The use of hardware methods for automatic counting of cellular elements during a general blood test has led to many misunderstandings among doctors and patients. This is due to the appearance of unfamiliar abbreviations in the results of such analyzes. One of them is the WBC blood test. Not everyone knows, but this is a routine test for white blood cell levels. In the classic version, they are counted by clinical laboratory assistants under a microscope. Most modern laboratories are equipped with special equipment that greatly simplifies this procedure and speeds up the time it takes to complete it.
When do you need to take a General blood test without leukocyte formula (capillary blood)?
- To assess general health (routine medical examinations, screening examinations, etc.);
- For diagnostics at the first stage of a wide range of diseases that may manifest themselves as changes in the characteristics of peripheral blood;
- Diagnosis of anemia, polycythemia along with the study of hemoglobin and hematocrit;
- Monitoring ongoing drug treatment for patients suffering from bleeding or chronic anemia;
- Determination of the activity of erythrocyte formation processes in the bone marrow.
Monocytosis
Monocytosis is a condition in which the number of blood monocytes exceeds the standard. The norm is from 2 to 9%. This may indicate:
- Specific infections with a long course (tuberculosis, chlamydia, viral and bacterial diseases);
- Parasitic infestations;
- Monocytic type of leukemia;
- Lymphogranulomatosis and other types of lymphomas;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- Condition after removal of the spleen.
A decrease in the level of monocytes practically does not occur.
Detailed description of the study
Blood is a multicomponent structure that is part of the internal environment of the body. It consists of plasma, which contains a suspension of formed elements - red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes and some others. This study is carried out to assess quantitative blood parameters. During a general blood test, the number of blood cells and cells of different types is determined, which gives an idea of their functioning, and, accordingly, the state of the body:
During a general blood test (CBC) without a leukocyte formula, the following parameters are assessed:
- number of leukocytes (white blood cells, WBC);
- number of red blood cells (RBC);
- hemoglobin level (hemoglobin content, Hb);
- hematocrit (hematocrit, Hct);
- mean erythrocyte volume (MCV);
- average hemoglobin content in erythrocytes (MCH);
- mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC);
- platelets (platelet count, PC).
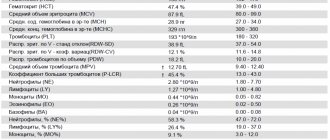
The main indicators that are included in the table of results of a general blood test:
Leukocytes (WBC, White Blood Cells)
Leukocytes, also called white blood cells or white blood cells, are a population of diverse but keyly similar immune system cells that are produced in the bone marrow. They are capable of active movement, capture and absorption of foreign particles and cells of their own body. In the first case, leukocytes provide protection from microbes and other foreign particles, in the second - maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body, ensuring the timely destruction of old or defective cells of the body's own.
Their number increases in the presence of inflammation - the degree of increase in the number of leukocytes indicates the severity of the infectious process.
CBC allows you to estimate only the total number of leukocytes. In order to assess the population composition, structure and structure of leukocytes, it is necessary to additionally undergo a leukocyte formula analysis. If a general blood test shows abnormalities, the doctor may prescribe a more detailed option.
You can also take a blood test with leukocyte formula and ESR at the Hemotest Laboratory.
Hemoglobin (Hb, Hemoglobin)
Hemoglobin is a protein that contains iron. Its main function is to transport oxygen to cells and remove carbon dioxide from them. The normal limits for it are well known, which vary somewhat depending on gender and age: in men, its content is, on average, higher than in women, and in children of the first year of life, a slight decrease in its content in the blood is normal. The combination of iron in hemoglobin with oxygen gives the blood a bright scarlet hue.
A decrease in hemoglobin levels beyond normal values is one of the types of anemia. This disease is also called “anemia”. There are several types of anemia depending on the causes, but with any of them the amount of hemoglobin per unit volume of blood will be reduced.
The most common cause of anemia is iron deficiency in the diet. In addition, anemia can occur due to blood loss and impaired absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract. The cause may also be too intense destruction of erythrocytes (red blood cells) or disruption of their formation. To clarify the diagnosis, additional tests will be required. A complete blood count can be a starting point in the diagnosis and treatment of anemia.
Hematocrit (Ht, Hematocrit)
Hematocrit is a numerical indicator of the ratio of the volume of blood cells, 99% of which are red blood cells, to the total blood volume. However, the statement is true only in cases where the size of red blood cells is normal. If the number of normal-sized red blood cells increases, the hematocrit also increases. In cases of large or small red blood cells, this is not always the case. For example, with iron deficiency, red blood cells decrease and the hematocrit will be reduced, but the number of red blood cells per unit of blood may be normal or even slightly higher.
Hematocrit increases with dehydration, lung and heart diseases, and while in high mountains. On the contrary, a decrease in hematocrit is observed with anemia of various origins, with liver diseases, with the consumption of large amounts of fluid or the administration of large volumes of fluid intravenously.
Red blood cells (RBC, Red Blood Cells)
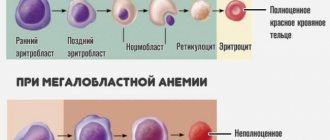
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) are the formed elements of blood, not entirely correctly called “cells”. They are indeed formed from precursor cells, but upon maturation they lose their nucleus - one of the key features of a living cell. In this way, they provide themselves with the opportunity to implement a highly specialized function: transporting oxygen to the cells of the body and removing carbon dioxide from them. These are the most numerous formed elements of blood, which have the shape of a biconcave disc. Their entire volume is occupied by hemoglobin in order to effectively transport oxygen to cells and remove carbon dioxide and metabolic products from them.
The number of red blood cells is a very important indicator of health. CBC allows you to identify deviations from the norm and prescribe additional studies to clarify the diagnosis and identify the causes of changes in the number of red blood cells, including:
Erythropoietin is a hormone that is synthesized in the kidneys and stimulates the formation and maturation of red blood cells. With a lack of oxygen - hypoxia, it is synthesized more intensely. The number of red blood cells may decrease due to a lack of this hormone.
Vitamin B12, folic acid and sufficient iron are necessary components for adequate hemoglobin synthesis and red blood cell formation.
Red blood cells live in the bloodstream for 120 days, after which they are destroyed in the spleen. Excessive destruction of red blood cells can also lead to a decrease in their number. Determining the number of red blood cells, together with assessing the hemoglobin content, establishing hematocrit and characterizing red blood cells, makes it possible to diagnose the type of anemia and its causes with a high degree of probability. Based on this data, it is possible to select the most effective treatment.
Color Index (CPU)
The numerical indicator of hemoglobin saturation of red blood cells indicates the amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell.
MCH (Mean Cell Hemoglobin, average hemoglobin content in red blood cells)
Numerical expression of the average hemoglobin content in one red blood cell. Together with MCV it is used for the differential diagnosis of anemia.
MCV (Mean Cell volume, average volume of red blood cells)
Numerical indicator of the average volume of red blood cells. Normally it has no diagnostic significance, but is necessary for the differential diagnosis of anemia in combination with MCH. If the range of red blood cell volumes is large, or there are many red blood cells of a changed shape, then averaging the indicator will not be so informative, but differences in the size and structure of red blood cells indicate the need to pay close attention to this: this is not the norm.
MCHC (Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration, mean hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells)
An indicator that shows the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells. A sensitive indicator of changes in hemoglobin synthesis processes - a possible cause of iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, and some hemoglobinopathies.
Platelets (PLT, Platelets)
Platelets are the formed elements of blood. Like red blood cells, they are formed from precursor cells, but they are not cells: they do not have a nucleus or other important intracellular structures, so their lifespan is only about a week.
The loss of cellular characteristics is due to the high specialization of these formed elements: almost their entire volume is filled with granules, which contain substances involved in the processes of blood coagulation and platelet aggregation. With the help of special receptors, platelets detect a violation of the integrity of blood vessels, form a clot there and stimulate local blood clotting to stop bleeding.
An increase in the number of platelets can occur as a result of taking certain medications, indirectly indicating malignant neoplasms, some inflammatory and infectious diseases. Some types of cancer, malaria and bronchial asthma can reduce their levels. Their levels may also be reduced as a result of disruption of their formation from progenitor cells in the bone marrow or due to increased consumption during wound healing. The main symptom of a low platelet level is bleeding, up to life-threatening conditions: from the appearance of bruises even with light pressure and bleeding gums, to internal hemorrhages.
Eosinophilia and basophilia
An increase in the number of eosinophilic leukocytes, which are designated EOS in the WBC analysis, is when the resulting figure exceeds 5%. This is possible when:
- Allergic reactions;
- Skin diseases (atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema);
- Worm infestation;
- Autoimmune processes;
- Some infections (scarlet fever);
- Eosinophilic type of leukemia.
The norm for basophil content is no more than 1%. These cells are usually not detected by WBC analysis. Their appearance may occur in some forms of myeloblastic leukemia.
Important Notes
Material for research
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications).
Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood.
Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications).
According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
Tasks of white cells in the body
To say what specific functions these elements perform, you need to understand the types of shaped cells. Are they the same? No, absolutely not.
If we talk about leukocytes in more detail, we can distinguish two large groups of structures. The first is the so-called granulocytes. They got their name due to the presence of a complete nucleus in the cytoplasm.
These include the following elements:
- Basophils. Special large components that are involved in the production of antibodies. Also, along with other structures, they fight cancerous tumors, prevent the division of foreign elements and altered tissues. Therefore, they are considered one of the main ones in the primary immune response.
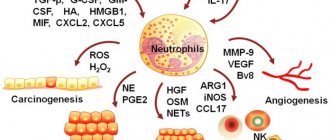
- Neutrophils. They make up up to 70% of the total mass of leukocytes and even more (divided into band and segmented). These white blood cells are rated as "private soldiers." They are the ones who reach the affected area the fastest and are the first to enter into a simulated battle with foreign agents.
- Eosinophils. Mainly considered mediators of the inflammatory process and allergies. They are also actively produced during helminthic infestation. Moreover, regardless of the location of the pathological condition. As for simple infections, viral or fungal, bacterial phenomena, an increase is not always observed. But often.
Thus, granulocytes are a kind of first line of defense. They enter the battle before everyone else and are responsible for developing initial immunity.
That is, the antibodies that are produced during the course can be detected within a short period of time. Up to several weeks. Plus or minus. Also among the functions is the fight against parasites and cancer formations.
There is a second group of white blood cells. The so-called agranulocytes. From the name you can understand that they do not have a nucleus in their structure. The genetic material, however, is still present.
These wbc in the blood act as a second line of defense. They are also heterogeneous in nature.
Among them, lymphocytes are identified, which can also be divided into three groups.
- B-lymphocytes. Responsible for creating lasting immunity to a specific pathogen. This is no longer the same short-term reaction. We are talking about a long-term condition. Lifelong resistance to the pathological process. For example, to chicken pox, measles and others. Vaccination as a special medical method is based on this principle.
- T lymphocytes work as regulators of the body's natural response. At one moment they accelerate the synthesis of antibodies, at another they promote the opposite response and slightly inhibit the natural phenomenon.
- NB lymphocytes. They are also called killers because they mainly fight cancerous structures. Although they also perform functions characteristic of other cells.
- There is another type - the so-called monocytes. They also do not have a core. These are large cells capable of phagocytosis. That is, direct physical absorption of foreign agents. Of course, these components are also able to produce antibodies and synthesize protective substances.
The functions of WBC (white blood cells) are to ensure normal immunity, fight against foreign agents, that is, everything that can be called the body’s defense against viruses, bacteria, fungi and tumor structures.
References
- Nazarenko G.I., Kishkun A.A. Clinical assessment of laboratory research results // M.: Medicine - 2006. - 544 p.
- Tatkov O.V., Stupin F.P. General blood test. Information collection // M.: Publishing solutions. — 2021. — 72 p.
- Fauci, Braunwald, Kasper, Hauser, Longo, Jameson, Loscalzo Harrison's principles of internal medicine, 17th edition, 2009
- Mosby's Diagnostic and Laboratory Test Reference 14th Edition, 3251 Riverport Lane
- St. Louis, Missouri 63043: Elsevier Publishing Hall 2019
Change in lymphocyte level
Lymphocyte cells, like neutrophil leukocytes, provide immune surveillance in the body. But in contrast to them, lymphocytes are responsible for both cellular and immunoglobulin immunity. Their norm is 18-40%. Explanation of possible results of WBC analysis is given in the table.
| Lymphocytosis (increased blood lymphocytes) | Lymphopenia (decreased blood lymphocytes) |
|
|
Video about the functions of different types of leukocytes, their norms in the blood:
WBC blood test is an excellent alternative to the classic study of its leukocyte composition. The main thing is to know the subtleties of correct interpretation of the results obtained.
Laboratory microscopy
Calculation of the hematocrit number is included in the general clinical blood test. A separate study of this indicator may be prescribed in case of unsatisfactory results of OKA: anemia (anemia) and high concentration of red blood cells, as well as in case of bleeding of various etiologies (origins), in case of dehydration (dehydration) of the body. HCT is an important indicator of chronic hematological diseases.
To obtain objective final data, on the eve of the study, the patient is recommended to eliminate heavy foods (fatty and fried foods) from the diet, eliminate alcohol-containing drinks, and limit sports and other physical activities. The blood sampling procedure is carried out in laboratory conditions, in the morning.
Before the analysis, it is advisable to give up breakfast and smoking. The hematocrit value is determined using a laboratory device into which a glass graduated tube containing the blood sample being tested is placed. An anti-clotting agent is first added to the biofluid.
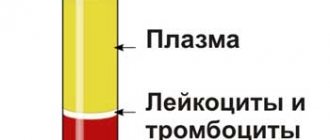
Under the influence of centrifugal forces (centrifugation), the blood is stratified. Red blood cells precipitate, clearly demonstrating their volume, and the plasma rises to the top. The remaining formed elements (leukocytes and platelets) are concentrated between them.
Brief scheme for hematocrit allocation
In modern laboratories, the process of measuring red blood cell volume is fully automated. The measurement value of hematocrit in clinical microscopy is taken as percentages or units (% multiplied by a factor of 0.01).
Where to get tested for leukocytes
It is the CBC, abbreviated or with a leukocytogram, that can be done by any laboratory; the quality of such blood tests will not differ. The issue is a little more complicated with studies of vitamin levels, since there is no single form for such a task. In each case, the doctor prescribes a list of microelements and vitamins that are priority for study.
For example, you can donate blood specifically for the group of fat-soluble vitamins or group B. Microelements are most often studied according to the following list: iron, magnesium, manganese, calcium, zinc, copper.
The choice of tests is made on the basis of personal complaints about health or regarding a specific purpose for collecting information.
For this purpose, bioniq has developed comfortable programs for assembling personalized bioniq LIFE and bioniq BALANCE micronutrient complexes, with the ability to collect material at home or in a place convenient for you.
Tables of norms by age
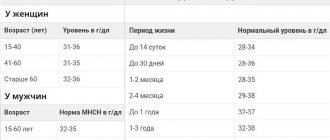
Among women
| Age | Indicator in units *109 per liter of blood |
| 16-25 | 4-10.5 |
| 25-50 | 4-12.1 |
| After 50 years | 3.6-12.4 |
The wbc norm in women is 3.6-12-4 U *109 per liter of blood and changes over the years and reaches its peak after 50 years and during pregnancy.
In men
| Age (years) | Norm of leukocytes Units * 109 / per liter |
| 16-25 | 3.3-8 |
| 25-50 | 4-9 |
| 50 and older | 3-7 |
In children
| Age (years) | Norm in units * 109 / per liter |
| Up to 1 | 6-17.5 |
| 1-5 | 5.7-17.5 |
| 5-10 | 4.4-15.5 |
| 10-16 | 4.6-13.2 |
The wbc rate also depends on gender: in men it is initially slightly lower and ranges from 3 to 9 U * 109 / per liter, in children - more than in adults (4.6-17.5 U * 109 / l) due to active formation immunity.
Causes of low RBC in the blood
The condition when rbc is low in blood tests is called erythropenia. Erythropenia occurs when:
- bleeding;
- disruption of red blood cell formation;
- increased destruction of red blood cells;
- pregnancy.
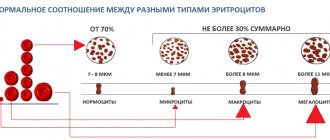
When red blood cells are low in the blood, they change their shape and size:
- anisocytosis - cells of different sizes, a sign of anemia;
- microcytosis - cell diameter less than 7.5 microns, occurs with hemolytic anemia, oncopathology;
- macrocytosis - cell diameter more than 7.5 microns, occurs with liver and lung diseases, malaria, B12 deficiency.
A reduced amount of rbc in a blood test is accompanied by signs of oxygen starvation:
- increased fatigue;
- dizziness;
- feeling of lack of air;
- pale skin;
- attacks of nausea.
People with anemia do not tolerate temperature fluctuations or physical activity well.
Increased values
An increase in the volume of white blood cells in the blood is called leukocytosis. There are physiological leukocytosis (occurs in healthy people in some situations) and pathological leukocytosis (indicates the development of diseases).
Possible reasons
A physiological increase in leukocytes in the blood occurs in the following conditions:
- a few hours after eating food;
- after psycho-emotional stress;
- after excessive physical exertion;
- after taking a cold or hot bath;
- in women before menstruation;
- in the second half of pregnancy.
In this regard, it is recommended to take a blood test in the morning on an empty stomach, avoiding significant physical and emotional stress the day before.
According to the WBC blood test, leukocytosis is a symptom of the following diseases:
- infections of various nature;
- meningitis is an inflammatory process of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord;
- erysipelas;
- otitis;
- bronchitis, pneumonia;
- inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue - abscess, phlegmon, panaritium;
- inflammation and suppuration of the abdominal cavity - appendicitis, peritonitis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- leukemia (tumor diseases);
- diabetic coma;
- chronic renal failure;
- heart attacks;
- traumatic tissue damage;
- eclampsia;
- uremia;
- thyroid diseases;
- acute bleeding.