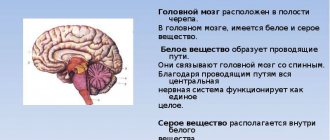
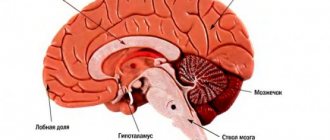
Stroke is a serious condition that is characterized by an acute disruption of the blood supply to parts of the brain and leads to morphological and functional damage to the central nervous system. Depending on the type of damage, hemorrhagic and ischemic types are distinguished. The brain stem includes the medulla oblongata, midbrain and pons. It is a connecting structure between the spinal cord and the brain and is of great importance, since the structures that ensure the vital functions of the body are concentrated in it. In case of damage to the brain stem, the statistics are disappointing: no more than 25% of such patients survive, and only 2% of them can count on a full recovery without severe complications.
Brainstem stroke is the least favorable type of cerebral stroke. The structures of the trunk are responsible for providing the following life support functions: breathing, blood circulation and cardiac activity, vital reflexes. Patients who have had this stroke have a poor prognosis, which is further worsened by hemorrhage. Mortality reaches 75%. Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and MRI data.
Among the clinical signs, disturbances of consciousness and bulbar syndrome prevail. The standard for diagnosis is MRI, which gives an idea of the topography and volume of the lesion. At the same time, rehabilitation and partial restoration of lost functions are possible with timely diagnosis and immediate initiation of therapy. The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with a ventilator, necessary during the acute period of a stroke, and simulators for restoring motor skills.
The effectiveness of treatment most of all depends on the timing and quality of the treatment measures.
Causes of brainstem stroke
The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- Hypertonic disease. It is the most common cause of vascular damage to the brain stem. With high blood pressure, the walls of the arteries become brittle, which in turn leads to their rupture and hemorrhage.
- Atherosclerosis, thrombosis. When the lumen of a vessel is blocked by an atherosclerotic plaque or thrombus, the blood supply to the surrounding tissue is disrupted, which leads to the development of ischemia.
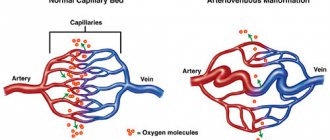
- Aneurysms, collagenosis, vascular malformations. Pathological changes in the structure of the vascular wall increase the risk of its rupture. This anomaly can cause a stroke at a young age.
- Diabetes mellitus, rheumatological diseases, heart pathologies, blood clotting disorders, etc. Features of the course of some diseases lead to the development of atherosclerosis, blood clots, macro- and microangiopathy.
- Lifestyle. Smoking, alcohol abuse, physical inactivity, poor diet, stress, and chronic fatigue increase the risk of vascular accidents.
- Age. Each subsequent 10 years increases the likelihood of developing ischemia or hemorrhage by 5-8 times.
- Genetic predisposition. Cohort studies have revealed that the risk of stroke increases by 30% if a person has a history of this disease in their family.
Make an appointment
Mechanism of formation
The development of the disorder is based on one factor or several pathogenetic factors at once. What exactly can affect the likelihood of a violation:
- Cardiovascular diseases. Represented by a wide group of diagnoses. In the vast majority of cases, hemorrhagic stroke develops as a complication of long-term and untreated hypertension. That is, a stable and pronounced increase in blood pressure.
Statistics show that the mechanism accounts for up to 85% of the total number of hemorrhages. This is the absolute majority. The only way to prevent an emergency condition is to undergo high-quality treatment of the underlying pathology.
- Metabolic disorders. Basically, deviation of lipid movement. That is, a disorder in which the rate of deposition and elimination of fats significantly deviates from the conventional norm.
The pathological process leads to another problem - atherosclerosis. When cholesterol deposits form on the walls of blood vessels, which interfere with blood flow. The result is that the likelihood of hemorrhagic stroke and death from complications increases significantly.
- Hormonal imbalance. We are talking about a variety of disorders: from changes in the quality and intensity of the synthesis of sex substances to problems with the production of insulin and compounds of the adrenal cortex.
- Hereditary causes. The mechanism is associated with a not yet fully understood method of transferring risks from parents to children. The disease itself, of course, is not transmitted.
If a mother, father, grandmother, grandfather has a hemorrhagic stroke, this does not mean that the same thing will happen to a descendant. But the likelihood is growing. Apparently - by several tens of percent. The topic has not been fully studied, research continues.
- Toxic damage to the body. Poisoning by vapors of non-metals, some medications. The risk of hemorrhagic stroke increases with the systematic use of antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, and hormonal agents.
- Some forms of anemia, blood diseases. Changes in the rheological properties of connective tissue lead to disruption of the speed and quality of trophic systems and an increase in blood pressure. In some cases, vascular permeability increases. The result is an increased risk of cerebral hemorrhage.
Mechanisms exist in isolation or are combined with each other. This question needs to be clarified, since the therapy strategy and its essence depend on the origin of the pathological process.
How does a stem lesion differ from other types of stroke?
Depending on the location and extent of the pathological process, disruption of the blood supply to the trunk can have a variety of clinical manifestations.
The first signs of the disease may be severe pain in the back of the head, dizziness, and in 70-80% of cases loss of consciousness occurs. The clinical feature of vascular damage in this particular department is expressed in the appearance of alternating syndromes - damage to the cranial nerves on one side in combination with motor and sensory disorders on the opposite. The functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and thermoregulation are disrupted, and paralysis of the muscles of the face, pharynx, and muscles of the limbs develops. The development of “locked-in person” syndrome is possible. All symptoms are severe and, if timely medical care is not provided, lead to death in the first two days of the disease. An imbalance of blood circulation in this part of the brain brings serious consequences associated with a person’s life. Basic health parameters are affected. In particular, the following symptoms result from a stroke:
- dysfunction of the heart muscle. There is a change in the heartbeat rhythm, which causes bradycardia, arrhythmia or fibrillation. A distinctive feature of damage to the stem structure is a poor prognosis for rehabilitation;
- failure in the respiratory system. Shortness of breath and inability to take in air appear. In such a situation, the presence of an artificial respiration apparatus is of great importance, otherwise death is possible;
- speech and swallowing problems. The first is more harmless in nature due to the inability to pass saliva. The latter leads to profuse salivation, and some body positions allow fluid to enter the oxygen-receiving organs, thereby provoking the onset of pneumonia.
In addition to all of the above, there is a possibility of problems with vision and coordination, and a decrease in muscle activity.
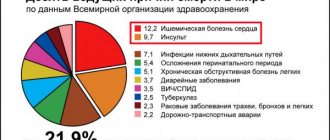
If timely assistance is not provided, the outcome can be fatal. In ICD-10, brainstem stroke is designated by code G 46.3. According to WHO statistics, stroke occupies a leading position in the structure of morbidity and mortality. Every year, cerebrovascular accidents are detected in 3 people per 100 thousand population. Death at the onset of the disease occurs in 15–30% of cases. With a second episode of stroke, the mortality rate is 70%. According to statistics, the five-year survival rate after a stroke is 40–60%. The prognosis is influenced by the form of cerebrovascular accident. Brainstem stroke affects the brainstem. Doctors consider this type of disease to be the most dangerous.
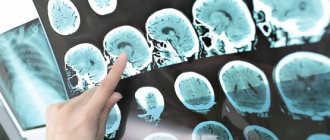
To diagnose stroke, the Yusupov Hospital uses modern equipment. CT and MRI are considered the most informative ways to determine the localization of a pathological focus in the brain. Therapy includes methods of drug treatment and surgical intervention if indicated. The drugs used meet quality and safety standards. The duration of rehabilitation is determined by the severity of the condition.
Thanks to an individual approach to each patient, positive results are achieved in the shortest possible time.
Expert opinion
Author: Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Brainstem stroke is the least favorable type of cerebral stroke. The structures of the trunk are responsible for providing the following life support functions: breathing, blood circulation and cardiac activity, vital reflexes. Patients who have had this stroke have a poor prognosis, which is further worsened by hemorrhage. Mortality reaches 75%.
Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and MRI data. Among the clinical signs, disturbances of consciousness and bulbar syndrome prevail. The standard for diagnosis is MRI, which gives an idea of the topography and volume of the lesion.
At the same time, rehabilitation and partial restoration of lost functions are possible with timely diagnosis and immediate initiation of therapy. Patients with brainstem stroke are less likely to lose interaction and communication skills, allowing them to participate in their own recovery.
The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with a ventilator, necessary during the acute period of a stroke, and simulators for restoring motor skills. The effectiveness of treatment most of all depends on the timing and quality of the treatment measures.
Consequences
A brain stem stroke is dangerous not only due to death, but also to a large percentage of patients’ disability. Often people who have had an attack cannot walk or even sit on their own. Their speech is impaired and they become completely dependent on the people caring for them. In addition, patients may experience a second attack at any time or develop dangerous complications. With this course of the disease, patients most often die.
The most common cause of death after a stroke is swelling of the brain stem. The resulting hematoma infringes on the trunk, and as a result, cardiac or respiratory arrest occurs. This complication develops in the first days after the attack.
In a later period, the patient may develop complications such as:
- Pneumonia.
- Vein blockage.
- Infectious diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
- Internal bleeding.
- Heart attack.
These are only those complications that can lead to the death of the patient, but there are others that significantly complicate patient care and bring the patient a lot of suffering, among them:
- Bedsores.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Psycho-emotional disorders.
Those patients who can ambulate a little are often injured as a result of falls. Caring for post-stroke patients requires special patience from relatives. Treatment can last for years and often does not bring the desired results.
Characteristic symptoms
The fact that the pathological process has affected the brainstem can be understood in 95% of cases from examination data.
Focal neurological manifestations can be observed in the first hours of the disease and during the recovery period. The clinical picture of brainstem damage appears suddenly and develops at lightning speed, compared to other parts. The prognosis for recovery is usually worse. Signs of brain stem pathology are directly related to its purpose. It belongs to the nervous system and is its central part. Responsible for perspiration, heart function, body temperature, swallowing and chewing. Therefore, brainstem strokes are extremely dangerous, even fatal. The defeat of the department manifests itself sharply. The state of health quickly deteriorates, temperature fluctuations begin, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, loss of consciousness, and coma often occurs.
In medicine, indicators for a disorder of this type are divided into two groups, depending on the form of the ailment, but there is a more general list suitable for all types:
- speech dysfunction;
- failure to regulate body temperature;
- poor coordination;
- muscle paralysis;
- change of voice after swallowing;
- change in pulmonary ventilation;
- inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- bradycardia or tachycardia;
- deterioration of vision of space;
- clouding of consciousness;
- poor sensitivity of the limbs;
- loss of consciousness;
- coma.
Hemorrhages occur suddenly, and the speed of assistance plays a big role. As soon as the severity of symptoms becomes obvious to others, you need to immediately call an ambulance. Most often, loss of consciousness or complete paralysis occurs. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of breathing.
Dizziness and loss of coordination
The harbinger is a feeling of pain in the skull or dizziness, accompanied by deterioration in coordination of movements and loss of balance.
This is often the earliest symptom of a pathological process in the trunk. Due to a persistent feeling of dizziness and pain in the back of the head, it is difficult for a person to stand on his feet and maintain balance. In such cases, the patient may suddenly fall or be forced to take a horizontal position. Coordination of movements suffers: the patient may not understand the position of body parts, an unsteady gait develops, hand movements are uneven and slow, and handwriting changes. All manifestations have a similar picture, but there are signs that are more noticeable than others or appear earlier. Unfortunately, a symptom such as dizziness will not allow you to accurately determine the cause of its occurrence, but will help you prepare for all possible outcomes. If the patient exhibits the described signal, place him in a lying or sitting position and wait for improvement. If none are noted, call a team of medical workers.
Make an appointment
Movement disorders
A brainstem stroke causes motor problems that become noticeable in the period following the stroke.
It occurs due to damage to the area of the brain responsible for cognitive activity. At the initial stage, programmatic decay manifests itself, which is expressed in changes in gait, frequent motor errors and focusing increased attention on arbitrary objects. Morphological damage in the nervous tissue of the trunk leads to impaired motor activity. This defect can progress and provoke structural disintegration of the statolocomotor system, which leads to disorganization of dynamic control of movement. At the final stage of development, the basic characteristics of the central generator of the step rhythm are affected. In this case, the patient experiences asymmetry in movements of both legs and arms, as well as freezing in place while walking. In other cases, while consciousness is preserved, a person is struck by paralysis of one half of the body (hemiparesis) or spreads to all limbs (tetraparesis). The prognosis for the restoration of motor functions is more favorable in the first 2-3 months of the disease.
Swallowing disorders - dysphagia
This is a severe manifestation of an acute disorder of cerebral blood supply.
It is observed in 65% of patients with brain stem stroke. When the nerve center is damaged, vital parameters, for example, the swallowing of saliva, are significantly affected. These tasks involve a significant number of muscles that can fail due to illness. Imperfect swallowing is called dysphagia. The danger of this complication is associated with a high risk of developing respiratory disorders and aspiration pneumonia. Most of these patients require tube feeding. The prognosis is usually unfavorable. In approximately 85% of cases, the ability to swallow is restored on its own within 2-3 weeks after the incident. Rarely does this defect remain for the rest of one's life. In this case, complications will follow:
- poor nutrition will lead to a deterioration in overall health;
- constant inflammation of the lungs due to unwanted microorganisms entering the respiratory tract;
- suffocation.
Timely treatment will allow you to get rid of all possible consequences and recover. To do this, it is recommended to contact a speech therapist, he will determine the severity and prescribe appropriate complex therapy.
Speech disorders - dysarthria
The cause of this disorder is a violation of the motor functions of the muscles of the tongue, facial muscles, and pharynx.
It is observed in approximately 30% of cases and manifests itself in changes in sound pronunciation, timbre, and intonation. Speech is distorted, losing intelligibility and articulation. In severe cases, speaking skills are completely lost. Dysfunction is accompanied by paralysis of the facial muscles located on the face and responsible for the ability to speak. This phenomenon is medically called dysarthria. The ability to communicate is lost due to disturbances in the brain stem. Associated symptoms are as follows:
- poor facial mobility;
- distorted, unintelligible speech;
- uneven speed of pronunciation;
- stops in the middle of a phrase;
- lack of emotional coloring.
To restore speech functions, the supervision of a speech therapist is required. Based on clinical information about the patient, he will select a personal plan of classes and exercises, after which he will begin rehabilitation. It is worth noting that the speed of recovery directly depends on the moment you contact a specialist.
Eye symptoms
If the part where the oculomotor center is located is damaged, the patient loses the ability to control the movements of one or both eyeballs.
This is reflected in the inability to fixate on an object, double vision, strabismus, outward deviation of the eyes and drooping eyelids. Sometimes fields of vision may disappear. Vision plays one of the main roles in the perception of surrounding information. It allows you to distinguish colors, objects and significantly affects the quality of life. Damage to critical areas leads to deterioration of visual perception. The described disadvantage can be determined by the following characteristics:
- black spots before the eyes;
- difficulty concentrating on one object;
- impossibility of recognition.
A problem with seeing the environment can haunt the patient throughout his life and cause disability, but it is not uncommon for him to be restored through medical practice.
Alternating syndrome - paralysis and distorted face
This symptom complex occurs as a result of dysfunction of the cranial nerves on the side of the lesion and conduction disorders on the opposite side of the body. Due to paralysis of the facial muscles, the patient on the affected side experiences sagging skin, drooping of the corner of the mouth and upper eyelid. In this case, the upper and lower limbs from the opposite area of the body remain immobilized. Paralysis or distortion of the face is one of the main symptoms of the disease. This has a significant impact on the ability to speak, causing dysarthria or dysphagia. To confirm, ask the victim to smile. If asymmetry is observed, then specialists should be called immediately.
Disorders of breathing, heartbeat and thermoregulation
Damage to the respiratory, vasomotor centers and thermoregulation center in a large percentage of cases ends in death.
Impaired respiratory function during a trunk stroke manifests itself in the form of severe shortness of breath or complete loss of the ability to breathe independently. Such patients are completely dependent on a ventilator. In other cases, when the center is not completely affected, the period of wakefulness may be accompanied by spontaneous breathing, but during sleep periods of apnea are observed. A change in the functioning of the cardiovascular system is expressed in an increase in heart rate, which is then replaced by bradycardia and a drop in blood pressure. Arrhythmias and fibrillations may develop. Taking traditional antiarrhythmic drugs in such cases is ineffective. Unstable thermoregulation is observed in rarer cases and is characteristic of the most severe degree of the disease. It manifests itself in the form of a sharp and persistent increase in body temperature to 39ᵒC and above, and cannot be corrected with medication.
In other cases, critically low temperatures may occur. Both options have a disappointing prognosis for recovery.
Symptoms of various types of pathology
The signs of a stroke are very varied. They depend largely on which part of the brain is affected.
The most common symptoms:
- Impaired movements of the torso, arms, legs (from decreased strength to complete cessation of movement).
- Reduction of all types of sensitivity.
- Distortion of speech – the patient seems to be tongue-tied, speech is slow, unintelligible.
- Violation of statics - the patient is not able to stand independently, without outside support.
- Impaired consciousness: constant atypical drowsiness, “dullness” and even loss of consciousness.
Diagnosis of brainstem stroke
Diagnosis of the disease begins with examination data and collection of the patient’s medical history. Based on the characteristic symptoms, a brain stem stroke can be suspected in the first minutes. Such patients are hospitalized on an emergency basis. In a hospital setting, a number of procedures are performed to confirm the diagnosis. The following have the greatest diagnostic capabilities:
- Computed tomography is an x-ray method for studying the layer-by-layer structure of organs and tissues. With a high probability it helps to recognize foci of hemorrhage in the brain.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is an effective method for detecting pathological lesions using nuclear magnetic resonance. Allows you to assess the degree and volume of tissue damage.
- Doppler ultrasound. Using ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain, pathological changes (stenosis, occlusion) can be detected in the carotid and vertebral arteries, as well as in their branches.
- Electroencephalography. It is also a non-invasive diagnostic method. By recording bioelectrical activity, it reflects qualitative and quantitative changes in the function of the cortex and deep structures of the brain.
In addition, it is possible to conduct laboratory tests of the composition of blood and cerebrospinal fluid. According to indications, a neurologist is able to draw up an almost complete clinical picture, which reflects the depth and localization of the damage that has occurred. But to confirm the diagnosis, additional studies are required using CT or MRI, which will show:
- type of disorder;
- the extent of the pathology;
- presence of hematoma or ischemia.
The more fully and accurately the factors of change are identified, the easier it is to draw up a rehabilitation plan.
Providing emergency first aid
A stroke occurs suddenly and requires immediate outside help.
The first step is to call a team of medical workers, and while it is on its way, take care of the victim, providing him with support. The process is often accompanied by vomiting, and the accumulated masses interfere with breathing. If problems with perspiration are detected, it is necessary to clear the pathways through which oxygen enters the lungs. To do this, the person should be laid on his side and with a finger wrapped in gauze or a piece of clothing, clean the oral cavity. If you have instruments with you that can measure pressure or blood sugar levels, it is recommended to record the values of these parameters and report them to the arriving doctors.
An important indicator is the moment of onset of symptoms. It would not be amiss to note the time of its occurrence. The use of drugs aimed at lowering blood pressure is contraindicated. Increased pressure after a circulatory disturbance in the brain stem is a normal reaction of the body necessary to adapt to an emergency situation. Eating food or water is also contraindicated; there is a possibility of a negative effect that will aggravate the matter. If a person loses consciousness, it is allowed to be moved, despite existing myths that state the opposite.
The place should be arranged in such a way that the upper body and head are raised, and clothes are unbuttoned to facilitate the flow of oxygen into the lungs. If the incident occurred in a confined space, it is advisable to open the windows and provide fresh air and peace.
If the victim experiences convulsive muscle contractions and foamy discharge from the mouth, it is necessary to place a pillow or rolled up clothing under the head, and also monitor the position of the arms and legs so that the patient does not injure himself and others. Holding the limbs while contracting is strictly prohibited; this will lead to worsening of the situation. The person providing assistance must be prepared for repeated attacks and remove foam from the mouth in a timely manner.
You cannot take measures to restore consciousness, much less use ammonia for this. Its effects can cause lung failure and ultimately death. During the period of pre-medical measures, it is necessary to monitor the heartbeat and pulse. If cardiac arrest is determined, immediate resuscitation is required through chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose artificial respiration.
Treatment
Therapy is etiotropic and symptomatic. That is, it is necessary to fight both the manifestations and the causes of the pathological process.
If we talk about correcting the main factor:
- Hypertension. Drugs are prescribed to lower blood pressure. Calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, sartans, centrally acting agents, diuretics. In strictly controlled dosages.
- Diabetes. Diet low in carbohydrates and without sugar. Insulin as needed during an acute attack.
- Bad habits. Refusal of cigarettes, alcohol, drugs. If necessary, get help from a narcologist.
- Arrhythmias. Specialized means for recovery: Amiodarone, Quinidine, beta blockers.
- Atherosclerosis. Fibrates, statins, nicotinic acid. Diet correction.
- Heart and vascular defects. Operation. Plastic or prosthetics.
- Anemia. Depends on the type. The use of iron supplements, vitamins, etc.
- Hormonal imbalances. Correction with synthetic substituents or other methods. Depends on a situation.
- Wrong lifestyle. Sufficient level of physical activity, drinking regime, etc.
- Use of certain medications. Refusal or replacement of medications.
Treatment of cerebral hemorrhage concerns eliminating the very cause of the pathological process and correcting the symptoms of the disorder.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment is an integral part of patient resuscitation, prevention and recovery.
The therapy provided should be comprehensive and aimed at preserving the vital functions of the body. The main directions for this: Correction of disorders of the respiratory system. If necessary, connection to a ventilator. In the acute period, infusion therapy with plasma preparations and rheopolyglucin is carried out. Normalization of blood pressure indicators. At high blood pressure levels, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed, making sure that changes to normal values occur smoothly and gradually. The main drugs used are from the group of ganglion blockers and ACE inhibitors. In case of severe hypotension, glucocorticosteroids and dopaminomimetics are administered. Reducing body temperature is carried out using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
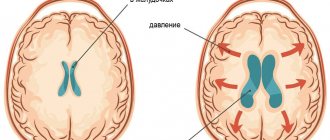
Reducing intracranial pressure and cerebral edema - with the help of diuretics. In some cases, a hypertonic saline solution is administered.
Restoring blood supply to the affected areas and preventing thrombosis. Here they use drugs from the group of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants.
Improving the nutrition of brain tissue and intracellular metabolism is carried out with the help of nootropics, antioxidants, and cytoprotectors.
The treatment of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke has its own characteristics. In case of hemorrhage, the use of anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents is contraindicated. The main treatment is aimed at stopping the bleeding and removing the hematoma. Treatment with medications is carried out in the intensive care unit. The following substances are prescribed:
- diuretics aimed at preventing edema;
- sedatives;
- oxygen therapy - if the patient is able to breathe on his own, catheters are installed, otherwise a special support device is connected;
- muscle relaxants to prevent seizures;
- blood thinners that increase blood flow;
- antihypertensive drugs to prevent recurrent vascular ruptures.
At first, all drug therapy is aimed at eliminating repeated attacks and severe consequences.
Doctors keep an eye on the patient until the body’s functioning is completely normalized, and when the patient’s well-being improves, they are transferred to a ward for further recovery. Make an appointment
Surgical intervention
Any surgical intervention on the brain is a high risk and can often lead to serious complications, including the death of the patient. Therefore, surgical treatment is carried out in the presence of strict indications:
- Swelling or compression by hematoma of the medulla oblongata, which leads to the progression of neurological symptoms. In this case, to save the patient’s life, craniotomy is performed using a certain technique.
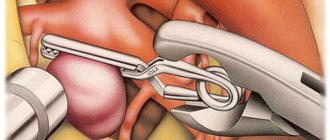
- Pathological changes in cerebral vessels (aneurysms, malformations), accompanied by bleeding. For treatment, special clips are used, which are surgically applied to the neck of the aneurysm.
- For ischemic stroke, when conservative therapy is ineffective, carotid endarterectomy followed by stenting can be performed. The operation is performed endovascularly (without incisions).
In the postoperative period, the patient's condition remains unstable for a long time. It can often be complicated by swelling of the brain tissue, which lasts up to two weeks. In the future, therapeutic measures are carried out aimed at restoring lost functions and preventing a recurrent stroke.
Prognosis after brainstem stroke
The type of stroke, the extent of the pathological process, and the timeliness of medical care are of great importance for the prognosis.
The ischemic type is more favorable - mortality is about 25%. In case of hemorrhage, according to statistics, every second patient dies within a month. The main reasons: cerebral edema with entrapment in the foramen magnum, death of stem structures. Even if life is preserved, the majority of such patients remain deeply disabled. According to research, a negative outcome is more often observed in cases of respiratory failure, persistent bradycardia, changes in thermoregulation, and loss of speech. An uncertain prognosis is given if the patient has dysphagia, movement disorders, or impaired eye movement functions. In any case, treatment of patients with brainstem stroke requires competently selected therapy and the use of all possible rehabilitation methods.
The prognosis of brainstem stroke and further condition is determined by the degree of manifestation of symptoms. Doctors see the most favorable recovery in patients with less pronounced signs of the disease, but, of course, there are always exceptions. The most skeptical view of complete recovery is captured by the following observations:
- problems with speech and breathing;
- dysregulation of blood pressure and body temperature.
A more positive prognosis can be heard when:
- weakness of swallowing;
- complete or incomplete paralysis of the limbs;
- problems with eye rotation;
- frequent dizziness.
Important factors when forming a prognosis are the speed of referral to specialists and the age of the patient. The older a person is, the more difficult the recovery process is.
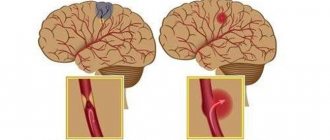
Mechanism of brainstem stroke
Brainstem stroke may result from hemorrhage or ischemic injury. In the first case, a hemorrhagic form of acute cerebral circulation disorder is diagnosed. Most often, the pathological focus is localized in the bridge, but another location may be observed. Massive hemorrhage often ends with a breakthrough into the cavity of the fourth ventricle. Multiple hemorrhagic foci in the brain tissue significantly complicate diagnosis, blurring the clinical picture.
Disturbance in the flow of arterial blood to the brain structures causes the ischemic form of the disease. In this case, nerve cells begin to die from lack of oxygen and nutrients. The resulting reactive inflammatory process is accompanied by swelling of brain tissue, difficulty in venous outflow and pinching of the medulla oblongata in the foramen magnum. Without adequate therapy, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable, and the disease quickly ends in death.