Cardiosclerosis, or the development of connective scar tissue in the heart muscle, is an irreversible process that gradually impairs the contractility of the heart. Cardiosclerosis can occur not only after myocardial infarction, but also as a result of myocarditis. In this regard, it is necessary to know in which cases the formation of cardiosclerosis is more likely, and how to prevent these processes.
Myocarditis is a rather serious disease that can not only cause dangerous cardiac disorders, but also provoke the development of serious complications and long-term consequences.
In order to talk about the occurrence of complications after myocarditis, both in acute and long-term periods, it is necessary to understand what this nosological form is.
Myocarditis is an inflammatory pathomorphological change in the thickness of the heart muscle, causing disturbances in the activity of cardiac smooth muscle cells.
(cardiomyocytes) at the molecular level, as well as causing certain clinical manifestations.
Symptoms and signs
The severity of clinical manifestations directly depends on the degree of proliferation of connective tissue in the myocardium and the percentage of damaged cardiomyocytes. As a result of a decrease in the number of functioning cells, the ability of the heart muscle to pump blood is impaired, which leads to its stagnation in the systemic or pulmonary circulation. If the left side of the heart is affected, congestion occurs in the lungs, which causes shortness of breath (difficulty breathing), which worsens with physical exertion.
Lack of air is especially common at night, which is caused by the horizontal position of the body. The patient is forced to take the “orthopneic” position (sitting on the bed, leaning widely on it with his hands).
When the right side of the heart is damaged, blood stagnates in the systemic circulation. There is coldness and a feeling of chilliness in the arms and legs, heaviness and aching pain in the right hypochondrium, swelling mainly in the lower third of the legs.
Due to heart rhythm disturbances, attacks of dizziness, lightheadedness, and darkening of the eyes appear. With more severe arrhythmias, a person may lose consciousness.
Causes of myocarditis and mechanisms of formation of cardiosclerosis after it
Myocarditis, like any inflammatory process, can occur due to the introduction of viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoan microorganisms into normal tissue
(Toxoplasma). Any infectious agent leads to the release of inflammatory mediators; in other words, a septic melting of normal tissue is formed. Due to the fact that cardiomyocytes cannot regenerate and restore to normal sizes, they are gradually replaced by connective tissue - first tender and finely fibrous, and then coarse scar.
In this regard, the muscular frame of the heart gradually loses its firmness and elasticity, which causes a loss of contractility of the heart. Plus, under the influence of fairly high blood pressure, with which blood is pushed from the left ventricle into the aorta, an expansion of the chambers of the heart gradually forms, because only muscle tissue, but not scar tissue, can withstand such pressure. As a result, the patient develops chronic heart failure, usually due to dilated cardiomyopathy due to diffuse cardiosclerosis.
The process of development of CHF can last for years and decades, or it can proceed quickly, over several months, with the development of severe decompensation of CHF and its rapid progression to the terminal stages.
In addition to infectious agents
, the development of inflammation can be caused by the introduction into the myocardium
of immune complexes and auto-antibodies
, the formation of which is caused by rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma and some other rheumatological diseases. In this case, the patient, along with damage to other internal organs, develops myocarditis of an autoimmune nature, which can also lead to the development of connective tissue in the myocardium.
Other reasons that can trigger the occurrence of acute non-infectious myocarditis may be exposure to chemotherapy drugs
, used for the treatment of malignant tumors, as well as radiation used in radiation therapy of tumor processes.
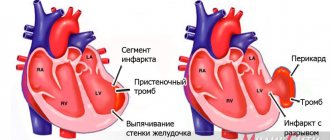
example of changes in the heart muscle during cardiosclerosis
Depending on the volume of damage that occurs in the heart muscle, focal and diffuse cardiosclerosis are distinguished. In the first case, the patient may experience both single and multiple foci of sclerosis in the myocardium; in the second, a circular uniform replacement with scar tissue is formed. Focal cardiosclerosis, represented by a single lesion, is undoubtedly more prognostically favorable if it does not cause significant disturbances in heart rhythm, which in themselves can lead to wear and tear of the heart muscle with the development of acute or chronic heart failure.
Causes
Myocarditis, and, consequently, this type of cardiosclerosis develops due to the following reasons.
- Coxsackie viruses, ECHO, herpes simplex viruses, influenza viruses, Epstein-Barr viruses, cytomegaloviruses.
- Bacteria: staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, mycobacterium tuberculosis, less often - chlamydia, mycoplasma, rickettsia, borrelia, diphtheroids.
- Parasites and fungi: toxoplasma, trichinella, echinococcus, candida, aspergillus.
- Taking medications. Inflammation in the heart muscle can be caused either by the direct toxic effect of medications or by an indirect allergic reaction. Such medications include antibiotics, antituberculosis drugs, antidepressants and antitumor immunosuppressants (cytostatics).
- Autoimmune pathologies: acute rheumatic fever, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis).
The mechanism of pathology development
The pathogenesis (mechanism of development) of cardiosclerosis is as follows: after the resolution of acute inflammatory processes in the myocardium, so-called fibroblast growth factors are released from the destroyed cells. They stimulate the production of the main protein of connective tissue - collagen.
Large quantities of it form fibers that gradually replace normally functioning areas of the heart muscle. As a result, the pumping function of the myocardium deteriorates, and various rhythm disturbances occur.
However, this scenario does not always occur. Most people recover completely from myocarditis without significant residual effects. Why some patients develop cardiosclerosis and others do not is still a mystery. This may depend on the amount of cellular damage, the state of the immune system and many other factors.
Complicated form
Healthy cardiac myocardium has good elasticity and contracts well. When it is replaced by fibrous connective tissues, which do not have elasticity and do not take any part in the contractile function of the myocardium, they lead to the fact that with insufficient contraction of the cardiac muscle, a load on the cardiac organ occurs.
If there are foci of cardiosclerosis in the cardiac organ, it is likely to be asymptomatic, but if the localization of cardiosclerosis is located on the cardiac impulse line, or near the sinus node, then the probability of developing arrhythmia is 100.0%.
The development of changes of the sclerotic type provokes the pathology of compensatory hypertrophy, as well as expansion of the myocardial muscles.
When the muscle reserve of hypertrophy is exhausted, the contractile function of the myocardium decreases and cardiac organ failure develops. Scarring processes in the heart valves provoke deformation of the heart valve apparatus and heart valve insufficiency.
The larger the area of the cardiac myocardium is affected by myocardial cardiosclerosis, the higher the likelihood of disruption of the functioning of the cardiac organ, until it stops completely.
The most dangerous and complex complication of post-myocardial cardiosclerosis is progressive heart failure, as well as aneurysm of the cardiac myocardium, disturbances in the rhythm and conduction of impulses of the cardiac organ.
The larger the area of the cardiac myocardium is affected by myocardial cardiosclerosis, the higher the likelihood of disruption of the functioning of the cardiac organ
Diagnostics: how to suspect and determine
From personal practical experience I can say that the main thing is to know how the disease developed. A thorough survey allows you to establish the fact of myocarditis. It may be indicated by the appearance of pain in the heart, a feeling of palpitations, shortness of breath and constant weakness.
A general examination (physical examination) of the patient also plays an important role. In such patients, I usually pay attention to the color of the lips (it may be bluish), swollen veins in the neck, thickening of the terminal phalanges of the fingers (the so-called drumstick sign) and an enlarged liver.
Auscultation of the heart and lungs occupies a special place. The patient can hear noises, dull tones, irregular rhythm, and moist rales in the lower parts of the lungs. In severe and advanced cases, when there is severe circulatory insufficiency, an auscultatory phenomenon appears - “gallop rhythm”, characterized by the appearance of a third tone between two physiological ones.
After a survey and general examination of the patient, I make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm or exclude it, you need to undergo an additional examination, including the following.
- General and biochemical blood tests - they do not provide enough data to diagnose cardiosclerosis itself, but sometimes they reveal abnormalities that could cause the development of myocarditis.
- Electrocardiography. The ECG shows nonspecific changes: ST segment elevation and negative T wave. Cardiac rhythm and conduction disturbances are often detected in the form of supraventricular and ventricular extrasystoles, atrial fibrillation and flutter, atrioventricular block and bundle branch block.
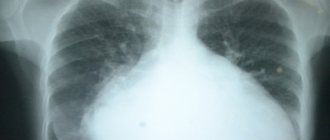
- Chest X-ray - may reveal enlarged heart borders and signs of pulmonary congestion.
- Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart, ECHO-CG) - allows you to see thickening of the myocardial walls, dilatation (expansion) of the atria and ventricles, areas of impaired muscle contractility.
- Endomyocardial biopsy - according to modern recommendations, the diagnosis of cardiosclerosis is established by histological examination of the myocardium. However, due to the technical complexity, I rarely prescribe this procedure to my patients.
Diagnostics
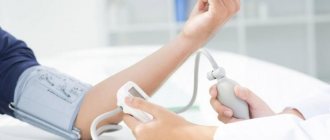
At the patient’s first appointment, the cardiologist performs a visual examination and medical history, and also measures the blood pressure index and cardiac cardiogram.
Based on the first diagnostic results, the doctor prescribes a more in-depth study of the heart organ using an instrumental diagnostic method, as well as a detailed biochemical analysis of the blood composition with a lipid spectrum, which reflects the glucose index in the blood, as well as the concentration of total cholesterol and all its fractions.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing post-myocardial cardiosclerosis:
- Echocardiography reveals myocardial wall aneurysm and dilatation,
- Signal-averaged electrocardiography,
- Magnetic resonance imaging reveals ventricular dilatation, myocardial fatty deposits, aneurysm and myocardial fibrosis,
- The angiography method shows the presence of an aneurysm in the cardiac organ.
Treatment and its methods
The need for hospitalization depends on the severity of the patient's condition. In most cases, outpatient treatment is sufficient. The use of antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal drugs is pointless, since at the time of the formation of cardiosclerosis the pathogen has already left the body.
The first stage of treatment is to limit physical activity. Professional sports are strictly contraindicated. Aerobic exercise and physical therapy are allowed. I explain to my patients that they should follow a low-salt diet, consuming no more than 2-3 grams per day. This is necessary to prevent fluid stagnation in the body.
The basis of treatment is drug therapy. To slow the progression of heart failure, I use medications from the following pharmacological groups: ACE inhibitors (Perindopril, Ramipril), beta-blockers (Bisoprolol, Nebivalol) and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (Spironolactone). For severe congestion, I prescribe diuretics—loop diuretics (“Furosemide”, “Torasemide”).
Treatment methods for arrhythmias are determined by their type, severity and accompanying symptoms. With atrial fibrillation and flutter, blood clots form in the cavities of the heart, which can migrate and clog a vessel in an organ, such as the brain, thereby causing an ischemic stroke. Therefore, to prevent thrombosis, I use anticoagulants (Warfarin, Dabigatran, Apixaban, Xarelto).
If arrhythmias are accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness and fainting, it is worth considering the option of taking medications that normalize cardiac activity, such as Propafenone, Sotalol. If there is resistance to drug therapy, surgical intervention is performed - radiofrequency ablation. For severe atrioventricular blockade, installation of a pacemaker is indicated.
Complications: what causes death and in what cases
Adverse consequences are observed in diffuse forms of cardiosclerosis. These include acute heart failure, including pulmonary edema and cardiogenic shock (a sharp decrease in the pumping function of the heart).
With severe rhythm disturbances, sudden cardiac death may occur due to ventricular fibrillation and asystole (complete cardiac arrest). These conditions very often end in death. They occur in approximately 5-10% of cases of post-myocardial cardiosclerosis.
Symptoms of post-myocardial cardiosclerosis
As already described above, cardiosclerosis is a pathomorphological concept, therefore, any symptoms in a patient after suffering myocarditis occur if he is already developing chronic heart failure. Therefore, all symptoms of post-myocardial cardiosclerosis are caused by the following symptoms of CHF, such as:
- Paroxysmal shortness of breath during physical activity, first with significant activity, for example, when walking long distances or when climbing a high floor of stairs, then with lesser breath - when moving around the house, when tying shoelaces, when preparing food, etc.
- Swelling of the skin of the legs, feet, and in later stages - the skin of the abdomen, perineum, mammary glands,
- Accumulation of fluid in the internal cavities of the body - in the pleural (hydrothorax) and abdominal (ascites),
- A feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart, provoked by various rhythm disturbances, most often extrasystole and atrial fibrillation.
In the case when the patient has minor foci of cardiosclerosis in the myocardium, or has not yet developed pronounced manifest heart failure, the patient can feel great for many years, and only as the listed symptoms arise learn that he has post-myocardial cardiosclerosis. That is why all patients after suffering acute myocarditis need to regularly visit their local doctor and be examined at the clinic at their place of residence at least once a year.
Clinical case
A 49-year-old man came to see me with complaints of weakness, increased fatigue, difficulty breathing, and frequent attacks of dizziness.
Last night I lost consciousness, which was the reason for visiting the doctor. During the interview, it turned out that six months ago, after a cold, the patient developed chest pain, to which the patient did not attach much importance. Auscultation revealed a weak, irregular heartbeat of 42 beats per minute. The ECG revealed complete atrioventricular block, the ventricular contraction rate was 35-47 per minute. Echo-CG showed thickening of the myocardial walls, zones of hypokinesis (reduced contractility) and a small ejection fraction (45%). I suspected postmyocardial cardiosclerosis. At the medical consultation, it was decided to perform an endomyocardial biopsy. The resulting histological specimen revealed myocardial fibrosis and degenerative cell changes.
The final diagnosis was: “Myocarditis, unspecified. Complications: NYHA class II CHF, complete AV block.” The patient was prescribed medications to treat heart failure and had a permanent pacemaker implanted. After the operation, the patient feels satisfactory, dizziness and shortness of breath are no longer bothersome.
Symptoms
Postmyocardial cardiosclerosis has similar symptoms to many pathologies of the heart organ, but an experienced cardiologist will be able to identify the difference.
It is also necessary to know that when the focus of atherosclerosis is localized in many areas, symptoms do not appear at all, or these signs are not pronounced.
Symptoms of post-myocardial cardiosclerosis:
- Rapid heartbeat, tachycardia,
- Violation of the rhythm of the heart organ - arrhythmia.
These heart symptoms can occur either suddenly or after a nervous overstrain or stressful situation.
There are also symptoms of a heart attack that are similar to many cardiac pathologies:
- Severe shortness of breath. With the development of postmyocardial cardiosclerosis, shortness of breath and lack of air supply increase. Shortness of breath can occur during sleep and during rest periods,
- Pain in the chest, as with unstable angina,
- Weakness that is systematic
- Severe and dry cough. Coughing attacks occur at night, and shortness of breath almost always appears as a precursor to coughing,
- As a cough develops, symptoms of hoarseness and sputum appear,
- Swelling of the lower and upper extremities, as well as swelling of the abdomen. This symptom occurs due to stagnation of fluid inside the body,
- Pre-syncope and fainting,
- Severe body fatigue
- Sharp swelling of the jugular vein,
- Pallor of the skin,
- Cold upper and lower extremities,
- Pathology hepatomegaly,
- Decreased intellectual and physical abilities,
- Instantly fatal attack.
In order to confirm the diagnosis of cardiosclerosis, it is necessary to diagnose the heart organ.