Science knows that different living organisms on the planet have different blood colors.
However, in humans it is red. Why is blood red? This question is asked by both children and adults.
The answer is quite simple: the red color is due to hemoglobin, which contains iron atoms in its structure.
What makes blood red is hemoglobin, which consists of:
- From a protein called globin;
- The non-protein element heme, which contains the ferrous ion.
It was possible to find out what gives the red color, but its elements turn out to be no less interesting. What elements give it this color is an equally interesting aspect.
Blood contains:
- Plasma.
The liquid is light yellow in color, with its help the cells in its composition can move. It is composed of 90 percent water, with the remaining 10 percent made up of organic and inorganic components. Plasma also contains vitamins and microelements. The light yellow liquid contains many useful substances. - The formed elements are blood cells.
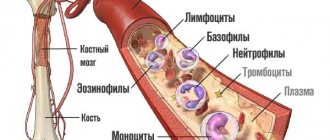
There are three types of cells: white blood cells, platelets and red blood cells. Each type of cell has certain functions and characteristics.
These are white cells that protect the human body. They protect it from internal diseases and foreign microorganisms penetrating from the outside.
This is a white element in color. Its white tint cannot be ignored during laboratory tests, so such cells are identified quite simply.
White blood cells recognize foreign cells that can cause harm and destroy them.
These are very small colored plates whose main function is coagulation.
These cells are responsible for ensuring that the blood:
- It coagulated and did not flow out of the body;
- Coagulates quite quickly on the surface of the wound.
More than 90 percent of these cells are in the blood. It is also red because red blood cells have this hue.
Explanations for children should be extremely simple, but at the same time informative. Blood contains many substances that differ in function.
Consists of plasma and special cells:
- Plasma is a liquid that contains useful substances. It has a light yellow tint.
- The formed elements are erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets.
The presence of red cells - erythrocytes - explains its color. Red blood cells are red by nature, and their accumulation leads to the fact that a person’s blood is exactly this color.
There are about thirty-five billion red cells that move throughout the human body in the blood vessels.
Why are veins blue
The veins carry burgundy blood. They are red, like the color of the blood that flows through them, but not blue. The veins only appear blue.
This can be explained by the law of physics about the reflection of light and perception:
When a ray of light hits the body, the skin reflects some of the waves and looks light. However, it transmits the blue spectrum much worse.
The blood itself absorbs light of all wavelengths. The skin gives a blue color for visibility, and the vein is red.
The human brain compares the color of the blood vessel against the warm tone of the skin, resulting in blue.
Blood of a different color in various living creatures
Not all living organisms have red blood.
The protein that gives this color in humans is hemoglobin, contained in hemoglobin. Other living beings have other fat-containing proteins instead of hemoglobin.
The most common shades besides red are:
- Blue.
Crustaceans, spiders, mollusks, octopuses and squids boast this color. And blue blood is of great importance for these creatures, as it is filled with important elements. Instead of hemoglobin, it contains hemocyanin, which contains copper. - Violet.
This color is found in marine invertebrates and some mollusks. Typically, such blood is not only purple, but also slightly pink. The blood of young invertebrate organisms is pink. In this case, the protein is hemerythrin. - Green.
Found in annelids and leeches. The protein is chlorocruorin, close to hemoglobin. However, iron in this case is not oxide, but ferrous.
The color of blood varies depending on the protein it contains. Whatever the color of blood, it contains a huge amount of useful substances necessary for a living organism. Pigment is important for every organism, despite its diversity.
General recommendations
If you experience any unusual symptoms, it is important to contact your doctor immediately. Don't trust your friends' advice or go to charlatans
Every woman should have minimal knowledge about her health, carefully monitor the body’s signals and changes in physiological processes.
It is necessary to avoid, or better yet completely eliminate, unprotected sexual relations with casual partners.
It is advisable to undergo examination by a gynecologist at least 2 times a year, regularly do ultrasounds and take the necessary tests.
Following these rules will help you avoid many diseases and detect the onset of illness in time.
What is blood really?
Human blood is not just a liquid. It contains a lot of different elements that distribute nutrients throughout the body and fill our tissues with oxygen. Most of our blood consists of plasma, in which blood cells (formed elements) are suspended, and any substances that are carried (besides oxygen) dissolve here. Plasma is the most important component of this important liquid and is very pale in color with a yellow tint. But as soon as the formed elements dissolve in it, it sharply changes its color and becomes slightly cloudy. The most common type of blood cell found in plasma is red blood cells, which contain a protein called hemoglobin.
Why does black blood bleed during menstruation? Main reasons
It is normal for every woman to have bloody menstruation every month. Their quantity is approximately 50 ml. Sometimes dark discharge appears before menstruation, which is often within the normal range. It is known that menstruation is the result of the death of an egg. It is excreted with the dead layer of the endometrium. Therefore, the appearance of dark strokes in the first days should not worry. But if they appear for more than a day, then consultation with a specialist is necessary. Especially if your periods are black. There may be several explanations why this happens.
Black periods should be a reason to see a doctor
What about blue blood?
As for people of aristocratic origin, the so-called blue-blooded individuals, they have almost the same red liquid as everyone else. But in hypoxia (dangerously low levels of oxygen in the blood), the wavelengths of reflected light reach the purple end of the spectrum. And then you can see blue veins through the skin.
On the Internet you can often find a myth that blood and veins are not red, but blue. And you shouldn’t believe in the theory that the blood actually flows through the vessels is blue, but when cut and in contact with air it instantly turns red - this is not so. Blood is always red, just in different shades. The veins only appear blue to us. This is explained by the laws of physics about light reflection and our perception - our brain compares the color of a blood vessel against the bright and warm tone of the skin, and ends up showing us blue.
So why is blood still red and can it be a different color?
Our blood is made red by red blood cells, or otherwise red blood cells - oxygen carriers. They have a shade of red depending on hemoglobin - an iron-containing protein found in them, which can bind with oxygen and carbon dioxide to transport them to the right place. The more oxygen molecules connected to hemoglobin, the brighter the red color the blood is. That’s why arterial blood, which has just been enriched with oxygen, is so bright red. After the release of oxygen to the cells of the body, the color of the blood changes to dark red (burgundy) - such blood is called venous.
Of course, the blood contains other cells besides red blood cells. These are also leukocytes (white blood cells) and platelets. But they are not in such significant quantities compared to red blood cells as to affect the color of the blood and make it a different shade.
Diagnostics
Having discovered dangerous symptoms that accompany black menstrual discharge, a woman should definitely contact a gynecologist and undergo diagnostics:
- initial external examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- cytological analysis - collection of the mucous layer of the uterus, which will show the presence of cancer cells or metastases;
- donate urine and blood for hormones and other substances, as well as viruses;
- a vaginal swab to detect a bacterial or fungal infection.
Only after diagnosis can treatment begin. If the cause of black periods is hormonal imbalances or anorexia, you need to take a course of drugs with progesterone or estrogen, and (in the second case) gain weight.
If the color of the discharge has changed due to an STD, then you need to determine the nature of the pathogen (bacterial, viral, fungal) and undergo treatment (antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal medications). If cancerous tumors are detected in the uterus, they are surgically removed, after which the woman must undergo restorative therapy.
A change in the color of your period from red to dark brown or black can occur due to normal physiological processes. If this process is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist, because the cause may be various diseases, which in the future will lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle and give serious complications.
Compound
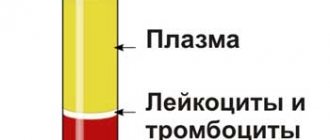
Blood is a rapidly renewing connective tissue that circulates throughout the body and carries gases and substances necessary for metabolism. It consists of a liquid part, called plasma, and formed elements - blood cells. Normally, plasma makes up about 55% of the total volume, cells – about 45%.
Plasma
This pale yellow liquid performs very important functions. Thanks to plasma, cells suspended in it can move. It consists of 90% water, the remaining 10% are organic and inorganic components. Plasma contains microelements, vitamins, and intermediate metabolic elements.
Cages
There are three types of shaped elements:
- leukocytes - white cells that perform a protective function, protecting the body from internal diseases and foreign agents penetrating from the outside;
- platelets - small colorless plates responsible for coagulation;
- Red blood cells are the same cells that make blood red.
Red blood cells give blood its red color
These cells, called red blood cells, make up most of the formed elements - more than 90%. Their main function is to transfer oxygen from the lungs to peripheral tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs for further removal from the body. Red blood cells are continuously produced in the bone marrow. Their lifespan is about four months, after which they are destroyed in the spleen and liver.
The red color of red blood cells is given by the hemoglobin protein found in them, which is capable of reversibly binding to oxygen molecules and transporting them to tissues.
The color of blood varies depending on whether it flows from the heart or to the heart. The blood that comes from the lungs and then travels through the arteries to the organs is saturated with oxygen and has a bright scarlet color. The fact is that hemoglobin in the lungs binds oxygen molecules and turns into oxyhemoglobin, which has a light red color. Upon entering the organs, oxyhemoglobin releases O₂ and turns back into hemoglobin. In peripheral tissues, it binds carbon dioxide, takes the form of carbohemoglobin and darkens. Therefore, the blood flowing through the veins from the tissues to the heart and lungs is dark, with a bluish tint.
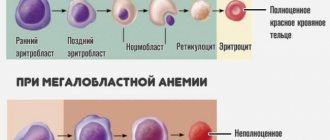
An immature red blood cell contains little hemoglobin, so at first it is blue, then becomes gray, and only when ripe it becomes red.
Black clots
If the discharge is accompanied by the presence of black blood clots, then their cause may be some kind of pathology. But this condition is also typical for healthy women. This is explained by the anatomical features of the body:
- A woman's cervix is very narrow.
- When staying in a stationary position for a long time, during sleep. Blood is retained in the vagina, changing color to dark.
- Heavy exertion increases bleeding, and clots are pushed out.
- Black blood clots are sometimes caused by blood left over from previous periods. It coagulates and when a new period begins, it comes out in the form of clots.
- During ovulation, black periods are considered normal. This condition may last for some time. Such discharge is medically called cervical mucus.
If such signs are present, a visit to the doctor is necessary.
After sleep, the discharge may be dark in color.
Hemoglobin
This is a complex protein that includes a pigment group. One third of the red blood cell consists of hemoglobin, which makes the cell red.
Hemoglobin consists of a protein - globin, and a non-protein pigment - heme, containing ferrous ion. Each hemoglobin molecule includes four hemes, which account for 4% of the total mass of the molecule, while globin accounts for 96% of the mass. The main role in the activity of hemoglobin belongs to the iron ion. To transport oxygen, heme reversibly binds to the O₂ molecule. Ferrous oxide is what gives blood its red color.
Compound
Plasma
As already noted, one of the components of blood is plasma. It takes up about half of the blood composition. Blood plasma turns blood into a liquid state, has a light yellow color and is slightly denser in properties than water. The density of plasma is ensured by substances dissolved in it: antibodies in the blood, salts, fats, carbohydrates and other elements.
Shaped elements
Another component of blood are formed elements (cells). They are represented by erythrocytes - red blood cells, blood leukocytes - white blood cells, platelets - blood platelets. It is red blood cells that answer the question why blood is red.
Pathological causes of black periods
Why the periods turned black and are accompanied by new unpleasant symptoms, only a gynecologist can say for sure, because various diagnostic measures are required to make a diagnosis. There are several pathological reasons that change the color of the discharge:
- STD;
- cancerous tumors;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- anorexia.
STDs are infectious diseases transmitted through sexual contact, often they negatively affect menstruation, for example, chlamydia and candidiasis cause blood retention in the uterus, which is why it changes its color, pathogenic microorganisms have time to develop in it, so the discharge smells bad.
Cancerous tumors in the uterus disrupt the functioning of its smooth muscles, contractions become weak and rare, therefore, during menstruation, blood lingers for a long time in the cavity of this organ and darkens.
Inflammatory processes in the genital organs, like STDs, negatively affect the menstrual cycle; the discharge often becomes too abundant, dark and with a large number of clots, while the woman experiences severe pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, and her body temperature rises.
If, while losing weight, a woman develops anorexia, menstruation becomes irregular, its abundance is significantly reduced, so the iron in menstruation quickly has time to oxidize before it enters the vagina. Over time, menstrual flow may disappear altogether.
Red blood cells
At the same time, about 35 billion red blood cells move through the circulatory system. Appearing in the bone marrow, red blood cells form hemoglobin in the blood, which is a red pigment rich in protein and iron. The task of hemoglobin is to deliver oxygen to vital parts of the body and remove carbon dioxide. Red blood cells live on average 4 months, then they disintegrate in the spleen. The process of formation and breakdown of red blood cells is continuous.
Red blood cells give the blood a red color
Hemoglobin
The blood, enriched with oxygen in the lungs, disperses to the vital organs of the body. At this moment it has a bright scarlet color. This occurs due to the binding of hemoglobin in the blood with oxygen, resulting in oxyhemoglobin. As it passes through the body, it distributes oxygen and becomes hemoglobin again. Next, hemoglobin absorbs carbon dioxide from tissues and is transformed into carbohemoglobin. At this moment, the color of the blood changes to dark red. Immature red blood cells also have a bluish tint, and as they grow they turn gray and then turn red.
Signs of bleeding
First aid for bleeding is stopping or reducing blood loss before the ambulance arrives. It is necessary to distinguish between types of bleeding and correctly use the necessary means to stop them. It is important to have dressings in your home and car first aid kits.
The most dangerous types of bleeding are arterial and venous. The main thing here is to act quickly, but do no harm.
- During arterial bleeding, blood flows in bright scarlet intermittent fountains at high speed in time with the heartbeat.
- With venous, a continuous or weakly pulsating dark cherry stream of blood flows from the injured vessel. If the pressure is low, a blood clot forms in the wound and blocks the blood flow.
- With capillary, bright blood slowly spreads over the entire wound or flows in a thin stream.
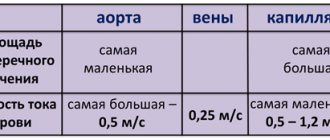
Shades of red
The color of the blood may vary. Answers to the questions why blood is dark red or bright red. A person’s blood takes on a different shade depending on whether it moves towards the heart or away from it.
Dark red and bright red blood
Very often people wonder why veins are blue and blood is red? The fact is that venous blood is the blood that flows through the veins to the heart. This blood is saturated with carbon dioxide and deprived of oxygen, has lower acidity, contains less glucose and significantly more final metabolic products. In addition to being dark red, venous blood also has a bluish, blue tint. However, the blue tint of blood is not so strong as to “stain” the veins blue.
Why is blood red? It's all about the process of passing light rays and the ability of bodies to reflect or absorb solar rays. In order to reach venous blood, the beam must pass through the skin, the fat layer, and the vein itself. The sun's ray consists of 7 colors, three of which the blood reflects (red, blue, yellow), the remaining colors are absorbed. Reflected rays pass through tissues a second time to enter the eye. At this point, red rays and low-frequency light will be absorbed by the body, and blue light will be transmitted. We hope that we have answered why a person has dark red and bright red blood.
Why is blood red? This liquid mobile tissue contains a special dye - hemoglobin. This is a complex protein. Its molecules are located inside red blood cells - erythrocytes. Their main task is to ensure the supply of oxygen to every cell of the body. Blood flows very quickly to muscles and tissues and hemoglobin turns this body fluid red.
Diagnosis of diseases
Diagnostic procedures help determine why black periods appeared:
- inspection is carried out using mirrors;
- general anamnesis is studied;
- pelvic ultrasound is performed;
- a biopsy is performed;
- hormonal levels are examined;
- a general blood test is required;
- A diagnostic study of the endometrium is performed.
Every woman should be attentive to her health. The slightest deviations are the reason why you should undergo a full examination by a gynecologist.
Cancel reply
(c) 2021 Women's diseases
Copying materials is permitted only with an active link to the source
Questions and suggestions
Consultation with a doctor on the use of any drugs and procedures posted on the site is mandatory.
Red blood cells and hemoglobin
Since ancient times, blood has been called the carrier of life. It is pumped by the heart muscle into large and.
Formed elements of blood
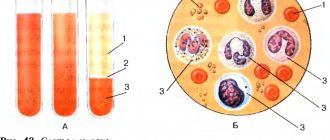
Human blood cells are formed in red bone marrow. This is a real factory of formed elements. During centrifugation, the blood is clearly divided into two layers:
- The upper light layer, plasma, is an intercellular substance. This yellowish liquid is about 60%. It contains minerals, water, proteins.
- The bottom layer is dark, red. This is the second part of the blood, its cells. The formed elements include red blood cells - erythrocytes, as well as platelets and leukocytes. They differ from each other in shape, size, quantity and function.
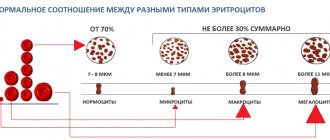
Erythrocytes - red blood cells
Most of the blood contains red blood cells. These are the main, most numerous. In the circulatory system, their number reaches 20 trillion. There are 4-5 million of them in one microliter. They move in the center of blood vessels.
Red blood cells are small cells without a nucleus. They can only be seen under an electron microscope. Here they can be seen in the form of biconcave disks. Each red blood cell is covered with a membrane. Its cytoplasm is 1/3 full. The human liver and spleen contain the maximum amount of these postcellular blood structures.
The life of each red blood cell is short - only three months. Then it is destroyed. Obsolete, defective iron-containing cells are dissolved or absorbed by phagocytes - protective microphages and macrophages. They destroy damaged red blood cells in the spleen.
How can you find out the number of red blood cells in the body?
To calculate the level of red blood cells per unit volume of blood, samples are placed in a special chamber. Counting is carried out under a microscope. In a medical facility, this analysis is performed very quickly using modern electronic equipment.
Hemoglobin is a complex substance
This biological iron-containing structure contains:
Non-protein group of globin and simple protein heme.
Globin protein contains amino acids.
Hemoglobin (Hb) consists of 4 amino acid chains. They are a group of molecules called amino acids. They look like curly ribbons. Each chain has a hemogroup.
Hemoglobin has a bright red color due to the content of divalent iron oxide. The iron molecule in hemoglobin helps maintain normal levels.
In nature, not all living organisms have a red blood tint. In some species of insects and invertebrates, red blood cells contain iron-containing proteins and ferrous iron, rather than hemoglobin. Therefore, their blood has a purple or green tint. Scorpions, crabs, octopuses, spiders, and octopuses have blue blood because the substance in their blood that binds oxygen is hemocyanin, which contains copper, and not hemoglobin.
Physiological causes of black periods
Black discharge is actually dark brown in color, but can sometimes appear brown. This shade of bloody discharge is normal on the first or second day of menstruation and already at the end of it. The color becomes “black” due to the fact that little blood is released during these periods of the menstrual cycle, it is retained in the uterus, the iron in it has time to oxidize and change its shade from red to dark brown.
When your periods become heavy, the discharge does not remain in the body for so long and the hemoglobin does not have time to break down, so it looks dark red.
There are also other normal reasons why menstruation is black:
- recovery after childbirth;
- the onset of menopause;
- hormonal contraceptives;
- hormonal fluctuations due to weight fluctuations;
- recovery after abortion or curettage;
- damage to the uterus during laparoscopy.
Recovery after childbirth
During pregnancy, the body changes its hormonal levels and menstruation stops. After the birth of the child, everything is restored, menstruation begins within 2-3 months, but due to the enlargement of the uterus in which the fetus grew, this organ contracts worse, blood is retained in it longer, so it changes color from red to dark brown. It takes 4-5 months to restore the uterus, after which menstruation will return to normal.
The onset of menopause
As a woman ages, she begins menopause - the period before menopause, when menstruation becomes less abundant and longer due to hormonal changes (lack of estrogen secretion). During this period, the cervical canal between the uterus and vagina narrows, blood during menstruation is retained longer in the cavity of the first organ, the iron in it has time to oxidize, endometrial clots accumulate, so the discharge looks thick and black.
Hormonal contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives are birth control pills that regulate a woman’s hormonal levels so that a fertilized egg does not attach and the embryo develops in her body. Since they affect sexually active substances, they change the course of the menstrual cycle.
Some drugs can cause black discharge only for the first 3 months, until the body adapts to it; there are also pills that permanently reduce the volume and duration of menstruation, so the blood has time to oxidize and darken before leaving the vagina.
Sudden weight fluctuations
Many girls who lost weight quickly using extreme methods: dieting, starvation, etc., had to deal with dark brown, light periods. When weight fluctuates, the body is in a stressful state, so it “reduces the power” of all non-vital functions: hair growth, nails, menstruation, etc. Menstruation becomes short and irregular, and so little blood is released that it oxidizes before leaving the vagina.
Recovery after abortion and curettage
Abortion and curettage for medical reasons violate the integrity of the mucous layer of the uterus; it may take several months to restore it. During this period, the organ cannot contract normally, so during menstruation, blood and large clots accumulate in it for a long time, iron has time to oxidize, and the discharge becomes dark brown. This condition should not last longer than 3 months; black periods further indicate inflammation or poor-quality surgery that has touched the endometrium of the uterus too deeply.
Recovery after hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy in gynecology is the introduction of operating instruments or diagnostic devices into the uterine cavity without an incision, that is, through the vagina. During this procedure, the cervix and the organ itself may be damaged, as in the previous case, the contractility of the uterine muscles is disrupted, so for several months the discharge is dark in color. Recovery after laparoscopy takes about a month, after which periods become normal.
How hemoglobin releases oxygen
The main feature of hemoglobin is that it is capable of attaching carbon dioxide and oxygen. In this way, hemoglobin in red blood cells transports oxygen in the body. It moves it from the lungs to every cell of the body.
The transfer of oxygen to tissues is a complex process. There are iron ions in the center of hemoglobin. These are four oxygen binding points. As soon as hemoglobin binds to one oxygen molecule, its shape changes in such a way that it is convenient for its other hemogroups to attach oxygen. Due to these properties, hemoglobin, when moving through the pulmonary capillaries, is a good acceptor of oxygen.
In the vessels of the lungs, oxygen joins hemoglobin and is transferred to tissues in the form of oxyhemoglobin, where it is split off. If there is an acidic environment - carbon dioxide, oxygen can be released. In the human body, tissue cells are very active in the quadriceps muscles. They release a lot of carbon dioxide into the capillaries. This substance attaches to hemoglobin. A chemical reaction occurs. Oxygen begins to be released exactly where it is needed in the human body.
When muscles use oxygen, tissue cells release carbon dioxide. Therefore, venous blood darkens, becomes purple, dark red. It has a blue tint because it lacks oxygen. Hemoglobin in red blood cells picks up carbon dioxide in the tissues and delivers it to the lungs. Here carbon dioxide passes into the tissues of this organ. The brain receives a signal about this. The center of the nervous system gives the command and the body exhales. As a result, carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide) is released into the surrounding air.
The red blood cells then reabsorb pure oxygen. As hemoglobin combines with oxygen, it turns bright red again.
Red blood, enriched with oxygen, is sent to the heart muscle. Here, as a result of contraction of the left ventricle, blood is pushed into the systemic circulation, which carries oxygen throughout the human body.
Without hemoglobin, life is impossible, since tissues lack oxygen when the level of this protein is low. This type of blood is liquid and carries little oxygen. There are not enough nutrients, the person feels tired. All internal organs are not working well. Anemia develops.
Iron-containing substances supplied with food are of two types:
- Hemic iron. Contained in the heme molecule. It is present in fish, poultry, and red animal meat.
- Non-hemic iron. Contained in plant products.
It is believed that the body's absorption of hemic iron is more efficient than non-hemic iron.
It is not difficult to determine the hemoglobin content in the blood. This is done using a hemometer.
The blood taken into a test tube is mixed with hydrochloric acid and diluted drop by drop with distilled water. When the blood color matches the standard, the divisions on the hemometer will show the percentage of hemoglobin.
In clinics, an electrocalorimeter is used to determine hemoglobin levels.
How can you find out your hemoglobin level at home?
If this indicator is normal, the lines on the palm should be slightly darker than the skin. If these folds are lighter, the hemoglobin level of the owner of the palm is low.
If white spots or stripes appear on the nails, this is a sign of iron deficiency in the body.
What is necessary for normal hemoglobin levels?
For this you need iron. Its deficiency in the body can be prevented with the help of a proper diet. But if hemoglobin is below normal, it is almost impossible to solve this problem only with the use of products.
Doctors use modern hematology analyzers to determine the causes of iron deficiency in the body.
Stagnation
The presence of venous blood in vessels and organs for a long time is called stagnation. This condition can have varying degrees. Venous blood can accumulate near the walls of blood vessels and in organs in small quantities or almost completely displace a separate section of the circulatory system.
When stagnation occurs, nutrients and oxygen cease to flow into individual vessels and organs. Gradually, the skin may become blue and painful when you press on certain areas of the skin. Stagnation of venous blood provokes inflammatory and purulent processes in certain areas of the body and can cause inflammatory processes in organs.
Symptoms and signs
Stagnation of venous blood does not immediately manifest symptoms.
The following symptoms gradually develop:
- headache, especially in the morning;
- pain when pressing and moving in certain parts of the body;
- the appearance of bluish integuments;
- the appearance of slight congestion in the ears;
- development of nervous diseases.
Causes
Venous blood has the property of carrying viruses, bacteria, and cellular metabolic products for their removal from the body and always flows from the organ.
Due to this feature, stagnation of venous blood can lead to the development of serious disorders in the body, the causes of which may be:
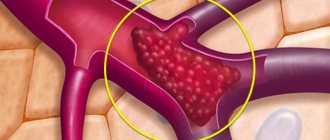
- Injury due to blows and bruises. Hemorrhages and stagnation of venous blood appear not only after injury, but also as a result of improper fusion of vessels in which venous blood can stagnate.
- Blood clots or complete or partial blocking of vessel walls with blood clots disrupts the normal flow of venous blood, the pressure of which is not high. As a result, venous stagnation of blood occurs in the area with the thrombus.
- A sedentary lifestyle , in which the pressure in the pelvis increases as a result of prolonged sitting. Increased pressure in the lower abdomen in the presence of thick blood causes venous stagnation and serious health problems (hemorrhoids, varicose veins).
- Pinching certain areas of the body when wearing tight shoes, tight clothing) noticeably narrows the blood vessels in the compressed parts of the body. Circulation in these areas is disrupted and stagnation occurs.
- Neoplasms of any nature (malignant and benign) cause circulatory problems when they grow large. As a result of tissue compression, the blood circulation process is disrupted and venous stagnation occurs in certain areas of the vessels.
- Varicose veins change the course of the vessel, creating irregularities and depressions. In such places near the walls, there may be a slight stagnation of venous blood, which also provokes pain and discomfort.
- Congestion of the brain develops due to disorders of the blood vessels inside the brain. Damaged tissues swell and become inflamed, and oxygen starvation and congestion form inside the head.
- Stasis of the lungs or lower extremities , resulting in swelling and a marked increase in the size of the lungs and vascular tissues of the lower extremities. Blood circulation is disrupted, and venous blood stagnates in the tissues.
- Hyperemia of the kidneys or their significant thickening and enlargement provokes spasm and low blood flow to the organ.
Treatment methods
Venous blood can stagnate in different parts of the body and human organs, so treatment of stagnation is carried out using various methods, which include:
- review of the nutrition system and the use of dietary products, cessation of tobacco and alcohol;
- physical exercises in the form of race walking, combined with a contrast shower, help restore blood circulation;
- surgical intervention, which involves removing the damaged area, growth and restoring the normal functioning of blood vessels;
- drug therapy includes:
- ointments and gels for topical use that help restore blood microcirculation and promote vascular restoration. These include heparin ointment, troxerutin gel, venen-gel. Ointments and gels are applied to the damaged area of the body 2-3 times a day with massaging movements for 5-7 days;
- taking medications that help restore the condition of blood vessels and blood microcirculation. Such drugs relieve symptoms of heart failure and help eliminate symptoms of varicose veins. Curantil relieves venous blood stagnation by restoring the blood supply to damaged tissues. The drug is taken 1 tablet. 3 times a day before meals for 30-60 days;
- Taking diuretics helps accelerate blood flow and remove all harmful substances from the body along with the fluid. Furasemide also helps remove sodium and lower blood pressure. It is taken for stagnation, 1 tablet. 2-3 times a day for 7 days.
- taking antithrombosis drugs (warfarin, Plavix), which help clean blood vessels and restore blood circulation. Plavix is taken 1 capsule. 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
- taking antispasmodics allows you to relieve spasm of cerebral vessels and restore blood flow and remove congestion in the vessels of the head (no-spa, drotaverine, cordaferon). No-shpu during stagnation, take 1-2 tablets. 2 times a day for 2 weeks.
Traditional methods
Venous blood passes through the vessels of the circulatory system, therefore, to treat stagnation, traditional methods are often used, which have an effect on the circulatory system and the condition of the walls of blood vessels.
Folk remedies are used only after consultation with a specialist and in combination with other treatment methods. The following are used as folk remedies:
Sweet clover decoction
A decoction of sweet clover leaves helps restore blood circulation. It promotes the restoration of blood vessels and helps cleanse the blood of excess cellular metabolic waste products.
Cooking steps:
- To prepare the decoction 2 tbsp. l. dry sweet clover leaves combined with 1 tbsp. hot water. Then the mixture is boiled in a water bath for 20 minutes and filtered through a sieve.
- It is recommended to take 100 ml of the finished decoction. morning and evening on an empty stomach.
Nettle juice
Nettle juice helps restore the condition of blood vessels, improves blood circulation and has anti-inflammatory properties.
Cooking steps:
- Nettle leaves and stems are passed through a juicer or crushed in a blender and filtered.
- Store fresh nettle juice in the refrigerator and drink 100 ml. 3-4 times a day.
Grape juice
Fresh grape juice has the ability to strengthen the walls of blood vessels. It cleanses the walls of blood vessels and has diuretic properties.
Drink 1 tbsp of freshly squeezed grape juice. 3 times a day for 20-30 days.