The main focus of the study is the registration of the electrocardiogram of the heart (atria, His bundle, ventricles), and the use of diagnostic stimulation to assess the electrophysiological parameters of the heart. There are non-invasive and invasive cardiac EPI.
Transesophageal electrophysiological study (TEC cardiac EPS)
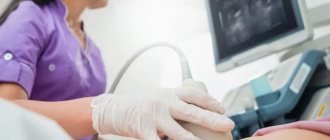
– a non-invasive method of electrophysiological examination of the heart, by introducing a diagnostic esophageal electrode through the nasopharynx (oropharynx) to a depth of 40-50 cm and recording an ECG. The examination is performed under local anesthesia (although more often without it) of the nasopharynx, the patient is in a supine position. The procedure usually does not require hospitalization. The study is performed on an outpatient basis (an EPI room or a cath lab) and usually takes no more than 20 minutes. Complications, as a rule, are not observed.
Endocardial electrophysiological study of the heart
Endocardial electrophysiological examination of the heart (endoEPI of the heart) is carried out in a cath lab in compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis under local anesthesia (“freezing”) from a small puncture (puncture) of vessels (femoral veins) and placement of introducers (“tubes”) through which into the heart catheters-electrodes are inserted under X-ray control. Using methods of electrical stimulation of the heart through inserted electrodes, the functional state of the cardiac conduction system is assessed and the mechanism and possibility of catheter ablation (destruction) of the tachyarrhythmia focus or an additional conduction pathway (WPW syndrome, etc.) is clarified. To conduct the study, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital, usually for 2 days. The study usually lasts up to 30-45 minutes.
Indications
The main indication for EPI of the eyes is the impossibility of using other diagnostic methods. Thus, the method is used when the optical media of the eye are opaque, preventing ophthalmoscopy:
- hemorrhage in the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye;
- penetrating injury to the eyeball;
- having a tattoo on the eyeball;
- thermal or chemical burn with clouding of structures (cornea, lens, vitreous fibers) in the area of study.
Electrophysiological ophthalmological diagnostics are indicated for young patients for objective reasons - children under 3 years of age are not able to adequately and completely describe the symptoms that bother them. For the same reasons, diagnostics are carried out using EPI of the eye in the presence of mental disorders: mental retardation, autism, etc. Indications for electrophysiological studies in these groups of patients are:
- prevention of visual impairment with examination of basic eye functions;
- history of pathological childbirth - fetal hypoxia or malnutrition, prematurity;
- congenital unilateral strabismus;
- changes in the patient's behavior indicating a unilateral or bilateral decrease in visual acuity;
- previously identified eye diseases - myopia, farsightedness, retinal or optic nerve atrophy.
The reason for electrophysiological studies of the eyes may be signs of functional disorders of the visual organs or areas of the nervous system that affect visual perception. Their symptoms:
- narrowing of visual fields up to tunnel perception;
- disorientation in low light conditions;
- decreased color perception - decreased color contrast, lack of shades in the picture;
- the appearance of flies and blind spots in the field of vision.
Electrophysiological studies of the eye are also carried out for amblyopia, degenerative diseases of the retina and optic nerve, nerve atrophy, and multiple sclerosis as a means of tracking the dynamics of pathology. An ophthalmologist can, if necessary, prescribe EPI for the eyes while constantly taking medications that can affect the central nervous system and visual organs.
Contraindications for endoEPI
- acute infectious diseases,
- acute myocardial infarction,
- unstable angina for 4 weeks,
- chronic heart failure III-IV f.k. according to NYHA,
- left ventricular aneurysm with thrombus,
- blood clots in the cavities of the heart,
- cardiac mechanical prostheses of the left chambers of the heart with access from the left.
When performing endoEPI, the incidence of complications does not exceed 1%. In order to prevent the latter, all necessary measures are taken at all stages of diagnosis and treatment.
The X-ray endovascular diagnostics and treatment room provides diagnosis and treatment of all types of arrhythmias (brady- and tachyarrhythmias). The department carries out operations within the framework of the state program for the provision of high-tech medical care (HTMC). This type of medical care is provided according to quotas allocated by the Russian Ministry of Health. Patients can also be operated on on a self-supporting basis, taking into account the cost approved by the Clinic.
When is EPI indicated?
Any type of EPI is carried out if the patient has certain complaints that the doctor cannot associate with disorders identified by the ECG or which arise in the patient with satisfactory examination results, or when certain diseases are suspected.
Thus, invasive cardiac EPI is performed when symptoms of the following nature occur:
- Paroxysmal interruptions in the work of the heart, especially short-term, but causing significant subjective discomfort,
- Interruptions in the heart, accompanied by severe general poor health, as well as shortness of breath and wheezing in the chest at rest, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle or the skin of other parts of the body (cyanosis), severe pallor of the skin, very high or low blood pressure, intense pain in the chest or in the chest on the left,
- Loss of consciousness and presyncope, with the exception of pathology of the central nervous system or other diseases (in the case of cardiac causes, loss of consciousness is called an attack or the equivalent of a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack, an attack of MES),
- Episodes of cardiac arrest (asystole) leading to clinical death with successful resuscitation of the patient.
Among the diseases that require invasive cardiac electrophysiology to clarify the diagnosis, the following can be noted:
- Paroxysmal types of arrhythmias - atrial fibrillation-flutter, supraventricular tachyarrhythmia, frequent ventricular extrasystole with transition to ventricular tachycardia,
- Sick sinus syndrome (SSNS), accompanied by alternating tachy- and bradycardia (tachy-brady syndrome), as well as bradycardia with the above-mentioned attacks of MES,
- Ventricular fibrillation with transition to asystole,
- Cardiac ischemia.
In the case where TEE does not help to reliably establish or exclude a diagnosis, that is, in diagnostically unclear cases, the patient undergoes endo- or epi-EPI.
In addition, endoEPI is carried out as part of an intraoperative examination when performing an intravascular RFA (radiofrequency ablation) operation, in which the pathological paths of the impulse that are the cause of one or another type of arrhythmia are destroyed by an intracardiac probe.
Methodology
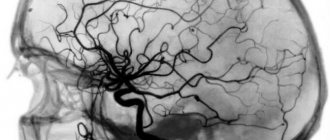
Early electrophysiological studies consisted of recording intrapolar electrical activity during spontaneous rhythm using conventional stimulation electrodes. Modern methods use electrodes installed at several points of the endocardium for simultaneous stimulation and recording. Thus, various electrophysiological parameters are determined both during the spontaneous rhythm and during stimulation. With the help of programmed stimulation, many different heart rhythm disturbances can be caused, the electrophysiological nature of which is determined by the mapping method.
EPI methods
Electroretinography . The graphic images obtained by this method indicate the level of electrical activity of the retina that occurs in response to a light stimulus. This method detects the activity of retinal cells, which is directly related to the number of healthy photoreceptors and neurons. Each curve of the electroretinogram graph is a separate cell layer. The doctor evaluates the function of all groups of cells by their response to certain stimuli.
Electrooculography . This method records changes in constant potential in the corneal-retinal zone during eye movement to the sides. The results of the procedure are directly related to the degree of preservation of the pigment epithelium. The electrooculogram will change depending on where in the retina (in Bruch's membrane, choriocapillaris layer) it is located.
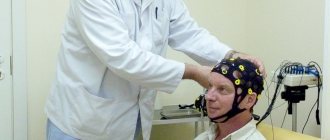
Visually evoked potentials . The method is based on studying the reaction of the visual zone of the cerebral cortex in the occipital region to irritation of the eyes with light (according to Brodmann, fields 17–19). The identified potentials are projected as an electroencephalogram, showing the possible functions of the cells of the visual analyzers. This method plays one of the most important roles in the topical diagnosis of emerging pathology. The stimuli in this case can be flashes of light or structured stimuli, such as black and white cells of different sizes, alternating with each other. It all depends on the objectives of the study and the performance of the patient’s visual system.
Multifocal electroretinography method . The result of the study is a three-dimensional map of light sensitivity that is most important in terms of the functionality of the central region of the retina. Also, this method detects even the smallest areas of damage to the central (macular) zone of the retina.
The ophthalmologist and the electrophysiologist performing the EPI work in full contact. The first is charged with setting the task, as well as deciding on the research method. In turn, the electrophysiologist develops a research scheme to obtain responses from retinal cells that are involved in the progression of the pathology. The results of examination using EPI methods when making a diagnosis, due to their objectivity, are paramount.
In our clinic, EPI is performed by highly professional specialists who are proficient in the research methodology. To conduct the study, you must undergo a preliminary diagnosis and consult a doctor or have a referral for this study.
Decoding the results
Interpretation of the results is carried out by the doctor performing the study and the attending physician who referred the patient for the procedure.
Normally, the electrogram obtained during EPI reveals sinus tachycardia with a heart rate of 100 to 120 per minute or more. Such tachycardia is transient and is not dangerous for the patient.
example of EFI results
If the study protocol contains the phrase that no rhythm disturbances were achieved using all types of stimulation, it means that the patient does not have a suspected type of arrhythmia, and the EPS results are regarded as normal. Also, normally there should be no depression or elevation of the ST segment and negative T waves, indicating myocardial ischemia.
If such changes are detected, their location is indicated, as well as the type of electrical stimulation in which they occurred.
When an arrhythmia is detected, its type is indicated (atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, frequent ventricular extrasystole, etc.), and the stimulation parameters that caused the rhythm disturbance.
Any of the disorders recorded on the electrogram requires careful medical supervision due to the need to prescribe certain antiarrhythmic drugs or perform RFA.
Carrying out, based on the results of EFI, RFA – “cauterization” of the area of pathological electrical activity of the heart