Among all diseases of the vascular system, atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is considered one of the main causes of disability and mortality throughout the world. According to statistics, every fifth man over 65 years old suffers from atherosclerosis of the lower extremities. A dangerous complication of this disease is the development of gangrene and often amputation of the limb.
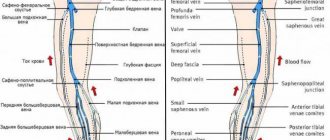
With atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, the arteries are affected and trophic changes develop in the tissues of the legs. Typically, blood circulation in the legs is disrupted in the popliteal, tibial and femoral arteries.
In 70% of cases, the disease occurs with obliterating syndrome, when partial or complete restriction of blood flow occurs against the background of a gradual narrowing of the lumen of the conducting vessels.
1 Swelling of the legs
2 Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities
3 Varicose veins
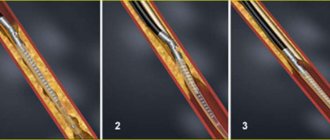
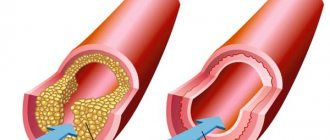
Chronic obliterating atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is associated with impaired blood circulation in peripheral vessels and the occurrence of changes in tissue trophism. With obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, excess cholesterol ingested with food spreads through the bloodstream, reaches the walls of arterial vessels, accumulates there and forms cholesterol plaques. Cholesterol plaques grow and make the lumen of blood vessels narrow.
If atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is not treated, complete blockage of the veins occurs, swelling occurs and gangrene may begin.
Types of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities
Chronic obliterating diseases of the arteries of the lower extremities (COLD) are a whole group of blood vessel diseases in which blood flow through the arteries is greatly reduced due to their narrowing (stenosis) or complete blockage (occlusion).
In KHOZANKA there are three main types of diseases:
- obliterating atherosclerosis (develops in old age);
- obliterating endarteritis (thrombangitis, nonspecific inflammation of the vascular wall, occurs more often at a young age);
- peripheral forms of nonspecific aortoarteritis.
The most common of these diseases is considered to be obliterating atherosclerosis.
Common diseases of blood vessels and arteries of the legs
Due to the global spread of vascular pathologies of the lower extremities, some people consider them to be normal, since disorders associated with them are observed in every second adult patient. But this does not mean that these diseases do not need treatment. Neglecting their therapy can result in extremely serious complications, therefore, if alarming symptoms are detected, it is important to consult a doctor for differential diagnosis and selection of the correct treatment tactics.
In medical practice, such diseases are divided into several groups:
Atherosclerosis obliterans (OAOS) is a chronic degenerative metabolic process associated with hardening of arterial walls against the background of excessive deposits of lipids and cholesterol. These substances, in turn, become catalysts for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, which can gradually narrow the lumens of blood vessels and lead to their absolute closure, associated with impaired nutrition and tissue viability.
Atherosclerosis is one of the leading causes of disability and mortality worldwide. Its characteristic features:
- pain in the legs, aggravated by running, climbing stairs and fast walking,
- intermittent claudication syndrome.
Obliterating endarteritis is a rapidly progressing disease of the arteries of the legs, associated with a gradual narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and necrosis of tissues deprived of blood supply. The nature of the pathology has not been thoroughly studied, but doctors consider the key cause to be an inflammatory process associated with the predominance of autoimmune antibodies in the vessel.
Signs of the disease:
- rapid fatigue of the limbs when walking,
- sudden cooling of the extremities without objective reasons,
- swelling,
- formation of ulcers.
Acute arterial obstruction is a disease that occurs as a result of an abnormal increase in blood clotting (hypercoagulation), as well as against the background of an inflammatory or atherosclerotic process, leading to modification of the vascular walls and a sudden cessation of blood flow. This pathology often causes acute arterial ischemia syndrome.
It is expressed mainly in arterial spasm of both the affected and healthy legs.
Varicose veins are a common disease characterized by degenerative changes in the superficial veins, in which there is a loss of their elasticity, stretching, rapid growth and the formation of additional nodes.
The symptoms of this pathology are quite specific:
- congestive swelling of the legs,
- convulsions,
- change in skin pigmentation,
- feeling of heaviness
- soreness and fatigue,
- Characteristic bumpy nodes appear under the skin, often accompanied by itching and burning.
This pathology is accompanied by such aggressive complications as acute thrombophlebitis and intense bleeding.
Thrombosis of the superficial venous system is a syndrome that often results from varicose veins with an adjacent infectious process.
Signs:
- severe hyperemia and acute pain in the limbs,
- the occurrence of infiltrates localized along the course of the affected vein.
Venous thrombosis is the process of thrombus formation associated with dysfunction of coagulation and blood flow, inflammation or disruption of the integrity of the venous wall.
Signs:
- rapidly growing swelling of the limb,
- severe hyperemia and hyperthermia,
- cutting pain
- bluish skin at the site of injury,
- arterial spasms.
An aneurysm is a diffuse or saccular protrusion of part of an artery associated with an expansion of the lumen of a blood vessel and a decrease in its tone (excessive stretching or thinning of the wall).
The disease manifests itself in:
- limb weakness,
- periodic pain that tends to subside on its own,
- numbness, pulsation, coldness of the affected area,
- formation of a tumor-like neoplasm under the skin.
Vascular network (telangiectasia) is an abnormal proliferation of subcutaneous capillaries, accompanied by a local accumulation of thin capillary lines of a blue, red or purple hue, resembling a cobweb, an asterisk or a chaotic mesh in shape.
It is painless and does not pose a potential risk to the health and life of the patient. Amenable to gentle surgical and hardware treatment. In the vast majority of cases, it brings purely aesthetic discomfort to the patient.
How does the disease manifest itself?
With atherosclerosis of the extremities, a person begins to experience sharp pain when walking and lameness appears. After walking short distances, the patient feels terrible fatigue, stiffness in movements, cramps, and his toes go numb. It seems that the leg suddenly became unbearably heavy, as if a weight had been put on it. Typically, one leg is affected by atherosclerosis of the lower extremities. After rest, the pain goes away, but not for long.
Cause of numbness in legs
Probably each of us remembers this unpleasant feeling when our legs go numb and you simply can’t feel them. This includes tingling throughout the body, a “chill,” and a feeling of temporary paralysis of the limbs. There are different reasons for this:
- uncomfortable sitting position, when nerve endings are compressed;
- diabetes mellitus;
- poor circulation in the legs,
- manifestation of osteochondrosis;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- migraine;
- multiple sclerosis;
- inflammation of the nerves in various diseases: arthritis, etc.
Fortunately, numbness in the legs is not always a harbinger of serious illness. However, this is always a reason to immediately contact a vascular surgeon.
Risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities:
- age 40 -50 years;
- male gender;
- large amounts of alcohol;
- smoking;
- high cholesterol levels;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- stress;
- sedentary and sedentary lifestyle.
Atherosclerosis of heart vessels
With atherosclerotic heart disease, the lumen of the aorta and coronary vessels narrows, and blood flow to the organ is limited. If the disease is not diagnosed in a timely manner, serious complications are possible, including coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and aneurysm. In the most severe cases, death occurs.
The main factor in the development of pathology is elevated cholesterol levels. Often the disease develops in people with excess body weight, metabolic disorders, and with an abundance of animal fats in the diet. The risk group also includes people with low physical activity, nicotine addiction, hypertension, and over the age of 45 years.
If the blood supply and functioning of the heart are impaired, the patient feels pain in the chest on the left side. Unpleasant sensations intensify with exertion
Atherosclerotic heart disease also manifests itself as shortness of breath, dizziness, anxiety, and sometimes loss of consciousness.
Classification of stages of arterial insufficiency of the lower extremities
- Stage 1 (a person is able to walk freely for about a kilometer);
- Stage 2 (the patient is able to walk about 200 meters without pain);
- Stage 3 (a person can move less than 50 meters, he begins to be very bothered by “pain at rest”, in which even during a night’s rest the patient feels the need to lower his foot to the floor several times a night);
- Stage 4 (necrotic changes develop in the toes).
At the last stage of the disease, amputation is possible.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities:
- lameness;
- rapid fatigue when walking;
- pain when walking in the calf muscles and thigh muscles;
- feeling of muscle contraction;
- numbness in the legs and a constant feeling of coldness in the extremities;
- in the stage of exacerbation of the disease, the color of the skin on the affected leg may change, it will become a pale bluish tint.
A more severe stage of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increasing lameness;
- legs constantly go numb;
- the pulse cannot be felt during palpation in the popliteal fossa, on the ankle and thigh;
- pain not only when walking, but also at rest;
- insomnia at night due to pain and numbness in the legs;
- cyanosis of the skin, the skin becomes brownish-red in color, hair falls out on the skin of the legs, nails peel, ulcers appear on the heel and toes.
Chronic arterial insufficiency of the lower extremities affects 2-3% of the population, while obliterating atherosclerosis of the arteries accounts for 80-90%. Unfortunately, at present KHOZANK has become much younger. If previously older men suffered from these diseases, now they affect even young men and girls. There is a high risk of developing diseases in this group in smokers. When smoking 20 cigarettes a day, the risk of developing COPD increases 4-6 times. Every year, tens of thousands of people die as a result of obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the legs.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis
With atherosclerosis, the inside of the vessels becomes covered with fatty plaque. Gradually it becomes denser, and the vascular walls can no longer expand and contract. Sometimes lipids form plaques inside the vessel, as a result of which the lumen narrows and blood circulation is impaired.
The accumulation of lipids occurs for years unnoticed by the patient himself. There is an asymptomatic period in the course of the disease, when the patient is not even aware of its existence.
The first signs appear when the lumen of the vessel narrows by 50% or more. Further in the course of the disease there are 3 stages:
- Ischemic. Insufficiency of the organ's blood circulation is diagnosed. Atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels leads to the development of angina.
- Thrombonecrotic. At this stage, thrombosis of the altered arteries appears.
- Fibrous. In organs with poor blood supply, connective tissue grows.
Clinical manifestations depend on the location of the disease. Atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta makes itself felt by flatulence, abdominal pain, constipation, and numbness of the extremities.
When the thoracic aorta is damaged, burning pain behind the sternum is bothersome, which radiates to the neck and arms. If blood circulation in the brain is disrupted, the patient's mental state changes. When the vessels of the extremities are damaged, numbness and chilliness occur.
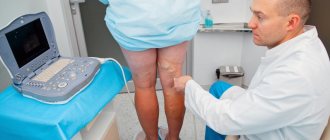
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the extremities
To make a correct diagnosis and find out whether you have atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, you need to undergo a full examination. This will help to identify the degree of vascular patency and blood supply to the legs, determine the level of occlusion and the extent of vascular pathology in atherosclerosis.
1 Determination of pulsation of arteries of the extremities
2 Determination of pulsation of arteries of the extremities
3 Determination of pulsation of arteries of the extremities
To do this you need:
- get advice from a vascular surgeon;
- measure blood pressure in the arms and legs;
- determine the pulsation of the arteries of the limbs;
- undergo MCT angiography;
- undergo duplex scanning of peripheral arteries.
1 Consultation with a vascular surgeon in MedicCity
2 Ultrasound of arteries in MedicCity
3 Ultrasound of arteries in MedicCity
Factors influencing the development of atherosclerosis
- Increase in blood cholesterol over 250 mg%.
- High blood pressure.
- Hormonal factors. For example, it has been proven that estrogens inhibit the development of atherosclerosis.
- Social factors play an important role in the development of atherosclerosis. The example of South Korea shows the connection between the development of atherosclerosis and the level of stress. Atherosclerosis is constantly being discovered in war-affected residents, despite a generally healthy lifestyle.
- Obesity and physical inactivity.
- Hereditary factor.
- Imbalance of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems.
Treatment
Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to completely cure atherosclerosis, but it can be stopped and thereby alleviate the patient’s condition. With the help of treatment, it is possible to reduce pain in the affected area of the limb, increase comfort when walking over certain distances, prevent the risk of complete blockage of the veins and prevent the development of gangrene, as well as stroke and heart attack. Therefore, treatment must be constant, comprehensive and continuous.
Great importance is attached to the prevention of the disease, so it is important to move more, lead a healthy lifestyle, stop smoking and drinking alcohol. With the development of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, it is important to choose the right diet by removing foods with high cholesterol content from your diet and adding foods containing polyunsaturated fats.
Remember, if your arms and legs are numb, this may be a symptom of incipient problems with blood vessels. Therefore, if you already feel numbness in your legs and pain when walking, seek help from a specialist! In the multidisciplinary clinic "MedicCity" you can receive treatment from highly professional vascular surgeons who use the most modern techniques.
Varicose veins of the legs
This is a very common disease of the veins of the lower extremities, characterized by decreased elasticity of the venous walls and valve failure, as a result of which blood stagnates in the veins, the vessels dilate, lengthen, and form protruding nodes under the skin. The disease most often affects women. The exact causes of varicose veins are not clear. Provoking factors include:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Valve defects and weakness of the venous walls.
- Significant loads on the legs.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives.
- Overweight.
Thrombosis
Inflammation of the deep veins and the formation of blood clots in them is called thrombosis. A thrombus quickly forms, and if it is not tightly attached to the wall of the vein, it can break off at any time and move along the vascular bed.
The main causes of thrombosis are as follows:
- congenital vascular pathologies;
- hormonal disorders;
- tumors;
- injuries with vascular damage;
- fractures;
- surgical interventions;
- leg paralysis and paresis;
- severe infections;
- excess weight.
In addition, provoking factors include:
- elderly age;
- heavy physical activity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- prolonged bed rest and immobility;
- bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking).
Symptoms of the disease are not always clearly expressed. Thrombosis can be suspected based on the following signs:
- Bursting, tugging, squeezing pain in the evening.
- Numbness and crawling in the lower legs.
- Heaviness in the leg at the end of the day.
- Swelling and increase in volume of the affected limb.
- Thinning of the skin of the affected leg, pallor and cyanosis.
- Glossy leather.
- Increase in temperature (general and local).
- Filling of the superficial veins with blood and their pronounced pattern under the skin.
- The temperature of the diseased leg is lower than that of the healthy leg.
Treatment of thrombosis can be conservative and surgical. In the first case, drugs of the following groups are prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory;
- anticoagulants of direct and indirect action;
- enzymes with thrombolytic properties;
- agents that improve microcirculation and blood fluidity.
In addition, elastic bandaging or wearing compression stockings is recommended.
Surgical treatment is prescribed for severe inflammation, a floating thrombus and a high risk of thrombus rupture with subsequent development of pulmonary embolism. The most common operation is thrombectomy, during which the clot is removed and blood flow is restored.