies have formed, it will not be possible to get rid of them once and for all. Therefore, the frequency of birth does not play a big role. If antibodies are already present, their number will not change between births. The only rule is that the birth of each new child must be approached responsibly and try to eliminate possible complications of pregnancy.
“I heard that a Rh-negative woman should be vaccinated with anti-Rh gamma globulin after every birth or abortion. Only then are her subsequent children protected from the consequences of Rh conflict. I'm going to have more than one child. What if antibodies are still detected in the blood during the next pregnancy?” Maria Menshova, Perm
— Anti-Rhesus gamma globulin must be administered to a woman after any manipulation of the uterus. Injection of this drug reliably protects against Rh conflict in subsequent pregnancies. It can be administered at 28 weeks of pregnancy or after childbirth. But this must be done within 72 hours. It doesn't make sense later.
In advance, ask the maternity hospital where you will give birth if it is available. If not, then buy gamma globulin at one of the city blood transfusion stations.
“Six years ago I had a daughter, after that there were three more pregnancies that ended in early miscarriage. Could this be due to the fact that I am Rh negative? Will I be able to have another child? “Gulnara V., 30 years old
— A test for Rh antibodies will help answer this question. It is done in any clinic. If they are discovered, it is possible that they were the cause of the miscarriage. Depending on the amount of antibodies in the blood, the doctor may suggest lowering their levels using plasmapheresis. During this procedure, the plasma is purified, and thus the risk of developing Rh conflict in subsequent pregnancies is reduced. This procedure is carried out before conception.
However, it is not only Rhesus conflict that can lead to miscarriage. Therefore, at the stage of pregnancy planning, it is necessary to undergo a full examination.
Elena DOPGANOVA Source: “Women's Health” Take the first step - make an appointment!
or call 8 800 550-05-33
free phone in Russia
Prevention and treatment
Until recently, a negative Rh factor in a mother was the reason for the birth of the only child in the family. Doctors advised such women to abandon their second and subsequent children, and in the case of the first pregnancy, they categorically did not recommend terminating it.
Today everything has changed, medicine has advanced so much that, thanks to prevention and treatment, an Rh-negative woman can have healthy children.
Thanks to effective methods of prevention and treatment, women with Rh- have the opportunity to bear and give birth to healthy children
When you first contact the antenatal clinic, blood is taken from each woman to find out the group, Rh, and antibody titer. If a pregnant woman has a negative Rh factor, but antibodies are not produced, she may be prescribed a course of immunoglobulins. If antibodies are detected in her blood, their levels are monitored throughout the entire period of gestation. The rules for managing pregnancy in such cases are as follows:
- preventing the mother's immune system from producing antibodies;
- if possible, avoiding procedures such as taking umbilical cord blood, chorionic villus sampling and amniotic fluid so that fetal red blood cells cannot reach the mother;
- suppression of antibody production with anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins to reduce the level of sensitization.
Thus, the following preventive measures are taken for pregnant women who have a negative Rh factor:
- donating blood for antibodies between the first visit and the 18th week of pregnancy;
- if the titer is less than 1:4, the analysis is done again at the 28th week, but in case of abnormalities in fetal development - earlier;
- if the titer is no more than 1:4, vaccination is prescribed at week 28;
- if the titer is more than 1:4, it is determined every week until the 20th week;
- if the mother has antibodies, the fetus is constantly monitored (using ultrasound); if the condition worsens, an intrauterine blood transfusion may be required;
- if a transfusion cannot be done, the issue of childbirth is resolved, since waiting in this case may result in the death of the child;
- within three days after delivery, the baby’s Rh is determined: if it is negative, then nothing is administered to the mother, if positive, antibodies are administered, but only if they are not in the blood;
- if antibodies were detected during pregnancy, then there is no point in administering immunoglobulins;
- Vaccination is needed after an abortion, spontaneous miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, after puncture of amniotic fluid, etc.
Let's sum it up
When conceiving a child, the compatibility of the parents according to the Rh factor does not matter, but this is one of the important criteria that affects the successful course of pregnancy. Therefore, it is so important to thoroughly prepare the female body for bearing a child.
Pregnoton, which contains folic acid, iodine, vitamins E, C, B6, and zinc, will help with this. It eliminates the lack of micronutrients important for conception and early pregnancy, and also normalizes the functioning of the reproductive system, reduces prolactin levels in hyperprolactinemia, increases the thickness of the endometrium in women with thin endometrium and increases the likelihood of pregnancy (more information about the product can be found here).
THIS IS NOT AN ADVERTISING. THE MATERIAL WAS PREPARED WITH THE PARTICIPATION OF EXPERTS.
How does the Rh factor affect the conception of a child and its intrauterine development?
- Spontaneous abortion.
- A frozen pregnancy, a negative Rh woman and a positive fetus can provoke a conflict in which, due to the effects of antibodies, the pregnancy stops developing.
- Antenatal (intrauterine) fetal death.
- After childbirth, a severe form of hemolytic disease may cause hearing loss and impaired intellectual development.
- Neonatal death of a newborn.
Hemolytic disease, which can occur in three forms:
- Edema;
- Jaundice;
- Anemic.