The human heart is a kind of trigger for the productive work of the whole organism. Thanks to the impulses of this organ, which are issued on a regular basis, blood is able to circulate throughout the body, saturating the body with vital substances. If the heart is normal, then the whole body works as productively as possible, but sometimes you still have to face certain health problems.
If a person comes for an examination to a doctor and the specialist suspects that something is wrong with his heart, he will send the patient for an ECG. Sinus rhythm on an ECG is a very important indicator and clearly provides data on the real state of the human heart muscle. What exactly can be determined by looking at the cardiogram is worth considering in more detail.
Peculiarities
ECG sinus rhythm what is it? Sinus rhythm detected on the ECG indicates good activity of the heart muscle, in which there are no pathologies. This rhythm characterizes oscillations that arise from impulses in a certain node and diverge throughout the atrium and ventricle. As a result, the heart muscle contracts. For the examination to show the correct result, the patient should not worry, he needs to be in a calm state.
What does sinus rhythm ECG mean? If the doctor notes on the transcript that sinus rhythm is present, then this means that the P peaks manifest themselves on a homogeneous basis, the pulse is 60-80 beats per minute, the distances between P-P and RR are similar.
Compliance of features is checked as follows:
- The elevations P are equal in height;
- Before the QRS complex, the presence of P armholes is mandatory;
- The PQ distance remains stable;
- The P notch in the second lead is positive.
Organic arrhythmias
Organic arrhythmias include:
- Arrhythmias arising from coronary heart disease (myocardial infarction, angina). Arrhythmia is caused by damage to the heart muscle. It makes it difficult for electrical impulses to propagate correctly through the conduction system of the heart. Sometimes damage can even affect the cells of the main pacemaker - the sinus node. In place of the dead cells, a scar of connective tissue (cardiosclerosis) is formed, which is not able to perform the functions of a healthy myocardium. This, in turn, leads to the formation of arrhythmogenic foci and the appearance of rhythm and conduction disturbances.
- Rhythm disturbances that occur after an inflammatory process in the heart muscle - myocarditis. As a consequence, after suffering from inflammation, the myocardium is also replaced by connective tissue (cardiosclerosis).
- Arrhythmias observed in cardiomyopathies. For an unknown reason, myocardial cells are damaged, the pumping function of the heart is disrupted, and heart failure develops. In addition, various rhythm disturbances are very often associated.
- Arrhythmias that appear with various heart defects (congenital and acquired during life). It should be noted that there are congenital primary diseases of the conduction system of the heart itself.
ECG results - sinus rhythm
If all the parameters reflected on the cardiogram correspond to sinus rhythm, this means that the innervation impulses correctly follow from top to bottom. Otherwise, the impulses come from secondary parts of the heart.
What does a vertical position mean when there is sinus rhythm on an ECG? This is the normal location of the heart in the thoracic region on the line of the conventional location of the central axis. The location of the organ is permissible at different angles of inclination and in different planes, both vertical and horizontal, as well as in intermediate ones. This is not a pathology, but only indicates the distinctive characteristics of the structure of the patient’s body and is detected as a result of an ECG examination.
Functional arrhythmias
This is also a fairly large group, including:
- Rhythm disturbances of neurogenic origin It is known that the heart is under the influence of the autonomic nervous system, which controls the activity of all internal organs. It consists of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Their effect on the heart is opposite. An increase in the tone of the vagus nerve (this is a parasympathetic nerve) inhibits the work of the heart, and an increase in the tone of the sympathetic nervous system, on the contrary, stimulates its activity. Usually the influence of the vagus nerve and the sympathetic nerves are in a state of balance. However, during the day the activity of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system prevails, and at night - the parasympathetic one. Excessive activation of sympathetic tone is promoted by stress, strong emotions, intense mental or physical work, smoking, drinking alcohol, strong tea and coffee, and spicy foods. The arrhythmias that arise at these moments are called sympathodependent. Often such rhythm disturbances occur in patients with neuroses. Activation of sympathetic tone also occurs in diseases of the thyroid gland, intoxication, feverish conditions, and blood diseases.
- Another group consists of vagus-dependent arrhythmias (from the Latin nervus vagus - vagus nerve). In such patients, interruptions in heart function occur at night. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: intestines, gallbladder, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, and diseases of the bladder can lead to an increase in the parasympathetic effect on the heart and, accordingly, to the appearance of gastrointestinal rhythm disturbances. Reflexes are formed in diseased organs, as a result of which the activity of the vagus nerve increases.
Pathologies
Tests of the heart muscle may reveal some abnormalities.
When deciphering an ECG, a discrepancy between heart activity and sinus rhythm indicates an arrhythmia or blockade. The blockade occurs as a result of the transmission of impulses by the central nervous system to the heart. An increased heart rate means that the vibrations are faster. If we talk about rhythm disturbances, then in total there is a discrepancy between the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle and the sequence.
Irregular cyclicity of sinus rhythm can be observed on the ECG by the difference in the distances between the peaks. This basically indicates a weak node. To verify arrhythmia, it is necessary to conduct Holter monitoring and a drug test. This way it is possible to identify disturbances in the self-regulation of the autonomic system and the source of oscillations.
Treatment of SSSU
Treatment tactics for sick sinus syndrome depend on the degree of sinus node dysfunction, the cause of the disease, clinical manifestations, and the severity of hemodynamic disorders. The secondary nature of the pathology implies treatment of the underlying disease.
For mild and moderate forms of SSSS, medications are used. If medications do not have an effect, or a complex, combined with other rhythm disturbances, or acute, severe form of sinus node dysfunction develops, disrupting regional and systemic circulation, installation of a pacemaker is indicated.
Signs of violations
Cardiac weakness syndrome is detected on the basis of clinical and ECG studies. To make sure of the diagnosis of arrhythmia, you need to compare the current results of the cardiogram with the transcript with normal data on the patient’s heart condition. Uniform and positive P waves in one lead, as well as uniform location at a distance of 0.11-0.20 s in front of the QRS complex.
In one minute, the number of blows should not exceed 90. This indicator is determined by the method of dividing 60 seconds. for the duration of the R – R segment. Or the number of complexes that occurred in 3 seconds. Multiply by 20 (this is approximately 15 cm of tape).
Conclusion ECG sinus rhythm may reflect pathologies such as:
- Arrhythmia. The R – R intervals on the cardiogram vary by values exceeding 0.15 seconds. Here there is a direct connection between the number of heart beats and respiratory activity (inhalation - exhalation);
- Tachycardia. Contractions of the heart muscle increase to 90 beats per minute. Other rhythm parameters remain normal. In such cases, oblique descending depression of PQ and ascending ST are often found. The image in this “picture of the disease” resembles an anchor. If the heart rate exceeds 150 beats per minute, there is a risk of second degree block;
- Bradycardia. The main indicators of sinus rhythm are present in the ECG, but the number of heart beats is reduced. Therefore, the P-P interval increases to 0.21 seconds;
- Rigid sinus rhythm. The frequency of contractions of the heart muscle is increased. The P-P interval has a difference of up to 0.05 seconds. In this case, there is damage to the node or pathology of neurovegetative regulation.
Symptoms of SSSU
Clinically significant dysfunction of the sinus node occurs when less than 1/10 of the working pacemaker cells remain.
The clinical picture of SSSU is formed by 2 main groups of symptoms: cardiac
(heart) and
cerebral
(brain).
Patients complain of a feeling of a slow, irregular pulse, a sinking heart, in the case of severe bradycardia, pain in the projection of the heart, a pressing, squeezing nature behind the sternum due to a decrease in blood flow through the coronary arteries. Arrhythmia may occur (paroxysmal tachycardia, supraventricular and ventricular extrasystole, fibrillation, atrial flutter - this is felt by interruptions in the heart, palpitations, “tumbling” of the heart. In an unfavorable course, ventricular fibrillation develops, which is often the cause of sudden cardiac death.
Brain (cerebral) symptoms
in the initial stages of SSSS is presented by nonspecific symptoms: general weakness, fatigue, irritability, emotional instability, decreased memory and attention.
As sick sinus syndrome develops, drowsiness, presyncope, and short-term loss of consciousness (Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attacks) appear, associated with a sharp deterioration in blood supply to the brain. As a rule, such fainting passes on its own.
Dizziness, tinnitus, weakness also progress, the emotional sphere suffers, performance and memory are significantly reduced, and sleep is disturbed.
Naturally, with SSSS, the blood supply not only to the heart and brain deteriorates - other organs also suffer. Kidney function is impaired, the patient notices a decrease in the amount of urine; digestive function is impaired; the tone and strength of skeletal muscles decreases.
Reasons for violations
Cardiac dysfunction in the human body occurs for the following reasons:
- Regular consumption of drinks containing strong alcohol;
- Constant smoking;
- Heart disease;
- Heart failure;
- Excess thyroid hormones;
- Mitral valve protrusion;
- Uncontrolled use of glycosides or drugs against arrhythmia.
An increase in heart rate eliminates disturbances in a person’s respiratory activity.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is not a new and time-tested method of identifying heart pathologies. This procedure requires very little time and does not require any preparatory steps. However, in order to get the correct result, transcript and doctor’s conclusion, sometimes you need to undergo such an examination several times. Based on the data obtained and clinical examinations, the cardiologist will diagnose the patient and prescribe treatment.
Why ECG readings may deviate from the norm
Irregular heart rhythm can be provoked not only by serious pathological abnormalities, but also by factors more familiar to a person’s daily life.
If the result of the electrocardiogram does not always correspond to the norm, this means that this state of the body could be provoked by the following factors:
- the person regularly drinks alcoholic beverages;
- the patient has been smoking cigarettes on a regular basis for quite a long time;
- a person is regularly exposed to various types of stressful situations;
- the patient often uses antiarrhythmic drugs;
- a person has problems with the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Of course, an accelerated heart rate or too slow may indicate problems of a more serious nature. If the results of the cardiogram are not normal, this may indicate acute heart failure, valve displacement, or congenital heart defects.
Diagnostics
During the appointment, the doctor examines the little patient. If a child has poor contact with strangers, in particular with doctors, it is worth asking him at home in more detail what exactly is bothering him. During the interview, the doctor analyzes the child’s complaints and collects anamnesis. Most likely, clinical blood tests will be required. Of course, an ECG for sinus arrhythmia in a child will be performed immediately. You may also need the results of Holter monitoring and echocardiography. Perhaps an orthostatic test will be informative.
All analyzes and instrumental studies are carried out in one place - you do not need to travel and waste time. We are located in the Central Administrative District, not far from the Mayakovskaya metro station.
Do cardiac arrhythmias manifest themselves in the same way?
All rhythm and conduction disorders clinically manifest themselves differently in different patients. Some patients do not feel any symptoms and learn about the pathology only after a scheduled ECG. This proportion of patients is insignificant, since in most cases patients note obvious symptoms.
Thus, rhythm disturbances accompanied by rapid heartbeat (from 100 to 200 beats per minute), especially paroxysmal forms, are characterized by a sharp sudden onset and interruptions in the heart, lack of air, pain in the sternum.
Some conduction disorders, such as fascicular blocks, do not show any signs and are recognized only on an ECG. Sinoatrial and atrioventricular blockades of the first degree occur with a slight decrease in heart rate (50-55 per minute), which is why clinically they can manifest only slight weakness and increased fatigue.
Blockades of the 2nd and 3rd degrees are manifested by severe bradycardia (less than 30-40 per minute) and are characterized by short-term attacks of loss of consciousness.
In addition, any of the listed conditions may be accompanied by a general severe condition with cold sweat, intense pain in the left half of the chest, decreased blood pressure, general weakness and loss of consciousness. These symptoms are caused by impaired cardiac hemodynamics and require close attention from a doctor.
How to make a diagnosis?
When should you worry?
Cardiography findings indicating pathological sinus tachycardia, bradycardia or arrhythmia with instability and irregularity of rhythm should be a cause for concern.
With tachy- and bradyforms, the doctor quickly determines whether the pulse is more or less abnormal than normal, clarifies complaints and refers for additional examinations - ultrasound of the heart, Holter, blood tests for hormones, etc. Having found out the cause, you can begin treatment.
Unstable sinus rhythm on the ECG is manifested by unequal intervals between the main teeth of the ventricular complexes, the fluctuations of which exceed 150-160 ms. This is almost always a sign of pathology, so the patient is not ignored and the cause of instability in the sinus node is found out.
Electrocardiography will also indicate that the heart beats with an irregular sinus rhythm. Irregular contractions can be caused by structural changes in the myocardium - scar, inflammation, as well as heart defects, heart failure, general hypoxia, anemia, smoking, endocrine pathology, abuse of certain groups of drugs and many other reasons.
An irregular sinus rhythm comes from the main pacemaker, but the frequency of the organ’s beats either increases or decreases, losing its constancy and regularity. In this case, they talk about sinus arrhythmia.
Arrhythmia with sinus rhythm can be a variant of the norm, then it is called cyclic, and it is usually associated with breathing - respiratory arrhythmia. With this phenomenon, the heart rate increases as you inhale, and decreases as you exhale. Respiratory arrhythmia can be found in professional athletes, adolescents during periods of increased hormonal changes, and people suffering from autonomic dysfunction or neuroses.
Sinus arrhythmia associated with breathing is diagnosed on an ECG:
- The normal shape and location of the atrial waves, which precede all ventricular complexes, are preserved;
- As you inhale, the intervals between contractions decrease, and as you exhale, they become longer.
sinus rhythm and respiratory arrhythmia
Several tests can help distinguish physiological sinus arrhythmia. Many people know that during the examination they may be asked to hold their breath. This simple action helps to neutralize the effect of vegetatives and determine a regular rhythm, if it is associated with functional reasons and is not a reflection of pathology. In addition, taking a beta-blocker increases arrhythmia, and atropine relieves it, but this will not happen with morphological changes in the sinus node or heart muscle.
If the sinus rhythm is irregular and cannot be eliminated by holding your breath and pharmacological tests, then it’s time to think about the presence of pathology. It can be:
- Myocarditis;
- Cardiomyopathies;
- Ischemic disease, diagnosed in most older people;
- Heart failure with expansion of its cavities, which inevitably affects the sinus node;
- Pulmonary pathology - asthma, chronic bronchitis, pneumoconiosis;
- Anemia, including hereditary;
- Neurotic reactions and severe vegetative dystonia;
- Disorders of the internal secretion organs (diabetes, thyrotoxicosis);
- Abuse of diuretics, cardiac glycosides, antiarrhythmics;
- Electrolyte disturbances and intoxications.
Sinus rhythm, when irregular, does not exclude pathology, but, on the contrary, most often indicates it. This means that in addition to “sinus”, the rhythm must also be correct.
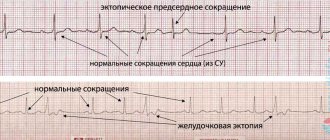
an example of interruptions and instability in the operation of the sinus node
If the patient knows about his existing diseases, then the diagnostic process is simplified, because the doctor can act purposefully. In other cases, when an unstable sinus rhythm was found on the ECG, a complex of examinations is required - Holter (24-hour ECG), treadmill, echocardiography, etc.
Interpretation of results and diagnosis
To make an adequate conclusion, a specialist needs to follow a certain sequence of actions:
- The correct rhythm is determined. All distances from R wave to R wave must be the same.
- The pulse is calculated.
- The P wave is studied - it denotes the pacemaker, which, when working well, always causes sinus contractions. Ventricular, atrial or atrioventricular are signs of serious diseases.
- The cardiac axis is determined. For thin people - a vertical position, and for overweight people - the location of the heart is usually closer to horizontal. It is dangerous if the axis spontaneously moves to the right (left).
- An assessment of cardiac conductivity is given. The doctor examines the segments, teeth, intervals and checks compliance with the norm.
At the end, the specialist determines the diagnosis; in conclusion, the doctor indicates the correct rhythm and pulse, evaluates the position of the axis, and notes the deviations found.
How to make an appointment with a specialist
Don't waste time - sign up for a consultation in just a few clicks. Leave your details in the feedback form or contact us at the contact number. If you need to call an ambulance at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg), you can call.
Geographically, the clinic is located in the Central District of Moscow, not far from the Mayakovskaya metro station, a 5-minute walk. Address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskoy lane, building 10.
Among our specialists there are candidates and doctors of science, highly experienced doctors who successfully solve complex clinical problems.
Do not delay visiting a specialist, even if your child is already feeling better. The sooner you seek treatment for sinus arrhythmia in children, the higher the chances of taking control of the possible disease and curing it forever.
What needs to be examined
Diagnosis is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist.
This is his prerogative. As needed, specialists in endocrinology and the nervous system are involved. An approximate list of activities is as follows:
- Interview of the patient orally with recording of complaints.
- Daily monitoring. Allows you to evaluate both indicators (BP and heart rate), at rest and within the framework of usual physical activity. This is an informative technique.
- Electrocardiography. The most important study. It is carried out both at rest and after activity (so-called stress tests). Typically, a treadmill and bicycle ergometry are used.
- Angiography.
- CT or MRI of the heart.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound technique.
- Blood tests (biochemistry, hormones and general).
At the discretion of specialists, other diagnostic methods are also used. As a rule, these are enough and even many.