ESR is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. This indicator does not diagnose a specific disease, but helps the doctor build a diagnostic hypothesis. Depending on your symptoms, you will be prescribed tests that will help determine the diagnosis.
In addition to inflammatory diseases, accelerated ESR can occur with increased physical activity, a starvation diet, or the use of certain medications.
The rate of erythrocyte sedimentation increases primarily due to an increase in the level of globulins and fibrinogen, this may indicate: the formation of necrosis, the development of the inflammatory process, the appearance of malignant tumors, and disorders of the immune system.
Detailed description of the study
ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is a nonspecific indicator that reflects the presence of any inflammation in the body.
This method is available in all laboratories and is easy to perform, which allows you to quickly assess the patient’s condition and the effectiveness of the treatment.
ESR is an indicator that indicates the rate of separation of blood into upper and lower layers with the obligatory addition of an anticoagulant - a substance that reduces blood clotting. The specific gravity of red blood cells is greater, so due to gravity they end up at the bottom. The top layer contains plasma, and the bottom layer contains red blood cells. The speed is estimated by the height of the appearance of the plasma and is measured in millimeters per hour.
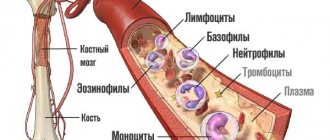
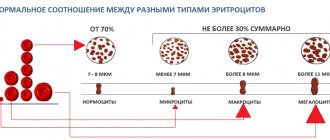
All red blood cells have the same electrical charge on their surface. This property allows them not to stick together in the blood, but to repel each other. When the charge on the membrane changes, they stick together and form so-called “coin columns”.
An increase in ESR is almost always proportional to an increase in the concentration of leukocytes and CRP (C-reactive protein) - other nonspecific markers of inflammation. With increased formation of proteins in the acute phase of inflammation, as well as with changes in the qualitative and quantitative state of red blood cells, a change occurs in the cell membrane, which leads to their gluing and, as a consequence, an increase in ESR.
The process of erythrocyte sedimentation is divided into 3 phases:
- Slow sedimentation in the form of individual cells;
- “Columns” form, and the settling process accelerates;
- Gluing of red blood cells with a gradual cessation of any movement.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a variable value and depends on a large number of factors, both physiological and pathological:
- In women, the ESR is normally slightly higher than in men;
- During pregnancy, ESR is slightly increased due to changes in blood composition, especially protein;
- With anemia - a reduced concentration of red blood cells in the blood) - an acceleration of ESR is observed;
- With an increased concentration of erythrocytes in the body, a slowdown in sedimentation rate is observed;
- During the day, there is a fluctuation in speed and the maximum value can be recorded during the day;
- Newborns have a minimum sedimentation rate, this is due to a high concentration of red blood cells and a small amount of serum proteins;
- A latent inflammatory process that can go away on its own within a few months (extremely rare);
- Oncological and autoimmune diseases;
- For diseases of the thyroid gland: thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism;
- Morphological changes in erythrocytes - anisocytosis, spherocytosis, macrocytes - also affect their sedimentation rate.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a nonspecific indicator and can change for various reasons. Therefore, for a complete diagnosis of the condition, it is important to supplement the analysis with a general blood test with leukocyte count and C-reactive protein. To assess the condition, it is important to perform a dynamic analysis, since an increase in ESR is observed a day after the onset of the inflammatory process, and a decrease is a long-term process that can last up to a week.
Assessing the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is important to detect inflammation in the body. In autoimmune diseases, the use of this indicator helps to determine the activity of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
The main clinical conditions that can increase ESR:
- Chronic and acute inflammatory processes;
- Blood diseases;
- Diseases of the pancreas, intestines, kidneys and liver;
- Rheumatological diseases (RA, SLE, gout, etc.);
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Diseases of the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus).
For a more accurate diagnosis, you need to seek help from a doctor, since identifying the cause of the disease may require a set of tests, which depends on the symptoms manifested. It is also important to remember that the level of ESR in many diseases does not increase immediately, but after a day, and after complete recovery it can remain elevated for up to four weeks.
Immunodiagnostics at the “Three I” Clinic is a multifaceted and comprehensive approach to identifying the exact causes of the disease. The specialists of the “Three I” clinic have many years of experience in accurately diagnosing the causes of accelerated ESR. Come, our specialists will help you. The teamwork of the clinic’s doctors and modern equipment will resolve all questions about the state of your immune system and provide qualified assistance in a variety of medical areas.
Price for consultation with a doctor: from 1500 rubles.
Make an appointment
Important Notes
Material for research Capillary blood.
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood. Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications)! According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible: in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
What is elevated ESR syndrome?
Previously, this laboratory research method was called ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation reaction). RPE is a special value that indicates the ratio of proteins in the blood. The diagnosis is made with the help of coagulants that reduce clotting. The time of red blood cell deposition is fixed.
Increased sedimentation rate syndrome - what is it? This is a deviation from the norm, which is characterized by rapid sedimentation of erythrocytes. In some cases this can last for several years. This usually indicates the presence of some disease, including tumors. But in cases where there are no symptoms of the disease for a long time and no pathology has been identified, treatment is not required.
In addition, pregnant women experience increased sedimentation time syndrome, which is not a deviation from the norm, but the body’s reaction to changes occurring in it.
Consequences and danger of the syndrome
Shortened sediment syndrome requires specialist supervision, as it is a sign of the development of quite serious diseases. The consequences of neglect and lack of treatment include pneumonia, tuberculosis, heart disease, cancer and more.
They are often assessed using a test for the presence of C-reactive protein, which can be used to determine the presence of inflammation.
Additional tests are needed to determine the cause of accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation. If there are no pathologies, neoplasms or inflammatory processes, and the patient feels well, sedimentation rate syndrome does not require treatment.
Reasons for accelerated ESR
Experts have identified several reasons why erythrocyte sedimentation time may increase. Most often this is caused by inflammatory processes in the body as a result of the development of various diseases.
Reasons for accelerated sedimentation time:
- Infectious diseases that are chronic or acute. These include sepsis, pneumonia, tuberculosis. Clinical studies of plasma determine the stage of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. With bacterial infections this figure is much higher than with viral infections.
- Rheumatic diseases characterized by changes in connective tissue.
- Diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract. These include pyelonephritis, gastritis, ulcers.
- Various pathologies of the endocrine system, for example, diabetes or hypothyroidism.
- Anemia or leukemia.
- An inflammatory process occurring in the heart muscle.
- Fractures or trauma also cause an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation time.
- Lead poisoning or ingestion.
- Cancer. But this indicator cannot accurately determine the presence of cancer cells, but is one of the symptoms of pathology.
- Increased cholesterol levels.
In addition, acceleration of sedimentation time is observed in cases where the patient takes drugs such as vitamin D, methyldopa or morphine. Often, an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation time occurs when the patient is not properly prepared for the test.
Prevalence of IDA
Iron deficiency anemia in women is a common pathological condition. Thus, according to WHO (2015), severe iron deficiency is observed in every third woman of reproductive age and in every second pregnant woman, being an important cause of chronic fatigue and poor health, and the third most common cause of temporary disability in women aged 15– 44 years old [12, 19]. In the Russian Federation, despite active preventive and therapeutic measures, the prevalence of IDA remains very high. For example, in Moscow, anemia occurs in almost 38% of gynecological patients [20, 21] and is the most common concomitant pathological process and the first manifestation of the underlying disease, determining the severity of its course and treatment tactics. The main reasons for the development of IDA in women are heavy menstrual bleeding, pregnancy, childbirth (especially repeated ones) and lactation. Anemia often accompanies uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, hyperplastic processes in the endometrium, and ovarian dysfunction. During normal menstruation, 30–40 ml of blood is lost (which is equivalent to 15–20 mg of iron). The critical level corresponds to a blood loss of 40–60 ml, and with a blood loss of more than 60 ml, iron deficiency develops. In women suffering from abnormal uterine bleeding of various origins, the amount of blood lost during one menstruation can reach 200 ml (100 mg of iron) or more. In such situations, the loss of iron exceeds its intake and IDA gradually forms [20].
The most important medical and social problem is anemia in pregnant women, which, according to WHO, is detected in 24–30% of women in economically developed countries and in more than 50% of women in countries with low economic levels [3, 22].
A survey of pregnant women conducted as part of clinical studies in the 2000s showed a high incidence of anemia even among residents of prosperous European countries. Thus, in Belgium (n=1311), Switzerland (n=381) and Germany (n=378) iron deficiency was diagnosed in 6% and 23% (serum ferritin (SF) <15 μg/l) in the first and third trimesters, respectively, of Belgian women; in 19% (SF<12 µg/l) - in Switzerland and Germany. The prevalence of IDA (Hb <110 g/L, SF <15 μg/L) was 16% in Belgium and 3% in Switzerland, although 65–66% of Belgian and Swiss women received dietary iron supplementation during pregnancy. In Germany, IDA was diagnosed in 12% of women [23].
In Russia, according to the Ministry of Health, the incidence of anemia in pregnant women varies from 39% to 44%, in postpartum women - from 24% to 27% [24]. A 2021 systematic review and meta-analysis found that in low- and middle-income countries, pregnancy anemia increases the likelihood of preterm birth by 63%, low birth weight by 31%, perinatal mortality by 51%, and neonatal loss by 2 ,7 times [25].
During pregnancy, there is a significant physiological increase in the need for iron for the normal functioning of the placenta and fetal growth. The total amount of iron required for a normal pregnancy is 1000–1200 mg. To complete a normal pregnancy without developing iron deficiency, a woman must have iron stores in the body at conception of ≥500 mg, which corresponds to an SF concentration of 70–80 μg/L [20, 23].
Treatment
The syndrome of increased sedimentation time is not a disease, but is a sign of the development of pathological processes in the body. These values return to normal after treatment of the underlying disease.
However, in some cases there is no need to lower the value because CRP levels will spontaneously return to normal after wound healing or medication administration or delivery.
During pregnancy, women should follow specialist advice, follow a special diet and take care of their health to prevent the development of anemia.
Anemia can be reduced to normal levels only after the inflammation has passed. To find the cause, the doctor prescribes additional tests, since a general plasma analysis is not enough.
ESR norm
The correct value of erythrocyte sedimentation time in the blood depends on the gender and age of the patient.
- In infants, this value ranges from 1 to 2 mm/hour. Other values are quite rare and are mainly associated with low protein levels, acidosis or hypercholesterolemia.
- In children under 6 months, the subsidence rate is 12-17 mm/hour.
- In older children, this figure decreases again, and the value ranges from 1 to 8 mm/hour. Fine.
- In men, the erythrocyte sedimentation time should not exceed 10 mm/hour.
- In women, values from 2 to 15 mm/hour are considered normal. This range is associated with the action of hormones. But depending on the period of life, the number of red blood cells varies from woman to woman. For example, from the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy this figure increases significantly and by the time of birth it can reach 55 mm/hour. This is normal.
After childbirth, this indicator gradually returns to normal values. During pregnancy, accelerated sedimentation is caused by an increase in blood volume, cholesterol, globulin and a decrease in calcium levels.