What the study shows
KTG allows you to monitor the condition of the fetal heart. It is important to understand that for a baby, “squeezing” through the birth canal during childbirth is not a pleasant journey, but a tedious job. During labor, the baby is exposed to certain dangers that can be recognized by observing its heart rate. A fetal heart rate that is too low may indicate, for example, hypoxia, and a rapid heart rate may be a signal of intrauterine infection.
Prevention of tachycardia in the fetus during pregnancy
Prevention of tachycardia in the fetus during pregnancy should be carried out at the stage of planning a child. The task of the expectant mother is to carefully monitor her health, give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse), treat existing diseases and prevent chronic damage to the body. The health of the unborn child depends entirely on the health of the mother. An important fact is an active lifestyle and a positive emotional state.
During pregnancy, you must regularly visit your doctor, undergo routine examinations and follow all medical instructions. The expectant mother must remember that her responsibility doubles, since now, in addition to her health and life, she is responsible for the life of the unborn child. The danger of pregnancy is that it is during this period that diseases can appear that the woman did not previously know existed. Such diseases include tachyarrhythmia and heart defects. That is why it is very important to prevent possible pathologies.
To prevent attacks of rapid heartbeat during pregnancy, a woman may be prescribed herbal-based sedatives that normalize the heart rate. A measured, calm lifestyle is of no small importance. It is contraindicated for an expectant mother to be nervous, worry and overexert herself. Instead, you need to walk in the fresh air more often, do special exercises and eat right.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in the prevention of this pathological condition. To prevent relapses of increased heart rate, a woman is recommended:
- Do not eat a lot of fatty and sweet foods. Poor nutrition leads to rapid weight gain, which negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- A pregnant woman's daily diet should include greens, vegetables, fruits and low-calorie dairy products.
- Coffee, alcoholic beverages and nicotine should be avoided during pregnancy. Since this negatively affects not only the mother’s body, but also the health of the unborn child.
- Do not forget about vitamin and mineral complexes, which are indispensable during pregnancy. You should take vitamins only with your doctor's permission. If there are no contraindications, the expectant mother is recommended to engage in light physical activity and go to the pool.
How long does a CTG take?
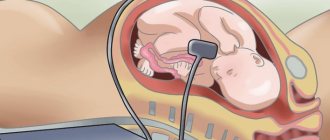
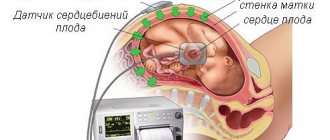
CTG is the most commonly used method for recording fetal heart rate. This is a non-invasive test and is not associated with pain or discomfort for the patient. The woman lies on her back, and doctors put two belts with electronic sensors on her stomach.
One of the sensors is an ultrasonic transducer that records the fetal heartbeat. The second sensor measures the strength and duration of uterine contractions. Both sensors are connected to a monitor on which these indicators are displayed in the current time and their dynamics are recorded. As a rule, CTG lasts half an hour; in some cases, the diagnostic procedure can be extended to an hour.
Causes of tachycardia
A person, even an unborn baby, may experience a rapid heartbeat for several reasons.
Very often, tachycardia is only one of the symptoms, sometimes the most pronounced, to determine serious health problems. Pathologies associated with the endocrine system, cardiovascular diseases and respiratory diseases can lead to the development of rapid heartbeat. Considering that it can be very difficult to diagnose an unborn child, recognizing tachycardia allows doctors to work in the right direction and identify pathology, if any. But it is worth remembering that not only diseases of the child’s internal organs, but also the use of medications by the mother can lead to the development of a rapid heartbeat. In addition, this is observed with severe blood loss and the presence of certain pathologies directly related to the baby’s condition. Tachycardia occurs with fetal anemia, intrauterine hypoxia, chromosomal abnormalities and infectious lesions.
To determine what exactly caused the development of heart rhythm problems, the doctor needs to carry out a series of procedures. Once the underlying disease is identified, proper treatment should be given if possible. With the right approach, the tachycardia should go away.
Decoding the results
The child's heart rate should be 120-160 beats per minute.
- If the fetal heart rate is below 110 bpm (bradycardia), doctors may suspect progressive fetal hypoxia.
- If the heart rate is more than 160 beats, the fetus has tachycardia (which can be caused by an intrauterine infection).
Such data allows specialists to quickly respond to alarm signals.
It is important to understand that an abnormal fetal CTG is not always an indicator of a problem! A result within the normal range is always a good sign, but if there are any warning signs, the specialist must take other factors into account. Sometimes increased or decreased indicators of fetal cardiac activity can even be caused by the mother’s uncomfortable position during the examination or her excessive anxiety.
Consequences, possible complications
With timely detection of pathology and correct treatment, in 90% of cases the problem can be solved. Despite this favorable prognosis, there is a certain risk of fetal death. The cause may be the drugs used.
- Cardiac tachycardia: what is it and how to treat it
The presence of tachycardia increases the risk of strokes and heart attacks. This pathology can cause heart failure, fainting, and hypertension.
Tachycardia can cause hypoxia, which is dangerous due to intrauterine growth retardation. With this disorder, pregnancy is often maintained, but childbirth can occur with complications requiring an emergency cesarean section.
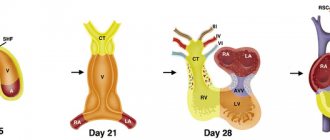
The process of formation and development of the heart in an embryo
The formation of the heart and its development is one of the most complex processes occurring in the fetus’s body and mother’s abdomen. 2 weeks after fertilization, the process of heart formation begins. After another 2 weeks, a hollow, curved tube had already formed. At the 5th week of pregnancy, the first contractions of the tube occur, the intensity of which increases.
At week 5, using ultrasound, you can already see the rudiments of the heart. At this time, the formation of the heart continues, transverse and internal septa appear, thanks to which the organ becomes two-chambered. Gradually, the formation of longitudinal partitions occurs.
By week 9, the baby’s heart becomes an “adult”, having two atria, two ventricles, valves separating them and vessels to ensure blood flow.
However, the heart of the embryo has its own characteristics related to the supply of oxygen from the mother: between the atria there is an oval window, which is connected to the ductus arteriosus. After birth, this window closes and the ductus arteriosus collapses.
The process of heart development ends only by the 22nd week of pregnancy, then only an increase in its muscle mass and growth of the entire blood supply system occurs.
The fetal heartbeat is monitored using ultrasound (US), cardiotocography (CTG), auscultation (listening with a special tube) and echocardiography (EchoCG).
Pregnancy management tactics
The more points you get based on the CHT results, the better. Depending on the indicators, the doctor chooses the method of pregnancy management:
| Points earned | Result | Doctor's actions |
| 9-12 | good | observation |
| 6-8 | the fetus lacks oxygen | repeat CTG in a week or earlier |
| 0-5 | severe hypoxia, the fetus lacks oxygen | for a long period - delivery, for an insufficient period - observation in a hospital; consultation with a gynecologist observing a pregnant woman |
Antenatal fetal death - symptoms and treatment
Antenatal fetal death is the intrauterine death of a fetus that occurs before the onset of labor, but after 21 weeks of pregnancy. Causes 39-42% of stillbirths. Such children have no heartbeat, breathing, movement or pulsation of the umbilical cord vessels [12].
According to the first comprehensive estimates, more than 7,200 stillborn babies are born each year. Even in highly developed countries of Europe and North America, the stillbirth rate does not fall below 1.3% [9]. The stillbirth rate in Russia in 2018 was 5.51%. At the same time, the proportion of antenatal fetal death was 91.8%. However, over the past five years, the rate of perinatal mortality (death of a child before and after birth) has begun to decline [13].
More often, intrauterine fetal death is observed in teenage girls due to the immaturity of the body, as well as in pregnant women 35 years of age and older. By this age, a woman, as a rule, develops a number of chronic diseases, and the ovarian reserve - the supply of follicles in the ovaries - decreases. All this is a risk of non-developing pregnancy due to chromosomal pathology of the fetus.
Also, the risk of antenatal loss is higher in women with a history of more than two births, recurrent miscarriage, induced abortions, multiple pregnancies, the presence of a postoperative scar on the uterus and in vitro fertilization (IVF) [23].
There are many causes of intrauterine fetal death. They can be both on the side of the fetus itself and on the mother’s side [8].
The immediate cause of death is fetal distress syndrome. It implies all violations of the functional state of the fetus, primarily its movements and heartbeat.
Indirect causes of antenatal fetal death:
- Congenital anomalies of fetal development - Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc.
- Infection of the fetus in the womb. Most often this happens when:
- invasive diagnosis and treatment of a pregnant woman - amniocentesis (during removal of excess amniotic fluid, administration of drugs or puncture of the amniotic membrane), puncture of umbilical cord vessels, etc.;
- violation of sterility during the introduction of blood products into the uterus through the vessels of the umbilical cord (for example, when transfusing red blood cells to a fetus with hemolytic disease);
- premature rupture of membranes in the case of prolonged pregnancy;
- common infections of pregnant women - TORCH infections, syphilis, tuberculosis, urogenital chlamydia and HIV infection[13].
- Extragenital diseases of the mother - diabetes mellitus, disorders of the thyroid gland, kidneys and adrenal glands, injuries, alcohol abuse and smoking, especially in the presence of inflammation of the urogenital tract.
- Features of pregnancy:
- various forms of late toxicosis;
- threat of miscarriage;
- isthmic-cervical and fetoplacental insufficiency;
- infectious diseases;
- disruption of blood flow in the uterus and placenta;
- breech presentation of the fetus.
- Unidentified reasons.
The infection can be viral (cytomegaloviruses, herpes simplex viruses, rubella, Coxsackie, HIV), bacterial (chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, group B streptococci, enterobacteria, E. coli) and fungal (candidiasis).
How is CTG done?
The examination is painless and safe for mother and child. A pregnant woman needs to take a pillow or blanket with her to sit comfortably on the couch. After the patient has taken a position, lying or reclining on her back, the abdomen is exposed and 2 electrodes are applied - 1 in the place of greatest audibility of the child’s heart rhythm, 2 in the lower abdomen (fundus of the uterus).
The duration of the study is from 35 minutes to 1 hour. During this time, the sensors read the values of the main indicators of the fetus’s condition to a device that prints them on paper tape.