There are a number of anatomical features of the human brain. In some cases, some nuances of its structure that differ from the norm are considered physiological and do not require treatment.
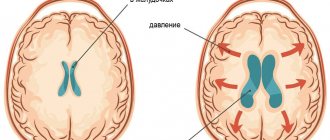
However, certain deviations from the norm can cause the development of neurological pathologies. One such condition is asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain. This disease may not cause clinical symptoms, but in some cases it indicates the presence of a number of diseases.
Indicators of normal sizes
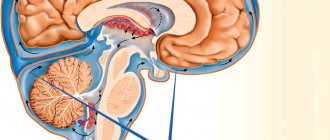
In the human body, the ventricular system consists of several cavities that anastomize with each other. They communicate with the subarachnoid space, as well as the spinal cord canal. A special liquid, cerebrospinal fluid, moves directly inside the cavities. With its help, tissues receive nutrients and oxygen molecules.
The largest intracerebral hollow formations are, of course, the lateral ventricles. They are localized below the corpus callosum - on both sides of the midline of the brain, symmetrical relative to each other. In each, it is customary to distinguish several sections - the anterior and lower, as well as the posterior horns and the body itself. The shape resembles the English S.
The normal size of the ventricles is assessed taking into account individual anatomical characteristics - there are no uniform standards. Experts focus on average parameters. It is important to know these sizes for babies under one year old - for the purpose of early diagnosis of hydrocephalus.
Normal values for children:
| Anatomical unit | Newborns, mm | 3 months, mm | 6 months – 9 months, mm | 12 months, mm |
| Lateral ventricle | 23.5-/+ 6.8 | 36.2 -/+3.9 | 60.8-/+6.7 | 64.7-/+12.7 |
For adults, the parameters should be in the range - the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle is less than 12 mm in people under 40 years of age, while its body is 18–21 mm in people under 60 years of age. Exceeding the age-related size of the brain ventricles by more than 10% requires additional research to identify and eliminate the root cause.
The size of the ventricles is normal
In infants, the ventricles are often dilated. This condition does not at all mean that the child is seriously ill. The dimensions of each ventricle have specific values. These indicators are shown in the table.
| Anatomical structure | Depth in mm. |
| First and second ventricles (lateral) | 4 |
| Third ventricle | 5 |
| Fourth ventricle | 4 |
To assess normal indicators, the determination of all structural elements of the lateral ventricles is also used. The lateral cisterns should be less than 4 mm deep, the anterior horns between 2 and 4 mm, and the occipital horns between 10 and 15 mm.
Classification
The main criteria for separating dilatations of the lateral ventricles in the brain are the size of the cavities, the etiology of the dilation, the age of the patient, and the localization of pathological changes.
Each neurologist chooses the optimal classification of the disorder for himself. However, most doctors adhere to the average principles of diagnosis:
- According to the time of expected appearance of the lesion in the brain:
- prenatal period;
- detection of enlarged cerebral ventricles in newborns;
- expansion of brain cavities in adults.
- By localization:
- left ventricle enlargement;
- right-sided lesion;
- bilateral defeat.
- By etiology:
- post-infectious ventricular dilatation;
- post-traumatic changes;
- toxic expansion;
- tumor focus in the brain;
- vascular diseases.
- By severity:
- slightly enlarged ventricles of the brain in infants;
- moderate dilatation;
- severe changes in the ventricles.
Additionally, the specialist can indicate in the diagnosis whether complications are present - for example, hydrocephalus or intellectual/neurological problems.
Causes
The stages of development of the central nervous system in humans provide that as the size of the brain increases, the parameters of the ventricles will also change. For each period, the reasons for dilatation of the lateral cavities have their own characteristics.
In general, the main provoking factors will be as follows:
- brain injuries or falls;
- neuroinfections - for example, meningitis or congenital syphilis;
- brain tumors;
- thrombosis of cerebral vessels;
- strokes;
- abnormalities in the development of brain structures - for example, the anterior horns of the ventricles.
The mechanism for the development of dilatation is the overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid, or a violation of its adsorption/outflow from the cavities of the brain.
In some cases, it is not possible to determine the exact cause of the expansion of the cavities - the idiopathic version of the disorder. The doctor will select the treatment regimen taking into account the main clinical signs. Less often, the basis of dilatation is seen as an atypical anlage of brain structures - it is necessary to carefully collect an anamnesis from the child’s mother, what diseases she suffered during pregnancy. Sometimes the pathology is hereditary in nature - genetic abnormalities.
General mechanism for the development of disturbances in the activity of cavities
At the first stage, there is difficulty in the outflow of cerebral fluid into the subarachnoid space from the ventricles. This provokes expansion of the cavities. At the same time, compression of the surrounding tissue occurs. Due to the primary blockage of fluid outflow, a number of complications arise. One of the main ones is the occurrence of hydrocephalus. Patients complain of sudden headaches, nausea, and in some cases vomiting. Disorders of autonomic functions are also detected. These symptoms are caused by an acute increase in pressure inside the ventricles, which is characteristic of some pathologies of the liquor-conducting system.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of formation of dilated ventricles of the brain in an infant, any special clinical signs may not be detected - the child behaves according to the age norm. After all, adaptation mechanisms are capable of combating overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid.
However, as the expansion of the lateral ventricles of the child’s brain increases, he begins to worry about the consequences of hydrocephalus - pathological pressure on the brain structures due to tissue swelling. The main signs of intracranial hypertension:
- frequent attacks of headache;
- slow growth of fontanelles;
- swelling of tissue between the sutures of the skull;
- nausea and vomiting without improvement of well-being;
- decreased appetite, frequent regurgitation;
- worsening sleep;
- throwing the head back;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- lack of interest in current events, apathy;
- tendency to epilepsy.
In adult patients, a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the lateral ventricles is manifested by a feeling of constant distension inside the head, persistent dizziness with nausea. A person’s ability to work decreases, and he develops anxiety-phobic conditions. At the same time, taking standard analgesics does not improve well-being.
With persistent hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, people develop paresis/paralysis, as well as serious difficulties with speech, vision, hearing, and decreased intellectual capabilities.
Consequences
The consequences of increased intracranial pressure are manifested in the following symptoms:
- The baby becomes lethargic and loses appetite.
- A pronounced venous network appears on the forehead due to obstruction of outflow from the cranial cavity.
- Muscle tone in the limbs changes, tendon reflexes, which normally should be moderate, are revived.
- Changes occur in the fundus in the form of congestion.
- Sometimes tremor appears in the limbs.
- Both grasping and swallowing and sucking reflexes are reduced.
- The baby spits up often. This is caused by the fact that increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure irritates the vomiting centers at the bottom of the rhomboid fossa (in the fourth ventricle). The adult equivalent is cerebral vomiting without nausea.
- Tension and bulging of the fontanelles appear, and an increase in their linear dimensions occurs.
- The baby has a disproportionately large head.
Of course, the symptoms described above are not necessarily associated with ventriculomegaly. As mentioned above, a slight increase in size, and even asymmetry of structures, in the absence of a clinical picture, changes in reflexes and the fundus of the eye, should not bother parents. They should simply observe the baby and do neurosonography on him regularly.
Diagnostics
If a specialist observes signs of a malfunction in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid through the cerebral ventricles, or the patient has complaints of deterioration in health, then instrumental confirmation of dilatation of the brain cavities is required.
It is possible to identify signs of slight dilation of the lateral ventricles using such a modern diagnostic examination method as magnetic resonance imaging. On the resulting images of brain structures, you can see in detail the area of expansion, the area of damage, and the involvement of neighboring brain tissues in the process.
Increased intracranial pressure will also be diagnosed using the following procedures:
- echoencephaloscopy;
- electroencephalography;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- examination of cerebrospinal fluid - identification of previous neuroinfections;
- blood tests - general, biochemical, for autoimmune processes.
Only after careful comparison of all information from diagnostic procedures, a neurologist will be able to assess the severity of dilatation of the lateral ventricles, establish the root cause of the pathological condition and select optimal therapeutic measures.
Treatment tactics
In itself, the expansion of the size of the ventricles of the brain does not require intervention - if there are no clinical signs of intracranial pressure failure. Whereas in the case of a violation of liquorodynamics and symptoms of deterioration of well-being formed against this background, doctors will recommend conservative therapy:
- diuretics – removing swelling from brain tissue;
- neuroprotectors – correction of the conduction of nerve impulses;
- vasoactive agents – improving brain nutrition;
- nootropics – improvement of local blood circulation;
- sedative medications – normalization of the psychosomatic background;
- anti-inflammatory/antibacterial drugs – if the disorder is caused by an infectious process.
Neurosurgical intervention will be required if ventricular dilatation is caused by brain tumors or thromboembolism of cerebral vessels. If necessary, ventriculostomy is performed to create a new connection between the cavities of the brain.
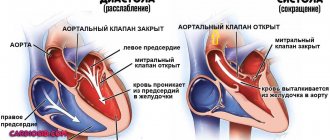
Aortic dilatation
The aorta is the largest vessel in the body, which receives oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle.
A dangerous condition is enlargement (dilatation) or aneurysm of the aorta. Typically, the aorta dilates at a “weak spot.” One of the reasons for this condition is arterial hypertension. Atherosclerosis and inflammation of the aortic wall can also lead to pathology.
The danger of an aneurysm is:
- In sudden rupture of the aorta. This results in severe internal bleeding, which is life-threatening.
- In the formation of blood clots. This condition is also extremely life-threatening.
More often, an aortic aneurysm is discovered during examination by chance. But still, some signs are sometimes present:
- Unreasonable sore throat and cough.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Difficulty swallowing due to compression of the esophagus.
- When the aorta ruptures, there is severe chest pain that spreads to the neck and arms. The prognosis in this case is unfavorable - the person quickly goes into shock due to large blood loss and dies.
Aortic dilatation does not develop immediately. This is a long process, as a result of which the vessel wall undergoes gradual changes. Timely detection of pathology can prevent the terrible consequences of the disease.
In addition to the aorta, smaller vessels also undergo expansion. This occurs due to abnormally increased blood volume, exposure to hormones or chemicals. Vascular dilatation leads to circulatory disorders, which affects the functioning of all body systems.
Prognosis and prevention
The consequences of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles are varied. Their severity and severity directly depend on the size of the pathological expansion and the age of the patient. Thus, in mild forms of the disorder, children experience short-term developmental delays, both intellectual and physical. With timely medical care, hydrocephalus is completely eliminated.
Whereas with severe dilatation of the cavities, various neurological diseases are formed - for example, cerebral palsy, or persistent mental disorders. There is no specific prevention of ventricular asymmetry, since it is almost impossible to predict its occurrence. However, experts point out that when the expectant mother strives for a healthy image, she contributes to the birth of a baby with normal sizes of brain cavities. To do this, you need to give up bad individual habits even before pregnancy, eat right, get good sleep, and avoid psycho-emotional and stress overload.
Provoking diseases
The main disease causing this pathology is hydrocephalus. It can interfere with the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. This leads to its accumulation in the lateral ventricles.
Excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid is also observed with serious lesions of the central nervous system. Poor circulation is also associated with the formation of cysts, tumors and other neoplasms.
A common cause of hydrocephalus is a defect of the Sylvian aqueduct. If this defect was discovered during the prenatal period, termination of pregnancy is recommended. At the birth of a child, complex systematic treatment will be required.
Another cause is aneurysm of the vein of Galev and Arnold-Chiari syndrome. However, in children, the disease can be caused by rickets or due to the specific structure of the skull, so observation by a specialist is important if there is a predisposition to the disease.