Diagnosis of diseases affecting the brain and the vessels that supply it is difficult due to the inaccessibility of the study area. Various pathologies may have similar symptoms or occur latently, without characteristic manifestations. An informative diagnostic method is magnetic resonance imaging, which reveals changes in gray, white matter, vascular wall and allows you to differentiate diseases in the early stages.
MRI procedure of the brain and blood vessels
What are the main advantages of magnetic resonance imaging?
MRI examination of the brain should not be neglected if the doctor prescribes a referral for such diagnostics. This procedure is very important for identifying serious deviations in its functioning in the early stages.
This is a non-invasive examination technique. During such diagnostics, the patient does not feel any discomfort, except for the fact that he has to be inside the tomograph. In this case, the devices are closed and semi-closed. The second type is used to examine people who are afraid of closed spaces.
The positive properties of this procedure include its painlessness. It does not require surgical intervention. It allows you to examine all parts of the human head.
MRI can be performed on patients of all ages. Diagnostics makes it possible to detect pathologies when they are just beginning. Timely diagnosis is very important when it comes to health.
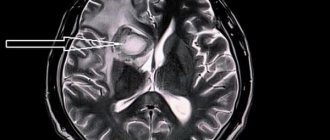
MRI images of the brain clearly show whether there are pathological changes in its parts or not. When they are identified, the doctor prescribes effective treatment. The earlier therapy begins, the greater the chance that it will be successful.
Other benefits of MRI of the brain include:
- Possibility of examining all parts of the head, regardless of the presence of bone structures.
- No toxic effects.
- Obtaining a clear “picture” of vessels and soft tissues located at different levels, even if a contrast agent is not used during the procedure.
The decision on how to perform an MRI of the brain with or without contrast is made by the attending physician, based on the available indications.
Why is the procedure performed?
The list of indications for which a brain examination needs to be performed includes:
- headache;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- memory problems;
- ischemic heart attacks;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
MRI makes it possible to assess the degree of activity of the cerebral cortex. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to assess how much damage this organ has suffered as a result of injury. With its help, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases, benign and malignant neoplasms are detected.
Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed for schizophrenia and other mental disorders to assess the impact they have on the structure of the brain.
If there are violations in the integrity of the myelin sheath of the cortex, MRI will reveal them. The procedure helps diagnose cysts, carcinomas, brain hemorrhages, and detect inflammatory and infectious processes. It is often prescribed for autism and multiple sclerosis. Cerebral perfusion makes it possible to assess blood flow in various areas. Before such a thorough diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo tests. Their results will indicate the area of the head that is subject to more detailed examination. For example, if a patient has elevated prolactin levels, this may indicate problems in the cerebellum.
An MRI image of the brain allows us to assess the condition of not only the cerebellum, but also other parts that are responsible for memory and the thought process. Carefully examine the occipital lobes, which are responsible for the visual perception of objects, and evaluate the density of gray and white matter.
X-ray radiation is not used during MRI and this is a big plus. You don’t have to wait long for the results of the procedure; deciphering them takes a minimum amount of time. This procedure is highly diagnostic. In recent years, it has become indispensable in identifying brain pathologies.
How often can I have a head MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging is safe for the health of patients; the number of procedures is determined by the doctor. The frequency of head MRI depends on the clinical picture and the disease being diagnosed:
- hydrocephalus requires scanning every 5 years, if necessary, dynamic monitoring is carried out, the frequency of which is determined by the attending physician;
- neoplasms are scanned up to 4 times during the first year, then 1-2 times a year if there is no tumor growth;
- for multiple sclerosis, examinations are prescribed 1-2 times a year;
- stroke - an MRI is performed to establish a diagnosis, then sent for preventive examinations every 4 years;
- Alzheimer's disease - a one-time scan is recommended to confirm the nature of the pathology;
- To monitor recovery processes after surgery, 3-4 procedures are carried out during the first year; in the future, the frequency of MRI depends on the clinical picture.
Alzheimer's disease on MRI
Scanning the brain with a magnet does not carry radiation exposure and does not have a negative effect on organs and tissues. The noise and the need to lie still during the entire examination create some inconvenience, but in general the method is painless and comfortable for the patient.
Features of the MRI procedure, principle of operation
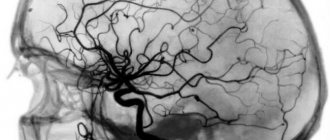
The tissues being examined are exposed to electromagnetic waves within a magnetic field that contain varying numbers of hydrogen atoms. They generate a certain amount of energy, which is recorded and processed by a special device. We are talking about a tomograph. This processing makes it possible to obtain images of various parts of the brain. The development of pathological phenomena is characterized by structural transformations in the tissues of the organ. As a result, the content of hydrogen atoms in the affected area changes. This leads to changes in the signals received during the examination.
MRI of the head visualizes various parts of the brain and gives their characteristics. The main goal of such diagnostics is to detect affected areas in the brain, determine their shape, size, nature and exact location.
When carrying out such a diagnosis, it is impossible to miss a tumor; it determines the tissue of origin of the tumor, distinguishes atrophic areas from post-traumatic ones. Allows you to determine the nature of strokes, identify infectious lesions, brain swelling, displacement of its structures, and assess the condition of the ventricles.
MRI of a healthy brain does not reveal any abnormalities. If there is a suspicion of a tumor in the head, this procedure must be carried out. It reveals not only primary tumors, but also metastases and pituitary lesions.
Even with a minor head injury, an MRI is recommended. The procedure allows us to exclude brain abscess and meningoencephalitis. It is carried out in the presence of symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Doctors prescribe magnetic resonance imaging for frequently recurring headaches and motor dysfunction. This examination is indicated for people who faint for no reason. Those who have behavioral and cognitive dysfunctions.
MRI is indispensable both in the neurological field and in endocrinology, psychiatry, and other areas of medicine.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography scans are often done after surgery to evaluate the results of surgery. The technique is indispensable in dynamic observation. With its help, they examine not only the brain, but also other organs - the pancreas, gall bladder.
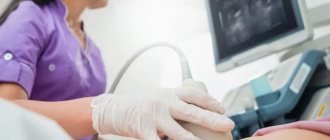
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck Synonyms for the name of the technique:
- duplex scanning
- triplex scanning
- ultrasound examination with color mapping of blood flow
- Doppler ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck includes 2 separate techniques:
- First of all, the patency of the vessels of the neck (brachiocephalic arteries, main arteries of the head in the neck) is assessed, since pathological changes that can lead to a stroke are most often detected in them.
- If indicated, the doctor may additionally prescribe a study of the cerebral vessels (intracranial arteries) - transcranial duplex (triplex) scanning. In 10-20% of people, especially the elderly, the study cannot be performed due to poor permeability of the skull bones for ultrasound, therefore, this study is performed first, and then payment is made.
Indications
- Prevention of stroke in people with risk factors (smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, arterial hypertension, age over 40 years)
- Suspected stroke: weakness and numbness in an arm or leg
- "facial distortion"
- speech disorder
- Lost vision in one eye
- dizziness or unsteadiness when walking
What is being studied?
- In the neck are the carotid, vertebral and subclavian arteries.
- In the head - middle, anterior and posterior cerebral arteries, basilar artery, vertebral arteries (intracranial segment).
What is visible?
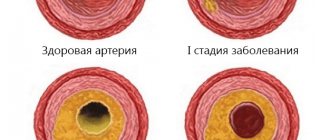
- Thickening of the vascular wall
- Atherosclerotic plaques
- Blood clots
- Dissection (separation) of the wall
- Tortuosity
- Aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations
Accurate assessment of the degree of carotid artery stenosis to determine indications for surgery. There are several ways to measure the degree of stenosis. Only one of them is the reference for determining indications for surgery. In our laboratory, the assessment of the degree of stenosis is performed in accordance with domestic and international recommendations. If there are indications for surgery, a consultation with a vascular surgeon is provided on the same day.
Preparation No special training is required.
Cost Duplex (triplex) scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries (main arteries of the head) - 3,000 rubles. Transcranial duplex (triplex) scanning - RUB 3,000.
Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging
There are few contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging, but they do exist. These include:
- The presence of an implant in the body (including a pacemaker).
- Excessive mobility of the patient, for example, if he is intoxicated. During an MRI, the subject must lie still.
- Foreign objects in the body (during the examination they may move and damage blood vessels).
Relative contraindications include illness, children under 7 years of age, metal prosthetic joints outside the range of electromagnetic waves, blood diseases (in this case contrast cannot be used), severe claustrophobia (the patient’s condition may sharply worsen in a closed space).
MRI of the brain: preparation for the study
The essence of MRI is the use of a magnetic field that affects water dipoles in the body's cells. The intensity of the response directly depends on the moisture saturation of the tissues. The examination takes about 30 minutes; when using a contrast agent, the duration of the procedure increases to 45 minutes.
The patient lies down on a mobile table, his head is fixed with restraints. The magnetic field generator and sensors that read information are located in the wide part of the tomograph, which has the shape of a pipe. The table with the patient moves to the annular section of the device, where the brain is scanned in sagittal, frontal and axial projections.
To improve the quality of the examination, a gadolinium-based contrast solution is used. The drug is administered intravenously, it has no toxic effect and is eliminated from the body within 1-2 days. The contrast illuminates the vascular system of the brain and visualizes the slightest changes in the area of soft tissue, veins and arteries.
During the procedure, the tomograph creates a lot of noise, so the patient is recommended to use special headphones provided by the clinic. Communication with medical personnel is maintained using an intercom. During magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor and technicians are located in an adjacent room, separated by a partition. The data obtained as a result of the study is received on a computer monitor in the form of layer-by-layer images.
Layered MRI photographs of the brain printed on film, axial projection
A tomogram visualizes the condition of internal organs and helps diagnose the following diseases:
- neoplasms in the head area;
- vascular development abnormalities;
- pituitary diseases;
- consequences of head injuries;
- pathologies associated with impaired blood supply to the brain;
- inflammatory changes in cerebral structures and membranes, cranial nerves;
- congenital pathologies.
MRI of the brain does not require complex preparation. The patient should consult a doctor and exclude the presence of factors that are absolute contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging. These include:
- the presence in the body of the subject of metal products used for medical purposes (pins, dental crowns, implants, dentures, knitting needles, etc.);
- the presence of implanted electromagnetic devices (pacemaker, insulin pump, etc.);
- the presence on the patient’s skin of tattoos made with paints with a high metal content.
If contrast is used, the patient must warn the doctor about the tendency to allergic reactions, the presence of renal and liver failure, diseases of the cardiovascular system and other previously diagnosed pathologies. Any medications taken immediately prior to the MRI should be reported. Patients suffering from claustrophobia should also warn their doctor. A specialist will help you avoid panic attacks during the procedure.
Women are not recommended to undergo an MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the insufficiently studied effect of a magnet on the embryo during the formation of vital organs. Nursing mothers should express milk for the next 2 feedings, which will avoid getting gadolinium salts during contrast MRI into the baby's food.
The subject prepares for the scan in advance: removes uncomfortable clothes, jewelry, accessories, and piercings. The patient then takes a horizontal position on the table and follows the doctor’s recommendations during the procedure.
MRI of the brain in a child, images in a sagittal projection
How to prepare for the examination?
There is no need to prepare long or thoroughly for an MRI of the brain. A couple of hours before the diagnosis, it is advisable to refrain from eating. You should not use decorative cosmetics before the procedure. You must leave your phone, bank cards and watches outside the room where the diagnostics are carried out.
The doctor will definitely tell the patient about the progress of the examination. If he suffers from a fear of closed spaces, he will prescribe sedatives.
If necessary, a procedure with contrast will be performed to obtain a more accurate picture. After administration of the contrast agent, headache and nausea may occur. Before using contrast, a sensitivity test must be performed.
How is the procedure done?
Before being diagnosed by an MRI machine, the patient is asked to sign a consent form. After this, he is asked to put on a robe (you can also be examined in your own clothes, the main thing is that there are no metal elements on them) and lie with your back on a special platform. The subject's head is fixed to ensure its immobility.
The platform, with the patient lying on it, slides into the “pipe” of the tomograph. The equipment makes noise during operation, so it is recommended to use earplugs.
The MRI room is equipped with a two-way voice communication system. The doctor monitors the progress of the procedure from the next room.
The examination takes approximately half an hour. When using contrast, about 50 minutes. The contrast is administered simultaneously or with a dispenser.
results
The interpretation of the results of magnetic resonance imaging is carried out by a radiologist with the appropriate qualifications. He analyzes the results obtained and draws a conclusion based on this. The patient receives the scan results on a DVD, after which he hands them over to the doctor.
In our medical center, MRI of the brain and abdominal organs is performed using modern equipment.
We use the best tomographs that guarantee high accuracy of examination results. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
What should you not do before an MRI of the brain?
On the eve of the study, it is prohibited to drink alcohol; this measure is especially relevant when preparing for contrast MRI of the brain and blood vessels. Ethyl alcohol affects the tone of the walls of veins and arteries, which distorts the picture and complicates the diagnosis of pathological processes.
48 hours before the test, you should not take energy drinks, you should reduce the amount of coffee and other tonic drinks. It is not recommended to overeat on the eve of an MRI, change your usual diet, or eat new foods that can cause an allergic reaction.
Self-administration of medications is prohibited without prior approval from the attending physician. Patients are advised to maintain a sleep schedule 2-3 days before the examination and avoid overwork and stress.