Palpitations - a feeling that the heart is beating too quickly or is beating too hard - is a reason to consult a doctor.
Heartbeat
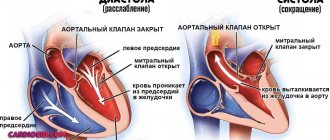
is a patient complaint about the subjective sensation of a rapid, arrhythmic or heavy heartbeat. Normally, we do not notice our heartbeat. But any deviation from the norm becomes immediately noticeable. Patients typically describe palpitations as the following: the heart pounding too hard (or “loudly”) in the chest, the heart “jumping” out of the chest, pounding, “jerking,” “spinning,” or “fluttering.” Increased heartbeat may be accompanied by a feeling of pulsation in the neck, temples, pit of the stomach or fingertips. Palpitations may also be accompanied by tinnitus, pain in the heart area, a feeling of tightness in the chest or difficulty breathing. Such symptoms may indicate heart pathology, but in most cases, complaints of increased heartbeat with accompanying symptoms, instrumental studies do not reveal signs of heart damage.
Palpitations should be distinguished from tachycardia. Tachycardia
– this is an objective increase in heart rate. The normal heart rate for an adult at rest is 60-80 beats per minute. If more than 90 beats per minute are recorded, then tachycardia is diagnosed. However, the patient may not feel that his heartbeat is rapid.
What it is?
The human heart beats at a rate of 60-90 beats per minute.
These values are considered normal, and an increase in heart rate above 90 is usually called tachycardia. Contrary to popular belief, tachycardia is not always bad! The heartbeat may increase as a result of the body’s adaptation to changed environmental conditions. For example, exercise in the gym, being a physical activity, activates the sympathetic nervous system, which leads to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. Another example is tachycardia in a patient with bleeding. Due to blood loss and a decrease in hemoglobin levels, hypoxia develops, the myocardium receives an insufficient amount of oxygen, and this causes an increase in heart rate.
After drinking alcohol
Heart palpitations after drinking alcohol are common. In this case, the heart always starts beating faster, and this is a normal reaction of the body. Such tachycardia is considered physiological if alcohol is taken occasionally. In chronic alcoholism, pathological tachycardia develops. An experienced alcoholic has impaired heart function, and most often it is no longer possible to restore it even after giving up the addiction.
After drinking alcohol, physiological tachycardia develops, but with alcohol abuse it becomes pathological.
Causes of rapid heartbeat
The reasons for this phenomenon may be different. Tachycardia can be physiological – the body’s reaction to irritating factors, and pathological – a manifestation of the disease.
In the first case, it occurs against the background of emotional excitement (stress) or as a result of increased physical activity (sports). People are taken by surprise and frightened by an increased heart rate, but the doctor’s task is to explain that a person’s heart rate does not remain constant throughout the entire time! We change and react to events around us: we get out of bed in the morning, go to work or to meet a friend, we are happy, we are upset - and all this is reflected in the heart rate through the activation of the autonomic nervous system.
Young boys and girls periodically turn to the therapist with complaints of high pulse. Their attacks are accompanied by autonomic reactions: sweating, pallor, increased blood pressure, sharp pain in the chest, panic attack with fear of death. Despite the pronounced clinical picture, after a comprehensive examination no pathology is detected. Such patients are given a mythical diagnosis of “VSD” and are recommended to take “Anaprilin” during an attack. The cause of this condition is disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. Sessions with a psychotherapist help in this situation better than IVs in a hospital. Why? The answer is in the video link below.
Pathological causes of rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) are congenital or acquired diseases of the heart or other organs. These include: rheumatism, myocarditis, heart attack, developmental anomalies, thyrotoxicosis, anemia, neurosis and others. Patients with a rapid pulse may be aware of the presence of one of these problems. In such a situation, it is necessary to consult with a cardiologist about possible ways to eliminate tachycardia in your particular case. After all, a person with a diseased thyroid gland will not be able to get rid of a rapid pulse without adjusting the level of hormones, since changes in their concentration in the blood directly affect the heart rhythm.
After sleep and in the morning
“Sleep is the kingdom of the vagus” is a law of physiology. Activation of the vagus nerve through a complex neurohumoral mechanism causes a decrease in pulse and respiration, and a decrease in blood pressure. In the early morning hours, vagal activity decreases and the sympathetic nervous system comes into play. Stress hormones (adrenaline, cortisol) enter the blood, which leads to an increase in heart rate.
In addition, a sudden rise from bed can also cause tachycardia: after a long stay in a horizontal position, the baroreceptors do not have time to adapt to the vertical position of the body. The overall vascular resistance and pressure decrease, the return of blood to the heart decreases, which, according to the feedback mechanism, predisposes to the occurrence of tachycardia.
Nocturnal tachycardia
At night, the heart rate should normally slow down, but it doesn’t always happen as it should. The use of psychostimulants, drinking drinks that stimulate the central nervous system (wine, strong tea, coffee), watching a horror movie, neurosis, smoking, insomnia - all this can cause a rapid heartbeat. This is why sleep hygiene is so important; it is not recommended to drink coffee and tea after 16:00. In addition, you need to learn how to cope with stress so that negative emotions do not cause your heart rate to increase.
The cause of nocturnal tachycardia may be sleep apnea (short-term cessation of breathing). It is observed in persons with abdominal obesity, hypertension and snoring. The occurrence of apnea can provoke various rhythm disturbances: from blockades with asystole pauses to atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
Fast heart rate at rest
A situation that should make you make an appointment with a doctor is a constant heart rate of more than 90 per minute at rest. Such tachycardia is almost always a symptom of a disease, and not necessarily of the cardiovascular system.
Chronic inflammatory disease, anemia or iron deficiency, thyroid disease, physical lack of training are the most common causes, the elimination of which will lead to normalization of the pulse.
Tachycardia can develop against the background of an acute infectious process: chills, an increase in body temperature by 1 degree increases heart rate by an average of 10 beats per minute. The use of adrenergic agonists (for example, for bronchial asthma or glaucoma), digoxin overdose, hypoxia (chronic and acute) also affect heart rate.
Prevention
To prevent attacks of nocturnal tachycardia from occurring, the best way out is to reduce the load from both physical labor and emotions, adhere to an active lifestyle that can enhance the reserve capabilities of the human body and bring the pulse back to normal.
You need to take control of the number of hours spent motionless (at the computer), remove all “nicotine poisoning sessions” from the regime, and avoid drinking 8 cups of coffee a day, especially before going to bed.
It is better to avoid heavy meals before bedtime and reduce the amount of quickly digestible carbohydrates. The body should receive almost the entire daily dose of calories in the first half of the day. Before going to bed, you should not engage in physical activity; it is better to take a walk or take a relaxing shower.
Main symptoms
Tachycardia manifests itself in different ways; clinical symptoms depend on age and concomitant diseases. Rapid heartbeat may be accompanied by a feeling of discomfort in the chest, a drop in blood pressure, and weakness. There may be a feeling of shortness of breath, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, fainting. A patient with angina pectoris experiences chest pain as a result of an imbalance between the heart's increased oxygen demand and decreased O2 delivery. In people with heart disease, an attack of tachycardia is accompanied by a sharp increase in shortness of breath.
Features of the floors
There are no particular differences between the manifestations of tachycardia in men and women, except for autonomic reactions and emotional overtones.
The heart beats and bubbles in the throat, gives rise to fever, severe sweating, trembling in the body - this is how the signs of tachycardia in women are vividly described. They are more likely than men to have chronic non-paroxysmal sinus tachycardia - a disease when heart rate does not correspond to the level of physical activity or emotional stress. A possible mechanism for its development is considered to be an anomaly of the sinus node or increased automaticity of the heart.
Postural orthostatic tachycardia is also predominantly characteristic of women. It is accompanied by an inadequate increase in heart rate when the body position changes from horizontal to vertical.
In children
Heart rate norms in children are higher than in adults. In newborns it can reach 160 beats/min, in one-year-old babies - 130-140, by the age of seven - 80-100. Changes occur quickly in a child’s body, and the heart adapts to new conditions, so it is not always possible to accurately determine the causes of tachycardia.
A fast heartbeat in a child can be dangerous and lead to heart disease in the future. It is important that the child leads a healthy lifestyle.
The causes of pathological tachycardia in children are the same as in adults. They are diagnosed with sinus, paroxysmal and chronic tachycardia. Paroxysmal is dangerous, in which the heart rate increases two to three times. The child develops shortness of breath, bluish skin, veins begin to pulsate, and he may become very frightened. During an attack, you need air flow and rest. It is usually relieved by intravenous injections of glycosides.
Clinical case
In my practice, there was a case of sinus tachycardia in a pregnant woman.
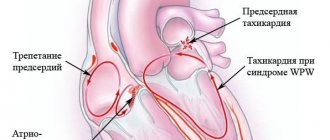
The woman constantly felt a rapid heartbeat, which was an adaptive reaction of the body: pressure decreased, heart rate increased; but the patient was also diagnosed with anemia. After correcting the hemoglobin level with iron supplements, her health improved and the feeling of palpitations disappeared. Although at first the woman was sincerely surprised when she was not prescribed drugs to slow down her pulse! Depending on the location of the source of excitation, tachycardias are divided into supraventricular and ventricular.
The first arise in the structures of the heart up to the level of branching of the trunk of the His bundle: in the atria, AV node, in additional conduction pathways. The source of origin of the latter is the His bundle, Purkinje fibers, and ventricular myocardium.
Based on the nature of the course, paroxysmal and non-paroxysmal types of pathology are distinguished.
According to the mechanism of occurrence - reciprocal, ectopic, with trigger activity, and so on.
Differential diagnosis of arrhythmias is a difficult and responsible task. In particular, when it comes to tachycardia with wide QRS complexes on the ECG. This may be a ventricular arrhythmia or tachycardia involving the accessory tract (accessory tract).
Ventricular tachycardia has a poor prognosis and occurs as a result of damage to the heart muscle. In contrast, arrhythmia involving the AP appears in a person without gross structural pathology of the heart.
To clarify the type of tachycardia, an ECG with an intrathoracic lead should be recorded or a transesophageal electrophysiological study should be performed. However, in real clinical practice, such an opportunity is rarely provided, and in these situations the doctor is guided by the following rule: assess the condition as the most dangerous to human health and life and begin appropriate treatment.
Diagnostics: when and with what to see a doctor?
Any first-time attack of tachycardia that negatively affects your well-being is a reason to consult a doctor! And the more pronounced the clinical manifestations, the sooner you need to consult. If a person loses consciousness during a paroxysm, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance and perform electrical cardioversion (impact of a pulsed current discharge on the heart).
Doctor's advice: check-up list for suspected tachycardia
To establish a correct diagnosis, the following studies and tests are necessary:
- electrocardiogram - at rest and at the time of rapid heartbeat;
- Ultrasound of the heart - data on the structural structure and valve apparatus;
- daily ECG monitoring;
- transesophageal EPI (TEPE);
- general blood test - will provide information about the presence of anemia and/or inflammation;
- blood test for thyroid hormones and TSH;
- consultation with an ENT doctor (if you have a history of frequent sore throats) and a dentist (caries) to identify and treat foci of chronic infection.
This is the minimum research that will help establish the cause of tachycardia, its nature and type, or allow you to choose a further diagnostic direction. Often, the doctor needs to seek help from fellow arrhythmologists who are able, using modern instrumental methods, to determine the area with pathological impulses. After its localization becomes known, the issue of minimally invasive destruction of the lesion can be decided.
If rapid heartbeat is the result of chronic tonsillitis, then by eliminating the cause (by performing surgical removal of the tonsils), you can forget about the heart problem. Such patients complain of pain in the heart area. Why chest discomfort occurs with a sore throat and how to act correctly - read here.
If the study reveals changes in thyroid hormone levels, or pheochromocytoma is suspected, then an endocrinologist will treat such a patient. It is worth noting that in clinical practice the first symptom of thyrotoxicosis is paroxysm of atrial fibrillation. Therefore, all patients with new-onset atrial fibrillation need to determine the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood.
Monitoring a person with tachycardia first of all involves monitoring by a specialist who treats the underlying disease. It is a competent approach to the pathology that causes arrhythmia that will help get rid of unpleasant symptoms and minimize the consumption of medications.
How to relieve an attack of tachycardia: first aid
Vagal tests can be used as an emergency aid. Their meaning is to irritate the receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system, as a result of which the vagus nerve is activated. Performing these techniques will help either interrupt the paroxysm or lower the heart rate and reduce symptoms.
- Valsalva maneuver. While sitting or standing, take a deep breath, then pinch your nose, close your mouth and try to exhale, while straining the anterior abdominal wall.
- The cough reflex is simple to perform: the patient needs to cough.
- The gag reflex is to press on the root of the tongue.
- Squatting with straining.
- Diving dog reflex: hold your breath, pinch your nose and lower your face into a container of cold water.
- Carotid sinus massage. Prohibited for patients with atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries and/or a history of stroke. It is carried out as follows: the pulsation point on the neck is determined and several pressures are applied on it for 3-5 seconds.
- Danini-Aschner test - pressure on the eyeballs; currently not recommended for use.
In addition to vagal tests, medications are used for emergency care. Verapamil is widely used, but its use is possible only when it is reliably known that there are no additional pathways in the myocardium. If atrial fibrillation has developed, then Propafenone, the “pill in your pocket” technique, can help. This drug is taken only if it has been previously successfully used in a hospital under the control of an electrocardiogram.
In my practice, during transesophageal pacing, patients often developed an attack of reciprocal AV nodal tachycardia. The use of vagal maneuvers (Valsalva and carotid sinus massage) made it possible to stop paroxysm. The entire process is demonstrated on the screen of the ECG installation: against the background of a smooth sinus rhythm, an attack of tachycardia with narrow QRS complexes suddenly occurs. This is accompanied by typical patient complaints (dizziness, nausea, darkening of the eyes, etc.), a massage of the carotid sinus is performed, and the attack suddenly ends.
If wide complex tachycardia develops during TEE, you can try to stop it using several electrical stimuli. The cessation of paroxysm in this way indicates the supraventricular nature of the arrhythmia. If the source is located in the ventricles of the heart, then stimulation will not affect the course of the attack in any way.
If you want to get quick, accessible and short information about frequent heartbeats, watch the video on our channel dedicated to this topic. Ask questions to experts in the comments.