Thyroiditis
is a medical term for inflammation of the thyroid gland.
In the practice of an endocrinologist you can find the following varieties:
- Chronic autoimmune;
- Subacute;
- Spicy.
In this article we will look at the second type. It is also called De Quervain's thyroiditis or granulomatous.
Why is thyroiditis dangerous?
Subacute thyroiditis is caused by viruses that cause destructive (destructive) damage to the thyroid gland. It is characterized by a 4-phase flow. Patients report severe pain in the neck area and symptoms of acute infection.
Subacute thyroiditis accounts for approximately 5% of all thyroid pathology. More often diagnosed in women. It is registered in various age groups, but the peak incidence occurs between 30-60 years. It also has seasonality (autumn, summer).
A gradual way to quit smoking
This method is recommended for smokers with many years of experience, the elderly, and those with chronic diseases. The consequences of quitting tobacco with this method will manifest themselves in a milder form and will be easier to tolerate.
When gradually quitting smoking, doctors advise using a technique based on a gradual reduction in the intake of nicotine in the body: reducing the number of cigarettes smoked daily, switching to lighter varieties of tobacco.
A system of self-restraints is being developed, the consistent application of which leads to a complete cessation of tobacco.
When not to smoke:
- on an empty stomach;
- 1-1.5 hours before meals;
- immediately after eating;
- At work;
- in the apartment;
- on the street;
- on vacation, on the beach, listening to music, watching TV.
Smoking rules:
- After each puff, remove the cigarette from your mouth;
- smoke a cigarette only halfway;
- do not inhale deeply;
- do not carry matches or lighters with you;
- buy different brands of cigarettes, not just your favorite ones;
- never borrow cigarettes if you run out of yours;
- Do not create comfortable conditions when smoking: smoke while standing or in an awkward position.
First, 2–3 rules are selected from the list and must be followed. Gradually, new ones are added to them until you follow all the restrictions.
Main signs of nicotine addiction
- An irresistible craving to take a substance.
- Difficulties in controlling one’s own behavior in conditions where it is impossible to obtain this substance in a timely manner.
- The development of withdrawal syndrome, a state of withdrawal (withdrawal) in situations when the substance stops entering the body.
- The appearance of signs of tolerance, that is, the need to constantly increase the dose of the substance.
- Narrowing the range of interests, the ability to refuse other pleasures and events if during them there is no opportunity to use a psychoactive substance.
- Continued use of the substance even when severe physical or mental health disorders appear.
All these signs are present in nicotine addiction, so smoking is considered not just a bad habit, as previously thought, but a chronic disease.
The average duration of nicotine withdrawal syndrome lasts about a month.
Many heavy smokers, hoping to reduce the discomfort that occurs when quitting smoking, switch to using electronic cigarettes. But modern gadgets, although less harmful to health, since they do not contain tar and acrid smoke, still contain nicotine, which continues to support addiction.
Nicotine withdrawal is a combination of various symptoms that have varying degrees of severity and cause psychophysical discomfort.
Nicotine withdrawal syndrome is characterized by a whole complex of symptoms:
- insomnia;
- muscle pain;
- mood swings;
- thirst, feeling of dry mouth;
- increased cough, shortness of breath;
- increased appetite;
- psycho-emotional lability: anxiety, irritability, short temper, aggression, apathy, depression;
- disruption of intestinal function: alternation of diarrhea, constipation;
- hand tremors;
- decreased performance;
- headache;
- instability of blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances (tachy- and bradyarrhythmias);
- mental dependence.
According to statistics, 70-80% of all smokers tried to give up this bad habit at least once, but were unable to cope with the consequences of withdrawal symptoms.
Treatment of thyroiditis
Mild subacute thyroiditis goes away on its own within 2-6 months. The fundamental principle of treatment is symptomatic therapy - that is, the elimination of external manifestations that cause discomfort to the patient. The drugs of choice are glucocorticoids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In the case of transient hypothyroidism and subacute thyroiditis, HRT is indicated.
The attending physician is faced with the task of reducing pain, relieving symptoms, as well as preventing possible relapses of the disease.
Classification of tachycardia
Depending on the reasons that cause increased heart rate, the physiological form of the pathology is divided, which is an adequate response of the body to the influence of external factors. These include:
- Physical exercise.
- Excessive emotional stress.
- Taking tonics and certain medications, for example, corticosteroids, adrenaline, caffeine, atropine.
In addition, increased contraction of the heart muscle can be caused by unfavorable climatic conditions, for example, extreme heat, high humidity levels. Pathological tachycardia is a consequence of various diseases of the heart and blood vessels, malfunctions of the endocrine and autonomic systems and can develop due to:
- Dehydration of the body.
- As a result of severe blood loss.
- Against the background of high temperature caused by infectious and viral diseases.
In addition, rapid heartbeat is observed in patients with anemia, hyperthyroidism, adrenal tumors, neuroses and psychoses. However, common causes of pathological tachycardia are:
- Heart failure.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Congenital or acquired defects.
And other organ pathologies.
Normally, the electrical impulse that causes the heart muscle to contract originates in the sinoatrial node. If this process is disrupted, sinus tachycardia occurs. The number of heartbeats can range from 120 to 220 beats. It is observed in patients who have had a heart attack, suffering from angina pectoris, ischemia and other cardiovascular diseases.
In addition to constant rapid heartbeat, a person notices heaviness and pain in the chest, dizziness, shortness of breath, night sleep is disturbed, appetite decreases, and mood drops. Due to impaired blood supply to organs and lack of sufficient oxygen supply, some patients experience fainting, cold extremities, and convulsions.
If the impulse that excites myocardial contraction is formed outside the sinus node, then we are talking about ectopic tachycardia. There are several types of this pathology depending on the location of the formation of electrical activity. With ventricular tachycardia, in addition to a rapid pulse, the number of beats of which reaches 220 per minute, the following is observed:
- Feeling of squeezing in the region of the heart.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of consciousness.
Atrial tachycardia is less common. The pathological condition manifests itself at times and can last from several days to months. It occurs without pronounced symptoms, which may go unnoticed in elderly patients.
A common form of pathology is artiventicular tachycardia. Characteristic features are:
- Sudden onset of an attack lasting from several minutes to a day.
- Fall in blood pressure.
- Sensation of pulsation in the vessels of the neck.
- Suffocation.
- Disorder of consciousness.
This form of tachycardia is more often observed in females.
Diagnostics
The doctor begins the appointment with a detailed medical history. Then he begins to examine the patient. Measures blood pressure and listens to the heart. However, to make a diagnosis it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations. These include:
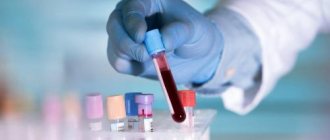
- Laboratory blood tests can determine the level of hormones produced by the thyroid gland.
- Ultrasound of the heart (ECHO GC) is carried out to assess the condition of the organ structure, identify pathologies and developmental anomalies.
- An important examination method is EGC and 24-hour Holter monitoring.
Sometimes echocardiography and cardiac MRI are prescribed to obtain more detailed information.
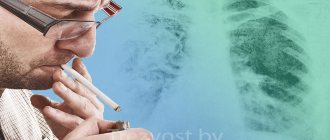
Effects of cigarettes on the heart
Every year several hundred thousand smokers die on earth. The main component of any cigarette is nicotine. Each cigarette smoked significantly shortens a person's life.
Do not self-medicate. Consult a specialist:
According to statistics, people who smoke live about 20 years less than people who do not have this habit.
A smoker suffers from metabolic disorders, problems with blood circulation, and all organs experience a lack of oxygen. This result is caused not only by nicotine, but also by a number of dangerous substances in the composition of the cigarette: cadmium, acetone, heavy metals. It is impossible to imagine the scale of daily poisoning of the body.
You get promotional code OZON - 300 points for your first order. OZONAPIE1I (applied in the cart)
Once in the blood, nicotine provokes the release of adrenaline, while the blood vessels contract, pressure increases, and the heart rate increases significantly - this is how tachycardia occurs.
All dangerous substances in cigarettes, including nicotine, interfere with the normal functioning of the body. The heart rate exceeds 90 beats in 30 seconds, this is a large deviation from the norm. Carbon oxides in the blood prevent its saturation with oxygen, after which oxygen starvation occurs.
The rate of blood clotting increases sharply, which provokes the formation of blood clots. When a blood clot suddenly breaks off, it causes a stroke or heart attack. Nicotine blocks the synthesis of the hormone prostacyclin, causing cell membranes to suffer.
Constant and long-term smoking causes increased cholesterol levels, plaques appear on the walls of blood vessels - the main cause of the development of atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.
A person who cannot quit a bad habit may become disabled due to a number of diseases; in more severe cases, death cannot be ruled out.
Consequences of abuse and overdose
Uncontrolled intake of nicotine in any form is fraught with the appearance of diseases such as:
heart diseases,- hypertension,
- overactive thyroid disease,
- disorders of the liver or kidneys,
- diabetes,
- asthma,
- chronic lung pathologies.
An overdose may cause paralysis of the muscles that control breathing or the heart, leading to respiratory arrest and coma. The prognosis depends on the dose taken, age, individual characteristics of the patient, the presence of severe concomitant diseases, and how long the nicotine overdose lasted.
A lethal dose for humans is considered to be 0.5 - 1 milligram of a substance per kilogram of weight . From one cigarette smoked, one milligram enters the body.
Nicotine overdose is a serious condition and should not be taken lightly. Timely intervention often saves lives.
Nicotine overdose: symptoms
Overdose occurs when any form of nicotine (tobacco, nicotine patch, gum, nasal spray, inhaler or cigarettes) is taken in excess. In most cases, it occurs with long-term abuse when a person is trying to quit smoking or participating in a nicotine withdrawal program. Among the main symptoms of chronic overdose of nicotine from cigarettes and other forms of this substance:
- extreme anxiety
- cold sweats,
- dizziness,
- headache,
- muscle twitching,
- insomnia,
- tingling sensation
- panic attacks,
- depression,
- heartbeat,
- high heart rate,
- high blood pressure,
- fatigue and weakness,
- loss of appetite,
- diarrhea,
- stomach ache,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- chest pain,
hearing or vision problems.
The appearance of several of the above signs of a nicotine overdose is a serious reason to contact a narcologist.
Taking a large amount of nicotine-containing products in a short period of time leads to a sharp increase in their content in the blood. In this case, an acute condition occurs, characterized by the appearance of:
- pronounced smell of tobacco from the mouth,
- symptoms of intoxication (salivation, nausea, vomiting),
- weakness,
- stomach ache,
- sweating,
- pale skin,
- a sharp increase in blood pressure and pulse rate,
- blueness of the nasolabial triangle,
- unsteadiness of gait,
- headache,
- problems with speech, swallowing, vision,
- seizures
Such consequences of nicotine overdose require immediate response. For signs of acute poisoning to appear, it is enough for an adult to smoke 6-7 cigarettes within an hour , for a child to eat the contents of one cigarette.