A general clinical blood test can deservedly be considered one of the most effective diagnostic procedures. It is impossible to underestimate the importance of laboratory blood testing along with external examination and questioning of the patient. It is by the structure, volume, quantity, and scale of distribution of formed cells in the blood flow that the condition of the internal organs and the functioning of the body systems can be determined with a high degree of probability.
In order to understand what pdw is in a blood test and why it is needed, you must first get an idea of the concept itself.
Detailed description of the study
An extended blood test is a primary study that is used to assess the general condition of the body, identify a wide range of diseases and monitor their treatment.
The main indicators that are included in the extended clinical blood test:
Erythrocytes are cells also called red blood cells. The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from them.
Hemoglobin is the main protein in red blood cells. It directly allows for gas exchange in tissues by combining with oxygen, or CO2. Insufficiency of hemoglobin in the body, along with a decrease in red blood cells, serves as the basis for the development of anemia.
Hematocrit is the ratio of all formed elements of blood (mainly red blood cells) to the liquid component of blood. Allows you to judge the excess or deficiency of red blood cells, dehydration or overhydration of the body.
The color indicator reflects how adequately the saturation of erythrocytes with hemoglobin is, helps the specialist to establish anemia and differentiate it into normochromic, hypochromic or hyperchromic.
MCH (Mean Cell Hemoglobin) - an indicator reflecting the average hemoglobin content in red blood cells, is a modern and more accurate analogue of the color indicator.
MCV (Mean Cell volume) determines the average volume of a red blood cell. Used in conjunction with MCH to identify anemia and its causes.
RDW (Red cell Distribution Width) reflects the heterogeneity of red blood cells by volume. The indicator is also important in the diagnosis of anemia; it depends on the mean erythrocyte volume (MCV), therefore, when MCV increases or decreases, its increase is observed, which indicates that there are cells of different volumes in the blood.
MCHC (Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration) helps estimate the mean hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells. Changes in the indicator are observed in cases of impaired hemoglobin synthesis, hypochromic and hyperchromic anemia.
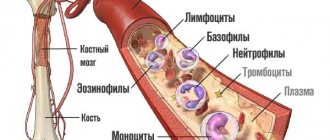
Platelets also belong to the formed elements of blood; they play a key role in the processes of hemostasis and ensure timely blood clotting in case of vascular damage. Changes in this indicator may be associated with impaired cell production in the bone marrow or their accelerated destruction.
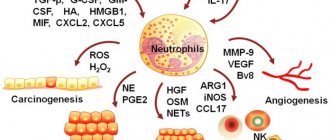
Leukocytes are called white blood cells. They participate in various immune processes and protect the body from infection. There are several types of leukocytes: eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, basophils, monocytes. Their percentage ratio allows you to evaluate the leukocyte formula to understand the current state of the immune system, identify and determine the severity of inflammatory and allergic processes in the body.
Neutrophils , the largest population of white blood cells, are aimed at fighting foreign microorganisms - including bacterial infections - in the body.
Lymphocytes play an important role in recognizing pathogenic microorganisms and forming and regulating immunity to various infections by releasing antibodies and destroying infected cells.
Monocytes are white blood cells that can differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells after they migrate to peripheral tissues. Viral and bacterial particles are absorbed, then target proteins appear on the surface of the cell to recognize the infectious agent by the immune system. This helps in fighting pathogens and building adaptive immunity. Monocytes also take part in cleansing the body of dead cells and tissue healing.
Basophils and eosinophils are actively involved in the development of allergic reactions. They contain many granules with bioactive molecules that cause allergy symptoms. Eosinophils also play a role in protecting the body from parasites.
Reticulocytes serve as precursors of red blood cells. Their number reflects erythropoiesis - the rate of formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. This indicator is important when assessing the effectiveness of anemia therapy. Additionally, the percentage of reticulocytes, the content of their immature forms and the production index of these cells are determined. Taken together, these data are used to manage patients with hematopoietic disorders.
Taken together, the indicators of an extended clinical blood test are necessary for the doctor as a stage of primary laboratory diagnosis of a wide range of diseases. The test can also be used to assess general health.
Platelets and the concept of pdw in the bloodstream
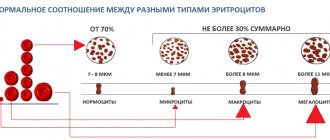
The abbreviation RDW can be deciphered as “platelet disintegration width by volume.” On the laboratory form it represents the platelet distribution index. These cells are the most microscopic in size compared to other elements of the blood channel, their size varies from 2–5 micrometers. Platelets are often called platelets because they have a flat, oval shape with projections. These shaped particles are transparent and do not have a nucleus.
Purpose of platelets:
- Release of factors for blood clotting with the aim of forming blood clots in the area of violation of the integrity of the internal or external soft tissues of the body.
- Production of growth factors for the restoration of blood vascular walls and their nutrition, by providing biologically active components.
- Supply of immune complexes to the sites of the inflammatory process to eliminate it.
- Filtration of blood from antigens destroyed by combining them with antibodies.
The synthesis of flat, nuclear-free bodies occurs in the main hematopoietic organ - the bone marrow. The predominant number of platelets, about 80%, is present in the bloodstream, while a small part of about 20% is constantly located in the spleen. Here and partly in the liver, the disposal of obsolete colorless, flat cells is carried out. The existence of platelets lasts only 8–12 days.
The formation and elimination of platelets and other formed microparticles of blood is carried out continuously. At the same time, the circulatory system contains cells that are at different stages of development.
There are five stages of platelet existence:
- Youth phase.
- Maturity stage.
- The period of old age.
- Stage of irritation.
- Degenerative moment.
The volume of the cell depends on the stage of formation - new cells are larger in size. As they mature and get closer to aging, they decrease in size. The pdw readings just demonstrate the heterogeneity and width of platelet distribution throughout the volume of the blood substance. In other words, this indicator determines the heterogeneity of platelets.
Data in laboratory forms are displayed in percentage terms and have an indirect meaning.
Consequently, if the coefficients of the remaining formed cells have a stable value, then non-critical changes associated with platelets do not indicate pathological processes in the body. Pdw blood test is performed at the same time as determining MPV, which means mean platelet volume.
References
- Nazarenko, G.I., Kishkun, A.A. Clinical evaluation of laboratory results. - M.: Medicine, 2006. - 544 p.
- Tatkov, O.V., Stupin, F.P. General blood analysis. Information collection. - M.: Publishing solutions, 2021. - 72 p.
- Fauci, A., Braunwald, E., Kasper, D. et al. Harrison's principles of internal medicine, 17th edition, 2009.
- Pagana, K., Pagana, T., Pagana, Th. Mosby's Diagnostic and Laboratory Test Reference. 14th Edition. Elsevier Publishing Hall, 2019. - 1094 p.
Normal pdw value
The predominant number of platelets in the blood should be in a mature form. It is at this stage that flat blood cells are able to cope with their main purpose - to influence blood clotting. The permissible fluctuation in the number of mature platelets, both upward and downward, is 10%. Severe excess of the norm threatens the formation of blood clots, which gradually clog the vessels. A significantly reduced level of platelets is fraught with blood loss.
In a healthy body, the normal width of platelet distribution in children under 18 years of age is from 10 to 15%. In adults, the normal pdw index ranges from 15 to 17%. In a situation where the norm has significant deviations from standard values, this may be a sign of a disruption in the functioning of certain organs and systems in the human body. This may also signal the possible development of pathology.
Decrease pdw
If a clinical study shows that the relative width of the platelet volume distribution is below normal, then this is a sign of a low number of flat blood cells. A low percentage of platelet index is not always a harbinger of various pathologies. It must be taken into account that pdw may be reduced in women during menstruation. It can be lowered due to an unhealthy lifestyle, poor nutrition and due to the physiological characteristics of the body.
The pdw index is lowered with certain deviations:
- Pathologists of the hematopoietic organs.
- Oncological diseases.
- Liver disorders.
- Ingress of viruses and infections.
- As a result of taking cytostatics.
- Myelodysplastic and DIC syndrome.
- Anemia associated with a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
A drastic decrease in the number of platelets and their incorrect distribution in the volume of the blood mass is no less life-threatening for a person than an excess. Because it leads to loss of integrity of the circulatory organs and other body systems. But even when the pdw index is not significantly reduced, this circumstance should not be neglected. It is necessary to normalize this blood indicator and maintain it at the proper level.
Indications for analysis
Determination of the number of neutrophils is included in the standard of performing a general blood test (CBC). A general blood test is recommended for all people without exception when referred for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures in a clinic or hospital.
Indications for determining the number of neutrophils:
- inflammatory diseases of any body system, for example, pneumonia or rheumatism;
- surgical inflammatory pathologies – appendicitis, peritonitis;
- significant burns to the body surface;
- destructive processes in the body, for example, myocardial infarction;
- oncological diseases;
- infectious pathologies – tuberculosis, measles, diphtheria, etc.;
- severe blood loss due to injury or internal bleeding;
- poisoning caused by chemicals and toxic substances.
Preparing for a blood test to determine the number of neutrophils
The number of neutrophils is determined during a general blood test. Before donating blood, a person is advised to refrain from drinking alcohol, fried or fatty foods. At least four hours before the procedure, the patient must completely avoid taking any products. Increased physical or psychological stress on the eve of the procedure should be limited.
Norms for the number of neutrophils in children and adults
In the results of a general clinical blood test, neutrophils are designated as NE and measured as a percentage.
- from 1 day to 15 days – 31.0%-56.0%;
- from 15 days to 1 year – 17.0%-51.0%;
- from 1 year to 2 years – 29.0%-54.0%;
- from 2 years to 5 years – 33.0%-61.0%;
- from 5 years to 7 years – 39.0%-64.0%;
- from 7 years to 9 years – 42.0%-66.0%;
- from 9 years to 11 years – 44.0%-66.0%;
- from 11 years to 15 years – 46.0%-66.0%;
- over 15 years old – 48.0%-78.0%.
Where to get a blood test for PDW
We have no doubt that you take your own health seriously and value the quality of life that is possible in the absence of disease. Blood tests are one of the good and useful habits, and you are a frequent visitor to the laboratory of your favorite medical clinic. It is recommended to undergo a check-up at least for the basic parameters of blood composition and quality at least twice a year.
If we talk directly about the study of the width of platelet distribution, this index is a mandatory part of the OAC for the platelet formula and is submitted to any medical center. clinic.
Perhaps there is no time to visit a doctor for no reason, solely for preventive purposes, so we offer a more convenient way: the tests will be carried out in one of the laboratories of medical clinics, but the collection of biomaterial will be carried out at your home in a calm environment for you or at a specified location .
- Sterile;
- Personnel of the highest category with medical education and work experience;
- Up to 50 research parameters;
- Free with bioniq BALANCE subscription
Information from the analysis is a priority principle for creating a personalized complex of micronutrients, vitamins needed specifically at the current moment.