Features of treatment
Lacunar cerebral infarct (LACI) is a disorder characterized by motor and sensory disturbances. Occurs due to thrombosis or embolism of small cerebral arteries. Thrombosis occurs due to vascular atherosclerosis. An embolism is usually caused by the formation of a blood clot elsewhere in the vascular system (often in atrial fibrillation) and its penetration into the cerebral vessels.
Lacunar cerebral infarction most often affects the mobility of various parts of the body, but early treatment (up to 3-6 hours after the onset of the attack) significantly increases the chances of completely curing the neurological consequences.
Features of lacunar cerebral infarction (stroke):
- possibility of unnoticeable manifestation - can only be detected on MRI;
- after the attack is completed, a cavity (lacuna) is formed;
- neurological manifestations are mild or transient (transient hemiparesis, hemihypesthesia, dysarthria, ataxia).
Complex treatment of lacunar stroke has the following goals:
- decreased blood pressure;
- restoration of normal nutrition of brain tissue;
- prevention of complicated situations (embolism, thrombosis).
This can be dealt with by competent and timely prescribed therapy, including:
- taking medications;
- rehabilitation;
- therapeutic nutrition.
Antihypertensive drugs are used to lower blood pressure:
- ACE inhibitors (lisinopril, enalapril);
- vasodilators (Diltiazem, Nifedipine);
- diuretics (Furosemide, Indapamide), etc.
To restore brain structures and improve microcirculation, Nootropil, Vinpocetine, Akatinol, B vitamins, etc. are prescribed. Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine) are used to relieve depressive conditions. Statins are used to combat atherosclerosis and lower cholesterol. To prevent complications, the patient is prescribed Aspirin, which can thin the blood.
A rehabilitation program for patients who have suffered a lacunar stroke is necessary to restore motor and speech functions and lost sensitivity. It includes:
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- speech training, etc.
If all medical recommendations are followed, the prognosis is considered favorable.
Development of the disease in the lesions
Currently, experts distinguish between small, progressive and complete strokes that affect the human brain.
Small has reversible neurological deficits. Basically, this type of pathology is diagnosed if the symptoms completely regress within 2 or 3 weeks. Today, according to statistics, this happens in 10–15% of cases. In addition, there is also a progressive stroke, which is diagnosed if the degree of neurological deficit increases over time. In this case, regression of neurological disorders or their stabilization become signs of a completed or, as it is also called, extensive stroke.
Lacunar stroke, which is a type of ischemic stroke, occurs in 15–30% of cases. The development of pathology begins in the formation of occlusion of small vessels in the brain. Often the site of localization is the subcortical nucleus.
According to the location, a stroke differs as follows: damage to the vascular and vertebrobasilar areas. In this case, the following is affected in the vascular basin:
- internal carotid artery;
- anterior artery;
- middle artery.
Damage to the vertebrobasilar area occurs through:
- vertebral artery;
- basilar artery;
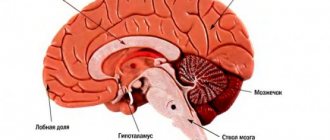
- cerebellum;
- posterior cerebral artery;
- thalamus.
What is lacunar ischemic stroke?
Gaps in brain tissue are like holes in cheese, but holes are formed from an abundance of fermentation gases, while lacunae are the result of a poor blood supply.
The central artery leading to the lacuna can be blocked by a microembolus or microthrombus against the background of damage to its walls by lipohyalinosis or atheromatosis, narrowing of the lumen and difficulty in the passage of blood through it.
As a result, small focal infarctions occur in the deep parts of the brain, and atrophy of the medulla ends with its resorption with the formation of microcavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Microinfarctions are caused by “fatigue” of the vascular walls as a result of atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases of the respiratory system and other conditions leading to loss tone and degeneration of the walls aa. perforans - small-caliber perforating arteries. The more lacunae in the medulla, the weaker its work and control over the activities of the body.
You may also be interested in an article on how to recognize a mini-stroke?
Rehabilitation period
During the rehabilitation period, a whole range of measures is carried out, both medical and pedagogical, legal, social and psychological. All of them are aimed at restoring lost functions as a result of a lacunar stroke.
Principles of the rehabilitation program:
- If rehabilitation measures are started as early as possible , for example, from the first days of the onset of symptoms of the disease, recovery occurs much faster and more fruitfully. This is an excellent chance to avoid possible secondary complications, such as contractures, congestive pneumonia, thrombophlebitis and others.
- Rehabilitation should be carried out only under the supervision of specialists . If events are organized incorrectly, the chance of full recovery will be significantly less.
- Recovery requires the participation of a physical therapy methodologist, a neurologist, a physiotherapist, a psychotherapist, an occupational therapist and a speech therapist .
- The rehabilitation process involves the presence and support of the patient's loved ones . It is best to entrust the patient with the most basic household chores on weekends or in the afternoon.
Causes
Any stroke, including lacunar, develops as a result of the following reasons:
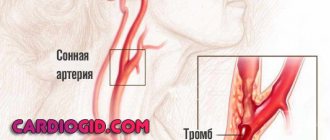
- Atherosclerosis and thrombosis. These pathologies cause ischemia (lack of blood supply to the organ) due to blockage of the vessel by a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque. The first signs of a stroke appear when the lumen of the vessel is blocked by more than 70%. With a lacunar stroke, collateral circulation (bypass as a method of compensation) does not have time to form.
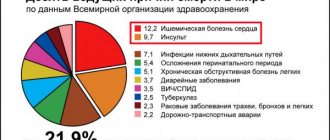
- Cardiogenic embolism. It is the cause of 20% of all strokes. An embolism forms in the heart and its valves, which is a consequence of cardiac arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation provokes a stroke in 4.5% of cases.
- Violation of hemodynamic properties, for example, with a sudden drop in blood pressure due to stenosis of the main arteries of the neck.
- Other diseases: Takayasu's disease (inflammation of the vascular walls and a decrease in their lumen), Moyamoya disease (the tendency of brain vessels to gradually narrow).
Systemic factors that increase the likelihood of developing a stroke:
- Arterial hypertension.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
- Blood diseases: blood clotting disorders, increased number of red blood cells per liter of blood.
Any of these reasons triggers a chain of pathological mechanisms that lead to ischemia and necrosis of brain tissue. Normally, the volume of blood flow in the brain is 55-60 ml per 100 g of substance per minute. Thus, the first pathobiochemical reactions occur when blood circulation decreases to 50 ml per 100 g. The first reaction is that the production of proteins in brain cells is inhibited. The primary marginal ischemic zone is formed.
When the blood supply drops to 35 ml per 100 g, an alternative pathway for energy production is activated - glucose is broken down (glycolysis). As a result of the oxidation of glucose, molecules of pyruvic acid and two molecules of ATP (one of the energy sources) are formed. An alternative pathway is the anaerobic pathway, that is, energy is generated without the participation of oxygen reaction, since during ischemia there is little oxygen in the brain. Due to the anaerobic pathway for energy production, lactate accumulates.
Lactate (lactic acid) is a normal compound that appears, for example, in muscles after intense exercise. However, due to increased glycolysis, lactate becomes too much. Lactate itself is a breakdown product that needs to be disposed of. But in the ischemic zone there is a lot of it. The accumulation of lactate shifts the acid-base balance towards acidity (pH decreases). Local acidosis occurs, which is manifested by a typical clinical picture for such a condition.
When the volume of cerebral circulation decreases to 20-25 ml, the cortex, due to lack of oxygen and nutrients, is inhibited. Drowsiness, apathy and indifference occur. When the minute volume of blood flow drops to 10 ml, irreversible organic changes occur in the brain due to the death of neurons. During the first two days, alternative sources of nutrition support the weakened vital activity of the cell. However, after 48 hours the cell dies completely.
Etiology of the disease
The causes of lacunar stroke are as follows:
- Uncontrolled arterial hypertension with severe pressure surges, crises in the absence or improper therapy;
- diabetes mellitus, in which the metabolism of carbohydrates and electrolytes is disrupted;
- pathologies with increased blood clotting and the risk of blood clots, including erythremia, extensive injuries and burns, shock, dehydration caused by prolonged vomiting and diarrhea;
- arteritis caused by infection or allergy and poor circulation;
- atherosclerosis, in which there is an imbalance in blood circulation, as a result of which the brain does not receive enough nutrients, which causes the progression of hypertension;
- genetic changes in the structure of the artery wall.
Sometimes the disease can provoke non-ischemia and tissue necrosis, as well as minor hemorrhages in the area, as a result of which the piercing vessels thicken, reduce the amount of hyaline and stick together.
Diagnosis of ischemic stroke
Timely diagnosis allows you to begin adequate therapy. It should be aimed at establishing the type of stroke, differentiating ischemia and hemorrhage.
Doppler ultrasound of head and neck vessels
Duplex scanning of the carotid arteries is necessary for all patients with stroke. Doppler ultrasound determines the causes of ischemia, as well as the need for surgical intervention. The scan reveals the degree of carotid artery stenosis.
Computed tomography of the brain
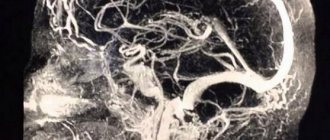
Computed tomography confirms the diagnosis of ischemic stroke. Sometimes supplemented by lumbar puncture to exclude meningitis or subarachnoid hemorrhage. The combination of CT and angiography determines vascular occlusions and tissue areas with restored blood flow.
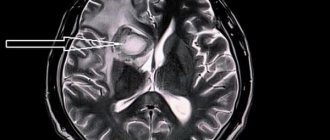
CT picture of ischemic stroke in the right hemisphere.
Picture of ischemic stroke.
Ischemic stroke in the right hemisphere.
MRI of the brain
MRI is a highly sensitive method for detecting acute intracranial hemorrhage. Imaging provides structural detail of the affected area and reveals early cerebral edema. However, CT is considered a more accessible option for emergency diagnosis.
Methods for diagnosing lacunar cerebral infarction
To establish a correct conclusion, a specialist in the field of neurology must take into account the presence in the readings of hypertensive diseases, severe arrhythmia, diabetes mellitus, transient ischemic attacks, the nuances of the clinical manifestations of the disease, the results of instrumental examinations, etc. The most popular procedures designed to search for such deformities include:
- Ophthalmoscopic testing.
- MRI scan or computed tomography.
- USGD analysis.
How long do you live after an ischemic stroke?
The prognosis for life after an ischemic stroke is of 3 types:
Favorable. It is placed when the brain damage is minor. The duration of the recovery period is reduced to several months. The person completely returns to normal life.
Average. Such prognoses for life are given if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, the patient suffers from diabetes, pneumonia or other diseases of the internal organs. Complications are of moderate severity.
Adverse. Placed in cases of extensive brain damage. Here the functioning of vital organs, in particular the heart, is usually disrupted. The chances of survival are minimal. Most often, this prognosis is given for left-sided stroke.
According to statistics, 12-25% of victims die from the consequences of a cerebral infarction in the first week. Of those who survive, 70% become disabled. However, over time, the severity of complications decreases. After six months they persist in 40% of patients, and after a year only in 25%.
The effectiveness of the rehabilitation period, life expectancy and prognosis for the future depend on several factors:
- Age. In elderly patients, even after a moderate stroke, recovery is more difficult than in younger people.
- Size and location of the affected area. If the areas of the brain responsible for the work of the most important centers are damaged, the risk of death increases greatly.
- Severity of damage. The more severe the pathology, the more difficult it will be for the body to recover.
- Cause. If the cause of an ischemic stroke is atherosclerosis or thrombosis, recovery will be much more difficult.
Among the consequences of ischemic cerebral stroke, several conditions stand out:
Mental disorders. Many find it difficult to realize their incapacity. The patient is afraid of becoming a burden to family and friends, which is why he develops depression. He experiences bouts of uncontrollable aggression. He becomes nervous and irritable. There are also frequent mood swings.
Lack of sensitivity in the face, arms and legs. The numbness goes away gradually because the nerve fibers are restored very slowly. In some cases, sensitivity does not return completely.
Impaired mobility. The victim is often unable to walk without special aids, such as a cane or walker. Sometimes it is difficult for him to do some simple things. Fine motor skills are impaired.
Cognitive impairment. First of all, they concern memory. A person forgets not only addresses and phone numbers. Sometimes he cannot remember the person with whom he had a dialogue a moment ago. It is also difficult for the patient to correctly assess what is happening around him. Therefore, in behavior he can resemble a child.
Speech problems. It becomes incoherent and meaningless. Often the victim utters some incomprehensible words and phrases.
Impaired coordination of movements. Due to frequent dizziness, a person falls.
Epilepsy. More than 10% of patients who have experienced ischemic stroke suffer from this disease.
How many years can a person live after a cerebral infarction? It all depends on how timely the assistance was provided. The sooner doctors begin treatment, the less dangerous the consequences will be.
Therapy must be comprehensive and carried out in a hospital. How long do you stay in hospital after a stroke? After the acute period ends, the patient is transferred to the general ward, where he will stay from 3 weeks to a month. If the functioning of vital organs is not impaired, the course of treatment is 21 days.
If the functioning of vital organs is disrupted, the patient must remain in the hospital for approximately 30 days. If there is no improvement, doctors hold a consultation at which they decide on his further stay in the hospital until his condition improves.
So, ischemic stroke is the most common pathology of the cardiovascular system. It's sad, but every year she gets younger. And if earlier stroke occurred mainly in older people, today even younger people face it. To protect yourself from it, you need to take your health seriously. You need to change your diet, give up bad habits and add moderate physical activity. If the slightest alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If a stroke occurs - assessment of the person’s condition, symptoms and first aid
If you notice the first symptoms, which is typical for an ischemic stroke, then you need to call an ambulance as soon as possible. A quick response will save time, and therefore increase the chance of reducing the various consequences of this unforeseen disease.
When diagnosing yourself, you need to pay attention to the following signs - what is included in an ischemic stroke, symptoms:
- weakness, loss of sensation, numbness in the face, arms or legs. Most often on one side of the body;
- decrease or loss of vision;
- loss of speech, difficulty pronouncing a word or sentence, impossible to understand someone else's speech;
- severe headache without any reason, which does not go away with the use of medications that previously helped;
- memory loss;
- it is difficult to navigate in space and perceive what is happening;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- swallowing disorder;
- loss of balance for no apparent reason.
The above signs of ischemic stroke are quite difficult to remember. To make it easier for you, experts have developed a special test that helps identify stroke symptoms and quickly provide assistance for ischemic stroke. It is called FAST - after the first abbreviations of human body parts.
FAST = FAST
Face - face
Arm - hand
Speech - speech
Time - time
We have described how to use the test in the instruction table:
| Part of the body | What to do | If it's a stroke, then... |
| Face | Ask the person to smile or show their teeth | An asymmetry appears on the face: the lips on one side of the face will rise in a smile, and on the other they will be lowered down. |
| Hand | Ask the person to raise both arms and hold them there for 5 seconds. | One hand will go down at once |
| Speech | Ask the person to say a simple phrase, for example, “the sun is bright outside.” | A person may not understand what you asked to do, and if he understands, the spoken phrase will sound incomprehensible, incoherent, and illegible. |
| Time | Call an ambulance if you see any of the signs above. | It is important not to waste time and seek help as quickly as possible. |
Diagnostics
The pathology is diagnosed using the criteria for lacunar stroke, objective examination and instrumental research methods.
Criteria for lacunar stroke:
- The clinical picture does not show a violation of cortical functions, but there is one of the five above-mentioned syndromes.
- The presence of diabetes mellitus or arterial hypertension has been established.
- Magnetic resonance imaging reveals a lesion measuring 1.5 cm.
Objective examination: a neurologist determines sensory disturbances, decreased muscle strength, impaired consciousness or impaired coordination.
Principles of treatment of lacunar stroke:
- Basic therapy: first aid, resuscitation measures (removal of cerebral edema, protection of cells from hypoxia, control of blood pressure, respiratory support).
- Specific therapy: maintaining metabolism in neurons and restoring blood circulation.
- Thrombolytic therapy (drugs that dissolve blood clots).
- Anticoagulants (drugs that prevent blood clots from forming).
- Restoration of hemodynamic properties of blood.
The life prognosis depends on the size of the stroke focus and complications (cerebral edema, pneumonia, old age). Statistically, 20% of patients die in the first month after a stroke. Patients die not from damage to brain tissue, but from complications, most often as a result of dislocation syndrome or cerebral edema. The remaining patients (80%) become disabled. The first signs of recovery in survivors appear 3 months after the stroke.
Brief information
Lacunar infarction is a type of serious malfunction in the functioning of the circulatory system of the brain, as a result of which small cavities begin to form in the human body in places where atrophied cerebral tissue is localized after suffering ischemia. The designations for such depressions were invented back in the 19th century, thanks to the medical scientist Fendal. It was he who was the first to name the identified pathological processes in patients suffering from arterial hypertension.
A detailed description of the presented disease was given later in the mid-60s of the last century. Professor Fisher revealed its direct dependence on encephalopathy of hypertensive nature. According to average statistics, a similar disease is diagnosed in approximately a third of patients diagnosed with stroke. Due to the small volume of lesions and minimal consequences, lacunar abnormalities have long been considered benign. But after carrying out certain studies in the field of neurology in a clinical setting, it became clear that such a disorder causes the development of cognitive deficits, the secondary stage of Parkinson's disease and some mental instability.
Symptoms
The main feature of lacunar stroke is its manifestation. With this pathology, any disturbances associated with consciousness, vision or speech are almost always absent. At the same time, the brain functions in its usual way, and there are no signs of damage to its trunk. The only obligatory symptom is a persistent increase in blood pressure. In most cases, it reaches its maximum values in the late evening, after which it returns to the patient’s usual level.
All the main symptoms of lacunar stroke that a person may experience are neurological. They manifest themselves in the form of specific syndromes. Their total number reaches 20 species, but only 4 of them are recorded with sufficient frequency. They differ not only in manifestation, but also in localization of disorders. These syndromes include:
- Isolated motor. It is observed in 60% of patients experiencing lacunar stroke. The pathology is concentrated in the internal capsule. Symptoms consist only of paralysis of one half of the body, which is opposite to the side where the disorders are localized.
- Isolated sensitive. About 20% of patients who have lacunar-type circulatory disorders encounter this syndrome. The localization of the problem focus is the ventral thalamic ganglion. The patient experiences problems with sensitivity, due to which he ceases to feel movements, does not feel pain, touch or changes in body temperature. All this manifests itself in the limbs, torso and head. Sometimes symptoms go away without medical intervention.
- Atactic hemiparesis. Occurs in 12% of cases, which makes it quite rare. Lacunae with this pathology are formed in the dorsal part of the internal capsule, as well as in the pons. The patient experiences severe weakness, as well as impaired coordination of movements, which manifest themselves on the left or right parts of the body, which corresponds to the side where the lesion is localized.
- Hand clumsiness, dysarthria. Only 6% of patients may encounter this, making this problem one of the least likely. Lacunae with such a stroke appear in the layers of nerve tissue. For this reason, a person experiences disorders that cause problems with speech or movement of the upper limbs, as well as complete or partial paralysis of the head, arms and legs.
If such symptoms appear that do not affect consciousness and brain activity, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. Timely medical assistance can save a person’s life, but delay will seriously increase the likelihood of death.
Additional signs indicating a lacunar infarction may include:
- Biliary dyskinesia;
- Pseudobulbar palsy;
- Parkinsonism syndrome;
- Decreased sensitivity of body parts;
- General muscle weakness;
- Change in gait, short step;
- Sudden urge to urinate, incontinence.
Other symptoms occur extremely rarely, which is why it can be argued that they are caused by specific conditions relating to the circumstances of the stroke and the general health of the patient.
Manifestations
Typically, the pathology manifests itself with a rapid onset of focal manifestations within a couple of hours. But there are cases when the violation occurs in stages with a gradual increase in the number of problems (this period can last from 72 hours to 6 days). At certain moments, transistor attacks of an ischemic nature are distinguished. In addition, with a lacunar infarction, cerebral symptoms, disturbances in the cortical regions and meningeal phenomena are not noticed. Consciousness remains clear and distinct. Also, the patient has the following symptoms:
- Hemiparesis.
- Sensory problems.
- Loss of the ability to independently perform physical activity.
- Problems with the speech apparatus.
- Pelvic dysfunction.
- Pseudobulbar anomaly.
- Neurological abnormalities.
- Depressive state.
- Difficulty concentrating and remembering received information.
- Decreased level of intellectual abilities.
- Slow thinking.
If such phenomena are neglected, a person begins a rapid progression of the disease, as a result of which the degree of cognitive imbalance begins to increase. The patient ceases to perceive any information, and there is a loss of motor reflexes.
Treatment tactics
For adequate therapy and in the future for the purpose of preventing recurrent cerebrovascular accidents, patients are prescribed aspirin to reduce the aggregation of blood elements (sticking together and forming blood clots) and improve its fluidity. The most acceptable dose is considered to be 75 mg of acetylsalicylic acid, produced specifically for these purposes.
If it is impossible to take aspirin due to intolerance or side effects, it is possible to replace it with dipyridamole at a dose of 200 mg daily or 75 mg of clopidogrel. Dosages are specified and regulated by specialized specialists.
Normalization of blood circulation is achieved by prescribing drugs that improve microcirculation. The optimal choice is nicergoline, vinpocetine, pentoxifylline. First, a course of intravenous drips is carried out, followed by a transition to long-term use of tablet forms.
At the same time, neurotrophics are recommended - medications that optimize the supply of oxygen to the brain and stimulate recovery. These are Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, citicoline and ginkgo biloba preparations (memantine, tanakan, bilobil).
With the development of signs of dementia and the formation of a lacunar state, anticholinesterase drugs and precursors of acetylcholine, a biologically active substance involved in the conduction of impulses along nerve trunks, are prescribed. These are prozerin, neuromidin, galantamine in the required dosages.
With parkinsonism, the patient needs to take specific drugs to reduce tremors (cyclodol, amantadine).
To restore mental abilities and reduce the manifestations of dementia, it is necessary to use the patient’s intelligence as much as possible, forcing him to memorize poems, allowing him to solve simple mathematical problems.
Since the leading cause is hypertension, its adequate reduction can be considered as one of the links in the treatment process. The therapist and cardiologist select an adequate dose and combination of drugs. When prescribing a correction regimen, the patient’s age and the presence of significant concomitant diseases are taken into account: diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease.
Consequences
The prognosis depends entirely on whether the stroke is isolated.
If yes, then the likelihood of a full recovery after rehabilitation is very high. Sometimes a recovered person may still have minor symptoms even after a long recovery, but this is very rare. In the presence of several foci of lacunar infarction, the prognosis is somewhat worse. Such patients are faced with lacunar disease of the brain, in which a person develops atherosclerosis, combined with thrombosis and damage to many arteries. In this case, recovery is much more difficult.
The main problem that worsens any prognosis is the person’s mental state. A lacunar-type stroke has a strong negative impact on the entire psyche, which is why it undergoes noticeable changes. A person develops memory lapses, finds it difficult to navigate in space, communicate with other people, and is constantly nervous and upset.
The consequence of a lacunar stroke for many patients is disability, which prevents them from working fully. However, with proper rehabilitation, there is every chance of returning to normal life, as well as eliminating the risk of relapse.
Rehabilitation
In cases of mild cerebral infarction, the recovery period takes about three weeks, but in more severe conditions it may take several months to achieve a full recovery, if possible. Rehabilitation includes revising your lifestyle and attending special procedures aimed at improving the general condition of the body.
Anyone recovering from a lacunar stroke will need:
Adjust your diet. Fatty foods, sweets, coffee, alcohol, as well as all foods that can increase blood pressure or trigger the return of the underlying cause of the stroke should be excluded from the diet. Spend enough time outdoors and move. Those who feel unwell can simply walk around the apartment or perform the simplest exercises possible with the windows open. Rest
It is important not only to avoid excessive mental stress, but also to sleep well. Proper rest eliminates the development of many complications and also reduces the risk of relapse
Do exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercises will help you quickly regain motor functions and improve the condition of muscle tissue, restoring their tone. Attend a massage. A high-quality head and whole body massage helps normalize physical and psychological well-being. With regular procedures, a person will feel a significant effect within a couple of weeks.
Rehabilitation is the most important component of treatment that should be considered. It allows you to regain your health as quickly as possible.
Possible complications
In cases where lacunar infarction occurs in a fairly mild form, the risk of complications is minimal. Nevertheless, it is there. And with a stroke that has several foci at once, complications almost always appear.
What can the patient expect:
- Motor skills disorders;
- Problems with orientation in space;
- Decreased intellectual abilities;
- Memory losses;
- Inflammation of nerve tissue;
- Tingling of the limbs;
- Problems with urination;
- Partial or complete loss of speech abilities;
- Death.
In the absence of the necessary treatment, a person can quickly develop any complication, which will soon lead to death, because It is impossible to survive after a stroke without medical intervention.
Symptoms
Lacunar stroke occurs without the clinical manifestations of a traditional stroke; a microstroke is often diagnosed. Speech does not undergo changes, there is no impairment of consciousness. There are no age restrictions. There are known cases of a young man suffering a micro-stroke at an age not exceeding 25 years.
Knowledge of the features of clinical manifestations of pathology can save the patient’s life:
- Hypertension for several hours may be accompanied by unbearable pain radiating to the head.
- Gradual deterioration in health, unexpected imbalance, appearance of neural symptoms.
- Unreasonably slow gait.
- Involuntary urination and diarrhea may occur during sleep.
- Rarely, loss of sensation in a part of the body and speech impairment occur.
After a micro-stroke, all damaged functions of the body are restored, which instills in the patient the idea of a past mild illness; he continues to live and work in the same rhythm. The forecasts in this case are disappointing. Complications will not take long to appear.
Doctors identify in patients many syndromes observed during lacunar cerebral infarction:
- An isolated motor variant is diagnosed in 60% of patients. The patient's half of the body, sometimes the face, is paralyzed. Lacunar lesions form near the internal capsule of the brain. Plegia occurs on the side opposite to the formed lacuna. There are no other neurological symptoms.
- The isolated sensitive variant is diagnosed in 20% of patients. All kinds of sensitivity are impaired: tactile, muscle, temperature. The disease affects the entire human body. After a while, all sensory organs and motor systems are restored.
- Atactic hemiplegia is diagnosed in 12% of patients. Muscular hypotonia of the legs occurs, and a person’s coordination in space is impaired.
- Impaired hand coordination during movement occurs in 6% of patients. Speech is impaired, and paralysis of the head and limbs on one side gradually develops.
Complications and prognosis
If the patient has once suffered a lacunar stroke, the prognosis for him is favorable. Lost brain functions are completely restored, only in some people partial disturbances of movement and sensitivity may remain.
If attacks recur, they can cause complications such as lacunar brain disease, which is common in people with vascular dementia.
As for life expectancy, the probability of death is 2%.
It is impossible to say exactly how long a person lives after a lacunar stroke. Much depends on the patient’s age, the location of pathological foci, the development of concomitant diseases, and the timeliness of medical care.
The formation of gaps in the brain stem is especially dangerous, because this is where the respiratory and cardiovascular centers are located.
The likelihood of death increases with a recurrent stroke.
Prevention
Lacunar ischemic stroke is a disease that mostly affects older people. Statistics are misleading and more and more young people are being affected. The reasons for the rejuvenation of the disease lie in the increasingly accelerating pace of life, increasing causes of stress, and bad habits. Having suffered a stroke, a person does not change his life and does not listen to the signals that the body sends. Lack of attention to yourself leads to irreversible consequences. For preventive purposes you should:
Use regular aspirin. It prevents vascular infarction. Attending physicians recommend that patients take soluble aspirin after discharge from the hospital. Take inventory of your menu. It is required to completely eliminate fast food and everything connected with it. Limit salt intake. After illness, it is strictly forbidden to use cholesterol- and sugar-containing foods in the diet. Closely monitor the dynamics of blood pressure values. Create a special notebook for daily recording of indicators and do not allow it to increase critically. Stop drinking alcohol and quit smoking. Do physical exercise, take walks in the fresh air. Monitor your body weight. After a myocardial infarction, it is necessary to undergo a recovery course. As prescribed by your doctor, take medications that prevent the formation of blood clots
Pay attention to the prothrombin index. If you suspect a stroke, immediately call a doctor and talk about how you are feeling. The consequences of an untreated disease will not allow the patient to lead a full life.
The lifestyle must be transferred to a calm, measured direction. Try to avoid unnecessary stress, heavy physical exercise, and forget about overwork. For those at risk, set a rule: undergo an MRI annually. Monitor the dynamics of the disease and, based on the results, make adjustments to therapy with the attending physician.
People around the patient should show patience and understanding. It must be remembered that after the development of lacunar syndromes ends, brain functions are restored. The period of recovery and return to a full life of a person who has suffered a lacunar stroke depends on a friendly attitude, sensitivity and attentiveness to the victim. First aid in case of recurrence should be provided by them.
Preventive actions
Lacunar stroke affects not only the elderly, but also the younger generation.
What is most noteworthy is that men are more susceptible to this disease than women. The main causative agent of cerebral infarction is an unfavorable lifestyle, being in a stressful state, constant stress on the neurons of the brain, blood vessels and heart. Despite the seriousness of the situation, the best medication for preventing the disease is Aspirin. It significantly reduces the risk of recurrence of the lesion. In this case, the drug should be taken only in its pure form.
In addition, to protect yourself from illness, you should take care and reconsider your lifestyle:
- It is imperative to follow a diet that does not contain foods with high sugar, cholesterol and other harmful substances;
- At the same time, it is recommended to take preventive medications, which are prescribed by a doctor during periodic examinations, which should be carried out at least once every six months;
- Blood pressure should always be monitored; it is best to measure it several times a day (and it is better to note all readings in a diary);
- if any of the symptoms of the disease appear, you must immediately contact a specialist;
- and of course you should completely give up alcohol and smoking;
- Get out into nature as often as possible and breathe fresh air.
Do not forget that overwork, stress and excessive loads only increase the likelihood of illness, so everything should be in moderation, and conflict situations should be avoided altogether. Sports should be present in life, but in such a way that it does not harm health.
Main reasons
The occurrence of a stroke is always associated with arterial hypertension. Chronic exposure to high blood pressure causes various pinpoint damage to cerebral vessels, up to 1 cm in length:
- death of artery wall cells, leakage of fibrin into the affected area (fibrinoid necrosis);
- release of plasma from the bloodstream (plasmorrhagia);
- impregnation of the vessel wall with a specific protein, making it look like a glass tube (hyalinosis);
- replacement of the artery wall with connective tissue;
- fat deposition, usually without the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
The nerve cells located around the affected artery begin to receive an inadequate amount of oxygen and nutrients. When their deficiency becomes critical, neurons die. Over time, a lacuna forms at the site of necrosis.
Another mechanism for the formation of cavities is typical for infarctions located at some distance along the main vessel. The middle layer of the artery consists of muscle cells - myocytes, which are destroyed under the influence of arterial hypertension. The vessel ceases to cope with pumping blood, its distant branches remain half-empty, which leads to necrosis of neurons.
Rarely, the death of neurons to form lacunae is caused by the rupture of tiny protrusions of brain vessels (aneurysms). This form of the disease belongs to the hemorrhagic subtypes of cerebrovascular accident.
Previously, it was believed that arterial hypertension was the only cause of lacunar stroke. More thorough studies have shown that in some patients, cerebral infarction develops as a consequence of a combination of atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries and high blood pressure. But atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries themselves, which supply the brain, extremely rarely cause the formation of cavities.
Other risk factors for lacunar stroke (3):
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- suffered micro-strokes;
- elderly age.
Pathogens
The described disease can manifest itself as a result of a failure in the blood supply in one of the perforating vessels of the arteries. In almost 80% of lesions, the area of change is the white matter of the cerebral region, located in the subcortical zone and the inner shell, in the remaining 20% - in the base and bridge. Typically, the main cause of progression of deformities is chronic arterial hypertension. Due to this, anomalies begin to appear in the walls of the vascular canals. In the case of such a process, the patient experiences a decrease in the lumen of the artery, which entails problems in the circulatory system, which supplies a certain area of cerebrotissue. After this, signs of ischemia and death appear in the affected lobe; subsequently, a hole is formed in place of the removed cells.
The main etiological sources of the disease are:
- Chronic disease of the arteries of the elastic and muscular-elastic type, renal failure with an increased number of creatinine in the blood cells.
- Diabetes.
- Alcohol abuse.
- The chronic stage of obstructive disorders occurring in the pulmonary apparatus.
- Infectious agents that have entered the body.
- Autoimmune diseases, etc.
Symptoms of lacunar stroke
In most cases, the lacunar form of the lesion occurs as cerebral ischemia with a transient attack, like a microstroke, but the course may not be accompanied by symptoms. Features of the pathology:
- history of complicated and prolonged course of hypertension;
- the patient does not lose consciousness;
- focal symptoms increase over several hours or days, mainly during sleep;
- prognosis – satisfactory, with maximum possibilities for restoration of brain functions;
- angiographic examination does not reveal pathological changes;
- according to CT and MRI data - the presence of small, loose, round-shaped foci in the structures, or the absence of changes.
There are several variants of the course of lacunar stroke; they are also distinguished by the localization of lesions in the brain:
- Isolated motor form - the formation of lacunar cavities in the body of the bridge and the posterior part of the thigh of the internal capsule. The patient's symptoms include paralysis of one side of the body opposite the lesion.
- Isolated sensitive form - the ventral thalamic ganglion is affected. It manifests itself as a violation of the patient’s sensory functions (sensory syndrome).
- Atactic hemiparesis - the dorsal part of the internal capsule and the Varoliev bridge are affected. The patient has ataxia localized on the side of the injury, weakness of the muscles of the arm or leg, and pyramidal disorders.
- Dysarthria and dysfunction of one hand - occurs when lacunae form in the basal cells of the bridge. The patient has speech impairment of the dysarthric type, clumsiness of the hand develops, and paralysis in the muscles of the upper and lower extremities or head is possible.
Other symptoms:
- body movements performed involuntarily and obsessively (hyperkinesis) - tremors of the limbs, twitching of the shoulders and head, impaired muscle tone;
- parkinsonism syndrome;
- walking with small steps, staggering, lack of coordination;
- pseudobulbar syndrome;
- tendency to fecal and urinary incontinence;
- memory impairment.
Most often, a lacunar stroke occurs during sleep, the patient lies down feeling a headache and general malaise, and in the morning symptoms of the pathology appear. If the lacuna has formed in the “silent” zone, then there may be no clinical manifestations.
If a patient with lacunar ischemia works, then symptoms may manifest as difficulty concentrating on performing duties, lethargy, and slow processes of memorization and thinking. Sometimes the patient experiences difficulties with writing and perceiving new information.
The mild, and sometimes asymptomatic, course of the lacunar form of stroke gives the patient a chance to quickly recover from the injuries received. On the other hand, an asymptomatic course becomes the reason for therapeutic assistance not provided in a timely manner, which in the future can lead to relapses of the disease in more severe forms, which are accompanied by severe neurological deficits.
If no significant stroke symptoms were observed, subsequent examinations may reveal round cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid in the brain structures. These formations have the nature of cysts and do not threaten the patient’s life, do not cause neurological disorders, but indicate that the patient has suffered a lacunar stroke.
Formations can be noticeable within a week after lacunar brain damage.
Further prognosis for lacunar cerebral infarction
Experts report relatively favorable recovery results. With timely medical care and specific intensive therapy, the patient experiences a complete regression of neurological impairment. But there is a 30% chance of dementia, vascular problems and mental disorders. The risk increases significantly if the described anomaly recurs with a frequency of more than 12%. The experiments conducted indicate a third of survivors, most of whom were diagnosed with a resumption of symptoms.