pharmachologic effect
Papaverine hydrochloride is a myotropic antispasmodic agent. Reduces the tone and reduces the contractile activity of smooth muscles and therefore has a vasodilator and antispasmodic effect. Causes dilation of arteries, increases blood flow, incl. cerebral. When used in average therapeutic doses, papaverine hydrochloride has virtually no effect on the central nervous system. In large doses, it reduces the excitability of the heart muscle and slows down intracardiac conduction. It is an inhibitor of the phosphodiesterase enzyme and causes intracellular accumulation of cyclic 3,5-adenosine monophosphate, which leads to impaired contractility of smooth muscles and their relaxation during spastic conditions.
Composition and mechanism of action
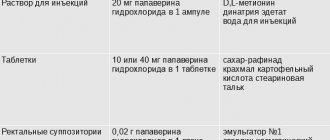
Each ampoule (2 ml) contains a 2% injection solution containing papaverine hydrochloride (20 mg/1 ml), with the addition of the following ingredients: D, L-methionine, disodium edetate, water for injection.
Papaverine in ampoules is packaged in cardboard packages in quantities of 5 and 10 pieces.
Treatment with Papaverine helps to relax smooth muscles in organs and blood vessels, reduce their tone, dilate arteries, which improves blood flow, including cerebral, and leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
The injection solution has a relaxing, but not paralyzing, effect with complete preservation of muscle movements.
The drug inhibits the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE), resulting in the accumulation of cyclic mononucleotides (cAMP) in cells. As a result of this process, calcium ions leave the cells and the contractile activity of muscle fibers decreases.
Injections of the drug in large dosages help slow intracardiac conduction and reduce the excitability of the heart muscle. This property of the drug gives it a sedative effect.
The therapeutic effect of the drug when administered intramuscularly occurs after approximately 20 minutes. after injection and lasts about 5 hours. Papaverine is excreted through the kidneys.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, coma, respiratory depression, atrioventricular conduction disorder, glaucoma, liver dysfunction, old age (risk of hyperthermia), children's age (up to 1 year).
Carefully
The drug should be prescribed with caution and in small doses to elderly and debilitated patients, as well as patients with traumatic brain injury, impaired renal function, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, prostatic hypertrophy, as well as patients with supraventricular tachycardia and those in a state of shock.
Analogs
Papaverine does not have generics, i.e. drugs containing the same active ingredient.
Domestic drugs have the trade name “Papaverine” or “Papaverine hydrochloride”.
Papaverine and No-shpa can not only replace, but also complement each other
However, there are numerous drugs from the group of antispasmodics that contain active ingredients different from Papaverine, but have the same therapeutic effects.
The closest chemical structure and mechanism of action are observed in drotaverine and mebeverine. Medicines have a stronger effect compared to papaverine, but have more side effects.
In some cases, Papaverine can be replaced:
- dibazole;
- hyoscine butyl bromide;
- bencyclane;
- theophylline.
In any case, both the use of the drug and its replacement should be carried out in consultation with the attending physician and after a detailed study of the instructions for the use of papaverine injections.
Directions for use and doses
The drug is administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly and intravenously. 1-2 ml of solution is injected subcutaneously and intramuscularly 2-4 times a day. Intravenously - 1 - 2 ml of a 2% solution with preliminary dilution in 10-20 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution. It should be administered very slowly and carefully, given that the drug can cause the development of atrioventricular block, ventricular extrasystoles and ventricular fibrillation.
A single dose for adults is 0.02-0.04 g (1-2 ml of 2% solution); the interval between administrations is at least 4 hours. For elderly patients, the initial single dose should not exceed 0.01 g. For children from 1 year to 12 years, the maximum single dose is 0.3 mg/kg body weight.
Pregnancy
Injecting the drug intramuscularly or into a vein maximizes its bioavailability.
Despite the fact that special studies have not been conducted to prove the harmlessness of using the drug during pregnancy, the popularity of papaverine during this period is beyond doubt.
The dosage is calculated by the doctor on an individual basis and is 1–10 ml 2 to 4 times a day.
The drug begins to act 10 minutes after its administration. There is a decrease in pain, elimination of uterine hypertonicity and symptoms of gestosis. The risk of miscarriage and premature birth is significantly minimized.
The use of papaverine is relevant both in the early stages of pregnancy and in the later stages.
High uterine tone, threat of miscarriage, premature labor do not exclude the use of Papaverine together with No-Shpa.
Side effect
Allergic reactions, nausea, drowsiness, decreased blood pressure, constipation, increased transaminase levels in the blood, eosinophilia, and increased sweating are possible. With rapid intravenous administration, as well as with high doses, atrioventricular block and heart rhythm disturbances may develop.
Overdose
Symptoms: blurred vision (double vision), weakness, drowsiness, hypotension. Treatment: gastric lavage (milk, activated carbon), maintaining blood pressure.
Reviews
Svetlana, 25 years old, Murmansk, young mother The pregnancy was long-awaited, but it was difficult. The uterus was constantly in good shape, suffered from severe swelling and increased blood pressure. She was constantly in the hospital due to the threat of a breakdown. Doctors prescribed papaverine along with other medications. The drug was injected 4 times a day. My health improved almost immediately. She gave birth to a healthy child.
Elena Gennadievna, 65 years old, Belgorod, pensioner High blood pressure is a problem that has haunted me for several decades. I have a small pension, so many effective medicines on the shelves of pharmacies remain inaccessible to me. The attending physician prescribed triad injections and explained how much of each component the ampoules contained and what they were intended for. The composition turned out to be very effective, it relieves pressure very quickly. Plus, all the ingredients are cheap and don't cause me any side effects.
Svetlana, 32 years old, Rostov, engineer The few days before the start of menstruation were real hell for me. Cramping pain in the lower abdomen did not allow me to live normally. Often I had to get sick leaves or certificates from the clinic, since work was out of the question. My mother advised me to take papaverine injections, arguing that it would relieve pain and would not cause harm. I still use her advice to this day. Injections two days before my period provide me with a full life.
Indications
Papaverine is taken once to relieve pain symptoms associated with:
- renal colic;
- spasm of the smooth muscles of the abdominal organs;
- cerebral vascular tone, leading to migraines;
- difficulty urinating due to spasm of the urinary tract;
- bronchospasm.
Papaverine is often used before abdominal surgery in the abdominal area. By relieving spasm of the abdominal area, the drug reduces the risk of complications arising during the intervention. In addition, the active substance facilitates proctological examinations and urogenital therapy procedures.
Papaverine: what is this medicine for?
According to its purpose, Papaverine is a widely used antispasmodic. Once in the body, the drug can not only relieve spasm of smooth muscles, but also relax the blood vessels, allowing them to expand, and also relieve spasm from the respiratory organs, for example, from the bronchi. As a result, blood circulation improves and tissues receive more oxygen. Special doses of the drug can reduce cardiac excitability and affect the central nervous system.
Indications for the use of Papaverine are:
- Pain due to inflammation of the gallbladder associated with spasm of the ducts, which prevents the passage of bile, which becomes the root cause of the formation of stones.
- Contraction of the gastric pylorus, which prevents food from entering the duodenum from the stomach.
- Bronchospasm of various etiologies.
- Spasms of blood vessels, including the brain.
- Angina pectoris (as a complex therapy).
Papaverine may be prescribed before certain types of surgery to prevent abdominal cramping.
Packaging and appearance
The tablets are snow-white, round in shape. Upon contact with the receptors of the tongue, they transmit a bitter taste. They have no smell. The drug for systemic treatment orally is packaged in plastic blisters of 10 pcs. The cardboard package contains 5 blisters. Companies that package papaverine in paper blisters allow individual releases of 1 blister.
Rectal suppositories are packaged in 5 pieces in an aluminum or plastic blister. Each cardboard box contains 10 candles (2 blisters). Suppositories are white, may have a yellowish tint. They are narrowed at one end, which facilitates insertion into the rectum.
The solution for intravenous administration is transparent, colorless. Packaged in glass ampoules, each with a volume of 2 ml.
Use in pregnant and lactating women
During pregnancy, Papaverine injection solution is used very rarely, only if there are serious indications for it. Injections are given under the strict supervision of a doctor. Most often, expectant mothers are prescribed Papaverine in the form of rectal suppositories to relieve uterine hypertonicity.
During breastfeeding, Papaverine injections are given under the supervision of a doctor. Studies have not revealed any negative effects on infants, however, self-medication is contraindicated; the drug must be prescribed by a doctor.
Papaverine for tone: how many times a day
Depending on the condition of the pregnant woman, two schemes for using suppositories with papaverine can be prescribed:
- Use the drug strictly at night for 5 days in a row. A one-time dose is acceptable in situations where the tone of the uterus increases only from time to time.
- With constant tone, 3 doses are prescribed during the day. Preferably in the morning, after bowel movements, during the day and before bedtime. The duration of administration according to this regimen can only be regulated by a doctor.
Why papaverine injections?
In addition to tablets and suppositories, there is also a dosage form in the form of a solution for intravenous or intramuscular administration. This method of delivering medicine to the body is used when there is no time to wait for the drug to be absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract. Among these patients are pregnant women. They may be prescribed Papaverine by drip method. While staying in hospital for preservation, women receive regular doses of Papaverine, and the result can be monitored by an obstetrician in order to promptly make adjustments to therapy if necessary.
Pharmacology
Papaverine belongs to the group of antispasmodics. Being an opium alkaloid, it affects smooth muscles, relieving tension and promoting relaxation.
The mechanism of action is explained by chemical reactions triggered by the drug entering the blood: papaverine affects muscle excitation by inhibiting phosphodiesterase. As a result, cells begin to accumulate cycloadenosine monophosphates and release calcium ions. The result of the reactions is relaxation of smooth muscles, relief of spasm of the esophagus, as well as the canals of the genitourinary and respiratory systems. In addition, vascular tone decreases, and therefore the walls become more elastic.