Clinical picture
Manifestations of cardiopathy differ depending on its form. The following symptoms are characteristic of the stagnant variety of the disease:
- painful sensations of a pressing and aching nature in the chest, not relieved by Nitroglycerin;
- the appearance of signs of cyanosis on the face (blue skin);
- deformation of the chest due to cardiac hypertrophy (appearance of a “heart hump”).
Signs of congestive cardiopathy progress extremely quickly. Gradually, the disease leads to limited ability to move.
The restrictive form of the pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the heart area;
- shortness of breath with any physical activity;
- swelling of the face;
- belly growth.
The restrictive variety of the disease is diagnosed mainly in the tropics. The patient's physical activity is significantly reduced due to the worsening condition.
The hypertrophic type of the disease has pronounced symptoms:
- sharp chest pain;
- manifestation of arrhythmia;
- constant shortness of breath;
- loss of consciousness;
- dizziness.
Gradually developing heart failure aggravates the patient's condition. In advanced cases, even with light physical activity, death is possible.
Ischemic cardiopathy is characterized by the following symptoms:
- arrhythmia;
- pain in the heart;
- frequent shortness of breath;
- general weakness;
- lack of oxygen;
- excessive sweating;
- paleness of the skin;
- loss of consciousness.
Symptoms become more pronounced with physical activity. Heart failure due to ischemia progresses rapidly and can lead to thrombus rupture and death.
The manifestation of the secondary type of pathology depends on the localization and severity of the primary pathological process. Most often it is expressed by the following symptoms:
- excessive sweating;
- swelling;
- feeling of squeezing in the heart area;
- cough;
- frequent shortness of breath.
Secondary cardiopathy in children usually progresses as the primary disease develops. During diagnosis, doctors see it as a violation of the integrity of the myocardium.
The functional variety is manifested by signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- fainting state;
- attacks of shortness of breath;
- arrhythmias (mainly tachycardia, extrasystoles);
- excessive sweating.
The development of the disease depends on the degree of overload of the child. If the problem is not identified in a timely manner, it will not be possible to avoid serious pathological changes in the myocardium.
It is difficult to detect cardiopathy in both newborns and adolescents. Symptoms characteristic of the disease are most often attributed to other pathologies of the cardiovascular system. A doctor can make an accurate diagnosis only with the help of a comprehensive instrumental examination.
Diagnostics
If functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract acquire chronic forms, it is necessary to conduct an examination by a gastroenterologist, which will help to find out the cause of poor health.
You may also need to consult other specialists. For example, a nutritionist who will help you choose the most suitable diet.
Diagnostics proceeds in several stages. The first is an initial visual examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis.
Then you need to undergo an examination. These include stool and urine analysis, colonoscopy, gastroscopy, abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography and a number of other procedures.
After diagnosis, treatment for functional gastrointestinal disorders is prescribed. Psychotherapists, physiotherapists, endocrinologists, and nutritionists are involved in treatment.
Medicinal methods of treatment of the disease are prescribed, special attention is paid to the rules of food intake, physical activity, work and rest schedule. Only compliance with all these components can guarantee relief from the disease.
Causes
Cardiopathy in children mainly develops for the following reasons:
- Genetics. Cardiomyocytes (heart cells) are made of proteins. They take part in all processes performed by the heart muscle. Information about the structure of heart cells is stored at the genetic level. If the baby has a defective gene, then there is a possibility of improper development of the main organ. In this case, we are talking about the primary form of cardiopathy.
- Infectious or toxic nature. The development of cardiopathy can be influenced by toxins and infections that enter the body. They are not detected immediately due to the frequent absence of pronounced symptoms. No abnormalities of the valves or coronary vessels are detected.
- Autoimmune failures. Immune system dysfunction is mainly caused by infections, toxins and hormonal surges. The body begins to destroy its own cells, thereby causing secondary pathologies.
- Fibrosis (cardiosclerosis). Replacement of heart tissue with connective fibers leads to impaired contractility due to loss of elasticity. Fibrosis most often occurs after a myocardial infarction, so its nature is predominantly secondary.
The listed cases are considered the main ones, but doctors can only stop their manifestations. It is virtually impossible to eliminate the causes due to the lack of effective treatments.
Among the pathologies of the cardiovascular system that influence the development of cardiopathy, the most basic can be identified:
- hypertonic disease;
- cardiac ischemia;
- amyloid dystrophy (failure of protein metabolism);
- disorders in the endocrine system;
- poisoning by toxins;
- connective tissue diseases.
What it is?
Functional gastrointestinal disorder is a separate type of pathology associated with disturbances in the process of digestion of food. It can appear in almost anyone, regardless of age or gender.
The reasons why the disease occurs are divided into two categories: biological predisposition and environmental features leading to this pathology. The latter include stress, poor nutrition and the like.
Symptoms of a functional bowel disorder include:
- Spasms
- Flatulence
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
Often the disease entails the appearance of other, no less acute ailments. Thus, women may experience inflammation of the genitourinary system, and both sexes may develop chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Important! To reduce the risk of developing this disease, it is worth limiting the provoking factors. The latter includes the consumption of spicy, fried or salty foods, it is necessary to eat in small portions, move after eating, and sleep with an elevated headboard.
Functional cardiopathy
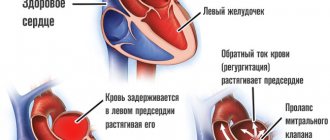
If the mitral valve sagging and there is an abundance of tendon threads, the doctor diagnoses functional cardiopathy. Such structural abnormalities are abbreviated as MARS (minor anomalies of the heart). They contribute to the occurrence of arrhythmia attacks during physical activity. If the child continues to overexert himself (in physical education, when playing with friends, in classes), then heart failure will begin to develop over time.
A cardiologist will need to draw up a treatment regimen if the child has persistent arrhythmia and manifestations of mitral regurgitation (backflow of blood). The doctor will prescribe magnesium-based medications and antiarrhythmic drugs as treatments. It is equally important to create a daily schedule to eliminate heart-straining activities.
When functional cardiopathy is detected, regardless of its severity, parents must protect their child from physical and mental overload and follow all the recommendations of the cardiologist. It is unacceptable to use medications to correct heart rhythm on your own, or to increase or decrease the dosages indicated in the treatment regimen. The child’s heart muscle has not yet fully strengthened, and the presence of pathological changes in the structure of the myocardium only aggravates the situation, so only a doctor can prescribe a course of therapy and change it.
To saturate the heart with useful substances, you will need to change the child’s diet. It is advisable to remove sweets, fast food and other unhealthy foods from it in favor of vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins and microelements.
Classification
Knowing what functional cardiopathy is, it is recommended to monitor the child. To make an accurate diagnosis, the changes are divided into groups according to the classification as follows:
- Mitral valve prolapse.
- Additional one or more papillary muscles.
- Their location is incorrect.
- Greater mobility of chords in the cavities of the heart due to increased length.
- Bifurcation of the papillary muscles.
- Attachment of chords outside the anterior or posterior valves.
- Enlargement of the ring at the site of attachment of the tricuspid valve.
- Displacement of the septal valve.
- Increase or decrease in the lumen of the aorta.
- Changes in the number of tricuspid valve leaflets in a child or adult.
- Valve prolapse in the inferior vena cava.
- An aneurysm of various sizes located in the interventricular or interatrial septum.
- Non-closure of the oval window.
If the listed functional changes do not disappear during adolescence, the pathology is called connective tissue dysplasia.
Secondary form of the disease
Secondary cardiopathy in children is a consequence of another pathological process. Often the cause of its development is the following body conditions:
- hormonal changes;
- metabolic disorders;
- poisoning with toxic substances.
Treatment of the secondary form of pathology is prescribed by the attending physician after an examination, the purpose of which is to determine the true cause of the development. The essence of therapy will be based on correcting nutrition, reducing stress on the heart and eliminating the underlying pathological process.
Treatment methodology
After the appearance of an acquired heart defect, the body compensates for the impaired circulatory function. That is, a sick child does not feel discomfort and does not feel the need for treatment.
Drug therapy is prescribed to stabilize the heart rhythm, reducing the risk of heart failure, relapses and complications of the disease that caused the defect.
The main method of treatment is surgery. During it, the heart valve can undergo changes, that is, the defect is corrected and proper function is restored. Or the damaged valve is replaced with an artificial one (prosthetics). Source: E.I. Kinoshenko Emergency conditions for acquired heart defects // Emergency Medicine, 2013, No. 4(51), pp. 9-24
Forecast
Cardiopathy in children has a favorable prognosis only if detected early. Stopping the pathological process in a timely manner will allow the child to live to old age, but he will have to follow the recommendations of specialists and lead a healthy lifestyle. If cardiopathy is detected late, complications may develop, leading to disability and death.
Surgical treatment (if successful) prolongs the patient’s life and can eliminate the main cause of cardiopathy. The disadvantage of the operation is the high risk of death. According to statistics, every 6 people die on the operating table during heart surgery.
Cardiopathy has been diagnosed more and more often in recent years. Experts say that the blame lies with the deteriorating environment and the consumption of unnatural products. In childhood, it can be stopped without fatal complications for the body if treatment is started in a timely manner. The basis of therapy is antiarrhythmic and magnesium-containing drugs and lifestyle correction. Severe cases require surgery.
Types of noise
The classification is carried out on two key grounds. The first is by type of deviation from the conventional norm.
Accordingly, they distinguish:
- Functional noise (physiological, FSH in abbreviated form). If in adults an objective symptom always indicates anomalies or defects, in childhood this is not an axiom, but in 97% a variant of the norm.
Moreover, in approximately half of the cases, or even more, in young patients extraneous sounds are detected during auscultation.
In the 1st, 2nd and 3rd years of life, the reason lies in the restructuring of the cardiovascular system, adaptation to existence outside the womb.
From the age of 4, a connection is found with maturation, body growth, and then with puberty. Conventionally, childhood ends at the beginning of puberty, that is, by the age of 12-13, then the noises disappear.
FFS in a child is not a diagnosis, but a functional heart murmur, a sound heard during auscultation.
- Pathological noises (organic). They account for the other half of the recorded situations.
They arise as a result of the influence of many factors. Including defects, congenital and acquired.
It will not be possible to delimit the conditions “by eye”. Instrumental diagnostics are required. You can assume there is a problem based on the symptoms.
Attention:
Within functional murmurs there is no clinical picture (symptoms). It may not be present in the disease, therefore it is not a reliable differential criterion.
It is possible to subdivide on a different basis. It concerns the moment when an anomalous sound occurs. Then they tell a couple more violations.
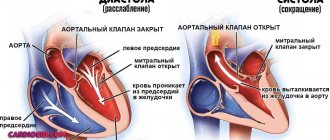
There are two normal heart sounds:
- The first is systolic. Occurs when cardiac structures contract and atrioventricular valves close. Normally, after it and until the moment of relaxation there are no symptoms on auscultation.
Murmurs most often indicate defects, such as mitral, aortic, valve prolapse, their defects and other phenomena.
- The second tone is diastolic. It is detected after the blood is pushed out into the systemic circle, when it returns to the pulmonary artery.
In this case, disturbances in auscultation are detected due to functional disorders (in an abnormal sense). For example, as part of the experience of myocardial inflammation and other issues.
In some cases, a violation of all tones is detected at once, then the murmur is recorded twice in one complete contractile cycle of the heart.
Classifications are widely used by doctors as part of the initial examination and development of treatment tactics.
Systolic heart murmur in a child is more indicative. But it does not give an unambiguous answer to the questions “what is it” and “why did it arise.” Electrocardiography and ECHO-CG put an end to it.
If necessary, additional methods, such as MRI, X-ray.