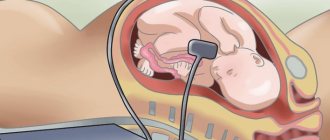
Fetal echocardiography is a modern method for studying the heart. It is carried out using a special ultrasound diagnostic device, which is equipped with special cardiac programs. Using this method, it is possible to timely detect anatomical changes in the heart, as well as the functional state of large vessels and the pericardium: increased wall thickness or dilatation of the ventricles, as well as the atria, ventricular contractility, the presence of blood clots or fluid in the pericardium, or the formation of tumors.
The peculiarity of an echocardiogram is that this method allows you to examine the internal state of the heart using sound waves. This study is carried out using a multifunctional special device called a transducer. It is installed on different areas of the pregnant woman's abdominal cavity and allows you to examine the heart and valves of the fetus from different positions.
The fetal echocardiography method is absolutely harmless. It has virtually no contraindications, so it can be performed on pregnant women more than once. The reflected signal of ultrasonic waves is transmitted to a computer system and displayed on the monitor in the form of bright dots, which then merge into a common image of the object under study.
Fetal echocardiography is an absolutely safe method that cannot harm either the mother or her unborn child. New generation devices from well-known manufacturers, such as the iE33 ultrasound machine, allow you to examine in detail unborn children in a variety of conditions and at the same time obtain the most accurate results. Ultrasound diagnostics gives doctors the opportunity to identify heart defects early enough in pregnancy and make an accurate diagnosis even before the baby is born. Thanks to it, sick children have a better chance of living a full life, since heart surgery is often performed on babies immediately after birth.
Heart in the life of the fetus
During fetal development, there must be structures in the heart that disappear after birth. Basically we are talking about the oval hole in the interatrial septum, which connects the atria of the heart during pregnancy and the ductus arteriosus of Botalla. Its presence is a physiological phenomenon that ensures the proper functioning of the circulatory system in the fetus.
Both openings close only after childbirth. Premature closure of the foramen ovale or duct of Botalla can lead to impaired cardiac function and performance. Fortunately, fetal echocardiography can detect this abnormality.
Fetal circulation and duct of Botalla
Fetal heart defects - how and when they are detected
Fetal valve defects may go undetected and may be acquired late in pregnancy due to gestational infection.
Some heart defects in utero may go undetected due to the small size of the fetal heart (about 10 mm at the second prenatal examination). Small holes in the septum, abnormal venous drainage, or coarctation of the aorta often go undetected.
In addition, heart health is affected by changes in pressure in the organ after birth, as well as the degree of closure of certain fetal circulatory structures - the foramen ovale, the ductus arteriosus, or the ductus venosus.
The fetus's lungs are filled with amniotic fluid, the fetus inside the uterus does not breathe, and oxygen comes through the umbilical cord from the mother. Therefore, fetal pulmonary circulation can only be assessed after birth, when the baby takes his first breath.
Limitations of the examination are associated with the small size of the fetal heart when examined during the period of 19-24 weeks of pregnancy, as well as with the hardware capabilities of ultrasound machines - their resolution and enlargement of structures. Therefore, all patients are recommended to undergo an additional third prenatal examination of the child at 28-33 weeks of pregnancy. The fetus is then much larger and certain structures, especially the fetal heart, are better visible.
Norm and interpretation of results
Fetal echocardiography is a non-invasive diagnostic method that is highly informative. An echocardiogram can only be interpreted by a cardiologist, since independent study of the indicators cannot clarify the full picture of the study.
Any echocardiogram conclusion contains a number of mandatory indicators, the values of which reflect the structure and functions of the heart chambers. In the conclusion, the parameters of the right and left ventricles, atria, interventricular septum, and the condition of the heart valves and pericardium must be indicated. With the help of special medical aids, certain standards have been established, deviations from which may indicate the appearance of various heart pathologies.
The following indicators must be recorded in the protocol after this examination:
- value of left ventricular myocardial mass;
- value of left ventricular myocardium;
- end systolic size;
- short axis;
- long axis;
- end-diastolic volume of the left ventricle;
- aorta;
- right atrium;
- left atrium;
- myocardial thickness of the interventricular septum systological;
- myocardial movement;
- myocardial thickness of the interventricular septum diastological;
- miltral valve;
- aortic valve;
- ejection fraction;
- wall thickness in diastole;
- pulmonary artery;
- stroke volume;
- diastolic wall thickness;
- diastolic size.
The main indicators that determine the normal development and functioning of the heart muscle are data indicating the functioning of the ventricles, as well as the development of the septum between them. Decoding the data after the study may indicate a manifestation of heart failure or stenosis. Failure develops when the heart valve leaflets, which prevent the reverse flow of blood, fail to cope with their functions, because of this, blood is directed into an adjacent chamber, and the heart becomes less efficient. With stenosis, there is a decrease in the diameter of the valve opening, as a result of which blood pumping worsens.
Interpretation of cardiac echocardiography necessarily includes data on myocardial contractility, as well as the pumping function of the left ventricle in dynamics, the presence of scars, aneurysms, tumors, blood clots, as well as their size and impact on the contractility of the walls. In addition, based on the study, the doctor has the opportunity to reliably assess the condition and functional characteristics of the heart valves, as well as the degree of hypertrophy of their walls. This technique allows you to examine blood flow through valves and large vessels, as well as detect the presence and existing degree of reverse blood flow through the valves.
When is it necessary to do an ECHO of the heart?
Although cardiac echo is extremely useful in detecting many cardiovascular diseases, the gynecologist orders fetal echocardiography first when she detects an arrhythmia or suspects that the baby may have a heart defect.
The risk of fetal heart defects among healthy pregnant women is approximately 4%. For this reason, every pregnant woman should undergo a complete fetal heart examination. The risk of karyologic problems is higher, including in children with increased neck transparency, abnormal karyotype, or generalized edema. This examination should also be carried out if:
- diabetes or gestational hypertension;
- phenylketonuria or other chronic diseases;
- autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto's thyroid disease;
- connective tissue diseases, systemic lupus;
- taking antiepileptic drugs or other drugs used for chronic diseases;
- a family history of heart defects or the presence of a child with such a defect;
- rubella, coxsackie virus, toxoplasmosis, parvovirus B19 or other infections;
- aged from 35 years;
- burdened with family genetic defects;
- If the mother has Rh-positive blood, and the child’s father has negative blood, this is the Rh factor (serological conflict).
Diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman
Indications for echocardiography also include a suspected genetic defect of the fetus, other previously identified fetal defects and abnormal ultrasound results, that is, increased arterial hypertension and abnormal biochemical results.
How is ECHO performed on the fetal heart?
A fetal echo is a completely safe, painless and non-invasive test. For a woman, it is practically no different from a standard ultrasound examination performed several times during pregnancy.
First, the doctor applies a special gel to the expectant mother’s belly, which improves the ultrasound. He then places the head of the ultrasound machine on the skin. The generated ultrasound reflects the structures of the heart and the fetal blood flowing in the heart, and is then returned to the device where the result is processed.
This will show the baby's chest and heart on the monitor. The doctor can evaluate the structure and function of the organ and check the heart rate. The equipment also provides images of blood flow through the heart (Doppler ultrasound). Thanks to this, the examination is even more accurate than standard ultrasound.
Echocardiography is usually performed between 19 and 24 weeks of pregnancy, when all the heart structures are developed and clearly visible. This takes from 15 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the specifications of the test.
It is also possible to do an early fetal heart echo at 14-18 weeks of pregnancy, especially in patients with abnormal double test results, serological conflict, after amniocentesis, infection during pregnancy. A complete fetal cardiac assessment should be repeated after 18 weeks of gestation.
Contraindications for the study
Fetal echocardiography is not a study that can harm the health of a pregnant woman or her child, therefore there are no contraindications to its conduct today. Carrying out a normal diagnosis can only be hampered by deformation of the abdominal cavity or serious changes in the skin of an allergic or inflammatory nature that are present in the area of the study.
In modern medicine, fetal echocardiography is divided into several types. It can be two-dimensional, which allows you to study the anatomy of the main structures of the heart. The condition of the leaflets, walls and valves of the heart can be examined using M-mode echocardiography, and Doppler echocardiography allows you to study and correctly assess the hemodynamics and rhythm of the heart.
The described technique allows you to study in detail the speed and direction of blood flow, and also gives doctors the opportunity to assess the degree of narrowing of the heart vessels and determine the volume of blood that leaves and returns to the heart. To carry out echocardiography as accurately as possible, new generation ultrasound machines are used, which are absolutely harmless to the health of the expectant mother and her baby.
If a serious pathology is discovered in a child during echocardiography, then a repeat examination is prescribed after one to two weeks to exclude a possible medical error. Sometimes, after the study, the expectant mother is referred for a more detailed consultation with a cardiologist, pediatric surgeon and neonatologist.
Some heart pathologies detected in the fetus may disappear on their own even before birth, so repeated examinations sometimes do not reveal deviations from the norm. The quality of the images obtained during the study can be influenced by factors such as the location of the fetus in the womb and the weight of the mother, since it is much more difficult for obese women with a large fat layer to make a diagnosis.
Benefits of detecting heart defects prenatally
First of all, this gives time to properly prepare for childbirth, both in its course and in the place of birth of the baby. A baby diagnosed with a heart defect should be born in a specialized center, where he will be under professional care.
Of course, we must not forget that modern medicine offers the possibility of prenatal treatment of cardiovascular diseases in a child, for example, the aforementioned arrhythmia or circulatory failure. Thanks to the so-called prenatal cardiology, pregnancy does not need to be terminated long before the due date, and the child has a chance to survive safely to the end in the best conditions - in the mother’s womb.
Intrauterine treatment of cardiovascular diseases in a child
Thanks to prenatal checkups, the fetus can be properly treated during pregnancy and delivered on time, avoiding premature birth.
conclusions
Thus, fetal heart echo is the main cardiac examination of pregnant women. The test is used to evaluate the anatomy of the fetal chest and heart and its functioning.
During the examination, abnormalities in the structure (heart defects) and function of the heart, as well as arrhythmia, can be diagnosed. The information provided by this test can determine the further course of pregnancy and childbirth. Children with heart defects should be born in specialized centers where they will receive professional care immediately after birth.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
[contact-form-7 id=”296" title=”Untitled”]
Abortion and contraception clinic in St. Petersburg - department of the medical gynecological association "Diana"
Make an appointment, tests or ultrasound via the contact form or by calling +8 (812) 62-962-77. We work seven days a week from 09:00 to 21:00.
We are located in the Krasnogvardeisky district, next to the Novocherkasskaya, Ploshchad Alexander Nevsky and Ladozhskaya metro stations.
The cost of a medical abortion in our clinic is 3,300 rubles. The price includes all pills, an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound to determine the timing of pregnancy.
Reviews
Ekaterina, 25 years old During the second screening at week 20, the doctor identified an additional chord. The gynecologist sent me for an echo kg, 7 days after the ultrasound. The procedure took about 15 minutes, after which the conclusion was issued. Based on the screening results, it turned out that this is a structural feature of the heart, and all parameters are normal.
Valentina, 36 years old This screening took place at the 24th week of pregnancy, since I belonged to a risk group (I have diabetes). The procedure was done in a specialized paid clinic, where a highly qualified cardiologist works. I had a Doppler echocardiogram done, it showed not only the structure of the heart, but also the flow of blood through the arteries leading to the heart. The results revealed no defects.
Anna, 27 years old During an ultrasound scan at week 22, the doctor discovered a defect in the interventricular septum. I was given a referral for an echocardiogram, which I underwent 12 days later. Based on the screening results, the diagnosis was confirmed; the child was diagnosed with a small membranous defect of the VSD. I was registered with a cardiologist, with whom I was constantly examined. Immediately after birth, the defect closed spontaneously, as it was small in diameter.