Blood pressure (BP) can vary depending on the form of pancreatitis and the phase of acute inflammation of this organ, concomitant diseases and the age of the patient. Inflammation of the pancreas is accompanied by changes in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which can affect such a vital indicator as blood pressure. In this article, we will introduce you to possible variations in blood pressure during acute or aggravated pancreatitis and possible fluctuations in this vital indicator during chronic inflammation of the pancreas.
What is pancreatitis
Pancreatitis in medicine refers to the inflammatory process in the pancreas, the development of which is caused by:
- Galloon pathologies, stomach, duodenum;
- Unhealthy diet;
- diabetes;
- Severe poisoning;
- Injuries, surgery in the abdominal area.
The disease often occurs during pregnancy or during drug therapy with estrogen, glucocorticosteroids, sulfonamides, tetracyclines. The risk of developing pancreatitis is present in infectious diseases (hepatitis, chickenpox, swine), and the presence of a genetic predisposition to gastrointestinal disorders.
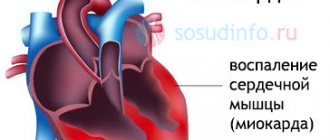
The disease develops against the background of impaired outflow of enzymes and digestive juices in the small intestine. Their accumulation leads to compression of the pancreatic wires, the development of inflammation and swelling. Destructive processes are activated in the Orguard patient, and Gland begins to digest.
Disease progression is associated with the death of pancreatic tissue and the vessels and organs adjacent to the pancreas. This leads to a serious deterioration in the patient's condition and even death.
Pancreatitis in children
In young children, pancreatitis is usually a consequence of congenital malformations of the digestive system or enzyme deficiency. It can also be a complication of mumps (mumps). In older children, the development of the disease may be associated with poor nutrition (including abuse of sweets and carbonated drinks) or caused by intestinal parasites.
Children are often unable to clearly formulate their complaints, what and how they hurt. Therefore, at the first signs of the disease (the child’s complaints of abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, unstable stool with impurities of undigested food), you should immediately consult a doctor. Infants with pancreatitis cry hysterically and quickly lose weight. Their tummy is swollen.
It is necessary to diagnose the disease promptly and begin treatment to prevent loss of the pancreas.
More information about pancreatitis in children
How does it affect blood pressure?
You may be under the impression that there is no strict relationship between blood pressure and the pancreas. In fact, the situation is completely different. Blood pressure in pancreatitis can both rise and fall. The first option is possible during the attack of an acute disease, while the second option more often appears in patients with a chronic form of pathology and internal bleeding (bleeding).
During exacerbation and in the acute stage
Increasing severity of pancreatic disease causes the most severe feelings of pain. This condition releases stress hormones into the bloodstream and increases the activity of the autonomic nervous system. The patient's blood vessels are disturbed and the overall blood flow is impaired.
Increased blood pressure in the acute phase of pancreatitis occurs against the background of psycho-emotional stress and metabolic disorders. This leads to disruption of the mechanisms that control the arteries.
Worsening of pancreatitis can lead to the development of a breakthrough of excess pressure and its typical complications. Often the increase in pressure is short-lived and gives way to hypotension.
In remission and chronic course
Chronic inflammation of the pancreas is characterized by hypertensive pressure, leaving patients alternately with hypertension and hypotension.
Factors that contribute to frequent fluctuations in blood pressure:
- Inability of the pancreas to perform basic functions (this leads to nutritional deficiency, insufficient absorption of micro- and macroelements necessary to maintain the proper functioning of blood vessels and myocardium, provokes poisoning of the body).
- Swelling of the patient, leading to depression of the surrounding lymph nodes, blood vessels, nerve endings, activation of the autonomic system and increased pressure.
- Insufficient production of insulin by the pancreas, a hormone necessary for the proper use of glucose. As a result of this malfunction, the development of diabetes occurs.
Patients with pancreatitis often develop diabetic nephropathy, in which sodium is not excreted from the body, stopping fluids. This leads to an increase in total blood volume and blood pressure increases.
Acute pancreatitis has been dealt with. What about chronic?
If the toxic effect on the pancreas does not stop (for example, a person continues to drink excessively) or the organ was very damaged during the first (acute) episode of pancreatitis, the pain returns again and again.
During exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis, blood tests may remain normal. But over time, external signs may appear, which doctors detect by examining the pancreas using ultrasound (ultrasound), X-rays (CT or computed tomography) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These are narrowing of the pancreatic ducts, the appearance of compactions in it - calcifications, as well as the appearance of cysts - bubbles with liquid in place of dead tissue. An examination for suspected chronic pancreatitis is carried out with another important goal - not to miss pancreatic cancer, which may initially be accompanied by the same symptoms.
With constantly renewed inflammation of the pancreas, its function—the secretion of enzymes that digest food—is disrupted over time. As a result, a person is bothered by constant bloating, diarrhea, and the stool becomes greasy (for example, it is difficult to flush from the toilet). This condition - exocrine insufficiency - is most conveniently identified by determining the content of pancreatic elastase (a pancreatic enzyme) in the stool.
Symptoms of high blood pressure with pancreatitis
If high blood pressure and pancreatitis occur together, the patient will experience the following symptoms
- dizziness;
- Impaired temporary vision;
- headache;
- Ears;
- Palpitations;
- numbness of fingers;
- "Goose bumps" on the skin;
- sleep disorders;
- Excessive nerve stimulation.
Pancreatic hypertension can cause swelling of the face and limbs, hyperhidrosis (increased sweating) and heart pain. A sudden increase in blood pressure is often accompanied by severe epigastric pain, which then moves to the lumbar region.
A sudden increase in blood pressure is a symptom that accompanies pain shock, indicating the development of an attack of acute pancreatitis or the manifestation of pancreatic necrosis.
Symptoms of pancreatitis
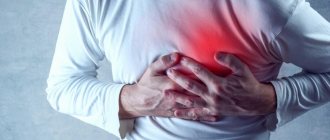
The main symptom of pancreatitis is severe pain. Along with it, nausea, vomiting, a slight increase in temperature, flatulence, stool disorders and some other symptoms may be observed.
Abdominal pain
The main symptom of acute pancreatitis is severe pain, which usually begins in the left side and then becomes encircling. The pain is not relieved either by antispasmodics (“no-spa” and analogues) or by painkillers (analgesics). Lying on your back may intensify. An attack of pain with pancreatitis is usually observed after eating or drinking alcohol. When eating against the background of pain, the pain intensifies.
Vomit
The onset of acute pancreatitis may be accompanied by bouts of vomiting. Vomit with pancreatitis usually contains bile. During this period, you must completely stop eating.
More about the symptom
Temperature
During an attack of pancreatitis, the temperature may rise to 37.5°C.
More about the symptom
Flatulence
The attack disrupts intestinal motility. This leads to bloating.
More about the symptom
Stool disorder
The lack of necessary enzymes does not allow food to be properly digested, which causes stool upset.
Diagnosis
According to medical statistics, in 65% of cases, arterial hypertension is caused by a malfunction of the pancreas. Therefore, in the case of periodic increases in blood pressure, mandatory examination for pancreatitis is recommended.
The main diagnostic measures will be:
- Anamnesis collection.
- External examination of the skin, palpation of the abdominal cavity.
- Clinical and biochemical blood test.
- Urine and stool analysis.
- Ultrasound examination of internal organs.
If complications occur, the patient is prescribed computed tomography (CT) or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCPG). Less commonly, in case of damage to the pancreas, laparoscopy, abdominal radiography and fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) are used.
Acute pancreatitis: prevent and neutralize
There are many causes of abdominal pain. One of the most serious illnesses accompanied by pain is acute pancreatitis. Despite the modern state of medicine, this pathology, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to the development of serious complications and even death.
We talked about this disease with the surgeon at the Expert Clinic Smolensk, Efim Semenovich Asnin.
— Efim Semyonovich, in October 2021, the public was stirred up by the news about the death of the Minister of Health of Lithuania. A young 35-year-old politician died of pancreatitis. What kind of disease is this and how dangerous is it?
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas tissue. Normally, this organ produces, among other things, digestive enzymes, which are released into the lumen of the duodenum through special ducts. For some reason, these ducts may overlap. As a result, enzymes do not enter the intestines and begin to “digest” the gland tissue. Pancreatitis develops.
THE CONSEQUENCES OF ACUTE PANCREATITIS MAY BE, IN PARTICULAR, FORMATION OF CYSTS, DEADNESS OF GLAND TISSUE, FORMATION OF UPRESSURES IN IT
Depending on the course, it can be acute, chronic, or hidden.
The consequences of acute pancreatitis can be, in particular, the formation of cysts, necrosis of gland tissue, and the formation of ulcers in it.
— What are the symptoms of acute pancreatitis?
These are signs such as:
- severe pain in the upper abdomen, which can be girdling. Sometimes the pain is diffuse, so the patient does not immediately understand what and where exactly is bothering him;
- pain can radiate to the lower back, kidneys;
- increased body temperature, chills;
- skin is pale, with an earthy tint;
- bad breath;
- shortness of breath;
- surges in blood pressure (both increase and decrease);
- nausea, as well as indomitable vomiting, which does not bring relief;
- bloating;
- possible belching, heartburn, diarrhea;
- there may be particles of undigested food in the stool, it may turn green and have an unpleasant odor;
- deterioration of the patient’s condition as the inflammatory process in the gland progresses. This is a rapid process, which may result in a transition to a chronic form or its aggravation (for example, necrosis of gland tissue).
IF SIGNS OF PANCREATITIS SHOULD SEEK IMMEDIATE MEDICAL CARE
It should be remembered that the signs that occur in acute pancreatitis can also be observed in a number of other diseases. In any case, you should seek medical help immediately.
“Pathologies of many organs, in addition to the digestive system and the abdominal cavity as a whole, can be accompanied by pain.” Quote from the material “Insidious pain-mask. Does abdominal pain always indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract?
— What is the right thing to do if you discover signs of acute pancreatitis in yourself or your loved ones?
First aid and tactics are as follows:
- do not take any food;
- lie down;
- apply cold to the epigastric area;
- Call an ambulance immediately.
You should not take any painkillers or other medications. You can take an antispasmodic - in particular, no-shpu, drotaverine in a therapeutic dose (subject to their tolerance).
— How is acute pancreatitis diagnosed?
Only in a hospital setting. The patient is interviewed and examined by the doctor.
The following studies are assigned:
- blood, urine and stool tests;
— Ultrasound of the pancreas;
- plain radiograph of the abdominal cavity;
— CT, MRI;
- according to indications - also fibrogastroscopy, laparoscopy.
— Despite the complexity of this disease, is modern medicine able to effectively treat patients with acute pancreatitis?
The effectiveness of treatment and prognosis critically depend on the speed of contacting a doctor: the sooner, the better! It is important to remember that acute pancreatitis today remains a serious disease that can result in the death of the patient. Therefore, you should seek medical help without delay.
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS CRITICALLY DEPEND ON THE SPEED OF CONTACTING A DOCTOR: THE EARLIER THE BETTER!
— Efim Semyonovich, why does acute pancreatitis develop? What leads to the development of this disease?
Among the causes and predisposing factors:
- food or alcohol poisoning (or if it is high-quality alcohol, but consumed even in small quantities and regularly);
- overeating;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- consumption of out-of-season vegetables and fruits containing pesticides and chemical additives;
- injuries of the anterior abdominal wall with contusion of internal organs, penetrating wounds in this area;
— undergone operations during which the pancreas could have been accidentally affected;
— pathologies of the biliary tract, gall bladder, stomach, intestines;
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- any circulatory disorders in the abdominal cavity;
- pregnancy;
- taking certain medications, chemicals.
— Under what conditions can acute pancreatitis become chronic?
If the factors I have listed to some extent, little by little, affect a person, and at the same time he does not go to the doctor (according to the principle “if it hurts, it goes away”), pancreatitis can become chronic.
— How does chronic pancreatitis proceed? Are there any differences in manifestations?
The course of the disease in chronic pancreatitis is characterized by veiled, “blurred” symptoms that occur during its acute course. They can disappear and appear.
— Is it possible that the clinical picture is erased and a person does not even suspect that he has pancreatitis?
Yes. In addition, this can happen with alcohol intoxication or taking painkillers.
— How to avoid problems with the pancreas and prevent the development of acute pancreatitis? Tell us about the prevention of this disease
This is, first of all, rational nutrition and diet. The intake of alcoholic beverages is limited; fatty, fried, spicy foods; strong coffee and tea; sour fruits and vegetables - especially on an empty stomach. Heavy physical activity, injuries, and smoking should be avoided.
If you suspect chronic pancreatitis, you must also follow a diet. You should completely exclude fried foods, mushrooms, pork, lamb, offal, lard, butter, pasta (vermicelli is allowed). You cannot drink alcoholic beverages, strong coffee, chocolate, cocoa, baked goods, cakes, fresh bread, or sweets.
“Festal and Mezim are considered representatives of the old generation of enzymes; more modern drugs are used instead.” Quote from the material “How to survive the New Year holidays without health consequences?”
The basis of the diet is cereal and vegetable dishes, boiled (boiled), stewed, with a minimum of oil.
While eating, you should take modern enzyme preparations.
If there are intestinal disorders, probiotics can be prescribed to restore the intestinal microflora.
All questions about dietary habits and medications should be discussed with your doctor.
Other materials:
Gallstone disease: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Is it possible to cleanse the liver?
At an appointment with a nutritionist. Soup: is it good or bad?
For reference:
Asnin Efim Semenovich
In 1972 he graduated from the medical faculty of the Smolensk State Medical Institute (today - Smolensk State Medical University), in 1973 - an internship in surgery.
He underwent advanced training in various areas of surgery and orthopedics.
Doctor of the highest category.
Works as a surgeon at the Expert Clinic Smolensk. Receives at the address: st. March 8, no. 20.
Treatment methods
To normalize blood pressure, pancreatitis and other parallel diseases are successfully treated. When the pathology worsens, the patient is hospitalized. In addition to pharmacological treatment, the patient is advised to fast and rest. Chronic pancreatitis requires adherence to a diet and a course of enzyme analgesics.
Medication
Among the drugs for acute pancreatitis, arterial hypertension progresses:
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa).
- Painkillers (Analgin, Baralgin).
- Anti-dehydration medications (Regidron, Alvogen).
The patient is prescribed detoxification therapy, administration of saline and colloidal solutions. General treatment helps eliminate vascular spasm, relieve swelling of the pancreas and adjacent tissues, and reduce the activity of the autonomic nervous system. Patients with acute pancreatitis are not prescribed antihypertensive tablets. This helps avoid the risk of a sudden drop in blood pressure and the development of collapse.
In the chronic form of pancreatitis, accompanied by increased blood pressure, the patient requires constant antihypertensive maintenance therapy. The administration of ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers and diuretics becomes important.
To normalize the functioning of the pancreas, it is advisable to take Pancreatin, Festal. To suppress secretory functions, a course with Contrical helps. The patient still needs to follow the diet rules.
Patients who simultaneously suffer from pancreatitis, hypertension and diabetes mellitus need to additionally take medications that lower blood sugar levels, stimulate insulin production, hormonal drugs, and statins.
Surgery
The department of surgical intervention is decided by specialists in cases where traditional treatment of pancreatitis does not bring relief to the patient. In such cases, irrigation, abdominal irrigation and drainage are indicated. In rare cases, surgeons perform necrectomy, that is, removal of diseased tissue from a diseased organ. If there are appropriate indications, resection of the gallbladder is performed in remission.
ethnoscience
Before using folk remedies for pancreatitis complicated by hypertension, it is necessary to obtain the consent of the attending physician. If the specialist deems it necessary, the patient can supplement basic therapy:
- fresh potato juice;
- milk thistle seeds;
- dill infusion;
- mumiyo solution;
- propolis tincture with milk.
Alternative medicine offers a significant number of herbal combinations that help avoid the progression of pathology - token + chamomile + wormwood (in a ratio of 4: 3: 2), celery + corn silk + fertilization + anise + tricolor (1: 1). ratio). Water infusions are prepared from such herbal mixtures, which are recommended to be taken several times a day.
Diagnosis of “Pancreatitis”
True (primary) pancreatitis is a very rare diagnosis. Its cause in most cases is alcohol abuse. Frequent drinking of alcohol causes impaired motility in the sphincter of Oddi, because of this, protein plugs form in the pancreatic ducts, the outflow of enzymes is disrupted and pressure of pancreatic juice occurs on the tissue of the gland itself. This causes pain and inflammation. Long-term use of large amounts of medications is also a fairly common cause of pancreatitis. The disease can also be triggered by systematic poor nutrition, alcohol, frequent stress and hormonal imbalances.
More common is secondary (reactive) pancreatitis, which occurs against the background of disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. The main reason for the development of secondary pancreatitis is problems with the gallbladder (for example, cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder, cholelithiasis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, bile duct dyskinesia and chronic gastroduodenitis). Thus, the development of pancreatitis is a consequence of other previous diseases of the stomach and gall bladder. In children, the disease may appear after viral infections and influenza. True, this happens quite rarely.
Preventive measures
To avoid increased blood pressure during pancreatitis, it is recommended:
- Compliance with a dietary diet (exclusion from the menu of high-calorie, spicy and salty foods).
- Regularly engage in accessible sports and breathing exercises.
- Stay in the fresh air every day (at least 1 hour a day).
For patients with symptoms of pathology, it is equally important to quit smoking and get enough sleep. Avoid stress, minimize the consumption of alcohol, strong tonic drinks - coffee and black tea.