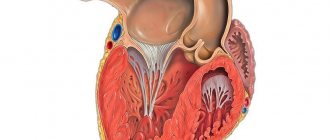
Cardiac aneurysm (aneurysma cordis) is a limited protrusion of a thinned area of the heart wall. Most often develops as a result of myocardial infarction. Congenital, infectious, traumatic, and postoperative cardiac aneurysms are much less common. Traumatic aneurysms occur due to closed or open heart injuries. This group also includes aneurysms that occur after operations for congenital heart defects.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, cardiac aneurysm is a complication after a myocardial infarction (usually transmural). Up to 25% of heart attack patients may be affected by this disease.
Dangerous complications of chronic cardiac aneurysm are gangrene of the limb, stroke, kidney infarction, pulmonary embolism, and repeated myocardial infarction. When a cardiac aneurysm ruptures, death occurs instantly.
Based on the time of occurrence, aneurysms are divided into acute (1-2 weeks from the onset of myocardial infarction), subacute (3-6 weeks) and chronic. Most often, post-infarction aneurysms are localized on the anterolateral wall and at the apex of the left ventricle; in 50-65% of cases they spread to the anteroseptal region.
Left ventricular aneurysm is diagnosed so often because of the maximum blood pressure in this ventricle. Up to 50% of the surface of the left ventricle may be damaged as a result of the pathological process.
1 Left ventricular aneurysm
Aneurysm of the posterior wall of the left ventricle is observed in 2-8% of patients. Blood clots are often found in the aneurysm cavity, but the incidence of thromboembolic complications is no more than 13%.
Symptoms
Clinically, the manifestation of LV aneurysm is almost invisible. However, due to the fact that the pathology leads to dysfunction of the heart, it has general signs of cardiac failure:
- Pain in the chest, radiating to the left.
- Heart pain after significant psychological and physical stress.
- Uncomfortable feelings in the chest.
- Increased heart rate, shortness of breath.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of consciousness, fainting.
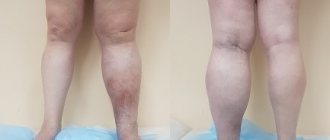
- Swelling in the arms and legs.
- Feeling of lack of oxygen, suffocation.
Different types
When talking about an aneurysm, they often mean an aortic aneurysm. At the same time, there are quite a lot of different types of this pathology.
Thus, one of the first to be called is a cerebral aneurysm. Here, both single and multiple defects can be observed, which naturally aggravates the situation. Such neoplasms may not manifest themselves for a long time, but as they grow, they often give nonspecific symptoms. You can recognize the presence of such a problem by:
- Visual impairment
- The appearance of hallucinations
- Coordination and balance problems
- Failure of one limb
- Speech disorders
- Headaches
This is due to the fact that the aneurysm compresses tissue and brain structures. Due to the fact that it takes on some of the blood, a person may experience neurological disorders and even a stroke. When a vessel ruptures, half of the victims die from hemorrhage.
Aortic rupture: where aneurysms occur and how to avoid them Read more
An abdominal aortic aneurysm is a defect that affects the largest vessel in the human body. Its walls are very dense and can easily separate into components. If there is such a problem, a person will be tormented by:
- Burning
- Chest pain
- Pulsation in the stomach area
- Cold feet
When such an aneurysm ruptures, acute abdominal pain and vomiting are observed. If the blood flows too quickly, then within a few minutes the person will feel an unpleasant tingling sensation in the legs. A complication in this case may be a stroke.
Article on the topic
Thick means dangerous. What you need to know about blood clots
Aneurysm of peripheral vessels causes increased thrombosis. The thrombus can break away from the wall of the aneurysm and move into the vessels of vital organs: heart, brain, lungs, kidneys. Symptoms vary depending on the location of the defect.
A cardiac aneurysm usually results from a heart attack or other cardiac problems. This is due to the fact that the wall of the heart, having experienced such a strong load, cannot withstand the pressure. As a result, it begins to stretch. Indicates the presence of such a problem:
- Weakness
- Edema
- Stagnation of mucus in the lungs
- Dyspnea
- Increased heart rate
Pathology cannot be underestimated. For example, in the United States alone, every year as many people die from this defect as from AIDS: about 24,000. Acquired aneurysm is often considered to be the lot of the elderly. But young people are also susceptible to it: they develop it due to injuries received in car accidents or during extreme sports.
Aortic aneurysm - how to detect this deadly disease? More details
Complications without surgery
Small LV aneurysms usually do not pose a threat to the patient’s life, although in rare cases they can provoke thromboembolic complications due to the formation of parietal thrombi in the heart cavity, which are carried by the blood flow to other arteries and can cause a heart attack, stroke, pulmonary embolism or mesenteric artery thromboembolism (PE). and mesenteric thrombosis).
Complications with aneurysms of medium and giant sizes are more common and are as follows:
- Thromboembolic complications,
- Progression of chronic heart failure, development of acute heart failure,
- Rupture of an aneurysm, leading to the rapid death of the patient.
Prevention of complications is the timely detection of aneurysm growth, regular examination by a doctor, as well as timely identification of indications for surgical treatment.
How to detect
Diagnosing an aneurysm is one of the important points of prevention. Moreover, it is often discovered completely by accident. One of the most informative options is computed tomography, which allows you to accurately and in detail see the presence of the problem. Angiography is also used: a study using contrast. This allows you to more accurately determine the presence of a problem, the size and location of the aneurysm. MRI is often used.
Article on the topic
Stroke with a happy ending. Surgeons removed an aneurysm through a keyhole
Clinical picture
Symptoms are nonspecific. The classic triad is represented by:
- Shortness of breath;
- Pain syndrome;
- Feeling of irregularities and rapid heartbeat.
Shortness of breath is of a mixed nature and is manifested by difficulty in both inhalation and exhalation. The pain syndrome develops like angina pectoris - within 10-15 minutes after physical activity. The feeling of interruptions is due to developing arrhythmia and can be paroxysmal or permanent.
Other manifestations:
- Fainting;
- Edema;
- Decreased exercise tolerance;
- Insomnia;
- Sudden cardiac death.
Correction of the situation
Treatment is selected by the doctor individually. So, for example, if the defect is small, the doctor may recommend observation and risk monitoring. In addition, those diagnosed with an aneurysm are prescribed a gentle diet, excluding fatty foods, and also have to give up alcohol and smoking.
Another option for correcting the situation is clipping. In this case, the patient has a metal clip applied to the aneurysm stalk, which limits the growth of the defect and prevents rupture.
A replacement for surgical intervention is endovascular occlusion. This option is considered new and involves the use of a special catheter. Metal spirals are placed in it, which fill the aneurysm, as a result of which the blood does not press on the walls of the vessels.
This pathology should not be ignored; it is better to undergo examinations on time. Then there is a chance to save health and life.
What examination is necessary if a cardiac aneurysm is suspected?
Equally important in establishing the diagnosis of an aneurysm is a thorough examination of the patient. So, in the vast majority of cases, the doctor can see pathological precordial pulsation, which is defined as periodic protrusion of the anterior chest wall in the 3-4 intercostal spaces to the left of the sternum, coinciding with the heart rate. This phenomenon is called the “rolling wave” symptom or the “yoke” symptom.
- Category “Cardiac aneurysm”
In addition to examination, during auscultation of the heart, a systolic-diastolic murmur, called a “squeaking noise,” can be heard, but it is heard in a small proportion of patients. In addition, when listening to the lungs, one can determine single or multiple, dry or moist rales in the lower parts of the lungs in heart failure.
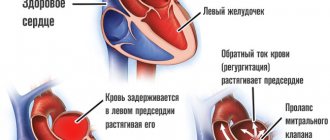
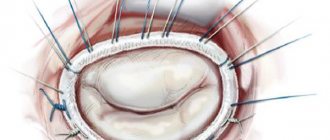
Also, in addition to the true aneurysm of the left ventricle, it is customary to distinguish a false one, caused by protrusion of a section of the heart sac - the pericardium. The differences are in the figure below:
If the doctor suspects the formation of a cardiac aneurysm, he will refer the patient for examination. The following diagnostic methods are informative:
- Electrocardiogram. On the ECG, an aneurysm that has reached a significant size is characterized by signs of acute myocardial damage and necrosis. In this case, they say that the ECG has a “frozen appearance” of acute myocardial infarction. However, the absence of signs of a heart attack on the ECG does not mean that the patient does not have a cardiac aneurysm.
- Radiography. An x-ray of the chest organs in patients with an aneurysm that has reached a large size is characterized by an increase in the diameter of the heart shadow, as well as protrusion of the cardiac contour. In cases where the aneurysm is small in size, X-ray diagnostic methods are not very informative.
- Echocardioscopy (echocardiography, ultrasound of the heart). It is an informative diagnostic method, as it allows not only to clarify the shape, location and size of the aneurysm, but also to identify the presence of parietal thrombi, which can pose a significant danger to the patient.
- Computer, magnetic resonance and multi-slice computed tomography of the heart (CT, MRI and MSCT) are the most informative methods for identifying aneurysms and are used as a complement to ultrasound of the heart in diagnostically unclear cases.
Video: thrombosed left ventricular aneurysm on echocardiography
Treatment of cardiac aneurysm
It is impossible to eliminate a cardiac aneurysm using conservative treatment methods, and when the first signs of heart failure appear, the question of surgery is raised. The main treatment method for cardiac aneurysm is surgical excision and suturing of the defect in the heart wall. In some cases, the aneurysm wall is strengthened using polymer materials.
In the preoperative period, cardiac glycosides, anticoagulants, antihypertensive drugs, oxygen therapy, and oxygen barotherapy are prescribed. Patients are advised to strictly limit physical activity.
The cardiology department of MedicCity has all the necessary equipment to carry out comprehensive diagnostics of a wide range of cardiac diseases. Reception is conducted by highly qualified cardiologists who have completed professional internships in Russia and abroad.
General classification of the disease
Experts distinguish the following types of aneurysms:
- True aneurysm. It is characterized by stretching of the vessel walls, and all three layers of the vascular wall are susceptible to similar pathology. A true aneurysm does not cause trouble for the patient for years, but it has dangerous consequences if it ruptures. Stroke, thrombosis, vessel dissection, embolism and destruction of adjacent tissues are the consequences of an advanced form of a true aneurysm.
- False aneurysm is a disease that can occur due to traumatic damage to the vessel wall. As a result of a puncture or other injury, blood seeps through the damaged vessel wall and accumulates in the connective tissue, taking the form of a pulsating hematoma. This pathology is especially dangerous on vital vessels. If a true aneurysm is formed by stretching all layers of the vessel, then a false aneurysm does not contain vascular tissue; the blood is enclosed in a “sac” formed in the connective tissue.
- Dissecting aneurysm can be a consequence of a true aneurysm or occur independently. Blood flows between the inner and middle walls of the aorta, creating the threat of a breakthrough in the outer wall of the vessel, which can lead to death.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to diagnose an aneurysm without an instrumental examination. Therefore, after collecting anamnesis and examining the patient, the doctor issues a referral to:
- ECG;
- Echo-CG;
- MRI;
- MSCT of the heart (multispiral computed tomography);
- Heart PET (positron emission tomography);
- myocardial scintigraphy (isotope scan) - intravenous administration of radioactive isotopes (radionuclides) to assess absorption by the heart muscle;
- EPI (electrophysiological study) - stimulation of various parts of the heart to detect life-threatening arrhythmias;
- coronary angiography and cardiac probing - X-ray contrast examination (catheterization) - insertion of a special catheter through the artery.
Types and symptoms of false aneurysm
A false aneurysm can occur as a result of injury, for example, after a puncture wound that hits a vessel. Pathology can also appear after surgery.
Experts distinguish three types of false (traumatic aneurysms);
- An aneurysm on an artery (“sacs” may be several in the case of a through wound).
- Arteriovenous aneurysms that occur in the event of a through lesion affecting an artery and vein. In this case, a connecting channel in the form of a vessel appears between them.
- Combined aneurysms. They may combine the characteristics of the first two types.
The arteriovenous connection must be eliminated as quickly as possible, since the increased direction of blood flow from the artery to the vein leads to disruptions in the functioning of the heart and can lead to myocardial hypertrophy and decompensation of cardiac activity.
For a false aneurysm to appear at the site of an artery injury, the lesion site must be small, and the wound area must be “wrapped” in soft tissue at the entrance and exit holes.
Traumatic aneurysms are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Swelling in the area of the aneurysm;
- Increased pulsation;
- Redness of the skin;
- Painful sensations of varying degrees at the location of the aneurysm.
Prevention of aneurysm in children
With a congenital aneurysm, preventive measures are pointless, but such a disease can be prevented. Teenagers should never smoke, as this habit has a detrimental effect on the condition of the heart and blood vessels. If you have problems with blood pressure, constant monitoring is recommended.
The child's diet should be balanced and consist of healthy foods. Dishes with trans fats and semi-finished products are excluded from the diet, and the amount of sweets is reduced. The diet should consist of vegetables, fruits and unrefined carbohydrates.
The child should regularly engage in physical education or sports activities. Excess weight negatively affects the condition of the heart and blood vessels, so if such a problem arises, it is recommended to review the child’s diet. The teenager's height and weight should progress proportionally. To prevent aneurysm, children and adolescents should sleep at least 7 hours a day and, if possible, avoid stressful situations.
Causes of aneurysm in children
A cardiac aneurysm in a child occurs for a variety of reasons. The disease can be congenital or appear during the development of the child. Often the genetic predisposition of children leads to the development of pathology.
The following pathologies lead to a decrease in the elasticity of vascular walls:
- high blood pressure;
- chronic atherosclerosis;
- vasculitis;
- syphilis and sexually transmitted diseases.
Smoking in adolescence also becomes a serious risk factor. Such a bad habit leads to the accelerated development of an aneurysm, which becomes the main cause of hypertension. Blood clots and injuries to small vessels also lead to the disease. Pathologies quite often occur in adolescents who are involved in road accidents, emergencies, or engage in extreme sports.
The stages of aneurysm in children are closely related to the different stages of the ongoing impairment of the heart’s capabilities:
- stage of compensation, which is observed with a fairly stable size of the resulting aneurysm or with its slow growth. In these cases, the load on the organ increases slightly, which ultimately allows it to function within acceptable limits;
- the stage of decompensation is noted with a rapidly growing pathology with impaired contractile function of the heart. As a result, the organ stops normally releasing the required volume of blood into the circulatory system, which leads to complications.