Tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia characterized by an increase in heart rate above normal values. Typically, tachycardia is diagnosed when the heart muscle contraction frequency is more than 90 beats per minute.
Tachycardia is an objective characteristic (as opposed to the patient’s complaints of increased heartbeat). A person may complain of increased heart rate, and at the same time have a normal pulse rate. And vice versa: in some cases, tachycardia does not attract a person’s attention, and he does not notice that his heart is beating faster than normal.
Types of tachycardia
Tachycardia may be due to a normal reaction of the body. In this case, doctors talk about physiological tachycardia
. Physiological tachycardia (that is, increased heart rate in a healthy person) can be caused by:
- strong emotional arousal or stress;
- physical activity;
- sudden change in body position (sudden rise from a lying position, etc.);
- lack of oxygen;
- high air temperature;
- taking coffee, strong tea, alcohol, and some medications.
If tachycardia is not associated with these reasons, then the increased heart rate is apparently caused by the disease. In this case we are talking about pathological tachycardia
.
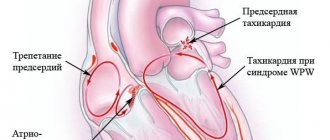
There are also sinus and ectopic (paroxysmal) tachycardia.
Sinus tachycardia
occurs when the activity of the sinus node increases. The sinus node is a bundle of specific cardiovascular tissue in which electrical impulses are generated. These impulses travel throughout the heart, causing the heart muscle to contract. That is, our heart beats at the rhythm set by the sinus node. If it begins to produce impulses at a higher frequency, then sinus tachycardia occurs.
However, in some cases, electrical impulses are generated outside the sinus node. They are called ectopic (“ectopic” means, specifically, “abnormally located”). The frequency of contractions of the heart muscle in this case can reach up to 200 or more beats per minute. Typically, such an increase in rhythm is observed in the form of attacks (paroxysms). This tachycardia is called ectopic
or
paroxysmal
.
How to correctly calculate your pulse?
For self-counting, the most common method is palpation (palpation) of the radial artery of the wrist. You need to count your pulse at rest, no earlier than 2 hours after eating, bathing, or massage. The accuracy of the result depends on the correct counting technique.
First, you need to take a watch or stopwatch. Sit down with your hand on a horizontal surface, palm up. Place the index, middle and ring fingers of the opposite hand on the wrist approximately 3 centimeters from the base of the thumb;
When you feel the pulsation, you need to lightly press the artery to the inside of the radius. There is no need to press with force, as the pulse wave may disappear under pressure.
Then you need to count the number of blood pulses within 1 minute. Pulse waves should follow each other at regular intervals; then count the pulse on the second hand.
An increase in heart rate at rest greater than 90 beats per minute is considered tachycardia.
Causes of tachycardia
Physiological tachycardia should not be a cause for concern.
But if the heart rate is increased for no apparent external reason, this is worth paying attention to. Tachycardia is often caused by pathologies and heart diseases, in particular:
- acute or chronic heart failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- angina pectoris;
- heart defects;
- myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle;
- endocarditis (inflammation of the endocardium - the inner lining of the heart);
- pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium - the outer lining of the heart).
In addition, tachycardia occurs in the case of:
- increased temperature (typical of various infectious diseases, such as pneumonia, sore throat, sepsis, etc.);
- lowering blood pressure (for example, due to blood loss);
- anemia;
- increased thyroid function;
- states of shock.
What can you do
The principles of treatment of sinus tachycardia are determined, first of all, by the causes of its occurrence. Treatment should be carried out by a cardiologist together with other specialists.
It is necessary to eliminate factors that contribute to an increase in heart rate: eliminate caffeine-containing drinks (tea, coffee), nicotine, alcohol, spicy foods, chocolate; protect yourself from psycho-emotional and physical overload. Physiological sinus tachycardia does not require treatment.
Treatment of pathological tachycardia should be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. In case of extracardiac sinus tachycardia of a neurogenic nature, the patient needs to consult a neurologist. Treatment uses psychotherapy and sedatives (luminal, tranquilizers and antipsychotics: tranquilan, relanium, seduxen).
In the case of reflex tachycardia (with hypovolemia) and compensatory tachycardia (with anemia, hyperthyroidism), it is necessary to eliminate the causes that caused them. Otherwise, therapy aimed at reducing heart rate can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure and aggravate hemodynamic disorders.
For sinus tachycardia caused by thyrotoxicosis, β-blockers are used in addition to thyreostatic drugs prescribed by the endocrinologist. Preference is given to β-blockers of the oxyprenolol, practolol and prindolol group. If there are contraindications to β-blockers, alternative medications are used - non-hydropyridine calcium antagonists (verapamil, diltiazem).
For sinus tachycardia caused by heart failure, cardiac glycosides (digoxin) are prescribed in combination with beta-blockers.
Symptoms of tachycardia
Tachycardia is established by measuring the pulse rate. Patients with tachycardia may also complain of:
Cardiopalmus
Patients with tachycardia usually complain of a feeling of palpitations. However, such a feeling is subjective. It can be observed without an objective increase in rhythm.
More about the symptom
Dyspnea
With tachycardia, shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air are possible.
More about the symptom
Weakness
Tachycardia may be accompanied by symptoms such as general weakness, dizziness, and increased fatigue. worsening mood, loss of appetite.
More about the symptom
Sleep disorders
A rapid heartbeat can make it difficult to fall asleep and often causes insomnia.
More about the symptom
How to relieve an attack of tachycardia?
Unbutton your clothing collar, open a window or balcony, inhale deeply and exhale very slowly; breathe like this for 5-10 minutes. Then hold your breath and, as it were, “push” the air into the lower abdomen - this stimulates the vagus nerve, as a result of which the heartbeat will slow down;
Take Corvalol or Valocordin: dissolve 15-20 drops of the drug in half a glass of water at room temperature;
Wash your face with cold water, lie down on a high pillow, place a towel soaked in cold water on your forehead, try to relax;
Close your eyes and simultaneously press on your eyeballs for 2-3 minutes: press for 10 seconds, break for 10 seconds;
Find the right carotid artery (immediately under the jaw, at this point it connects to the cervical artery) and gently, without pressure, massage it. This technique also stimulates the vagus nerve and slows the heart rate.
If the condition does not improve, the heart rate does not decrease, dizziness appears, a feeling of shortness of breath, darkened vision, call an ambulance.
Treatment methods for tachycardia
Tachycardia is more a symptom than a disease. Therefore, treatment of tachycardia consists of treating the disease that caused the tachycardia.
It is also important to eliminate the factors that provoke tachycardia, that is, the reasons that can cause physiological tachycardia, primarily emotional and physical overload, consumption of caffeine-containing drinks, alcohol. Doctors strongly recommend quitting smoking.
Specialist consultation
If there are signs of tachycardia, you should consult a doctor, since tachycardia can be a manifestation of various, including dangerous, diseases. A cardiologist treats tachycardia. Regarding tachycardia in Moscow, you can contact cardiologists at the clinics of JSC “Family Doctor”.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Forecast
Cardiac arrhythmias are dangerous because they can lead to sudden cardiac arrest due to complete blockade of conduction. In severe arrhythmia, there is a high risk of ventricular fibrillation, which can be fatal. Atrial fibrillation leads to the formation of blood clots in the atria and their transfer to other organs with the development of stroke and gangrene of the extremities. The probability of an unfavorable outcome in patients with arrhythmias depends on the form of rhythm disturbance and is more than 20% per year. You should not rely on folk remedies - arrhythmia is very dangerous and requires correction by a professional cardiologist.
Cardiac ischemia
A severe consequence of coronary heart disease is acute myocardial infarction. During a heart attack, blood circulation in the myocardium is disrupted, as a result of which it receives an insufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients. Hypoxia leads to accelerated contraction of the myocardium, against the background of which cardiomyocytes die.
Patients suffering from regular heart palpitations require careful diagnosis to prevent complications
Predisposing factors in the development of the condition are:
- chronic hypertension;
- chronic vascular diseases;
- increase in myocardial size.
If there is insufficient oxygen supply, any pathology can provoke a heart attack.
Sources
- Utsumueva M.D., Mironov N.Yu., Shlevkov N.B., Kiktev V.G., Gupalo E.M., Kashtanova S.Yu., Mironova N.A., Golitsyn S.P. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in a patient with dilated cardiomyopathy and concomitant cardiac conduction disorders. Clinical case and discussion of the problem. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention. 2020;19(3):2368.
- Salami Kh.F., Shlevkov N.B., Sokolov S.F. Possibilities and limitations of standard electrocardiography for the differential diagnosis of tachycardias with widened QRS complexes. Almanac of Clinical Medicine. 2019;47(4):350-360.
Diagnostics: when and with what to see a doctor?
Any first-time attack of tachycardia that negatively affects your well-being is a reason to consult a doctor! And the more pronounced the clinical manifestations, the sooner you need to consult. If a person loses consciousness during a paroxysm, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance and perform electrical cardioversion (impact of a pulsed current discharge on the heart).
Doctor's advice: check-up list for suspected tachycardia
To establish a correct diagnosis, the following studies and tests are necessary:
- electrocardiogram - at rest and at the time of rapid heartbeat;
- Ultrasound of the heart - data on the structural structure and valve apparatus;
- daily ECG monitoring;
- transesophageal EPI (TEPE);
- general blood test - will provide information about the presence of anemia and/or inflammation;
- blood test for thyroid hormones and TSH;
- consultation with an ENT doctor (if you have a history of frequent sore throats) and a dentist (caries) to identify and treat foci of chronic infection.
This is the minimum research that will help establish the cause of tachycardia, its nature and type, or allow you to choose a further diagnostic direction. Often, the doctor needs to seek help from fellow arrhythmologists who are able, using modern instrumental methods, to determine the area with pathological impulses. After its localization becomes known, the issue of minimally invasive destruction of the lesion can be decided.
If rapid heartbeat is the result of chronic tonsillitis, then by eliminating the cause (by performing surgical removal of the tonsils), you can forget about the heart problem. Such patients complain of pain in the heart area. Why chest discomfort occurs with a sore throat and how to act correctly - read here.
If the study reveals changes in thyroid hormone levels, or pheochromocytoma is suspected, then an endocrinologist will treat such a patient. It is worth noting that in clinical practice the first symptom of thyrotoxicosis is paroxysm of atrial fibrillation. Therefore, all patients with new-onset atrial fibrillation need to determine the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood.
Monitoring a person with tachycardia first of all involves monitoring by a specialist who treats the underlying disease. It is a competent approach to the pathology that causes arrhythmia that will help get rid of unpleasant symptoms and minimize the consumption of medications.
Clinical case
A 39-year-old woman consulted her local physician with complaints of constant rapid heartbeat up to 110 per minute and periodic dizziness. These symptoms have been bothering the patient for a month. According to the patient, the pulse was always within 70-80/min. Upon examination, a high heart rate (106/min) and a slight increase in blood pressure (130/80 mmHg) were revealed. The ECG showed sinus tachycardia. No clinical or laboratory signs of heart disease or other pathologies were found. Upon detailed questioning, the patient noted that she suffers from chronic rhinitis and takes vasoconstrictor nasal drops (Naphthyzin) 8-10 times a day for 2 months. A referral to an otolaryngologist was issued. Some time after the prescription of competent therapy, the pulse and blood pressure returned to normal.
Prognosis and prevention
If you follow all medical recommendations and switch to a healthy lifestyle, the prognosis is favorable. The success of therapy depends on the time of contacting a doctor and the adequacy of treatment of the underlying disease.
In order to reduce the risk of developing tachycardia, you should:
- eat varied and regularly, include vegetables, fruits, fish, dairy and seafood in your diet,
- regularly do exercises, cardio exercises,
- avoid stress,
- do not abuse coffee and alcohol, stop smoking.
Photo: DCStudio / freepik.com
Asthenia and weight loss
Prolonged and frequently repeated attacks of palpitations without acute disruption of myocardial activity lead to weakening of the body. Due to frequent interruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle, there is a deficiency in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the organs, which entails metabolic disorders. Poor absorption of vitamin and mineral complexes results in a decrease in the body's defenses and insufficient weight gain.
Chronic hypoxia syndrome accompanied by rapid heartbeat is characterized by the following symptoms:
- unreasonable weakness;
- constant drowsiness;
- weight loss;
- increased susceptibility to infections.
Formation of thromboembolism
When your heart rate increases, the risk of blood clots forming in the heart structures increases. Impaired blood flow contributes to the breakdown of a small number of red bodies, which causes activation of the coagulation system. When a blood clot forms, there is a possibility of its migration to any organ, where it can cause blockage of the vessel and lead to acute hypoxia.
Supraventricular tachycardia is the main cause of thrombosis
In most cases, the following structures are susceptible to thrombus formation:
- the formation of a blood clot in the right heart affects the pulmonary artery;
- cerebral arteries;
- arteries of the digestive tract;
- blood vessels of the legs;
- splenic artery.
Thromboembolism of the cerebral arteries leads to the development of ischemic stroke, irreversible functional damage, and death. Thrombosis of the vessels of the lower extremities can result in their amputation.
Patients who often suffer from attacks of rapid heartbeat are advised to have a full diagnosis of the condition by a cardiologist, since this symptom can cause a wide range of serious complications.
During an attack of tachycardia, predisposing factors to the formation of a blood clot are:
- age-related changes in the cardiovascular system;
- history of stroke;
- metabolic disease;
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- congestive processes in the heart;
- expansion of the structural elements of the heart;
- arrhythmias lasting more than 48 hours.
Typically, predisposing factors relate to malignant arrhythmia. However, in their presence, the patient needs to reduce stress and reduce physical activity, since the physiological increase in heart rate also increases the risk of clot formation.
Folk remedies
Photo: evrikak.ru
There are traditional medicines that can slow down the heart rate. However, it is worth noting that in no case should you self-medicate; you must carefully follow all the recommendations of your doctor. Before using any folk remedy based on medicinal herbs, you should consult your doctor. We offer you the following recipes:
- Pre-grind the valerian root and dry it. Take 1 tablespoon of the resulting raw material and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let it brew for 1 – 2 hours, after which the infusion is ready for use. It is recommended to take 1/3 cup 3 times a day. The average course of treatment is 3 weeks;
- take 1 tablespoon of pre-prepared motherwort and pour 200 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 10 - 20 minutes. It is recommended to drink a glass of the resulting infusion throughout the day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks;
- take lemon balm and valerian root. Mix the listed collection components in equal proportions. Then a small amount of yarrow is added to the resulting collection. One tablespoon of the collection is poured into a glass of cold water and infused for 3 hours, after which the infusion is simmered in a water bath for 20 - 30 minutes. The finished broth should be carefully strained to prevent the ingress of small parts of raw materials. It is recommended to take 2-3 sips throughout the day. The course of treatment is 2 – 3 weeks;
- take 1 tablespoon of dried hawthorn leaves and flowers, pour 1 glass of boiling water, let it brew for 2 - 3 hours. After carefully filtering through a strainer, the infusion becomes ready for use. It is recommended to take 2 tablespoons 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 2 – 3 weeks;
- Grate the turnips on a fine grater, take 2 tablespoons of the resulting mass and pour a glass of boiling water. Place on the fire and simmer over low heat for 15 - 20 minutes. Let the broth cool, after which it should be strained. It is recommended to take ½ glass 2 times a day after meals;
- Take 1 tablespoon of dried rose hips and rinse them thoroughly under running water. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over the dried berries and let it brew for 6 hours, after which the finished infusion should be strained. It is recommended to drink half a glass 3 times a day.
It is important to emphasize once again that before using traditional medicine, you should consult with a qualified specialist. In addition, the use of folk remedies without medications is allowed only for mild tachycardia, when there are no hemodynamic disturbances.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.