How does the embryo develop in the period from 3 to 5 weeks?
The period of pregnancy from the 3rd to the 5th week is considered very important for the development of the fetus. This is due to the fact that it is at this time that embryogenesis occurs. The embryo has the appearance of the auricle, as it is curved in the shape of the letter C. At this time, when performing an ultrasound, specialists can already examine the rudiments of the head, back, upper and lower extremities.
In the period from 3 to 5 weeks of development, the spinal cord is released in the embryo (the development of the spinal cord and spine begins). The correct formation of the brain can be indicated by the process of flattening (at the wide end of the embryo) of the neural tube, which should occur gradually. During an ultrasound examination, specialists can see how tissue segments called somites are formed and subsequently rapidly increase, which are responsible not only for the development of muscles, but also of all tissue structures present in the human body.
Gynecologists pay close attention to this period also because the fetus begins to develop vascular and cardiac systems, which develop very quickly. Using a highly sensitive ultrasound machine, it is possible to examine the process of formation of large blood vessels. They are located in the central part of the embryo and are closely connected with a glomerulus of tissue, which at this time is only a prototype of the future heart. This tangle is a very important substance that takes an active part in the process of organogenesis.
If pregnancy is successful, it is from these tissues that the respiratory tract (upper) will begin to develop. In this case we are talking about the trachea and larynx. They also take an active part in the process of laying the pancreas, liver, gonoblasts (germ cells), which determine the sex of the child.
A photo of an embryo at the 3rd – 4th week is not informative, since the size of the embryo does not reach 0.2 mm
In the period from 3 to 5 weeks of pregnancy, gynecologists and uzologists are unable to hear the baby’s heartbeat (even when using ultra-sensitive equipment), but they confidently claim that the embryos already have all the necessary rudiments of the vascular and cardiac systems.
Characteristics
Throughout pregnancy, based on the characteristics of the fetal rhythm, it is possible, without interfering with the woman’s body, to monitor the development and physical condition of the child, notice violations in time and prescribe therapy.
Physical features of embryonic heart rate
Fetal heart rate is a variable value. The rhythm changes constantly: when the baby moves in the womb, during rest, after the mother eats, as a reaction to a drop in serum glucose.
Due to the characteristics of the embryo’s circulatory system at different stages of gestation, the heartbeat is determined by several factors:
- the stage of formation of the heart chambers;
- the presence of structural abnormalities;
- ingrowth of fibers of the autonomic nervous system into the myocardium;
- change in the fetal rest/activity cycle;
- maternal blood glucose level;
- the amount of hemoglobin in the blood;
- state of uteroplacental blood flow;
- the presence of umbilical cord compression;
- state of amniotic fluid;
- the general health of the mother.
Table of normal indicators at different periods
Fetal heart rate changes depending on the stage of pregnancy. Up to 9-10 weeks, the frequency progressively increases to 170-180/min, and then, by the 33rd week, it gradually stabilizes at around 140-160/min.
Table of fetal heart rate norms by week of pregnancy
| Gestational age (in weeks) | Average beats/min. | Variable fluctuations |
| 6 | 125 | 92—150 |
| 7 | 142 | 122—160 |
| 8 | 168 | 150—185 |
| 9 | 175 | 160—190 |
| 10 | 172 | 160—186 |
| 11 | 168 | 155—180 |
| 12 | 165 | 150—176 |
| 13 | 162 | 147—170 |
| 14 | 157 | 145—168 |
| 15—32 | 145 | 110—170 |
| 33—42 | 140—160 | 110—170 |
Some of my patients try to determine the sex of the unborn child using the fetal heart rate during the first ultrasound. They rely on the theory that a girl's heart beats at a frequency of 150-160 per minute, and a boy's - 140-150. But from the point of view of medicine, as well as my observations, the chances of guessing the gender in this way are 50%: the rhythm of the embryo is influenced by many factors, and not its gender. Moreover, these figures do not fit into the tabulated weekly fetal heart rate norms corresponding to the time of the first ultrasound screening.
How do the heart and blood vessels develop in a human embryo?
Two weeks after fertilization, the embryo begins to develop heart rudiments. This occurs in the cervical region, and the visceral layer of mesoderm is directly involved in this process. Even with hardware diagnostics, doctors are unlikely to be able to consider this point. This is due to the fact that the embryo is very small in size (length does not exceed 2 mm).
Many pregnant women are interested in the question of the formation of the hearts of their future children, since their health and life expectancy directly depend on this. This organ is formed in the form of two rudiments (paired and identical), which are located in front of the foregut. In the 3rd week of pregnancy, the process of the embryos bringing each other closer together occurs, due to which the embryo begins to form a heart tube (single).
Ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy will help you find out whether the heart is developing normally in the embryo:
Experts gave such a rudimentary organ a name - a simple heart, the location of which is the center of the embryo. If at this time doctors conduct an ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman, they will be able to detect one interesting point - the heart bud will be located slightly below the cervical region of the child. A thorough ultrasound will show that the cardiac rudiment has not only an arterial trunk and a venous sinus, but also a single ventricle, as well as a single atrium.
If a three-week embryo does not stop developing, then at approximately the 5th week specialists will be able to detect significant changes. When performing an ultrasound examination, you can notice a changed heart primordium, which by this time has acquired an S-curve. During this period, septa (internal and transverse) develop in the sigmoid heart of the embryo, due to which the organ becomes two-chambered. With a successful pregnancy, the baby's heart and longitudinal septa begin to develop.
Starting from the fifth week of pregnancy, the doctor performing ultrasound diagnostics can clearly hear the fetal heartbeat
If you perform an ultrasound at the 5th week, you will see that the unborn child’s heart becomes three-chambered. This is due to the completion of the process of formation of longitudinal and transverse partitions. At this time, specialists can already determine the heartbeat, since thanks to the developed interatrial septa (secondary and primary), blood is pumped from the right atrium to the left.
During this period, the embryo's arterial trunk finally divides into the pulmonary trunk and aorta. A septum (dividing septum) also grows into the ventricular cavity, which connects to the longitudinal septum (it grows in the direction of the interventricular septum, which is the main one). When the embryo reaches eight weeks of age, its heart becomes four-chambered.
How to prepare for research
We found out at what stage an ultrasound shows pregnancy. Now let's talk about how the expectant mother can prepare for the procedure. Since it is quick and completely safe for mother and baby, preparation will be simple and will not take much time.
- It is advisable to give up foods that contribute to gas formation two days before the examination: legumes, raw vegetables and fruits, dried fruits, dairy products, etc. The accumulation of gases in the intestines will interfere with the procedure.
- Depending on the type of ultrasound examination, the drinking regime may change. Thus, it is forbidden to drink water before a transvaginal ultrasound; the bladder must remain empty during the examination. When performing a transabdominal examination, in some cases it is necessary to drink water: the doctor will warn you about this in advance.
At what age does a baby's heart begin to beat?
Even during the process of heart formation, a small part of the tissue begins to contract (later it is transformed into full-fledged cardiac ventricles). It is worth noting that such contractile movements are in no way connected with the nervous system of the embryo. Modern medicine has proven that nervous tissue does not regulate the heartbeat process.
If, during an ultrasound examination of the patient (using heavy-duty devices), specialists are able to determine heart contractions in the 5th week of fetal development, then pregnant women will experience these amazing sensations between the 6th and 8th weeks.
How is an ultrasound performed at 6 weeks of pregnancy?
There are two options for how doctors do an ultrasound in the 6th week of pregnancy:
- The transvaginal method
is the insertion of a vaginal ultrasound sensor protected by a special condom into the vaginal cavity of a pregnant woman. - Transabdominal method
- through the skin of the abdomen. Before the scan, women apply a special gel to their abdomen.
The first method may cause some discomfort to the woman, but its results will be more accurate and complete. Contraindications to transvaginal ultrasound for a pregnant woman may include bleeding or abdominal pain.
How do doctors monitor a baby's heart activity using ultrasound?
Thanks to modern diagnostic techniques, specialists are able to determine the heartbeat of the embryo. Pregnant women today undergo transvaginal ultrasound examination, thanks to which it is possible to detect heartbeats earlier. Unlike a transabdominal study (detects heart rate only at 6–7 weeks), performed on the abdomen, a vaginal sensor allows you to determine the heartbeat at 5–6 weeks.
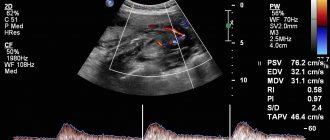
A very important point is heart rate (HR). Modern medicine has established the following standards that are used by gynecologists when examining every pregnant woman:
| Gestational age (in weeks) | Heart rate (beats per minute) | Deviations from the norm |
| 6-8 | Heart rate appears, 110-130 | Reduced shocks to 85-100 |
| 9-10 | 170-190 | Increased heart rate, exceeding 200 beats |
| 11-40 | 140-160 | Can't hear the heartbeat |
The digital difference can easily be explained by the formation of the nervous system (vegetative) at different stages of pregnancy. The work of all internal organs and systems of the baby will depend on it. If, during an examination of a fetus whose size exceeds 8 mm, the specialist does not detect heartbeats, he will make a diagnosis of a non-developing pregnancy.
In such a situation, the woman is prescribed a repeat ultrasound examination, the purpose of which is to confirm or refute the primary diagnosis. This diagnosis is prescribed 5-7 days after the last ultrasound, and during the examination of a pregnant woman, the doctor pays attention to the following indicators:
- heart rate (at this stage the child can hear 140-160 beats per minute);
- location of the heart (in an embryo at this age, the organ should occupy 1/3 of the chest and be located on its left side);
- the nature of heart contractions (a specialist must determine irregularity or rhythmicity), etc.
The baby’s heartbeat is one of the most important points that people pay attention to when examining an expectant mother.
In later stages of pregnancy, the child’s heart rate may change, since this process can be affected by various factors: the mother’s physical activity, the child’s mobility, the presence of diseases, etc.
Heartbeat indicators and causes of deviations
When the heart rate is less than 120 per minute, this indicates: in the first weeks, a short period of time, a period of more than 12 weeks of fetal hypoxia and possible compression by the umbilical cord.
The number of beats is more than 170. In the early stages, it indicates a placentation disorder, however, in most cases this is the norm. From the 12th week, this indicator is affected by the motor activity of the fetus and mother, stressful situations of the mother and hypoxia. During labor, it indicates contraction or hypoxia.
When heartbeat sounds are difficult to hear: in the early stages, this indicates a short period of time, old equipment, excess weight in the mother, or heart defects. Muffled tones, starting from the 12th week, are a sign of: maternal obesity, placental insufficiency, presentation, high or low water, uncomfortable fetal position for examination or defects of the cardiovascular system.
During childbirth, dull sounds occur when contractions are active or the baby is starved of oxygen.
The absence of heart contractions indicates a short term, frozen pregnancy and spontaneous incipient abortion. At 12 weeks and during labor, the cause of this may be fetal death or incorrect examination.
The fetal heart goes through a difficult stage of formation, which is carefully examined by doctors at every appointment with the pregnant woman. When you can hear the fetal heartbeat on an ultrasound depends on the timing, quality of the equipment and the absence of pathologies.
Video: Fetal heartbeat in early pregnancy
- The venous and arterial sections, which have grown over time, are separated by a deep constriction, after which the formation of a two-chamber fetal heart begins. This happens in the 4th week of development.
- Now the baby has only a systemic circulation. After the lungs are formed, the pulmonary circulation will develop. The size of the heart is tiny and resembles a poppy seed, but it works clearly and rhythmically.
- At the 5th week or at the beginning of the 6th (this is the seventh obstetric week), the baby’s heart is already three-chambered due to the appearance of the interatrial septum.
Stages of Heart Development
- 6th week of development: the ventricular chamber is divided by a septum. At this stage, valve formation also occurs. The common arterial trunk is now divided. As a result of this division, the aorta and pulmonary artery appear. This is how the fetus develops a four-chambered heart. Heart rate is recorded: about 150 beats per minute. The heart rate of an adult is half that.
- At 6-7 weeks the fetal heart is almost formed. At this stage, the construction of the septum between the ventricles continues. Once the septum has formed, the left and right ventricles will be separated.
- At the 8th week, the baby’s heart is shaped like an adult’s heart, with the only difference being that inside the small heart there is an oval window located between the atria and the ductus arteriosus. This window connects the aorta to the pulmonary artery and ensures the supply of oxygen from the mother’s blood directly to the fetal organs. Since after the baby is born there is no longer a need for such a window, it closes.
Supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus