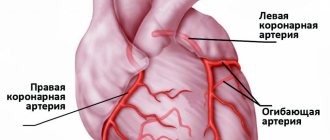
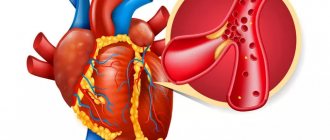
Causes of myocardial infarction
Etiology of MI
- sudden obstruction to blood flow in the branches of the coronary artery (vessels supplying the heart). Most often, such an obstacle is an atherosclerotic plaque with a blood clot.
Atherosclerosis in the walls of the arteries is the formation of peculiar “growths” - plaques consisting of fatty, fibrous tissue, calcium, and which, as they progress, narrow the lumen of the vessel up to 90% or more. At the time of increased blood pressure, physical effort, or psycho-emotional stress, rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque is possible, the reaction to which is thrombosis.
Less commonly, the cause is a prolonged, prolonged spasm
coronary artery in the absence of significant atherosclerosis, or a complication of other diseases: congenital malformations, trauma to the coronary arteries, vasculitis, embolism, tendency to hypercoagulation (increased blood clotting), syphilis.
There are a number of risk factors
, repeatedly increasing the likelihood of myocardial infarction.
There are non-modifiable ones, that is, those that cannot be influenced:
- male gender (up to 50-55 years, then the incidence levels off),
- age,
- genetic conditioning (coronary artery disease and other manifestations of atherosclerosis in blood relatives);
- low physical activity (hypodynamia),
- obesity or increased body weight,
- smoking (active or passive),
- arterial hypertension,
- diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome,
- dyslipidemia.
And
modifiable, by changing which you can significantly reduce the likelihood of disease:
How long to stay in hospital if you have a stroke
Poor blood circulation in the brain, in other words, stroke, treatment involves three stages:
- prehospital;
- stay in the intensive care unit;
- treatment in a general ward.
The length of stay of a patient in a hospital, according to treatment standards, is 21 days, provided the patient has no violations of vital functions, and 30 days in case of serious violations. When the length of a patient’s stay in a hospital is insufficient, a medical examination is carried out followed by the development of an individual course of rehabilitation.
All patients diagnosed with stroke are subject to hospitalization. The length of stay in intensive care depends on a number of factors, including:
- depression of vital functions;
- degree of damage to brain tissue. With a major stroke, patients stay in intensive care longer;
- the need for constant monitoring if there is a high risk of recurrent stroke;
- severity of the clinical picture;
- level of depression of consciousness and others.
Basic and differentiated therapy
Treatment of a patient in the intensive care unit involves basic and differentiated therapy.
Basic treatment is aimed at:
- fight against cerebral edema;
- restoration of normal functioning of the respiratory system;
- patient nutrition;
- maintaining hemodynamics at an acceptable level.
Differentiated therapy involves:
- normalization of arterial and intracranial pressure, elimination of cerebral edema after hemorrhagic stroke. In the first two days, a decision is made regarding the need for surgery. Neurosurgeons at the Yusupov Hospital daily perform surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of stroke and save the lives of hundreds of patients. All manipulations are carried out using modern medical equipment using effective proven techniques;
- accelerating metabolic processes, improving blood circulation and increasing the resistance of brain tissue to hypoxia when diagnosed with ischemic stroke. The length of stay in intensive care directly depends on the timely and adequate course of treatment.
In most cases, young people recover much faster than older patients.
It is possible to transfer a victim from the intensive care unit to a general ward after meeting a number of criteria:
- the patient can breathe independently, without the support of devices;
- the patient is able to call a nurse or doctor for help;
- there is a stable level of heart rate and blood pressure;
- the possibility of bleeding is excluded.
Only after the patient's condition has stabilized can the doctor transfer the patient to the ward. In a hospital setting, various rehabilitation procedures are prescribed to quickly restore lost functions.
In the neurology department of the Yusupov Hospital, patients are not only developed an individual course of rehabilitation therapy, but also given psychological support.
If necessary, psychologists work with loved ones and relatives of the patient to teach them the basics of caring for a person who has suffered a stroke.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
The main manifestation of a heart attack is very intense, burning, baking, squeezing, pressing, tearing or “dagger” pain behind the sternum
. The pain may spread to the left arm, scapular region, shoulder, neck, and lower jaw.
The duration of the episode is always more than half an hour, the slightest physical stress causes increased pain. An important sign is the lack of analgesic effect of nitrates. Patients may also experience severe weakness, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, sweating, and nausea. Most people feel anxiety, doom, and fear of death.
In addition to the typical variant, there are several more atypical
, capable of masquerading as other diseases of the internal organs. Among these are abdominal (epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting), asthmatic (nasty dry cough, suffocation), cerebral (headache, loss of coordination of movements), arrhythmic, erased version (deterioration of sleep, emotional background, feeling of inexplicable discomfort in the chest, sweating ). It is also possible that there are no symptoms—a “silent” heart attack, which accounts for up to 20% of all MIs.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction
It is possible to recognize acute myocardial infarction taking into account:
- A characteristic clinical picture
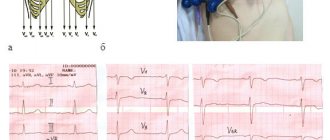
(severe pain in the chest area or the heart area), medical history (duration of a painful attack of more than 30 minutes, lack of results from taking nitroglycerin, presence of previously established coronary heart disease, risk factors) - Changes in the ECG
(negative T wave, pathological Q, QS complexes, ST segment elevation in leads corresponding to the location of the damage to the heart muscle) - Laboratory diagnostic data
(general blood count: increased ESR, leukocytes; biochemical indicators: increased aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, fibrinogen, appearance of CP protein; presence in the blood of cardiac-specific markers of cardiac muscle cell death: myoglobin CPK, LDH, tryponins). - Valuable information is provided by EchoCG, which reveals a local violation of myocardial contractility and thinning.
Factors influencing the speed and quality of rehabilitation
There are many factors that influence the speed of recovery after a stroke, so predicting the duration of rehabilitation and likely results is quite difficult.
How long rehabilitation after a stroke will last depends on the individual parameters for each person, as well as on other factors:
- volume of damage: an extensive stroke significantly worsens the severity of the patient’s condition, and also causes many neurological complications that adversely affect the timing of recovery and its quality;
- patient’s age: the older the victim, the longer the recovery;
- localization of damage: circulatory disorders of deep structures are difficult to treat;
- type of stroke: hemorrhagic strokes are less common, but occur in a more aggressive form, and also have a high mortality rate, although the prognosis for rehabilitation is more favorable than for ischemic stroke;
- caused by disorders: the presence of multiple cerebral symptoms, comatose states, severe paralysis and sensory disturbances give an unfavorable prognosis for recovery;
- timeliness of therapy: the most positive results of therapy can be achieved by starting treatment measures in the first 4 hours after the onset of the first symptoms; seeking help at a later time worsens the prognosis;
- compliance with medical recommendations: after the patient is discharged from the medical institution, the patient is given recommendations that can improve the quality of life, prevent the formation of relapse and negative complications.
The severity of the lesion has the greatest impact on the likelihood of restoration of lost functions and the timing of rehabilitation. With extensive strokes, violations of the most important functions are observed, even if the prescribed rehabilitation program is followed, the prognosis is rather disappointing. The greatest difficulties arise with the complete return of speech and motor functions. Close relatives who will devote a lot of time to special activities with the patient can positively influence the situation.
Treatment of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
- an emergency disease in cardiology and serves as an indication for immediate hospitalization in intensive care.
The number one task for doctors is to restore blood flow
in a thrombosed vessel. They achieve this in different ways. The priority and most effective is surgical intervention - angioplasty with stenting of the affected area of the artery or coronary artery bypass grafting. In parallel, medications are used that inhibit the development of a blood clot - disaggregants (aspirin, clopidogrel) and anticoagulants (heparin), and if immediate surgery is not possible, thrombolytics - drugs that dissolve the blood clot (alteplase, prourokinase).
Pain relief
carried out with narcotic analgesics, neuroleptics, intravenous infusions of nitroglycerin.
The size of the necrosis zone can be reduced by reducing myocardial oxygen consumption by using beta-blockers (metoprolol, bisoprolol, atenolol), ACE inhibitors (enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril), and oxygen therapy.
For arrhythmias
antiarrhythmics are used (magnesium, lidocaine, amiodarone), atropine for bradycardia. Anxiolytics and sedatives are prescribed to ensure psycho-emotional peace of the patient.
Strict bed rest
in the early stages of treatment and fractional meals, limited in volume and calorie content.
Help in the acute period
Which doctors are needed in the treatment of stroke depends on the period of the disease, but in any case, they must be experienced, highly qualified specialists who know how to properly provide assistance in this situation.
When diagnosing an ischemic stroke in a patient, the doctor’s goal is to restore blood supply with subsequent rehabilitation. This may require blood thinning medications or mechanical removal of the clot using a catheter. To remove atherosclerotic plaques, endarterectomy is performed, and to increase the diameter of blood vessels, plastic surgery with stenting is performed.
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Prevention of coronary artery disease and its extreme expression - myocardial infarction - comes down to influencing modifiable risk factors, namely: physical activity, nutrition, body weight, bad habits, blood glucose and cholesterol levels, blood pressure.
After a heart attack, it is important to regularly independently measure blood pressure and heart rate, systematically undergo ECG and EchoCG diagnostics, and take daily medications to prevent the progression of heart dysfunction and recurrence of the disease.
Prognosis for recovery after stroke
Favorable factors for recovery after a stroke include:
- timely early start of rehabilitation therapy;
- spontaneous early recovery of lost functions.
Among the unfavorable factors of recovery after a stroke are:
- advanced age of the patient;
- large area of brain tissue damage;
- poor blood circulation around the affected brain tissue;
- damage to cells in functionally important areas of the brain.
Basics of Stroke Recovery
In the process of rehabilitation, the positive attitude of the patient himself and his desire to return to independent life are important. Psychological support and assistance from the patient’s relatives plays a huge role. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone.
Memory recovery after stroke
Treatment of patients after a stroke takes place in the neurological department. Memory restoration depends on many factors: the size of the area of brain damage, the location of the damage, and the timeliness of medical care. The faster blood circulation in the brain is restored, the greater the chance of memory recovery after a stroke.
Memory restoration after a stroke is possible with the participation of several specialists - a neurophysiologist, psychologist, neuropsychologist, neuropsychiatrist. Help for a patient after a stroke is provided at the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital. In the hospital, the patient is treated according to an individual recovery program; many specialists take part in the development of such a program. When developing the program, the patient’s health condition, the severity of brain damage, and memory impairment are taken into account.
In some cases, it takes several years to restore memory and speech; during recovery, the doctor prescribes medication, a special diet, various trainings - color therapy, rhythm therapy, music therapy and others. Memory restoration at home is not always successful due to the lack of a training program and knowledge in the field of rehabilitation of patients after a stroke.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital by phone. Consultation with a specialist, full patient care, rehabilitation using innovative equipment, massages and exercises will help the patient regain full memory.
Restoring a hand after a stroke
A positive attitude and support from family have an impact on rapid recovery from illness. Partial paralysis of the arm is a common occurrence after a stroke and is characterized by stiffness of movement and limited motor ability of the arm. Functional paresis (partial paralysis) refers to neurological syndromes, caused by disruption of the nervous system, damage to the nervous system pathway due to damage to the cerebral cortex after a stroke. Paralysis of the arm is the complete absence of voluntary movements of the limb.
Recovery from a stroke may involve the hand or the entire limb. With partial paralysis, the ability to move the arm or hand freely is impaired; the person cannot fully care for himself or perform basic actions. To restore motor ability, the patient must perform daily exercises for finger motor skills and limb motor skills.
The rehabilitation process of restoring motor activity of the limbs requires patience from the patient and a lot of work - this will allow you to return to a full life after a stroke. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone. The rehabilitation doctor will develop individual exercises for the patient, the patient will be under constant medical supervision and receive qualified assistance from specialists.