An additional chord in the heart is a congenital anomaly of the development of cardiac structures, which consists in the formation of one or more transverse cords that support the valve leaflets.
Formally, an additional (false) chord is extremely rarely considered a pathology. More often they talk about it as a minor anomaly, but not as a defect. Because in 90% of cases or more there are no symptoms or external signs that could indicate a disorder.
Manifestations in the remaining situations are variable and depend on the severity of the disorder. A thorough diagnosis is required, this is the only way to say more and put an end to the issue.
In the absence of symptoms, changes in the functional activity of the heart, there is no threat to life. This means that therapy as such is not needed. The task of doctors is to establish the nature and extent of changes. This may take a long time.
Formation mechanism
The development of a pathological deviation is based on a violation of the intrauterine period.
An additional chord in the heart in a child, and then in an adult patient, is the result of abnormal fetal genesis. As a rule, the disorder develops in the early stages, at the very beginning of the first trimester and a little later.
It is impossible to detect changes based on ultrasound results. It is not always possible to identify pathology even after birth; is it worth talking about early diagnosis and its prospects.
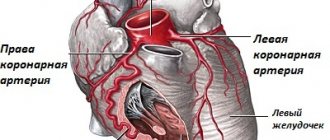
What is the essence of the violation? It is based on a slight change in the anatomical structure of cardiac tissues. Normally, the heart consists of four chambers.
Two atria and the same number of ventricles. They are delimited by elastic strips of connective tissue. The so-called partitions or valves.
The petals of these structures act as gates for the blood, allowing it to move strictly in one direction to ensure correct and efficient pumping function.
They themselves are attached to the myocardium by special elastic cords, which are called chords, and perform the function of maintaining the valves in their normal position, allowing them to contract correctly and return to their original location.
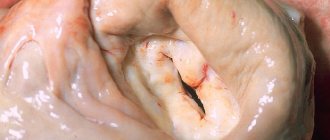
And this is where the differences in condition begin. If one or even several chords are present, but they have an anatomical structure identical to normal, and are not thicker or longer than the others, problems usually do not arise.
But if there are many of them or they have structural anomalies, dysfunction begins.
Blood is not able to move normally through the chambers. Contractions become weaker. All this can lead to heart failure of varying severity.
Such situations are minimal, as practice shows, no more than 10% of cases and even less. Treatment is required to avoid risks to health and life.
But more often the patient does not even suspect that some kind of violation is taking place. The extra chord is discovered accidentally during a routine examination, according to the results of echocardiography.
If there is no evidence of organic disorders, functional abnormalities, no complaints, and the patient leads a normal life, they speak of a minor anomaly and individual characteristics of the body. Then neither excessive diagnosis nor treatment is required.
Arc Interactions
If two segments subtend sections of a curve that are equal in size, then such axes are equal to each other. The following patterns follow from this rule:
- Two equal chords subtend equal arcs.
- If we consider two arcs whose size is less than half a circle, then the larger the arc, the larger the chord that will subtend it. On the contrary, a smaller arc will be subtended by a smaller chord.
- If the arc exceeds half the circle, then the opposite pattern is present: the smaller the arc, the larger the chord that subtends it. And the larger the arc, the smaller the chord limiting it.
A chord that subtends exactly half a circle is its diameter. If two lines on the same circle are parallel to each other, then the arcs that are enclosed between these segments will also be equal. However, one should not confuse enclosed arcs with those subtended by the same lines.
Causes
Why does an extra chord develop in the heart? The causes are always congenital; the formation of this structure during the biological existence of the patient is no longer possible.
Among the factors:
Smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy
The harmful substances that make up tobacco products, including ethanol, have mutagenic properties.
Organic disorders and disturbances in fetal formation are possible. An extra chord is only one of the options, and certainly not the worst.
Giving up a bad habit allows you to reduce risks to a minimum. Moreover, it is necessary to fight addictions and dependencies long before gestation. At the stage of pregnancy planning.
Past infectious diseases
In the recent past or right at the time of pregnancy, especially in the first trimester.
This is extremely dangerous. Sometimes the disease progresses so sluggishly that the woman does not notice the problems. This is especially true for carriage of herpes and human papilloma viruses.
There may be no symptoms, but the fetus will be infected. As in the previous case, an extra chord is one of the possible options.
Treatment and suppression of agents is required at the stage of pregnancy planning by a group of doctors.
Poisoning
Toxic lesions. When using certain medications (psychotropic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics). They cause not just anomalies, but deformities.
Pronounced defects are not always found. Heart defects, major or minor, are possible.
Heavy physical activity
Pregnancy is not a disease. It makes no sense to completely exclude mechanical activity. Quite the contrary. But overworking is strictly prohibited.
To avoid the development of hormonal imbalance, instability of the concentration of progesterone, estrogens and substances of the adrenal cortex, catecholamines.
How the changed background will turn out is a moot point. Obviously, such a process does not bode well for either the mother or the child.
For the same reason, it is worth avoiding stress and psycho-emotional overload whenever possible.
Failure to comply with this rule is fraught with the production of the same hormones of the adrenal cortex in huge quantities.
Hereditary factor
Research suggests an increased likelihood of developing the anomaly in children whose ascendant ancestor had a similar disorder.
The risks are greater if there are two or more relatives with a similar problem. The exact numerical expression varies from 30 to 80%.
Developmental anomalies
In some cases, an abnormal notochord or trabecula develops as a result of genetic abnormalities; it is the result of abnormal distribution of chromosomes.
But this is rather an exception, because the process under consideration is predominantly phenotypic. That is, genes do not play a role, the problem arises spontaneously, it is not developed in a particular person, and therefore is not directly transmitted to future generations.
An assessment of the causes is necessary for a correct understanding of the mechanism of development of the pathological process.
There is no practical significance for prevention in a particular patient. But knowledge makes it possible to plan general prevention within the framework of epidemiological work.
Despite this, effective prevention methods still do not exist.
Why do false chords of the heart appear?
False chords are quite easy to detect already in a child’s heart. Moreover, pediatricians do this while listening to the chest (by the presence of heart murmurs). Typically, additional chordae form during fetal development. The main reasons for their appearance are:
- Heredity - for example, parents or grandparents also had this diagnosis.
- The mother’s unhealthy lifestyle, especially during pregnancy (smoking, drinking alcohol, uncontrolled use of medications, toxic substances), and the presence of chronic or infectious diseases.
- Genetic factor - mutation of genes or chromosomes.
- Unbalanced diet - excess animal fat.
- Heavy workload during pregnancy.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Constant, severe stress.
- Deterioration of immunity for various reasons.
Symptoms
As is clear from the general situation, the clinical picture of an additional chord is absent in most cases.
The patient is unaware of the problem in 90% of situations or even more. That's why he doesn't go to doctors.
Deviations can be detected only by echocardiography results, and that is, by taking a closer look. Only in 10% of situations are there any signs of impairment.
Among them:
- Chest pain. Weak or medium in intensity. They are localized on the left side and can radiate to the shoulder blade, arm, or face. However, not always.
As a rule, they occur after physical activity. They pass at rest. The character is burning, pressing, bursting.
The sign indicates the onset of ischemic processes and becomes more and more distinct as cardiac dysfunction progresses.
- Arrhythmias. Like sudden onset tachycardia. The disturbance is especially noticeable when the load on the body increases. For example, after a brisk walk, climbing stairs, playing sports, even eating.
Suddenly the contraction frequency increases, reaching more than 90 beats per minute.
There may be a feeling of interruptions. Patients describe the condition as “the heart suddenly stops and starts beating again” or “misses contractions.”
These are the phenomena of extrasystole. In some cases, the arrhythmia is represented by paroxysmal (attack-like) tachycardia. There are many options.
- Shortness of breath due to physical activity. For many years, the deviation manifests itself externally as exercise intolerance. The patient cannot walk quickly or play sports. Sometimes the threshold when a symptom arises is so great that a person simply does not reach it. This means that the sign goes unnoticed. Unless the athlete has an extra chord.
- Weakness, drowsiness. Unreasonable lethargy and low performance. As cardiac dysfunction progresses, signs of asthenia become more pronounced. But this takes years.
- Headache, inability to navigate in space. The result of insufficient blood circulation in the brain. Fortunately, the sign does not support critical processes. In addition, other neurological deficits are also detected: problems with intelligence, thinking, memory, decreased visual acuity, and hearing. There are many options.
Clinically, an extra chord corresponds to heart failure and provokes it.
The rate of disease progression is low, extremely insignificant in the majority of cases.
At some point, decompensation may occur. The body will not be able to maintain acceptable functional activity of the heart. The process will begin to develop like an avalanche and lead to disaster.
Fortunately, this is unlikely. Because symptoms will force a person to see a doctor much earlier. In childhood, there are usually no signs.
Manifestation occurs at ages over 15-16 years. It is during this period that subcompensation occurs. The body still supports and stabilizes the functioning of the muscular organ, but it is no longer fully capable.
Military service
In the presence of a single false chord, young people who have reached the age of 18 are still drafted into the army for service. Representatives of the medical commission believe that it will not have any effect on well-being during the next year of life. The conscript does not need to undergo treatment in a hospital setting. He will be able to follow orders and engage in physical training on an equal basis with other military personnel. A contraindication to service in the armed forces is an abnormal heart rhythm and other severe complications caused by the anomaly.
Excess chords in the ventricles of the heart muscle are perceived by specialists as a minor anomaly that does not require treatment and does not limit human life. It is enough to do an ultrasound every year to monitor its development. If signs of disruption in hemodynamics and arrhythmia occur, drug therapy is prescribed. If it does not help to achieve relief of the condition, then surgical intervention will be required.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist, and if necessary, a specialized surgeon is involved. It is extremely difficult to identify a violation without patient complaints, because there are no clues.
An approximate list of methods if a targeted assessment of cardiac structures and search for anomalies is carried out:
- Analysis of symptoms. You need to understand what worries the patient. If there are at least a few signs, the question becomes simpler.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, nutrition, professional activity, family history, current and previous diseases and conditions, other points. It is also important to link them to the clinical picture, if any. For example, the occurrence or intensification of pain after physical activity, eating, etc.
- Echocardiography. The main method for visualizing tissues of cardiac structures. Used for early diagnosis and is considered the first method of examination. But with a small lesion or complex localization, ECHO does not always provide enough information.
- In this case, they turn to MRI. This is the gold standard in visualization. Allows you to demonstrate in detail the condition of the muscular organ and identify all possible deviations. No contrast required.
- Electrocardiography. Used to identify functional disorders and arrhythmias. It also does not show any changes if we are talking about a small anomaly. When symptoms are present, objective features of extrasystole, tachycardia, and fibrillation are detected. Depending on the case.
Other methods do not provide sufficient information. That's why they are rarely prescribed.
Based on the results, doctors draw a conclusion regarding the nature of the process and develop a strategy for possible therapy.
But the situation is not so obvious. Just because everything is normal now does not mean that the situation will continue. Therefore, the diagnosis is made several months later, after dynamic observation.
Aneurysm of the interatrial septum
The wall between the left and right atrium can sometimes be curved. It protrudes to the side - to the right or to the left. Most often, the cause of its development in children is a hereditary factor. Intrauterine infections can also provoke the development of an aneurysm of the interatrial septum. At each age, different clinical manifestations of this anomaly can be distinguished:
- 1-3 years. Children lag behind in physical and mental development and often suffer from viral infections. During an objective examination, doctors often detect right ventricular hypertrophy with signs of pulmonary circulation overload;
- older age (12-15 years). Children and adolescents are stunted and do not tolerate physical activity well. Symptoms include: heart rhythm disturbances, weakness, pain, pale skin.
To avoid rupture of the aneurysm, it should be regularly monitored and modern diagnostic procedures performed.
Treatment
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist and/or a specialist in specialized surgery. Recovery is usually medicinal.
Since radical surgical measures are required extremely rarely, the majority of cases involve long-term use of drugs.
What medications are used:
- Antihypertensive. If there is an increase in blood pressure. This doesn't always happen. ACE inhibitors (Perindopril), calcium antagonists (Verapamil), beta blockers (Metoprolol and others) are used. Strictly according to indications.
- Antiarrhythmic. If it is needed. The main one is Amiodarone.
- Means for restoring metabolism in the myocardium. Riboxin or Mildronate. They allow you to restore the functioning of the organ and have protective properties.
- Cardiac glycosides are extremely rarely required. Promotes normal contraction of the muscle organ. Restoring pumping function. Digoxin as a key name.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. Products based on potassium and magnesium (Asparkam, others).
Medicines are not prescribed in a vacuum. Doctors often take a wait-and-see approach and assess the patient’s condition over time. Only after this can we talk about using any means. The question is individual.
The situation is even more complicated with surgical treatment. It is required in only 1-2% of the total number of cases. It consists of minimally invasive or open destruction of an excess cord or bundle.
False chord in the left ventricle most often requires surgical intervention because blood circulation in the systemic circle is disrupted. If we can talk about this in the context of such a rare technique for eliminating anomalies.
In all cases, a certain limitation of physical activity, normalization of sleep and wakefulness (at least 8 hours of night rest), and regular visits to a cardiologist for preventive examination are recommended.
Quitting smoking, alcohol, caffeine in any form. It would not be superfluous to correct the diet, although this is not a mandatory measure. But you definitely need to fortify your own menu. Consume more plant-based products. That's the minimum.
It is recommended to consult a nutritionist to create an individual diet.
Relationship with radius and diameter
The above mathematical concepts are interconnected by the following laws:
- If the segment being described is not the diameter of this circle, and this diameter divides it in half, then this axis and the diameter are perpendicular to each other.
- On the other hand, a diameter that is perpendicular to any arbitrary contraction divides it into two equal parts.
- If the axis is not a diameter, and the latter divides it into two equal parts, then it divides in half both arcs that are subtended by this segment.
- If a diameter divides an arc into two equal parts, then the same diameter divides in half the segment that subtends this arc.
- If the diameter is strictly perpendicular to the described value, then it divides into two halves each arc that this line limits.
- If the diameter of a circle bisects a curve segment, then it is located perpendicular to the axis that subtends this segment.
Forecast
In most cases - favorable. Even when symptoms develop, many years pass before the process reaches a critical, decompensated phase.
This can only be achieved consciously. Typically, symptoms in the earlier stages are unbearable and significantly reduce the quality of life. There is no choice but to see a doctor.
The survival rate is good, the likelihood of maintaining working capacity is also good. But this does not mean that you need to sit idly by. You cannot do without the consultation and help of a cardiologist.
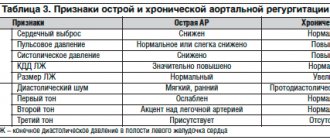
Mitral valve prolapse
Prolapse refers to an anatomical defect in the mitral heart valve. It is located between the left ventricle and the atrium. When the atrium contracts, it opens, which ensures the free flow of blood into the ventricle - and further, through the general blood flow. If a serious pathology of the mitral valve develops, its leaflets “bend”. In the worst case, the blood partially remains in the left atrium, which is fraught with unpleasant symptoms:
- heart pain;
- dizziness and shortness of breath;
- fainting;
- interruptions in heart function.
Typically, such symptoms are the exception to the rule, and minor mitral valve prolapse does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child. Severe prolapse is dangerous. It is manifested by severe deflection of the valves and more serious disturbances of cardiac activity (in the second and third degrees).