Tachycardia - symptoms and treatment
What to do during an attack
If a person is alone during a sudden attack of tachycardia, it is necessary to breathe deeply and also perform a Valsalva maneuver. To do this, close the glottis and strain the chest muscles for 10-15 seconds (can be compared to trying to push). For younger children, you can try exhaling from a syringe or drinking straw. For the same reaction in infants, you can apply ice packs to the face for a few seconds.
What actions should not be taken?
Without a thorough diagnosis and recommendations of the attending physician, you should not take any medications or dietary supplements. For some arrhythmic tachycardias, which are detected by electrocardiogram data, their use can be dangerous.
Elimination of the underlying disease
Treatment of prolonged tachycardia begins with eliminating the underlying disease of which it is a symptom, or some other causative factors. If the disease is known, then after appropriate treatment the tachycardia also stops.
For pheochromocytoma (adrenal tumor), which produces adrenaline, and sometimes for hyperthyroidism, treatment is surgery, after which one of the symptoms in the form of tachycardia disappears.
For thyroid diseases, treatment is either surgery or drug therapy.
For arterial hypertension, many drugs prescribed for its treatment not only reduce blood pressure, but also affect the heart rate, reducing it. If the use of such drugs is contraindicated, then cardiologists use a drug that acts only on the cells of the sinus node and exclusively slows down the pulse - ivabradine. The drug has a limited number of indications and is prohibited for independent use without consulting a specialist.
In case of anemia, restoration of hemoglobin levels and normalization of heart rate is facilitated by the administration of iron supplements (for iron deficiency anemia), vitamin B12 or folic acid (for B12-deficiency and folate-deficiency anemia), transfusion of blood components (for posthemorrhagic or aplastic anemia), as well as treatment of atrophic gastritis or parasitosis (diphyllobothriasis).
If tachycardia occurs in a healthy person and is associated with low physical development, then the solution is gradual endurance training. It includes increasing the activity of your lifestyle, increasing the complexity of physical training, performing static and dynamic exercises, walking at a moderate and fast pace, running at various distances with increasing difficulty, and swimming.
Treatment of supraventricular tachycardias
In the case of diagnosed supraventricular tachycardia (eg, atrial tachycardia, AVNRT, or atrial flutter), the first step is to assess blood pressure instability by the presence of the following signs:
- hypotension (low blood pressure);
- hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the body);
- dyspnea;
- chest pain;
- shock;
- signs of impaired perfusion (blood passing through the lungs).[2]
Electropulse therapy
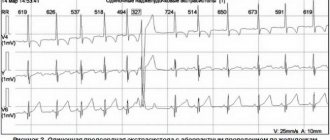
If the patient is unstable, then immediate cardioversion is necessary - stimulating the heart with an electrical discharge. In this case, it is important that the defibrillator is in synchronization mode with the QRS complex (the main impulses on the ECG line). This mode allows the defibrillator to prevent shock transmission while the heart is depolarized (otherwise cardioversion could lead to polymorphic ventricular tachycardia).
Initial energy for synchronized cardiac pacing:
- in adults - 100-200 J, can be increased stepwise if there is no success;
- in children - 0.5-1 J/kg, can be increased to 2 J/kg with subsequent attempts.[5]
A patient with stable blood pressure should be prepared for chemical cardioversion - restoration of heart rhythm using drugs. To do this, it is recommended to stimulate the vagus nerve using the Valsalva maneuver and massage of the carotid artery. These methods stimulate the parasympathetic system, slow down the formation of an impulse in the sinus node and more.
For long-term treatment of recurrent supraventricular tachycardia, patients should be counseled on how to self-increase vagal tone.
Valsalva maneuver technique : closing the glottis and tensing the chest muscles for 10-15 seconds (can be compared to trying to push). For younger children, you can try exhaling from a syringe or drinking straw. For the same reaction in infants, you can apply ice packs to the face for a few seconds.
Applying pressure to the eyeballs can also stimulate the parasympathetic system, but this method is not recommended because excessive pressure can cause eye damage.[4][8]
Carotid artery massage technique : the patient lies on his back, neck extended, while using his fingers he presses on one carotid sinus for about 10 seconds. This massage is contraindicated in people with a single artery, patients who have suffered a transient ischemic attack or acute cerebrovascular accident within the last three months, or children or infants.[5]
Drug therapy
If the effect on the vagus nerve has no effect, then adenosine can be used to normalize the heartbeat. It must be administered intravenously. The initial dose is 6 mg (child dose - 0.1 mg/kg). If this dose is ineffective, then 12 mg can be administered (for children - 0.2 mg/kg). A second dose of adenosine (12 mg) may be given one more time if the desired effect is not achieved. Each dose of adenosine should be quickly rinsed with 10–20 ml of saline solution. If the patient is receiving carbamazepine or dipyridamole at the time of treatment, it is recommended to reduce the dose of adenosine to 3 mg.[1][11]
If the rhythm is misinterpreted, administering adenosine may help slow the heart rate for a long time. This will determine whether the tachycardia is caused by another subspecialty complex tachycardia (eg, atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter).
If adenosine is ineffective, you can use:
- diltiazem (0.25 mg/kg intravenously followed by 5-15 mg/hour infusion);
- esmolol (0.5 mg/kg intravenously, then 0.2-0.5 mg/kg per minute - must be repeated with each increase in titer);
- metoprolol (2.5-5 mg intravenously every 2-5 minutes, but not more than 15 mg over 10-15 minutes).
If the above drugs continue to be ineffective, pacing the heart at a rate faster than its own rate may eliminate supraventricular tachycardia. However, there is a risk of ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation and should be used with caution and with immediate availability of cardioversion.[4]
Patients with recurrent supraventricular tachycardia without preexcitation syndrome may require long-term treatment with oral beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to maintain sinus rhythm. You may also need radiofrequency (catheter) ablation, a surgical treatment for arrhythmia using radiofrequency energy.
Treatment of AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
The primary treatment strategy for AVNRT also involves stimulation of the vagus nerve and administration of adenosine, which stops approximately 80% of arrhythmias. Second-line drugs include non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, or digoxin.[8]
Surgery
If treatment with the above methods is unsuccessful, or medication is not possible due to side effects, then patients may choose catheter ablation as a one-time definitive treatment. This AVNRT treatment method is highly effective (successful in 95% of cases).
Chronic drug therapy using class III or IC antiarrhythmic agents (flecainide, propafenone, amiodarone, dofetilide or sotalol) may be used in cases where the body does not respond to calcium channel blockers or beta blockers, or if the patient refuses catheter ablation . The choice of these antiarrhythmics is usually related to comorbidities and side effect profile.[6][10]
Treatment of tachycardia with folk remedies
The use of traditional medicine often results in the patient not receiving timely, qualified treatment. With tachycardia, this can cause life-threatening complications such as stroke and myocardial infarction.
How it appears
This disease can be diagnosed in completely healthy people of different age categories. However, it is more common in women and men of older age groups with heart problems. Sinus tachycardia can often be detected in a small child.
What causes an increase in the number of heart contractions, and what are the causes of a disease of this nature? In a healthy body, the automatism of the sinus node increases during psycho-emotional or physical overload, as well as with excessive consumption of coffee and other caffeine-containing products. Thus, the body ensures optimal blood supply to all organs during those moments when it performs strenuous work.
In other words, this is a completely adequate reaction of a healthy body to the active work of the sympathetic nervous system. Also, sinus tachycardia code ICD can also be observed in a person with a completely healthy heart, but if he is infected with any infection, suffers from anemia, or has problems with the thyroid gland. In addition, it is worth noting that such problems can be caused by such means as:
- aminophylline;
- glucocorticoid hormones, etc.
Causes
The disease is provoked by the following factors:
- heart failure and a high risk of heart attack, myocarditis, cardiosclerosis, etc.
- disruptions of the endocrine system: can be provoked by thyrotoxicosis, increased production of hormones such as adrenaline in pheochromocytoma;
- physical and psycho-emotional stress: stress, excessive enthusiasm, hard work;
- pregnancy: sinus tachycardia during pregnancy is quite common and requires close monitoring by the medical professional who is caring for the woman’s pregnancy;
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system: neurosis, affective psychosis; cardiopsychoneurosis;
- congenital anomalies of the body's development.
All these factors that cause problems with heart rhythm in a healthy person, in women during pregnancy or in children, can be observed in combination, or they can appear one at a time.
Expert advice: “5 signs that it’s time to see a doctor”
An increased heart rate in itself does not necessarily indicate any illness. It is important under what circumstances this happens and what is accompanied by it. The following are situations in which you should consult a doctor:
- rapid heartbeat appears at rest;
- an increase in heart rate is accompanied by severe pain in the heart;
- the person often loses consciousness;
- tachycardia occurs sharply and suddenly and also stops;
- an increase in heart rate worsens the symptoms of existing cardiac pathology.