Due to the characteristics of metabolism and rapid growth in children, the performance of the cardiovascular system differs from that of adults. This applies primarily to pulse rate and heart rate. In general, a child's heart beats faster than an adult's. Therefore, with a pathological acceleration of the baby’s heartbeat, parents have a greater chance of missing this condition. To do this, you need to be guided by age-related pulse rates, because sinus tachycardia in children can be the cause of any disease that requires consultation with a doctor.
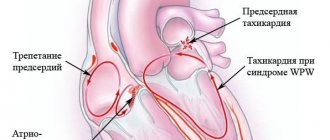
What is sinus tachycardia, and what are its types?
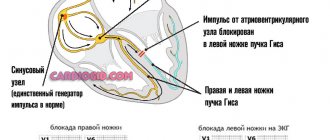
Sinus tachycardia is an increase in heart rate while maintaining the correct rhythm. Exceeding the age norm for sinus tachycardia is more than 10%. The definitions of “sinus” or “sinusoidal” tachycardia are incorrect and have nothing to do with this type of tachycardia. The name “sinus” means that the source of frequent generation of impulses is the sinus node of the conduction system of the heart. This structure is normally a first-order pacemaker, but when exposed to any factors, its activity may be disrupted and it initiates heart contractions more often.
The normal heart rate (HR) for an adult is between 60 and 90 beats per minute when at relative rest. For children, there are age norms for this indicator:
- for newborns - from 140 to 160 beats/minute;
- children under six months – from 130 to 135 beats/min;
- 1 year – from 120 to 125 beats/min;
- 2 years – from 110 to 115 beats/min;
- 3 years – from 105 to 110 beats/min;
- 5 years – from 100 to 105 beats/min;
- 8 years – from 90 to 100 beats/min;
- 10 years – from 80 to 85 beats/min;
- after 12 years – from 70 to 75 beats/min.
These data are averaged; fluctuations of up to 10% in any direction are quite acceptable.
Attention! Normally, the heart rate increases during physical activity or when the child experiences emotional experiences, both positive and negative.
Depending on the severity of the deviation from the normative heart rate values for a given child’s age, sinus tachycardia occurs:
- Moderate or I degree - exceeding the upper limit of normal is from 10 to 20%.
- Moderate or II degree - exceeding the upper limit of normal ranges from 21 to 40%.
- Severe or III degree - exceeding the upper limit of normal ranges from 41 to 60%.
The prevalence of sinus tachycardia, according to statistics, is up to 40% among healthy children.
Sinus arrhythmia in children
However, there is such a thing as sinus arrhythmia in children, also called respiratory arrhythmia, and if your child is diagnosed with such a rhythm disorder, you should not panic ahead of time. Sinus arrhythmia in children is normal if the differences in the duration of the RR intervals increase by more than 0.15 seconds. This means that the intervals between heartbeats are uneven, which may go unnoticed, but can also be felt as interruptions in the heart.
This type of arrhythmia is called respiratory if the cycle fluctuations are associated with the phases of breathing. In this case, the child’s heart rate increases as he inhales and decreases as he exhales. Thus, if the cardiogram was taken from a child in a cold room, there is a high probability that sinus arrhythmia will be reflected on the ECG, because the child reflexively holds his breath from contact with cold surfaces or sensors. Such a condition should not be a cause for concern, because in conditions of intensive growth of a child’s body, the heart does not have time to adapt to the new, constantly changing conditions of blood circulation.
This means that a recorded episode of sinus arrhythmia in children at 6, 7, 8 years old is not a pathology. Another situation is when the doctor has ruled out the possibility of respiratory fluctuations in the heart rate, but sinus arrhythmia still occurs. The period of recovery after acute infectious diseases and the presence of concomitant diseases of the body that are not directly related to the cardiovascular system, but affect the heart rhythm, should also be excluded. If sinus arrhythmia persists, the cause most likely lies in the heart itself. It may be myocarditis, congenital heart disease, chronic rheumatic heart disease, heart tumor, vegetative-vascular dystonia, or a hereditary rhythm disorder.
Causes of rapid heartbeat
Sinus tachycardia is not a separate disease, but is just a symptom. True, this does not always indicate the presence of a disease; often the cause of this condition is physiological:
- a child staying in a stuffy, poorly ventilated room;
- physical exercise;
- fear, crying, laughter;
- overeating or drinking large amounts of liquid;
- hypoxia at high altitudes;
- sudden temperature change;
- reaction to a doctor's examination in an infant.
Physiological tachycardia is observed during the action of the causative factor and disappears less than 5 minutes after its action ceases.
In infants, the automatism of the sinus node is increased, so tachycardia can be caused by almost any external influence, for example, swaddling, feeding, bathing, overheating. In schoolchildren, the most common causes are emotional and physical influences, hormonal surges during puberty, and iron deficiency anemia.
Pathological sinus tachycardia can occur both with cardiovascular pathology and with extracardiac diseases. Among the non-cardiac causes of increased heart rate in children, the following should be noted:
- decrease in hemoglobin in the blood;
- dehydration due to vomiting, diarrhea;
- hypoglycemia;
- hyperthermia;
- hypersecretion of thyroid hormones;
- obesity;
- pathology of the central nervous system;
- disruption of the adrenal glands (for example, with an adrenal tumor - pheochromocytoma);
- hormonal changes during puberty;
- acidosis;
- taking certain medications;
- various intoxications.
Sinus tachycardia of this type is characterized by a moderate increase in heart rate at rest, which increases sharply under conditions of habitual physical activity. The appearance of extracardiac tachycardia is often observed in girls aged 7 to 12 years.
Among cardiac pathologies, sinus tachycardia can be caused by:
- myocarditis;
- pericarditis;
- endocarditis;
- heart failure;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- degenerative processes in the myocardium.
Hyperkalemia or a decrease in the concentration of magnesium in the myocardium can also contribute to the occurrence of this condition.
Treatment of arrhythmia in children
Treatment of arrhythmia in children is carried out only after a thorough examination of the body and determination of the cause of its occurrence. Sinus tachycardia is treated in cases where the patient cannot easily tolerate the state of accelerated heart rate or further maintenance of such a rhythm will infringe on the body’s needs for oxygenated blood. If tachycardia is psychogenic in nature, auto-training or psychological assistance is possible. It is recommended to give up stimulants, strong coffee, tea, and spicy foods, as well as review the medications the child is taking.
The same thing - medications - must be carefully studied again, paying special attention to the list of side effects, and for bradyarrhythmia. In this case, it is also necessary to study the acid-base state of the child’s body, the volume of circulating fluid, as well as determine blood pressure. Treatment of sinus arrhythmia in children is not carried out if it is respiratory in nature and does not bring inconvenience to the child’s life. In opposite cases, contacting a pediatric cardiologist cannot be delayed, which has a positive side: everyone knows that early diagnosis is the direction in which modern medicine is moving. In addition, as mentioned above, arrhythmia in a child can be caused by concomitant diseases, the treatment of which in half of the cases gives a positive result without the need to act directly on the heart.
However, for timely, and more importantly, correct treatment, correct diagnosis is necessary, and in Moscow you will not find doctors more competent in this narrow specialty than the doctors working at the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center. Doctors here provide assistance every day and will take care of your child as if it were their own child. A friendly, open, pleasant atmosphere on the one hand and many years of experience in the relevant field on the other will make treatment for your child a comfortable and serious process at the same time. You will receive a diagnosis of the child’s objective condition, a careful analysis of each of the symptoms, strict implementation of the necessary diagnostic procedures and strict adherence to treatment protocols.
Regardless of how you are treated depending on the decision of the cardiologist - outpatient or inpatient, you can count on maintaining quality standards of care. The introduction of the latest examination technologies and maintaining experience with standard methods, modern diagnostic equipment, properly selected rational treatment, optimal timing of therapy and preventive examinations in the future - this and more is happily offered by the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center. By making the right choice in a medical facility for the treatment of your child, you ensure many years of health and a fulfilling life for your baby.
With prices for services of the medical center named after. Fedorov, check out the “Prices” page
Symptoms
For most children, sinus tachycardia does not cause any concern. Some young patients experience a feeling of rapid heartbeat. Sometimes it is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- dyspnea;
- feeling of fear;
- weakness;
- fatigue;
- exercise intolerance;
- substernal pain or discomfort in the chest;
- increased sweating;
- flickering “midges” or darkening before the eyes;
- fainting state.
The appearance of shortness of breath can simulate an attack of bronchial asthma, so this pathology must also be excluded
Important! Newborns and infants with sinus tachycardia may exhibit causeless anxiety, have difficulty sleeping and eating.
Most often, if these symptoms appear during tachycardia, it has pathological background. Sometimes this condition occurs as an attack, and if the episode lasts more than 10 minutes, myocardial hypoxia may develop, so you should definitely seek medical help to clarify the diagnosis.
Features of pediatric sinus tachycardia
Content
Sinus tachycardia in children is when the heart beats too fast when there is an acceptable sinus rhythm. A sign of it is a pulse of more than 100 beats per minute for adults. In children, the bar above which the heart rate is considered abnormal depends on age. The older the child, the lower the threshold beyond which pathology is determined.
Causes of this disease
The causes of heart palpitations are slightly different in infants and adolescents. If we talk about newborns, their heart rate increases greatly due to the fact that the automaticity of the sinus node is increased. The specific reasons are as follows:
- physiological reasons: overheating, swaddling, pain, anxiety, examination;
- pathology;
- myocarditis;
- hypoglycemia;
- damage to the central nervous system.
This syndrome is a benign condition in newborns.
If a baby has sinus tachycardia for a long period of time, myocardial metabolism may be disrupted. However, most often for newborns, the syndrome we are discussing is a benign condition. The reasons why sinus tachycardia occurs in adolescents are somewhat different:
- age-related characteristics, for example, strong growth of the body;
- emotional stress;
- diseases, endocrine, cardiovascular and so on;
- physical stress.
Types and symptoms
Sinus tachycardia can be of three types:
- Moderate, in which the heart rate increases by no more than 20 percent;
- Average, characterized by an increase in rhythm by no more than 40 percent;
- Pronounced – increase in rhythm up to 60 percent.
Symptoms of tachycardia are as follows:
- palpable episodes of increased heart rate;
- pain in the heart area;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea:
- fainting;
- fast fatiguability.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnostics includes a number of methods.
- ECG. Using it, it is easy to determine the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions in both infants and adolescents.
A nurse performs an ECG
- Daily ECG monitoring. The method is informative and safe for both infants and adolescents.
- Echo CG is performed to determine sinus pathology that can affect the heart.
- Electrophysiological study of the heart. Allows you to find out the mechanism of tachycardia and cardiac conduction disturbances.
- General blood analysis
- Determination of thyroid-stimulating hormones in the blood.
- EEG of the brain. It is with the help of this study that blood disease and central nervous system pathology can be excluded.
- Open access to fresh air into the room; it is better to go outside by loosening the collar of your shirt or sweater. The neck should be free.
- Place a cold, wet towel or handkerchief on your forehead.
If you witness an attack of tachycardia in a child, you must:
Treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor
If this does not bring relief, be sure to call a doctor. In most cases, the disease goes away on its own. The increased heart rate resulting from high temperature returns to normal after it decreases. Treatment of childhood tachycardia by doctors involves taking sedatives based on medicinal herbs. Only a cardiologist, knowing the medical history, can select individual treatment methods that are suitable for each patient. They are based on certain principles.
- In case of sinus disease of a neurogenic nature, you need to consult a neurologist, who will certainly prescribe his own treatment.
- It is worth distinguishing between reflex tachycardia (with hypovolemia) and compensatory tachycardia (anemia, iron deficiency). To do this, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of sinus disease.
- If a patient has endocrine disorders, they can be eliminated by an endocrinologist, to whom the patient goes for a consultation.
- If tachycardia is associated with cardiac dysfunction, the cardiologist prescribes cardiac glycosides.
Prevention
Preventive measures include three main principles.
- Early diagnosis. The earlier this disease is detected, the sooner a treatment method will be prescribed.
Diagnostics
After clarifying the complaints and medical history, a cardiologist or pediatrician conducts a physical examination of the patient. Upon examination, the doctor may notice a bluish appearance in the area of the nasolabial triangle. With congenital heart defects, the child may have deformations of the chest in the area of the heart and pathological pulsation of blood vessels. Blood pressure must be measured in both arms.
When determining the pulse, an increase in its frequency is noted. When auscultating the heart, the doctor detects an increase in heart rate, and in case of congenital defects, various noises and changes in heart sounds are determined.
It is necessary to conduct a general blood test to exclude anemia and other hematological diseases. For the purpose of differential diagnosis with endocrine pathology, the doctor may suggest donating blood for thyroid hormones and urine to determine the level of adrenaline. Instrumental confirmation of sinus tachycardia is an electrocardiogram.
The study has no age restrictions. When interpreting the ECG, attention is drawn to the regularity of cardiac cycles and accelerated sinus rhythm. In case of intermittent sinus tachycardia, which manifests itself in the form of attacks, it is necessary to carry out daily ECG recording - Holter monitoring. For a more detailed study of cardiac activity, functional tests are performed with recording of a cardiogram, for example, bicycle ergometry. An ultrasound of the heart is also prescribed to identify valve defects and contractility disorders. To exclude cerebral pathology, the child undergoes an EEG and is consulted by a neurologist.
Diagnosis and treatment
Vertical sinus tachycardia requires immediate diagnosis and treatment.
To identify such a disease, it is necessary to carry out a number of studies. Among them, the leading role is given to the ECG. After all, daily Holter ECG monitoring is highly informative and harmless to the patient.
How is sinus tachycardia treated? Heart rate must be brought to the optimal level.
It involves a number of measures to reduce the purity of heart contractions and is carried out with the help of sedatives, as well as consultations with a psychologist. If there is reflex or compensatory tachycardia, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of the problem. Otherwise, therapy to reduce heart rate can cause a drop in blood pressure and only worsen the situation.
How to treat this problem?
Treatment tactics for sinus tachycardia in children depend on the causes of its occurrence. First of all, the factor that provokes the condition must be eliminated, and without a doctor it will not be possible to determine it. If the cause of tachycardia is problems with the thyroid gland, an endocrinologist may prescribe hormonal correction of the pathology. For anemia, iron supplements are used over a long period of time. If tachycardia develops during hyperthermia, the child should be given non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol). With proper etiotropic treatment, tachycardia will disappear on its own.
Attention! Self-medication for sinus tachycardia is unacceptable; taking any medication should always be agreed with a doctor, especially if we are talking about a child.
If a child experiences attacks of tachycardia, which are accompanied by symptoms of insufficient blood supply to the brain. In this case, parents should be able to provide emergency assistance. If you experience dizziness, blurred vision, or loss of consciousness during an attack of sinus tachycardia, you should:
- provide the child with access to fresh air, for example, take him out of a stuffy room outside or open the windows;
- take off warm clothes, unfasten the collar so that nothing prevents the baby from breathing normally;
- You can apply a damp cloth to the forehead if the child is older than 1 month;
- in case of loss of consciousness, the legs should be raised above the level of the head for blood flow to the brain;
- If the child is conscious, you can ask him to hold his breath and strongly tense his abdominal muscles.
Attention! If the above measures are ineffective, you should call an ambulance; you may need medication to stop the tachycardia
In addition to treating the causative disease, the cardiologist may prescribe antiarrhythmic or other cardiotropic drugs:
- beta blockers (anaprilin);
- cardiac glycosides;
- potassium and magnesium preparations.
The doctor should select drugs for heart rate correction in accordance with the patient’s age and clinical diagnosis. Only a cardiologist can change the dose and frequency of taking the drug, as well as stop it.
The neurogenic genesis of tachycardia requires the use of sedatives. These can be herbal remedies based on valerian extract, motherwort, passionflower or synthetic preparations. Vitamin and mineral complexes will help strengthen the body's resistance.
In some cases, surgery will be required, such as adrenal pheochromocytoma or heart disease.
For the treatment of sinus tachycardia, therapeutic massage and exercise therapy are successfully used, including in sanatorium-resort institutions
A small patient with a tendency to tachycardia should change his lifestyle as follows:
- normalize excess weight;
- be sure to walk in the fresh air;
- exclude from the diet too spicy, sour, salty foods, tea, coffee, and also do not abuse sweets;
- normalize sleep, regulate activity and rest patterns;
- limit the time he spends in front of the TV and with gadgets;
- reduce the intensity of physical activity.
It is imperative to eliminate stress factors and normalize the psychological situation in the family.
Moderate sinus arrhythmia in a child
Moderate sinus arrhythmia in a child is not dangerous if its cause is immaturity of nervous regulation, as is the case with respiratory arrhythmia. However, even trained children may experience seemingly causeless sinus arrhythmia, and in this case, a visit to a cardiologist is mandatory. Each case of arrhythmia in a child must be subjected to observation and strict control, because if sinus arrhythmia occurs without an obvious reason, especially if the child makes complaints, which will be discussed below, a comprehensive examination of the body is necessary.
Regular observation by a cardiologist is the key to timely diagnosis of the transition of a moderate arrhythmia in a child into something more serious. Often respiratory arrhythmia is detected during a routine examination, but sometimes the child makes specific complaints. If the child’s age is too young for him to be able to formulate a complaint about poor health or pain, sufficiently observant parents themselves can notice changes in the child’s behavior if they look closely at the baby. When the heart stops working, the child may experience cyanosis (blue discoloration) or pale skin.
This is also accompanied by shortness of breath, which may manifest itself at a younger age as intermittent, “choking” crying. Such cases of arrhythmia can appear at any time of the day, and therefore the child is characterized not only by anxiety during the day, but also by sleep disturbance at night. The baby loses his appetite or continues to eat, but with great reluctance. Also, if you look closely, in some cases you can see the pulsation of large vessels. Older children may lose consciousness when a cardiac arrhythmia occurs or complain of dizziness. Also at this moment, the pressure may decrease, and some children feel the heart skip a beat or, conversely, make a strong push.
Of course, each of the listed complaints in itself seems to be a reason for a visit to the doctor, and if there is a combination of several of them, most likely the child suffers from something more serious than mild sinus arrhythmia. First of all, after the examination, the child will be sent for electrocardiography, and then two scenarios are possible: the baby can continue to be monitored on an outpatient basis or be sent to hospitalization. In case of hospitalization, tests include a clinical blood and urine test, an ultrasound examination of the heart, an echocardiogram, and a chest x-ray. In general, each diagnostic case is individual, and further tactics are determined by the attending physician.
Prevention and prognosis
Effective measures to prevent sinus tachycardia are:
- proper nutrition;
- adherence to sleep and rest patterns;
- education of stress resistance;
- regular physical exercise.
The prognosis for this pathology in most cases is favorable, since most types of tachycardia are functional. But with organic pathology, this heart rhythm disturbance will not go away on its own; you need to look for and eliminate the cause.
Thus, the wide prevalence of sinus tachycardia among children should alert both parents and pediatricians in order to detect the causative disease in time and begin treatment.
Sinus tachycardia
The causes of sinus tachycardia in adolescents may be neurogenic effects, organic heart damage, or increased thyroid function. An increase in heart rate is said to occur if it becomes more than 80 beats per minute.
The occurrence of neurogenic sinus tachycardia is also based on an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system, expressed in the increased effect of sympathetic innervation on the Kate-Fleck sinus node. In this case, the heart rate can increase to 100-120 beats per minute. Characteristic features of this form of tachycardia are its variability, periodic transition to a normal rhythm, and greater rhythm lability in response to exogenous influences, mainly neuropsychic.
The increase in rhythm is especially pronounced in a standing position, therefore the ortho-clinostatic test for this form of tachycardia is positive, the body temperature is normal, and the general state of health is satisfactory. The diagnosis of neurogenic sinus tachycardia should be approached in a strictly differentiated manner. It is necessary to exclude damage to the cardiovascular system.
Thus, the causes of tachycardia can be acquired and congenital heart defects, of which tachycardia is especially often observed with an open ductus arteriosus, atrial septal defect, etc.
Sinus tachycardia can occur with a small heart; in this case, a decrease in stroke volume causes a compensatory increase in rhythm. Making a diagnosis in all of the above cases does not cause any particular difficulties. It can be more difficult to exclude thyrotoxicosis, especially if thyroid function during testing turns out to be normal, despite its slight increase and the presence of other mild signs of thyrotoxicosis.
In this case, it is necessary to resort to treatment with microdoses of iodine, sometimes ex uvantibus, in order to come to a final conclusion.
“Clinic of diseases, physiology and hygiene in adolescence”, G.N. Serdyukovskaya