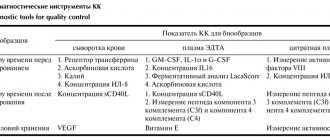
The table shows possible deviations (the norm is presented below)
| Index | Characteristic | Diagnosed pathology |
| Heart sizes | Increased | Cardiomegaly, chamber hypertrophy, cardiosclerosis, myocarditis |
| Myocardial characteristics | Thickened | |
| Compacted, heterogeneous | ||
| Istonchen | Organ failure, dilated cardiomyopathy | |
| Volume of ventricles and atria | Increased | |
| Reduced | Restrictive cardiomyopathy | |
| Valve condition | Thickened | Endocarditis |
| They don't close | Failure | |
| Do not open | Stenosis | |
| Pulmonary artery | Enlarged, expanded | Aneurysm |
| Dense | Atherosclerosis | |
| Emission volume | Reduced | Developmental defects, organ failure, cardiomyopathy |
| Residual volume | Increased | |
| Pericardial cavity | Thickened | Pericarditis |
| Liquid is visualized | ||
| Movement of blood between cavities and vessels | Regurgitation (backflow of blood during contraction) | Defects (congenital, acquired) – valve insufficiency |
| Shunt (shunt) between the aorta and pulmonary arteries | Congenital malformation | |
| Reset (shunt) at the level of the oval window | Open window | |
| Interventricular shunting | Defect (congenital, acquired) - ventricular septal defect | |
| Additional education | Nodes, thickenings, additional shadows | Neoplasms, blood clots, accessory chord, ventricular aneurysm |
The study does not allow assessing the nature of the rhythm and electrical activity (an ECG is required), the condition of the coronary arteries (coronary angiography is performed), and the blood supply to the myocardium.
Depending on the equipment and assessment methods, the following types of echocardiography are distinguished:
- Standard . Transthoracic option: the sensor is placed on the chest. The study can be one-dimensional, two-dimensional or three-dimensional.
- Doppler . Aimed at assessing the characteristics of blood flow in the cavities of the heart and large vessels.
- Stressful . Ultrasound examination during stress tests.
- Transesophageal . Examination of the heart through the wall of the esophagus.
The gold standard for examination is two-dimensional Doppler-enhanced echocardiography.
What does the specialist see?
During an echocardiogram, the doctor can evaluate the functioning of the heart using several criteria. Each of them has certain norms, and a deviation in one direction or another indicates the presence of various pathologies.
Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the following indicators:
- main characteristics of the heart chambers;
- characteristics of the ventricles and atria;
- functioning of valves and their condition;
- condition of the walls of blood vessels;
- direction and intensity of blood flow;
- characteristics of the heart muscles during the period of relaxation and contraction;
- is there exudate in the pericardial sac?
To make a diagnosis, doctors use certain standards of echocardiography, but sometimes minor deviations in one direction or another are allowed. It depends on the age, weight of the patient and other individual characteristics.
Important! The interpretation of the results obtained should be carried out exclusively by a cardiologist. Once you have the conclusion in your hands, you should not try to establish a diagnosis yourself.
Norms of indicators in newborns
Echocardiography is often performed among newborns. This method allows you to identify deviations in the functioning of the organ and its defects. Interpretation of echocardiography in children is a complex process, which is dealt with by a sinologist.
Normal ultrasound examination parameters in babies after birth are determined using a special table.
In this case, the end-diastolic size of the left ventricle in boys should be in the range from 17 to 22 mm, and in girls – from 16 to 21 mm. An indicator such as the end-systolic volume of the left ventricle in children of both sexes ranges from 11 to 15 mm. The diameter of the right ventricle in boys should not exceed the boundaries of 6 to 14 mm, in girls - from 5 to 13 mm. The size of the left atrium in boys should be from 12 to 17 mm, in girls - from 11 to 16 mm.
Ultrasound of the heart in newborns helps identify various defects
An important indicator is the condition of the septum between the left and right ventricles. It should not be hypertrophied, otherwise it indicates the presence of a defect.
Another vital indicator is the cardiac ejection fraction. This concept refers to the volume of blood that the left ventricle pushes out. It should be between 65 and 75%. While the speed of blood movement through the pulmonary valve is 1.4–1.6 mm/s.
With age, these indicators change. After 14 years, the child’s standards correspond to adults.
Important! An ultrasound of the baby's heart is sometimes performed in utero. This diagnostic method allows you to identify various defects at an early stage of development and select the necessary treatment.
In what cases is additional examination necessary?
Sometimes the results obtained using ultrasound do not allow an accurate diagnosis. Additional examination is prescribed for patients with the following disorders:
- suspicion of pulmonary hypertension arises when signs such as slow opening of the aortic valve, its closure during the systole phase, pathologically increased ejection of the right cardiac ventricle, deviation from the norm in the thickness of the ventricular wall;
- An open type arterial defect may be indicated by an increase in the wall of the atrium and ventricles, and the movement of blood from the aorta to the pulmonary artery. If such signs are detected, the patient needs to undergo additional examination methods;
- a defect in the septum separating the ventricles is indicated by thickening of the walls of the organ, developmental delay in the patient, blood entering from the left ventricle into the right;
- violation of the integrity of the valves and their branches often indicates the development of endocarditis of infectious origin;
- with a decrease in the number of heart contractions, a decrease in the ejection fraction and an increase in the volume of the organ chambers, a suspicion of an inflammatory process of the myocardium arises;
- The occurrence of exudative pericarditis is indicated by an excessive amount of fluid in the heart sac.
Echocardiography is a method for detecting many heart diseases
Myocardial infarction is often indicated by slow contraction of areas of the myocardium. Thickening of the walls of the left ventricle and atrium, weak compression of the mitral valve leaflets indicates its prolapse.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the heart
In order for the interpretation of cardiac echocardiography to be carried out without errors and completely, the patient’s age, general state of health, and the presence of chronic diseases (pancreatitis, tonsillitis, asthma, vasculitis, etc.) are taken into account. It is impossible to determine the pathology on your own (without knowledge and experience). Only a doctor can correctly assess the answer. There is no place for experiments and guesswork. It is inappropriate to look for answers on the Internet on the websites of companies with a dubious reputation. Trust your health to professionals who provide guarantees and value each patient.
Study parameters
Thanks to ultrasonic waves, you can accurately determine:
- myocardial parameters (sizes of all its parts);
- tissue structure, wall density;
- rhythms, abbreviations, etc.
Imaging will help detect scarring, thrombosis, benign and malignant tumors. The test informs about the condition of the mitral valve, blood volumes and the level of vascular blockage.
By interpreting cardiac echocardiography, the presence/absence of the following diseases can be determined:
- ischemia, when there is a persistent disturbance of blood supply against the background of vascular blockages;
- necrosis, during which tissue death occurs (infarction);
- blood pressure above or below normal (hypo-, hypertension);
- defect, that is, a structural defect of an acquired/congenital type;
- decompensation, when a whole syndrome of failures is noticeable;
- valvular dysfunction;
- rhythmic disruptions;
- rheumatism, when inflammation is observed;
- pericarditis, in which there is inflammation of the membrane;
- stenosis, which indicates a narrowing of the aortic lumen;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Competent image decoding is the basis for success. After all, it is thanks to him that one can establish the fact whether there is a disease or not.
Among the research parameters, several main areas are distinguished. When interpreting cardiac ultrasound in children and persons over 13 years of age, the diameter of the left ventricle and left ventricle, the thickness of the posterior wall of the left ventricle, and more are determined. Each number has a meaning individually. Also, all indicators are taken into account together, because many of them are related to each other and often form a single clinical picture.
How it happens
A painless examination is carried out in a hospital setting or at home, if the situation requires it. The manipulation takes from 20 to 45 minutes. This is a safe way to assess the functioning of the heart muscle and blood vessels, which has no contraindications and is not harmful to health. Step by step it usually looks like this:
- The visitor bares his torso, undresses to the waist and takes a horizontal position, lying on his back with his head towards the diagnostician.
- A special gel is applied to the chest area to help conduct ultrasound waves better.
- A special sensor is used, thanks to which the diagnostician carries out an inspection. The detector is moved slowly across the area being examined to ensure that nothing is missed. The attentiveness of the diagnostician will help with echocardiography decoding.
- The specialist can correct the patient’s position and condition, for example, asking him to hold his breath, roll over, raise his arm, bend his knees, and more.
The response is assessed by a competent specialist, a doctor. It is important that all indicators are taken into account, as well as the individual parameters of the patient’s body. The time of the diagnostic procedure and the state of health, that is, the well-being of the person being diagnosed, are taken into account. Standards and actual figures are reviewed. A comparison is being made. Only after a thorough study can a diagnosis be made and a course of therapy formed. A person who has nothing to do with modern cardiology will not be able to understand the indicators, even if he uses a plate with standard figures for this. Only a properly qualified doctor should be involved in forming a conclusion!
Differences in men, women and children
Normally, data by age and gender is different. EchoCG interpretation helps to analyze the full cycle of myocardial activity (1 systole + 1 diastole). With a heartbeat of 70 beats in 60 seconds, 1 cycle is normally 0.85 seconds.
Adult women and men, as well as children, have different normal values. For example, the heart mass of a representative of the stronger sex aged 25-30 years is about 135 g. In a woman - up to 100 g. The EDV of the left ventricle in men normally reaches 193 ml, in women it does not exceed 136 ml.
The LV wall mass index is an indicator of the ratio of the weight of the organ to the surface area of the human body. The strong half of humanity is characterized by indicators from 71 to 95 g/m2, the fair sex is characterized by a range from 71 to 90 g/m2.
Basic concepts and norms of ultrasound for adults
The heart consists of several sections, each of which plays an important role. Malfunction of any of the chambers can provoke heart failure and other serious complications. The organ consists of the left and right atria, ventricles and valves.
The echocardiographic diagnostic method allows you to visualize the condition of this organ, see the functioning of the valves, the thickness of the myocardium, the speed and direction of blood flow, the presence of vasoconstriction and blood clots in them.
There are no clear boundaries in this area, since each organism is individual. But certain standards still exist. For an adult, the indicators should be as follows:
- in the systole and diastole phase, the wall thickness of the left ventricle is 10–16 and 8–11 mm;
- the wall of the right ventricle should not be dilated and extend beyond the boundaries of 3 to 5 mm;
- interventricular septum in diastole and systole – 6–11 and 10–15 mm;
- aortic circumference – from 18 to 35 mm;
- in women and men, the total myocardial mass should be between 90–140 g and 130–180 g;
- heart rate – 75–90;
- the ejection fraction should not be less than 50%.
In addition, such parameters are assessed in adult patients as the volume of fluid in the heart sac (35 sq. ml), the diameter of the aortic valve should not exceed one and a half centimeters, and the opening of the mitral valve (4 sq. cm).
Why is cardiac echocardiography needed?
There are a myriad of reasons why a doctor might recommend an echocardiogram. A harmless and inexpensive procedure is indispensable for:
- constant pain in the chest, rapid heartbeat, disturbing in a calm state, after minor physical exertion;
- hypertension (stable high blood pressure);
- swelling of the lower extremities, when kidney disease is not diagnosed;
- breathing difficulties that occur after physical activity;
- feeling of a foreign object in the chest.
The attending doctor can prescribe a procedure, and then conduct a full interpretation of the ultrasound of the heart, in case of constant dizziness, arrhythmia, atherosclerosis, pericarditis, heart muscle defects, coronary artery disease. Indications are often multiple pregnancy, hereditary predisposition, medical examination at the enterprise.
Ultrasound cardiography is performed for both adults and children. When a baby is suspected of having abnormalities in myocardial development, shortness of breath appears without symptoms of an acute respiratory infection, loss of consciousness is observed, it is imperative to check the functioning of the main organ. The pediatrician can refer for diagnostics when, during the use of a phonendoscope, extraneous sounds were noticed against the background of normal contractile activity.
The above-mentioned cardiac examination also plays an important role for a teenager. The test is aimed at assessing the normal development of the organ during puberty, because it is at this time that a sharp increase in body size is often observed.
Decoding EchoCG
After the examination, the doctor draws up a conclusion. First, a visual picture with the presumed diagnosis is described. The second part of the study protocol indicates the patient’s individual indicators and their compliance with standards.
Decoding the data obtained is not a final diagnosis, since the study can be done not by a cardiologist, but by an ultrasound diagnostic specialist.
It is the cardiologist, based on the collected medical history, examination results, interpretation of tests and data from all prescribed studies, who can draw accurate conclusions about your condition and prescribe the necessary treatment!
Deviations from the norm
There are a huge number of indicators indicating deviations from the norm. Eg:
- Stenosis is said to occur when the valve opening is reduced in diameter, making it difficult to pump blood.
- If the valve leaflets interfere with the reverse blood flow, perform their natural function inadequately, insufficiency is suspected.
- Pericarditis is detected when, with a normal fluid level of 20-30 ml, all 500 ml are traced.
The list of deviations from the norm and possible diagnoses associated with this can be endless. But you shouldn’t take deciphering an ultrasound of the heart so lightly. Here it is inappropriate to guess and assume without the help of a doctor. Mistakes lead to irreparable consequences. Therefore, experiments should be abandoned.