- The designation HCT in a blood test is an indicator of the hematocrit value and is included in the parameters of the general examination (CBC);
- Other abbreviations – Ht, Crit, Hematocrit, PCV ( Packed C ell Volume )
- Hematocrit is the ratio of the volume of red blood cells, that is, red blood cells, to the liquid part of the blood (plasma);
- Red blood cells - cells containing hemoglobin, carry oxygen, and the hct index in the general analysis shows the usefulness of this process;
- Studying the hematocrit level is necessary to exclude or diagnose anemia, the degree of dehydration, as a monitoring step during treatment.
What does hematocrit show?
This is the volume of red blood cells in relation to the fluid mass of the blood, but taking into account the size and type of red blood cells. A huge number of processes in the body depend on red blood cells, since it is red blood cells (RBC) and the hemoglobin contained in them that deliver the necessary oxygen to cells.
It may seem that the hematocrit level and the volume of red blood cells in the blood are the same value. This is partly true, but only in the case when at least 70% of all red blood cells are of normal size, that is, no more and no less than 7-8 microns in diameter. These types of RBC are classified as normocytic, that is, complete, carrying a sufficient amount of oxygen.
This blood test should be considered in conjunction with other red blood cell indices so that the hematocrit data will be most useful and provide information to determine a treatment plan or select missing micronutrients.
Healthy red blood cells and abnormalities
When studying hematocrit, it is clearly visible that red blood cells differ in size. Such heterogeneity is considered normal, called anisocytosis, and is not a threat as long as the difference between healthy and altered red blood cells does not exceed the norm. A number of pathologies, including micronutrient deficiency and the consequences of their deficiency , alter the normal ratio between mature and non-functional red blood cells. When there are more red cells with atypical sizes, a blood test reveals deviations from the norm in hematocrit.
Hematocrit is reduced
This occurs due to the presence of microcytes in a larger volume than acceptable. The number of red blood cells in the test results is determined to be normal, but the distribution density of RBCs is reduced due to their small size.
Elevated hematocrit values
If there are more excessively large cells (macro- or megalocytes) among the red blood cells in the blood, hct indicators increase, but the total number of red blood cells themselves is determined to be insufficient.
HCT levels above 55% require close attention in blood tests and further diagnostics.
Hematocrit number
The hemorrhage value reflects the degree of saturation of the blood with red blood cells and their performance. Red blood cells act as a conductor of oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and carbon dioxide in the opposite direction. This is their main function. In addition, red blood cells are responsible for the delivery of vitamins, amino acids, cholesterol and glucose from the digestive system to cells.
Take part in:
- in maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body (homeostasis) and the processes of adaptation to biological changes;
- in nutrient metabolic processes;
- in protecting blood vessels from the negative effects of free radicals.
The hematocrit level shows how much the blood is filled with red cells to ensure the full functioning of the body.
What affects hematocrit
There are many reasons explaining the fluctuations in this indicator, but all of them can be divided into two parts. This is an insufficient intake of micronutrients into the blood and/or their incorrect absorption, as well as diseases: chronic, systemic, autoimmune. Both reasons are closely related, since impaired metabolism of useful substances leads to a number of pathologies, and such preconditions are observed not only in the aspect of the hematopoietic system. However, it is in the formation of blood quality that micronutrients play an extremely important role.
Diseases, consequences of treatment
Any pathology always has a reason, and most often it is an imbalance of micronutrients, metabolic disorders, sometimes aggravated by lifestyle. Less commonly – autoimmune reactions of the body and the administration of drugs prescribed in the course of treatment of various diseases.
The following diseases and methods of combating them are a priority for diagnosis if low hematocrit values .
— anemia – various types of this pathology occur against the background of a lack of a group of basic micronutrients or when their absorption is impaired;
- acute bleeding - both in injuries and in chronic forms;
- cirrhosis of the liver - the organ is the main “filter” of the blood, participates in the process of erythropoiesis, supplying the red bone marrow with the necessary iron for the formation of red blood cells;
- kidney pathologies - this organ produces the hormone erythropoietin (hemopoietin), also necessary for the formation of fully functional red blood cells;
- oncological diseases - affect the functioning of all body systems, one way or another, affecting the production of red blood cells;
- hydration - excess fluid in the body, also after drips with saline or other intravenous fluids.
Elevated hematocrit is characterized by another group of diseases and conditions:
-COPD – chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lack of oxygen and hypoxia directly affect the quality of gas exchange, leading to a weakening of antioxidant protection. Oxidative stress, in turn, reduces the efficiency of the transport function of red blood cells and changes the structural and functional state of red blood cells as a whole.
- heart failure - especially with a tendency to aggregation (sticking together) of red blood cells. Blood microcirculation is disrupted, swelling appears, and the quality of metabolic processes is lost;
- polycythemia - excess production of red blood cells;
- kidney disease, tumors - increased production of the hormone erythropoietin occurs;
-dehydration is dehydration, a reversible condition that can occur with any poisoning, injury, or during diabetes therapy.
It is worth noting that fluctuations in hematocrit do not always indicate pathology or impaired metabolism of vitamins and nutrients. HCT test results are closely related to fluid imbalance in the body, and these conditions are inevitable during pregnancy. During the gestation period, the value often drops below normal and this phenomenon is normal, since the expectant mother’s body is often swollen. When there is excess fluid in the tissues, the liquid portion of the blood also increases. Against this background, the hct volume looks reduced. There is no reason for concern, since the absolute values of red blood cells and in particular hemoglobin remain unchanged.
On the contrary, an increase in hct is often observed in smokers, as in the case of COPD, this is due to a lack of oxygen supply to cells.
Micronutrient deficiency
Iron and vitamins B9 and B12 play a critical role in maintaining a healthy hematocrit level.
— iron is an element involved in the formation of hemoglobin, which is part of the red blood cell and carries oxygen along with the blood, an essential element of most reactions in the body, a priority important part of cellular nutrition;
-vitamin B6 is water soluble, like the entire B group, that is, it does not accumulate in the body. Together with iron, it is required for the synthesis of hemoglobin;
— vitamin B9 or folic acid is an extremely important element for growth, development, in particular, of blood cells, the full functioning of the circulatory system, and immunity;
— vitamin B12 – a group of cobalamins. Actively affects hematopoietic processes; a lack of this vitamin can provoke megaloblastic anemia.
Both vitamins B9 and B12 are required for normal DNA synthesis and cell division. All four micronutrients (B8, B9, B12 and iron) are key, essential elements for meeting the needs of the hematopoietic system. Other compounds are also important, but their role can be considered secondary, auxiliary. These are copper, calcium, tocopherol (vitamin E), Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids.
Reference values
The volume of red blood cells in the body is not a constant value, so the hematocrit depends on the following conditions:
- patient's gender;
- age category;
- chronic pathologies.
Temporary conditions of the body (pregnancy, infectious viral diseases, physical overload) are of no small importance. A change in the hematocrit number indicates the density (level of concentration) of the blood. In women, the standard values are lower than in men, since due to physiological characteristics the blood is renewed more often. In addition, the total amount of fluid in the body decreases with age, so children's HCT changes as they get older.
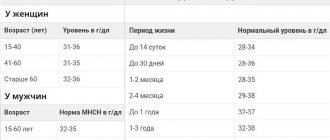
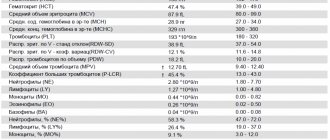
HCT reference values for adults
| Floor | Men | Women | ||
| Age | 18–45 | 45+ | 18–45 | 45+ |
| Norm (%) | 39–49 | 40–50 | 35–45 | 35–47 |
Reference! The average hematocrit for a healthy adult is 40–45% of the total volume of biological fluid.
The maximum permissible upper limit is 50%, the lower limit is 35%. The liquid part of the blood, accordingly, should not occupy less than 50% and more than 65%. When hematocrit values are less than 35%, as a rule, diet correction and systematic monitoring of TCA indicators are prescribed. A decrease in HCT by up to 25% is compensated not only by diet therapy, but also by taking medications. The patient's condition requiring hospital treatment is determined by a hematocrit value of less than 20%.
Normal children's indicators
Children's HCT norm is determined according to age category. Indicators approach adult values at puberty. Standard indicators for children and adolescents:
| Age | Newborn | Infants up to one year old | 1–5 years | 6–11 years | Puberty | |
| Boys | Girls | |||||
| Norm (%) | 33–65 | 33–44 | 32–41 | 33–41 | 35–45 | 34–44 |
Depending on the laboratory conducting the research, standards for children may have a more detailed gradation by age.
The high level of hematocrit in a newborn baby is explained by the transition from the intrauterine state, when the baby is in the amniotic fluid, to a full life (outside the liquid environment).
Micronutrients for the hematopoietic system
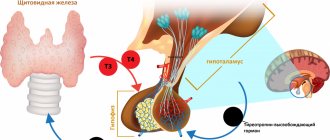
Hematopoiesis - that is, hematopoiesis - is a set of stages in the transformation of a stem cell into one of the elements that make up the blood. Let us repeat that the role of vitamins B6, B9 and B12 and iron in these processes is a priority, and jumps in hct levels always one way or another lead to the conclusion about a lack of these substances.
In addition to these four, attention should be paid to other nutritional compounds.
- Vitamin E is a fat-soluble form and can accumulate in any tissue, but mainly in fat. Protects red blood cell membranes from damage due to oxidative stress;
- Vitamin C – adds iron to the process of hemoglobin synthesis, starting with the formation of red blood cells in the red bone marrow;
- Vitamin A (retinol) – helps transfer iron from “reserves”;
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) – helps not to remove the necessary iron prematurely through the genitourinary system;
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) - helps transport iron from storage cells to the red bone marrow, where hemoglobin is produced in the red blood cell;
- Copper - helps iron oxidize to the level of digestibility (ferrous);
- Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids stimulate and regulate the formation of new cells in the process of erythropoiesis (the formation of red blood cells).
Often, if hct tests are questionable, you can turn to an additional blood test for vitamins and microelements that are involved in hematopoiesis. Based on detailed data, we can talk about developing a personal complex of micronutrients that will meet the needs within the framework of the individual characteristics of the body.
Where to take a blood test for hematocrit
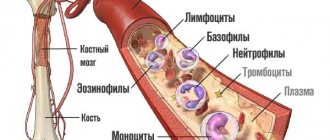
The study of the hct level is part of the erythrocyte indices, which in turn are included in the CBC - a blood test that was previously called clinical, and within the framework of modern laboratory standards - general. This analysis examines white blood cells, platelets and red blood cells. Blood is not donated separately for hct, but a general examination (CBC) can be ordered at any medical clinic.
Also, to collect blood in a place convenient for you, at home or at a specified location, and then conduct a study with a transcript and detailed recommendations on the plan for introducing a micronutrient intake program, you can contact bioniq specialists:
- We conduct studies of up to 50 blood parameters and various indices;
- Free with bioniq BALANCE subscription
- Sterile;
- Medical personnel of the highest category.
Laboratory microscopy
Calculation of the hematocrit number is included in the general clinical blood test. A separate study of this indicator may be prescribed in case of unsatisfactory results of OKA: anemia (anemia) and high concentration of red blood cells, as well as in case of bleeding of various etiologies (origins), in case of dehydration (dehydration) of the body. HCT is an important indicator of chronic hematological diseases.
To obtain objective final data, on the eve of the study, the patient is recommended to eliminate heavy foods (fatty and fried foods) from the diet, eliminate alcohol-containing drinks, and limit sports and other physical activities. The blood sampling procedure is carried out in laboratory conditions, in the morning.
Before the analysis, it is advisable to give up breakfast and smoking. The hematocrit value is determined using a laboratory device into which a glass graduated tube containing the blood sample being tested is placed. An anti-clotting agent is first added to the biofluid.
Under the influence of centrifugal forces (centrifugation), the blood is stratified. Red blood cells precipitate, clearly demonstrating their volume, and the plasma rises to the top. The remaining formed elements (leukocytes and platelets) are concentrated between them.
Brief scheme for hematocrit allocation
In modern laboratories, the process of measuring red blood cell volume is fully automated. The measurement value of hematocrit in clinical microscopy is taken as percentages or units (% multiplied by a factor of 0.01).