Preparation rules
- To donate blood from a finger prick, you need to come to the laboratory in the morning (usually collection occurs from 7.30 to 10 o’clock).
- The test must be taken on an empty stomach, that is, you cannot eat in the morning, you can only drink plain water. The last meal should take place the night before - no later than 8-12 hours before the procedure.
- You can eat a day earlier, but it is recommended that a day or two before the analysis, in order to avoid getting distorted results, you should avoid fatty foods and alcoholic beverages.
- The day before, you should avoid physical and emotional stress.
- In the morning before the procedure, you should refrain from smoking.
How to take a blood sugar test correctly
To ensure that the test results do not turn out to be false, it is necessary to follow some rules for preparing the patient for a blood sugar test. Otherwise, you may need to retake the test (which is a waste of your time and money), or an incorrect diagnosis and treatment may be prescribed.
Is it possible to drink water before testing for sugar?
You can drink water. But no more - it is necessary to exclude alcoholic drinks and drinks containing sugar and sweeteners.
Preparing for a glucose test
- On an empty stomach. 8-hour or better 12-hour fasting. Drink only water. Alcohol (it is better to exclude it for 102 days) and sweet drinks are strictly prohibited.
- Better get a good night's sleep
- Avoid intense mental work, stress and outbursts of emotions. The body can increase blood glucose levels during stressful situations. Excessive emotions can suppress insulin production.
- It is better not to brush your teeth with sugar-containing toothpaste.
- No smoking. (if you have diabetes, it is better to avoid smoking altogether)
- Be careful when taking medications. If it is necessary to treat acute or chronic episodes of the disease, you should warn the doctor about the existing problems and reschedule the study or interpret its results in accordance with the ability of some drugs to increase or decrease the studied parameters
- During the period of colds or other acute infections, the result may be false positive
- On the eve of the analysis, you should not take part in feasts, eat heavily before bed, drink alcohol, indulge in fatty foods, fast food, etc.
- Immediately after therapeutic procedures and serious examinations (massage, ultrasound, x-rays, physical therapy), you cannot take a sugar test.
- The day before and before donating blood for sugar, it is better not to engage in active sports. It is better to spend the day and morning before the analysis in a normal, calm manner.
What not to eat before a sugar test
- fatty and spicy foods;
- sweets, cakes and other sweet treats;
- packaged juices;
- sweet sparkling water;
- fast food.
What then can you eat before testing for sugar?
If you need to prepare for a blood glucose test but are feeling hungry, eat something light and healthy. For example:
- boiled/baked chicken
- green vegetables
- cereals
Is it possible to brush your teeth before donating blood for sugar?
It is not recommended to brush your teeth before the examination, because... Toothpastes contain sugar, which is well absorbed through the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and can affect the accuracy of the analysis. Avoid chewing gum as well.
Preparing for a blood sugar test during pregnancy
Preparing for a glucose tolerance test for pregnant women does not differ from the measures listed above. It is recommended to do a glucose tolerance test at 24-28 weeks.
Typically, such a test is prescribed for pregnant women to prevent excessive weight gain in the fetus, which can be caused by an increase in maternal blood sugar levels. And this can happen even if you've never had diabetes. After all, the heavy loads that the body experiences when carrying a fetus can reveal some pathologies that appear exclusively while expecting a baby. These diseases include diabetes mellitus.
Return to list
General analysis
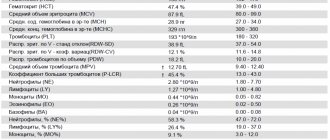
It can be shortened or expanded. The first option includes indicators such as the level of hemoglobin and all blood cells (erythrocytes, platelets, leukocytes), as well as ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
Capillary blood collection from a child
In a detailed analysis, other indicators are added, including:
- hematocrit;
- width of red cell distribution;
- average erythrocyte volume;
- average content of hemoglobin in the red cell;
- leukocyte formula and others.
What is detailed analysis?
A comprehensive blood test is called a biochemical blood test. Blood taken from a vein is examined. It is prescribed when clinical analysis does not provide enough necessary information.
The advantages of this type of analysis are as follows:
- Accurate diagnosis of the disease,
- The ability to determine the level of vitamins in the body,
- The ability to identify the disease at an early stage, in the absence of characteristic symptoms,
Tools
Many people are concerned about their own safety during the test, so they may have questions about what is used to pierce and take blood. Today, almost all medical institutions have switched to using disposable finger pricking instruments. This tool is called a scarifier. It must be removed from the unopened package in front of the patient. It should be said that such a puncture is quite painful, so children really do not like the procedure.
Today, donating blood can be painless. A new device is being used more and more often when blood is taken. This is an automatic lancet in a plastic case. The needle quickly penetrates the skin, so pain is not felt. The new lancets have many advantages:
- the sterile needle or blade is located inside the body, which ensures the safety of patients and medical personnel;
- the reliability of the trigger mechanism eliminates accidental release of the needle or blade;
- reuse is eliminated thanks to the automatic return of the needle or blade;
- the shape of the needle ensures a reduced pain effect;
- the puncture is targeted, its depth is controlled;
- convenient body shape.
Video: Biochemical blood test decoding, table and norm
Despite the fact that the general analysis shows less information, it also has its advantages.
These include the following:
- High speed of the procedure,
- Only pierce the skin surface. The depth of the wound does not exceed 3 mm,
- The fence rules are much easier to follow. This increases the reliability of the result,
- Capillary biomaterial is tested much faster than venous blood,
- In private clinics, the price for a general analysis is lower than the cost of a biochemical one,
Fence algorithm
To work, the laboratory assistant must prepare:
- sterile scarifier;
- cotton wool;
- alcohol;
- tincture of iodine;
- ether.
Disposable scarifier - a tool for pricking a finger
The algorithm and technique for taking are as follows:
- The patient sits opposite the laboratory assistant. The hand (usually the left) lies on the table.
- The puncture site is disinfected with alcohol and degreased with ether.
- Using a disposable scarifier, a puncture is quickly made in the pad of the ring finger, immersing the tool to the full depth of the cutting part (approximately 2-3 mm).
- The first drop of blood is removed using dry cotton wool.
- For the study, use the second and subsequent drops of blood, which are collected using a glass adapter, then placed in test tubes and signed.
- After the blood has been taken, the injection site is treated with alcohol or iodine and clamped with a cotton swab until the blood stops completely.
The algorithm for collecting capillary blood from a child is exactly the same as from an adult.
Technique for collecting capillary blood from a finger
- Soak a cotton ball (gauze) in an antiseptic.
- With one hand, take the 4th finger of the patient's free hand, massage it lightly, pinching the upper phalanx of the finger with the index and thumb.
- With the other hand, treat the inner surface of the upper phalanx of the patient’s finger with an antiseptic with a cotton ball (gauze) soaked in an antiseptic. Dry the surface of the finger with a dry sterile cloth (cotton ball).
- Place the used napkin (ball) in the consumables tray.
- After the skin has dried, take a scarifier and puncture the skin with a quick movement.
- Place the used scarifier in a puncture-resistant waste container.
- Wipe off the first drops of blood with a dry sterile cloth (cotton ball). Place the used napkin (ball) in the consumables tray.
- By gravity or using a capillary, collect the required amount of blood. The volume of blood drawn must correspond to the mark on the tube.
- Press a napkin (cotton ball) with an antiseptic solution to the puncture site. Ask the patient to hold a napkin (cotton ball) at the puncture site for 2-3 minutes.
- Invert the tube into a vertical position to transfer blood from the capillary to the tube.
- Turn the cap off the tube, remove it, and place it in a puncture-proof container along with the built-in capillary without disassembling it.
- Remove the cap from the base of the test tube, tightly close the test tube or close the test tube with a cap until it clicks (depending on the modification of the test tube).
- Mix the sample thoroughly by inverting the test tube.
Why from the ring finger?
Perhaps someone is interested in which finger the blood is taken from and why. The sampling occurs from the ring finger, although it is allowed from the middle or index finger. A puncture, like any violation of the integrity of the skin, can lead to infection. The ring, index and middle fingers have an isolated inner membrane, so if penetration occurs, the infection will first be localized, which means there is time to eliminate it. The thumb and little finger are directly connected to the lining of the hand, and when infected, the infection spreads to the entire hand. The choice of the ring finger is explained by the fact that it bears the least physical load.
FAQ
What is the difference between blood from a finger and from a vein?
There are no fundamental differences between capillary and venous blood. Therefore, for a general blood test, biomaterial can be taken from both a finger and a vein. However, capillary blood contains intercellular fluid, which can lead to the formation of microclots. In addition, the volume of finger-prick blood is insufficient for several tests, and capillary blood is not suitable for many tests. Therefore, finger blood is usually taken when a quick analysis with a small number of indicators is required - medical examinations, express diagnostics. If the patient, in addition to the CBC, requires other studies (biochemical analysis, tests for infections, hormones), venous blood is taken and used for general analysis.
Why is capillary blood taken from the ring finger for analysis?
The ring finger of the left hand takes part in movements and hand work less than other fingers, so the puncture on it will heal faster. Also, due to the small load on this finger, the skin on it is thinner than on others, so the puncture will be less painful. There is another reason - the inner membranes of the little finger and thumb are directly connected to the inner membranes of the hand, so if an infection occurs, there is a risk that it will spread to the entire hand. The membranes of the ring, middle and index fingers are isolated, which minimizes the risk of spreading infection. Blood is not taken from the middle and index fingers, since they are much more actively involved in everyday activities and stress on the hands. For left-handers, blood is taken from the ring finger of the right hand.
Is it necessary to donate blood from a finger prick on an empty stomach?
Yes, this is a prerequisite for a correct analysis result. One of the reasons is that after eating, the number of leukocytes in the blood increases. This is a natural process, but an increase in the white blood cell count may be misinterpreted in the test results. In addition, sugar contained in food causes an increase in glucose levels, and fatty foods provoke cloudiness in the blood serum, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Is it possible to smoke before donating blood from a finger prick?
Smoking before OAC is strictly not recommended. The substances that make up nicotine and tobacco tar change the cellular composition of the blood and affect the content of red blood cells, white blood cells, and glucose. This applies not only to ordinary cigarettes and cigarettes, but also to electronic devices.
When is the best time to donate blood from a finger prick?
Capillary blood is taken for analysis usually from 7 to 10-11 am. This is due to the fact that the test must be taken on an empty stomach, and it is easier to postpone the fasting period at night. In case of emergency, when a patient is admitted to a hospital, after operations, blood is taken from a finger at any time of the day.
When should you not donate blood from your finger?
There are no strict contraindications to donating blood from a finger prick. Women are not recommended to do the test during menstruation, as blood counts change at this time. An obstacle to collecting blood from a finger can be extensive injuries, damage, for example, burns to both hands, as well as the unstable mental state of the patient.
What to do if the blood from your finger does not stop after the test?
Most often, this situation occurs in patients with bleeding disorders. Hypertension and strong anxiety before taking the test can also lead to this. The person needs to calm down, press a sterile swab tightly to the puncture, and raise his hand up. The tampon should be pressed, but not rubbed or massaged onto the pad of the finger, as this will interfere with the formation of a blood clot. You can secure the tampon on your finger with an adhesive tape.
What does the analysis show?
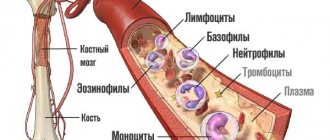
Taking blood from a finger is taken for preventive purposes, for diagnosis and treatment monitoring. This is a basic examination, and the main, most necessary characteristics for doctors that blood shows are the following:
- hemoglobin level;
- red blood cell level;
- ESR;
- leukocyte level;
- relative content of lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils.
Blood collection using an automatic lancet
Using clinical analysis, doctors can diagnose the following pathological conditions:
- leukemia;
- anemia;
- bleeding disorders;
- the presence of an infectious or inflammatory process in the body.
References
- Nazarenko G.I., Kishkun A.A. Clinical assessment of laboratory research results // M.: Medicine - 2006. - 544 p.
- Tatkov O.V., Stupin F.P. General blood test. Information collection // M.: Publishing solutions. — 2021. — 72 p.
- Fauci, Braunwald, Kasper, Hauser, Longo, Jameson, Loscalzo Harrison's principles of internal medicine, 17th edition, 2009
- Mosby's Diagnostic and Laboratory Test Reference 14th Edition, 3251 Riverport Lane
- St. Louis, Missouri 63043: Elsevier Publishing Hall 2019
Interpretation of results
Deciphering should be carried out only by the attending physician. You should not try to do this yourself based on tables that indicate the norm for each indicator. The doctor evaluates the main parameters not only individually, but also in aggregate.
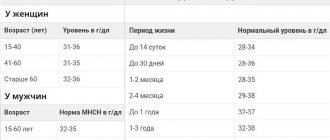
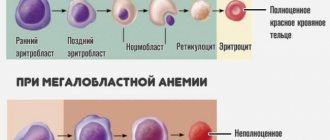
- Hemoglobin level. The norm for women is 120-140 g/liter, for men – 130-160 g/liter. If the content is higher than normal, dehydration, intestinal infections, and congenital heart disease are possible. A low level indicates anemia.
- CPU (color index). The norm is from 0.85 to 1.15%. Low values indicate anemia; elevated values are observed with folic acid deficiency and stomach cancer.
- Red blood cells. The norm for men is 4-5 g/l, for women – 3.7-4.7 g/l. An increase in level indicates renal pathologies, tumors, Cushing's syndrome. A slight excess of the norm can be observed with diarrhea, taking diuretics, and burns. Low levels indicate anemia, overhydration, and blood loss.
- ESR. The red cell sedimentation rate is an indicator of the level of plasma proteins. Normally, in women – up to 20 mm/hour, in men – up to 15 mm/hour. A high level is typical for inflammatory processes, infections, autoimmune diseases, intoxication, endocrine, renal and hepatic pathologies, and oncology. The reasons for the decrease are circulatory failure, hyperbilirubinemia, erythremia.
- Leukocytes. The norm of white cells is 4-9X10⁹/liter. The reasons for the decrease are cancer with secondary tumors in the brain, diffuse connective tissue diseases, typhoid fever, viral hepatitis, leukemia. Increased levels are observed in bacterial and fungal infections, acute inflammation, purulent infections, pneumonia, otitis media, pancreatitis, bronchitis, meningitis, and so on.
- Platelets. The normal content of blood platelets responsible for blood clotting is 180-320X10⁹/liter. High platelet counts indicate the development of rheumatoid arthritis, polycythemia, tuberculosis, and myeloid leukemia. A reduced content accompanies thrombocytopenic purpura, aplastic and hemolytic anemia, hemolytic disease, and lupus erythematosus.
Indications for analysis
Symptoms that may be caused by low blood sugar:
- constant lethargy, fatigue;
- increased sweating;
- anxiety;
- attacks of hunger.
Symptoms that high sugar levels can cause:
- rapid breathing;
- dry mouth, thirst;
- dry skin;
- decreased clarity of vision;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- poor wound healing;
- itching of the skin and mucous membranes;
- weight loss.
If you notice some of the listed symptoms, make an appointment with a general practitioner, he will conduct a diagnosis and write a referral for the necessary analysis.
With both deviations from the norm, an unstable mental state and mood swings may be observed.
Where to submit?
Doubts regarding your health sooner or later make you wonder how and where to take a general blood test.
The answer to this question depends on the patient's requirements and capabilities. There are three possible options:
- State clinic,
- Private clinic,
- Medical personnel visiting your home,
In the first case, the diagnostic procedure is carried out within the framework of health insurance. The analysis is absolutely free . The disadvantages of donating blood at a government institution include long queues and the procedure being carried out at a strictly fixed time. It takes more time to examine a blood sample, which cannot be said about private clinics.
You can take the test at a paid institution at any convenient time. The main condition is not to eat for more than 3 hours. It costs more to have a medical professional visit your home. The advantages of the service include the absence of the need to leave the walls of the house, which is especially important if the patient is seriously ill.