Thrombocrit became known to doctors after the introduction of imported laboratory analyzers into practice. It is impossible to determine the indicator manually. It should not be confused with the long-known hematocrit. They reflect different components of blood. If hematocrit (ht) is used to judge the mass of red blood cells and its changes in relation to the liquid part, then thrombocrit indicates the proportion of platelets, the smallest formed elements.
Due to the use of analysis decoding equipment using terms in English, doctors had to get used to unusual abbreviations and norms. Thrombocrit is designated as platelet crit (PCT or pct). The parameter has not yet received proper practical use.
Why do you need a thrombocrit test?
The purpose of determining thrombocrit:
- determine the patient’s tendency to bleeding or increased thrombosis;
- used in assessing the risk of complications to select preventive treatment.
The doctor needs to take into account the platelet count when testing a patient's blood clotting. Typically, platelets are not included in the total number of indicators, and the analysis is carried out at the special request of doctors.
This is due to difficulties in technology: preliminary lysis, peculiarities of coloring and “behavior” of cells. The fact is that platelets have the property, when moving into a “foreign” space, to grow in size almost 10 times due to the formation of false legs (pseudopodia). After this, they stick together into small particles - aggregates.
Such changes create difficulties not only in research, but also in storing platelet mass for blood transfusion needs.
Automatic analyzers do not have such difficulties; indicators and coefficients are calculated
This means that it is easy to determine the proportion of platelets and obtain objective information about the decrease or increase in their level in the patient.
The indicator is correlated with the average volume of measured platelets (MPV): the higher the MPV, the greater the PCT, respectively, both values will be reduced.
Thrombocrit in general blood test
The most accessible method of laboratory diagnosis of thrombocrit and other blood parameters is a general analysis. CCA (general clinical analysis) of blood allows us to identify disturbances in microprocesses in the body, indicating certain possible diseases. Blood, as a biological fluid, consists of plasma and a cellular part containing groups of formed elements: platelets, leukocytes, erythrocytes, etc.
Each group of blood cells is responsible for certain biochemical processes and has its own content norm in quantitative equivalent and percentage of the total blood volume. Basic parameters are assessed according to the reference values accepted in clinical hematology.
All indicators are correlated, so a comparative interpretation (an increase in some values against the background of a decrease or increase in others) gives the doctor an idea of which system of the body the failure occurred. Platelets are plate-shaped cells without a nucleus or color that are formed in the bone marrow.
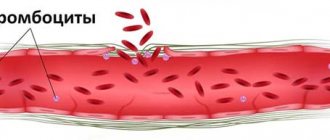
The functional responsibility of platelets is to protect blood vessels from damage and ensure normal blood clotting. If a vessel is damaged (serious rupture or microtrauma), flat shaped elements move to the site of the “accident”, form a clot and stop pathological bleeding.
The complexity of the analysis lies in the organic property of blood platelets to stick together (aggregation). To prevent cells from sticking together, the laboratory uses a special automatic analyzer that continuously rotates the blood placed in it. Thrombocrit (platelet mass as a percentage) is studied in combination with other platelet indices:
- platelet count (PLT);
- distribution range (PDW);
- average volume (MPV).
Such a comprehensive study makes it possible to obtain more complete results about the behavior of platelets in the blood composition. As cells increase in size, their distribution range increases, and an increased average value may be associated with hematological diseases, intestinal inflammation, and other pathological processes. An altered platelet count indicates problems with blood clotting and a risk of blood clots. The percentage is calculated using the formula PCT = MPV* PLT.
The PCT blood test deserves increased attention in case of suspected disorders:
- infections of bacterial etiology (origin);
- secondary infectious blood disease (sepsis);
- postoperative pathological processes;
- complicated pregnancy;
- hematological pathologies.
Formed blood elements to be assessed (briefly)
In relation to other indicators of general analysis, thrombocrit is assessed when monitoring the treatment of meningitis, pneumonia and other diseases of inflammatory origin.
Additionally
To determine platelet indices, venous blood is taken. To obtain objective results, clinical analysis is performed on an empty stomach. Three days before the procedure, the patient is recommended to eliminate heavy fatty foods and alcoholic beverages from the diet. On the eve of the analysis, you should avoid sports training and limit general physical activity. Avoid taking medications that affect blood clotting (antiplatelet agents, coagulants and anticoagulants).
What is considered normal?
According to various sources, the lower limit of 0.11–0.15% is taken as the norm, and 0.28–0.40 as the upper limit. Over the years, a person’s platelets do not change, so the norms for children and adults are the same.
Physiological fluctuations are observed depending on the time of day and seasonality. In spring, thrombocrit may be 10% lower. A similar decrease is observed at night.
In women, the rate is reduced during heavy menstruation, as well as during pregnancy. This mechanism protects the body from possible blood clots.
Thrombocrit is increased during physical activity; athletes have PCT almost 2 times higher than normal.
With the addition of "relative width of cell distribution depending on volume", these three indicators form a group of platelet indices
Results
The PCT indicator in the blood test form indicates thrombocrit - the percentage of platelets in the total mass of biological fluid (blood). Platelets are plate-shaped blood cells produced by the bone marrow. Their main function is to prevent bleeding when blood vessels are damaged. In addition to the percentage index, laboratory blood microscopy evaluates the platelet count (PLT), platelet distribution range (PDW) and mean volume (MPV).
The thrombocrit rate for adults and children ranges from 0.15 to 0.4%. A non-pathological decrease in values is the perinatal period and menstruation in women, as well as at night and in the spring season. An increase in the percentage, first of all, characterizes the danger of developing thrombosis, strokes and heart attacks. High PCT values accompany a number of chronic diseases.
A low platelet index indicates thrombocytopenia and insufficient platelet production, which is a clinical sign of anemia, blood cancer, autoimmune and other chronic pathologies. If the study results deviate from the norm, determining the cause of the violation and prescribing appropriate therapy is the responsibility of the attending physician.
When does thrombocrit increase?
The reasons for the increase in thrombocrit are associated with stimulation of the platelet germ of hematopoiesis, the body’s response to pathology. Most often, elevated PCT is found in:
- blood diseases associated with irritation of the myeloid germ (chronic myeloid leukemia, essential thrombocythemia, polycythemia, thrombocytopenic purpura);
- after splenectomy surgery (removal of the spleen), the increase lasts up to two months;
- iron deficiency anemia;
- inflammatory diseases of various etiologies (including bacteria, fungal infections);
- tuberculosis;
- viral attack (flu, measles, chicken pox in a child);
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- diabetes mellitus;
- ulcerative colitis;
- widespread vascular atherosclerosis;
- osteomyelitis;
- fractures of tubular bones;
- rheumatic attack;
- large-scale operation;
- nicotine intoxication in smokers;
- any tissue necrosis (acute pancreatitis).
Blood loss causes a decrease in the level of red blood cells and platelets, followed by increased cell reproduction during the rehabilitation period
If an increase in the indicator is detected, the patient is included in the risk group for the probable development of:
- acute thrombosis of coronary vessels resulting in myocardial infarction;
- disturbances in the blood supply to the brain (thrombotic stroke).
The possibility of increased thrombus formation is taken into account during hospital treatment, upcoming surgery, and long-term bed rest.
Conditions under which PLT reduction is acceptable
If a thrombocrit was detected below normal, what does this mean during pregnancy? Is the deviation associated with altered hormonal levels? Yes, pregnant women may experience a halving of the rate, since some of the substances produced are redirected to the child. This condition does not require treatment, but the health of the expectant mother must be carefully monitored.
Another question concerns mothers who have already given birth: when a thrombocrit is diagnostically determined to be below normal, what does this mean for the child? In children from birth to adulthood (15 years), thrombocrit has its own limits. In the period from 0 months to 1 year, the lower limit is 180 PLT. But upon reaching one year of age, its content may drop to 160, and this will still be within the normal range.
Before the end of the period of active growth, the child’s body is constantly being rebuilt, and platelets do not have time to be produced in increased quantities. After 16 years, the lower limit again reaches 180. If a child notices a decrease in platelets even to a value below 160, do not immediately panic: this may be a seasonal effect. In late autumn and early spring, people, especially children, lose some of the clogging bodies due to natural life processes.
For any serious deviation it is necessary to undergo additional examination. Timely diagnosis is especially important for pregnant women and children.
Thrombocrit is an important indicator of a person’s condition. Its deviation may indicate illnesses and hemorrhages, therefore, if deviations are detected, further therapy should not be neglected.
Why does thrombocrit decrease?
A low score indicates:
- inhibition of platelet synthesis by action on precursor cells (megkaryoblasts);
- increased destruction.
The most common reasons are:
- anemia (aplastic and megaloblastic);
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- lack of folic acid in the diet, if its content is below the normal requirement and is maintained for a month or more;
- systemic lupus erythematosus and other collagenoses;
- allergic diseases;
- blood tumors (leukemia, hemoblastosis);
- consequences of a course of chemotherapy;
- exposure to penetrating radiation;
- intoxication with toxic substances;
- negative effects of medications (cytostatics, antibiotics, diuretics, corticosteroids);
- viral infectious diseases;
- chronic liver and kidney failure.
It is observed in newborns with low weight, with fetal asphyxia. In older age groups, a connection between low thrombocrit and infection with a parasitic infection (helminthiasis) has been proven.
A dangerous consequence in the prognosis for the patient’s life is the tendency to bleed. Any minor injuries can be accompanied by large blood loss. A severe manifestation is hemorrhage in the brain and other organs.
Reasons for low pct
A doctor may necessarily prescribe a patient to donate blood for pct in the following cases:
- when diagnosing sepsis in order to clarify the severity of the ongoing process;
- in case of suspected bacterial or viral infections that lead to the general serious condition of the patient;
- febrile state of unknown origin;
- in case of infectious complications during organ transplantation;
- when connecting a patient to a ventilator;
- to understand what treatment to prescribe if the patient is immunosuppressed.
To take a thrombocrit test, both an adult and a child must follow the following rules:
- It is advisable to donate blood on an empty stomach before 9 am;
- Before taking the test, do not drink alcoholic beverages the day before, do not eat fatty, salty, or spicy foods;
- it is advisable not to smoke before the analysis, because this action may cause changes in thrombocrit;
- It would be best not to take any medications the day before OAC, but if you still need to take them, you should definitely notify your doctor;
- Women need to correlate their menstrual cycle with the test.
If the results of the analysis show that the thrombocrit is low, then you should not immediately try to prescribe treatment for yourself - this should be done by a qualified specialist, taking into account all the possible causes of this phenomenon.
READ Mechanisms of increased blood clotting during pregnancy
Video:
A condition in which a person has a persistently low thrombocrit is observed in approximately two percent of the world's population and most often refers to chronic blood diseases characterized by low coagulation.
A platelet level below normal values indicates that few platelets are synthesized in bone tissue, and they are quickly destroyed.
The reasons that a person has a low thrombocrit may be the following pathologies:
- anemia of various kinds, both megaloblastic and aplastic;
- autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus). In this case, the immune system, for some reason, marks platelets as cells harmful to the body and destroys them;
- disruption of bone marrow production of platelets;
- insufficient amounts of folic acid and vitamin B12 in the diet;
- oncological blood diseases;
- liver hemangioma;
- taking medications that thin the blood for a long time;
- poisoning of the body with various kinds of toxins, both when working in hazardous industries, and as a result of radiation or chemotherapy;
- state of chronic renal failure;
- liver cirrhosis and viral hepatitis;
- allergic diseases;
- damage to the body by worms.
If a child had a low weight at birth (less than 2.5 kg) and had breathing problems, then the thrombocrit in this case is often below normal.
Children may demonstrate low thrombocrit if they take a course of antibacterial and diuretic drugs after suffering viral and bacterial infections.
- Thrombocrit is increased in the blood of an adult and a child. What does this mean, treatment
Taking corticosteroid and cytostatic drugs can also cause a decrease in pct.
Clinical manifestations of altered thrombocrit
The attending physician must prescribe a blood test for thrombocrit if the listed diseases are suspected. Symptoms associated with changes in platelet counts must be taken into account.
A person develops:
- general weakness;
- regular headaches;
- fingers and toes turn blue;
- bruises form on the body;
- soreness in the fingertips;
- impaired vision;
- skin itching;
- nosebleeds;
- blood in urine and stool;
- Women have heavy periods.
Bruising appears without injury and causes confusion for the patient
What additional examination do I need to undergo?
For diagnostic purposes, it is important to find out the cause of the altered thrombocrit. For this, just a general blood test is not enough.
Checked:
- clotting factors;
- bleeding time;
- prothrombin index and fibrinogen;
- protein composition;
- liver tests;
- blood sugar;
- iron;
- residual nitrogen and creatinine;
- general urine analysis;
- if necessary, hormonal composition.
The patient is prescribed hardware examinations of internal organs using: ultrasound, radiography. To check the patency of blood vessels, Doppler examination is used; for certain symptoms, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is indicated.
If a blood disease is suspected, a bone marrow puncture is performed and the correctness of the hematopoiesis process is checked.