A choroid plexus cyst in a newborn is by far the most dangerous pathology in children in the first year of life. As a rule, it is detected during intrauterine development of the fetus at a period of 24-30 weeks. During the development of the fetus, education does not pose a threat to its health and life. In addition, in most cases, the cyst can resolve on its own after childbirth. However, it is necessary to conduct a comparative analysis to exclude the formation of a cyst of vascular origin, which forms against the background of pathological processes in the body.
What is education?
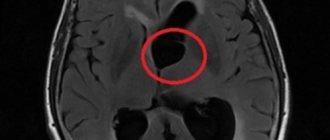
A choroid plexus cyst is a benign formation with clear contours, filled with fluid. It occurs among normal pregnancies with a frequency of approximately 3%.
Cystic formations of the choroid plexus tend to self-resolve, suggesting that they are pseudocysts. Bilateral choroid plexus cysts of the brain are very often observed, but by the 28th week of pregnancy they resolve, which is associated with the active development of the fetal nervous system. In cases where the cyst continues to be detected during an ultrasound scan until childbirth, then its significance does not particularly increase.
MRI images show cysts in both hemispheres
One of the early signs of the formation of the central nervous system in the embryo is the choroid plexus. They act as structural units in the formation of the right and left hemispheres of the brain. The choroid plexuses do not have nerve endings, but they ensure timely maturation and sufficient blood supply to the brain in the fetus.
A choroid plexus cyst of the brain has the following characteristics:
- minimal harm to health;
- lack of significance for concomitant pathologies;
- not affecting any of the vital systems and functions of the body;
- lack of growth and deformation.
Education does not cause significant harm or danger to either the fetus or the infant; it does not affect the functioning of the brain. However, they can increase the risk of developing other pathologies or cause functional impairment of all body systems.
Origin
The choroid plexuses are derivatives of the pia mater, which are localized in the ventricles of the brain. During embryogenesis at week 4, 3 brain vesicles are formed from the neural tube:
- front;
- average;
- diamond-shaped with internal cavities.
The walls of their cavities are lined with a layer of ependymal cells, and the blisters themselves are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (the contents of the future cyst). Blood vessels grow through the cells of the ependyma (the future pia mater) and ensure its protrusion into the cavity of the brain vesicles, where folds of cells form. The choroid plexuses are formed in the following order:
- 4-5 weeks – network in the fourth ventricle;
- 6-7 weeks – network in the third ventricle;
- Weeks 7-9 – lateral ventricles.
Thus, based on the characteristics of the formation of choroid plexus cysts, we can conclude that they do not belong to typical cystic formations (they are regarded as a congenital malformation).
Reasons for education
One of the hypotheses for the formation of cysts is the theory of congenital pathologies provoked by genetic mutations of cells. In this case, the localization of the formation cavity on the left, right or simultaneously on both sides does not matter. It is important to note that the cyst does not provoke the development of anomalies, but, on the contrary, pathologies of intrauterine formation contribute to their formation.
The main reason for the development of vascular pathology in the fetus is the presence of the herpes virus in the pregnant woman
Choroid plexus cysts in the fetus are detected at 14-22 weeks of intrauterine development. This type of education is safe for the child, as it does not cause neurological symptoms. In the future, the mental abilities of such children do not differ from the abilities of their peers.
In rare cases, this type of formation occurs in newborns, so its detailed diagnosis and constant monitoring of size are required. The causes of late lumps in infants are infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy. Quite common causes of formations can be herpes and toxoplasmosis. Also, the trigger mechanism in the formation of late seals is severe pregnancy and childbirth, as well as late toxicosis.
Pathologies visible on fetal ultrasound by trimester
In the first trimester, pathologies that arise due to chromosomal abnormalities are detected - frozen pregnancy and lack of embryo growth. In addition to them, signs of Down, Patau, Edwards, Cornelia de Lange, Smith-Opitz syndromes, as well as triploidy and omphalocele are clearly visible.
In the second trimester, in addition to the syndromes of the first trimester, Shershevsky-Turner, Klinefelter, hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndromes, as well as types of polysomy, polyploidy, deformations or absence of internal organs, heart defects, facial bone defects, hypertensive-hydrocephalic, multiple births, poly- or oligohydramnios, umbilical cord pathologies, fetal presentation, intrauterine growth retardation.
In the third trimester, infections of the fetus, defects of the brain, heart muscle, internal organs, intrauterine growth retardation, cleft lip, cleft palate, and fetal presentation may be detected.
The earlier fetal pathologies are detected, the better. If chromosomal abnormalities are diagnosed, the pregnant woman will likely be offered termination of pregnancy in the first and second trimester. Acquired pathologies are most often treated with medication during pregnancy and, if necessary, after the birth of the child.
Experts offer solutions to the problem, and future parents choose them, taking into account all the risks. Each situation is individual and there are no uniform schemes of action. But even if it happened that the pregnancy turned out to be problematic, you need to understand that the level of development of medicine and plastic surgery makes it possible to correct most abnormalities.
By what signs can you identify a cyst in a child?
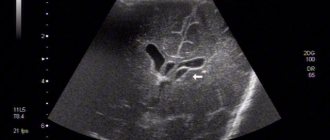
Vascular compactions are diagnosed during special diagnostic methods, so ultrasound and neurosonography can provide a complete description of the cyst. According to accepted WHO recommendations, these studies must be carried out on all children under one year of age to exclude possible neurological disorders.
In infants, cystic formation is practically asymptomatic
Mandatory indications for neurosonography are:
- trauma during childbirth;
- high risk of intrauterine infection;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- severe pregnancy;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the mother;
- intense physical activity during pregnancy;
- deviations in the physical development of the newborn (underweight, insufficient growth);
- severe deformation of the anatomical parts of the skull.
According to statistical data, cystic formations are recorded both in children without deviations in physiological development and in those with developmental delays.
Prevention
The most effective method of preventing the formation of brain cysts in newborns is pregnancy planning. A woman who undergoes a full examination before conception gets rid of hidden sources of infection, strengthens the immune system, and risks the health of her unborn baby much less. It is also important to follow all the rules for managing pregnancy, not to take medications unnecessarily, and to visit a gynecologist in a timely manner. In the event of a complicated pregnancy or traumatic birth, it is recommended to inform the pediatrician about this and undergo a series of preventive examinations with the baby.
Finding a cyst in a newborn’s head is not a cause for alarm, but the condition should not be ignored. It is strictly forbidden to try to cure a child on your own using traditional medicine, dietary supplements, or other dubious approaches. Such experiments can provoke cavity growth, creating additional problems. It is better to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and carefully monitor growth, development and well-being.
Types of cystic formations
The plexus of cerebral vessels takes an active part in the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which subsequently provides nutrition to the brain and is responsible for its functional development. Cystic formations are a consequence of intensive growth of the brain, when a free cavity appears between the plexuses of blood vessels, which is filled with fluid inside. Choroid plexus cysts in the fetus are a fairly common diagnosis, especially during fetal development and in children under one year of age.
Left choroid plexus cyst
Formations occur against the background of viral and infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother, as well as during severe pregnancy. The cyst is localized in the intracranial space close to the choroid plexuses. This type of formation does not require any therapeutic measures, since they do not pose a threat to the health and life of the child. In most cases, they resolve as the child grows.
Cyst of the right vascular formation
This type of formation is diagnosed in both newborns and infants. In some cases, it can be detected in adulthood, but since cysts do not have pronounced symptoms, a person may not be aware of the presence of pathology. Right-sided cystic formations do not harm the body and do not affect the psychomotor development of the child.
Bilateral pseudocysts
There are no visible changes or disturbances in the structure of the brain. The choroid plexuses of the lateral ventricle are involved in the process. As a rule, as the body grows, the neoplasm goes away without outside help. Bilateral cysts are numerous, they are recorded in adults and children. In some cases, the formation of a bilateral cyst may indicate a disruption in the course of pregnancy, but this does not mean that the baby will be born with a pathology.
Such cysts are called neoplasms of the choroid plexus; they are visualized in the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle as formations with clear, even edges. Neoplasms do not cause disturbances in the dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid and an increase in extracellular space.
Characteristics
The formation is an isolated cavity filled with clear liquid.
Structure Features:
- They are small in size and tend to dissolve on their own.
- More often they are localized closer to the caudal part of the choroidal glomus.
- It has clear, even contours.
- Does not show any upward trend.
- The presence of signs of malignancy is not typical. Due to the location, it should be differentiated from choroid carcinoma and choroid papilloma.
- There are no clinically significant symptoms. The exception is the development of occlusive hydrocephalus (disruption of the normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and its accumulation in the head). It is extremely rare.
- It is regarded as a stigma of dysembryogenesis (developmental defect). These newborns are at high risk of having chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy 18 - Edwards syndrome).
- The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. Discovered as an incidental finding during screening.
- The pathology does not have serious consequences and does not affect the life and health of the child, therefore it does not require treatment.
- The prognosis is favorable.
Possible complications
Echo signs of a vascular neoplasm should make a specialist wary. Cysts themselves are not dangerous, but their presence may increase the risk of developing chromosomal pathologies in the future.
Increases in the frequency of cysts are largely influenced by Edwards syndrome
With normal laboratory test results, a vascular cyst does not indicate a pathological process in the body. To exclude genetic abnormalities, the doctor prescribes amniocentesis (sampling of a small amount of amniotic fluid).
In cases where genetic abnormalities are detected in the fetus, their consequences are the following developmental anomalies:
- Down syndrome.
- Edwards syndrome.
Pseudocysts have no absolute influence on the development of genetic defects, since they also occur in healthy children.
Why are ovarian cysts dangerous?
There are cases when a follicular cyst or corpus luteum cyst bursts and its contents spill into the abdominal cavity. In this case, bleeding may begin, and, as a result, the need for hospitalization in a hospital. In addition, torsion of an ovarian cyst is possible, which is accompanied by severe abdominal pain and also requires treatment in a hospital.
During pregnancy, large ovarian cysts pose a potential danger, since cyst rupture or torsion may occur, in which case surgical intervention is not necessary.
In rare cases, the formation of multiple ovarian cysts causes infertility.
Diagnostic measures
Today, a vascular cyst is not a sign of the disease, but it can increase the risk of developing other pathologies.
For early detection of abnormalities in fetal development, all pregnant women must undergo ultrasound diagnostics
Diagnosis of cystic formation using special research methods:
- Ultrasound diagnostics. It is carried out during the intrauterine life of the fetus, which makes it possible to identify the formation at an early stage of its development.
- Biopsy of the placenta. At high risk of developing trisomy 18.
- Amniocentesis. It is highly accurate and is performed up to 22 weeks of pregnancy. The technique consists of studying the skin cells of the embryo.
- Neurosonography. It is carried out in children under one year of age. The procedure allows you to identify a tumor on both sides, but before the anterior fontanelle closes.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is used in adults to determine possible neurological disorders, during which cysts can be detected.
Symptoms of cystosis
Features of the clinical picture depend on the location of the cysts, their number, size, and type.
Sometimes the manifestations are very specific, which, combined with the medical history, allows one to immediately suspect the cause of the problems. Even if at least one of the symptoms below is mild, you should consult a pediatrician for advice.
The presence of a cyst in a child’s head is characterized by the following manifestations:
- headache – in young children it manifests itself in the form of moodiness, constant crying, and a negative reaction to external stimuli;
- change in general condition - drowsiness or problems falling asleep, slow reaction, loss of appetite, refusal of the breast or pacifier;
- swelling of the fontanelle or its pulsation is a clear sign of a cavity formation in the skull;
- problems with coordination, decreased motor activity;
- epileptic seizures, tremors of limbs;
- lack of sensitivity to pain;
- frequent or excessive regurgitation;
- muscle hypotonicity or hypertonicity;
- developmental delay.
The effect of a cyst in the head of a newborn on his condition may be insignificant, but not only this is taken into account when choosing a method to combat the problem. Often, even small formations must be removed due to the specifics of their location.
Features of treatment
As a rule, treatment for a vascular cyst is not carried out, since the body can cope with it on its own. However, there are cases when specialists are forced to prescribe medications to resolve the cyst.
Before using medications, you must consult your doctor.
Most often, neurologists prescribe the following medications:
- Cavinton. Used to eliminate cerebral circulation disorders.
- Cinnarizine. The product has a beneficial effect on the vascular system, which helps the body destroy pathological formations and stabilize.
In other cases, therapeutic measures are not carried out. For continuous monitoring of cysts, experts recommend undergoing ultrasound diagnostics of the brain once every 3 months until they are completely resolved.
Thus, the presence of a cystic neoplasm does not harm the baby’s health and does not affect his mental abilities in the future. It does not require the use of special treatment methods; it is only necessary to control the dynamics of education in a timely manner. The cyst is of great importance in assessing the risk of the formation of genetic mutations in the fetus, in cases where other pathological symptoms are also detected.
Preparation for fetal ultrasound, procedure progress
No special actions are required from the woman to prepare for the ultrasound examination, since all internal organs are displaced by the uterus and do not interfere with the view. But you will have to adhere to several recommendations to make the pregnant woman feel as comfortable as possible.
The doctor will recommend:
- Avoid foods rich in allergens one week before the procedure. Allergies are dangerous not only for the woman - her poor health will certainly affect the behavior of the fetus.
- In a couple of days you need to give up fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods. These products stimulate the secretion of bile and affect the liver - it increases in size.
- For 24 hours, do not consume carbonated water and foods that cause gas formation in the intestines. Air bubbles obstruct vision, distorting echogenicity characteristics.
- Immediately before the ultrasound, control the amount of food and liquid consumed so that the natural urge to empty the intestines and bladder does not constrain the pregnant woman
Failure to follow these recommendations certainly affects the results obtained during the ultrasound, but not so significantly as to refuse diagnosis if you ate a piece of meat or drank a glass of soda the day before.
The procedure is painless. As usual, the woman lies on her back on the couch, and the specialist rubs her stomach, which was lubricated a minute earlier with the gels necessary as conductors. The procedure lasts on average from 10 minutes to half an hour.
Often in the first trimester, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed - a sensor with a condom on it is inserted into the pregnant woman’s vagina. This does not cause pain, the procedure lasts no more than a few minutes. Transvaginal ultrasound may be repeated in the second trimester if a detailed examination of the cervix is necessary.
Reviews
Tatyana, 32 years old At 22 weeks of pregnancy, she underwent an ultrasound, where a unilateral cyst was discovered. The ultrasound specialist assured that this would not cause any harm to the child’s development, and with the further growth of the child, it could resolve on its own. The consultation prescribed screening. The results are good. They were sent to a geneticist. He recommended waiting for the third ultrasound, on the basis of which it would be possible to consider the dynamics of the tumor. And indeed, the baby grew in size and the cyst resolved.
Ekaterina, 36 years old Both children, 5 years apart, were diagnosed with a cyst; in the first child it resolved without a trace, although I was very worried. The second one was also diagnosed early in pregnancy; perhaps this is a hereditary trait. In the first and second cases, I always waited for the planned ultrasound, since there was no point in undergoing the study earlier. After identifying cysts, I underwent repeated diagnostics no earlier than a month after their discovery.
Elena, 26 years old At 20 weeks, she had an ultrasound, where she was diagnosed with a choroid plexus cyst. The specialist did not explain anything and referred me for a consultation with a geneticist, since the tumors were quite large - 8 mm. I took tests, 3 days later I found out the results, they turned out to be good, and the size of the formation was significantly less than 3 mm. The consultation prescribed an ultrasound scan at 32 weeks. During the waiting period, I was very worried, I studied a lot of specialized literature, all sources spoke of a benign outcome. Finally, the time came to undergo an ultrasound. It did not reveal any formations in the brain; they all resolved.
Detailed explanation of fetal ultrasound results, norms and pathologies
Since the goals and subjects of medical interest in ultrasound examinations of different trimesters differ, the abbreviations and abbreviations in the reports are different.
First trimester
Estimated date of birth (EDD) - in fact, this is the same as the exact date of pregnancy, only from a different angle. Determined by data on the menstrual cycle and the size of the fetus
- The cervical-neck space (CN) is the main criterion for ultrasound examination in the first trimester. The norm is from 1.5 mm at the 10th week to 2.7 mm at the 13th. If the indicator is increased, the pregnant woman needs to undergo further examination.
- The coccygeal-parietal size (CPR) is one of the main parameters for assessing the size of the fetus. Normally, it should range from 41 mm at week 10 to 73 mm at week 12
- Heart rate - (h/s, heart rate) normally for the first trimester should be 146-179 beats per minute, and this figure is lower the longer the pregnancy period
- Nasal bone – starting from the 12th week should be at least 3 mm, otherwise Down syndrome is suspected
- Biparietal size (BSD) should be from 14 mm at 10 weeks to 26 and higher at 13.
- The yolk sac is studied as an indicator of gestation-appropriate development. It grows in the first weeks and then decreases. Should be round in shape and 4-6 mm in diameter. If the shape is different, and the internal length of the incision is less than 2 mm at 8-12 and more than 6 mm after 10 weeks, a frozen pregnancy is stated.
Diagnosis of cysts
The first stage of diagnosing cysts is an examination by a gynecologist in a chair; the doctor may detect unilateral (less often bilateral) enlargement of the ovary; with large cysts, pain is sometimes noted during the examination.
To diagnose ovarian cysts, ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is widely used, which makes it possible to determine the type of cyst, since all the formations described above have their own distinctive features.
In some cases, to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct repeated ultrasound examinations during one or more menstrual cycles. In case of controversial issues, the doctor may additionally recommend an MRI of the pelvic organs.