Symptoms
As mentioned earlier, in the early stages, signs of hypoplasia may be completely absent.
The development of the pathological process can last for years and only when the arterial lumen narrows to a certain value will some symptoms appear. The paradox is that in the complete absence of manifestations of pathology in the early stages, the entry of the disease into the so-called active phase is accompanied by a rich clinical picture. However, in each patient with narrowing of the vertebral artery (right or left), symptoms manifest themselves completely differently:
- Headaches of different nature and specificity. Painful sensations can be periodic or constant, intensify after intense physical activity or occur at rest. With hypoplasia of the cerebral artery, the pain also differs in intensity, from strong, which has to be relieved with analgesics, to weak, which many tolerate without medication. As for the specifics, in most cases we are talking about dull and aching pain, however, they can also be sharp, stabbing.
- Unreasonable dizziness indicates cerebral circulatory disorders. This clinical sign is the second most common and also varies in nature. In some cases, dizziness is not associated with physical exertion, emotional state and other factors; they simply occur more frequently and disappear as quickly as they appeared. In other cases, dizziness begins after a change in body position, any load, stress, etc.
- Often hypoplasia of the right vertebral artery is accompanied by emotional disturbances. A person experiences frequent and sudden changes in mood, depression, which can last up to 2-3 days, then disappear without a trace, constant lethargy, states of apathy and even depressive states.
- If we talk about hypoplasia of the left vertebral artery, this form of the pathological process is more often characterized by changes in blood pressure. Yes, with right-sided hypoplasia they are also present in the clinical picture, but in this case they are noted more often.
- The pathology affects the patient’s body with a state of drowsiness, fatigue, and a feeling of weakness. People with hypoplasia do not get enough sleep even with a full, sound eight-hour sleep, are in a lethargic state, and often yawn.
- The pathology may be accompanied by disorders affecting the vestibular apparatus. In this case, dizziness is also present among the clinical signs, but they become more intense, and are accompanied by nausea, excessive sweating, and changes in skin color (pallor or, conversely, redness of the face). The clearest signs of damage to the vestibular apparatus and the progression of this pathology will be impaired coordination. A loss of balance appears, the gait becomes uncertain, the person sways from side to side, all movements become unclear, and loss of space may develop.
Over time, the symptoms worsen; severe forms of vertebral artery hypoplasia are accompanied by damage to the nervous system. On the one hand, this is expressed in numbness of certain parts of the body (usually limbs), on the other, visual hallucinations. In some cases, partial paralysis even occurs.
Consequences and complications
In general, VA hypoplasia significantly impairs quality of life. The most serious complications of VA hypoplasia primarily include a high risk of cerebrovascular accident/ stroke , which is caused by a decrease in blood supply to brain structures. In addition, frequent complications of the pathology of the vertebral arteries include neurological symptoms: headaches ( migraine ), irritability, depression, severe fatigue, disorders of the autonomic nervous system, impaired auditory/visual function, weakened cognitive abilities, dementia, decreased ability to work, arterial thrombosis
Causes
Hypoplasia, that is, an anomaly in the development of tissues or an organ, which in this case concerns the vertebral arteries, as mentioned earlier, is a congenital pathology. This means that the main reason for underdevelopment of the artery is problems in the embryonic stages. At the same time, a number of factors can be identified that contribute to the fact that hypoplasia of the vertebral artery occurs in a newborn and manifests itself at a certain age:
- Infectious diseases transmitted by the mother during pregnancy.
- Exposure of the fetus to radiation or ionizing exposure.
- Mechanical injuries, including blows, bruises and other injuries to the abdominal cavity during pregnancy.
- Narrowing of the artery in a newborn can be caused by a genetic predisposition, for example, if the family history includes pathologies of a vascular nature.
- Toxic factor - if during pregnancy a woman smoked, abused alcohol, worked at a chemical plant, or took any potent drugs for a long time, there is a high probability that hypoplasia may be associated with each of these factors.
Everything about the treatment of hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries
Most diseases affecting the brain are vascular in nature. Hypoplasia is no exception. This is a congenital pathology affecting the intracranial blood supply. The essence of the disease, its symptoms, diagnosis and treatment - this is the subject of research in this article.
Most diseases affecting the brain are vascular in nature. Hypoplasia is no exception. This is a congenital pathology affecting the intracranial blood supply. The essence of the disease, its symptoms, diagnosis and treatment - this is the subject of research in this article.
Diagnostics
It is extremely difficult to identify hypoplasia in the early stages of its development due to the lack of characteristic symptoms and manifestations. There are three main methods for diagnosing narrowing of the lumen of the vertebral arteries, which include:
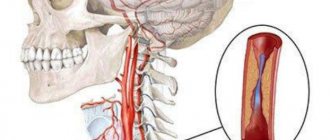
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck . During the procedure, the image of the artery is recorded using an ultrasound machine, after which the type, intensity and diameter of blood flow is analyzed (a narrowing of the diameter of the vessels to 2 mm or less is considered a serious defect).
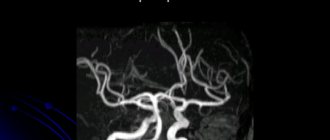
- Tomography of the head and neck . Using computer and magnetic resonance imaging, the condition of the vessels filled with a special contrast agent is assessed.
- Angiography . X-ray examination, which reveals abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels and vertebral arteries.
In addition, to diagnose concomitant diseases that may affect the course of hypoplasia (for example, pathology of the cervical vertebrae), the doctor may prescribe additional studies.
- Hypoplasia of the left vertebral artery: what is it, causes and treatment features
At the stage of pronounced clinical symptoms of hypoplasia of the right or left vertebral artery, conservative treatment with vasodilators - they eliminate unpleasant phenomena and improve the patient’s quality of life. In cases where there is a risk of blood clots, taking anticoagulants (blood thinning medications) is indicated.
When is vertebral artery hypoplasia diagnosed?
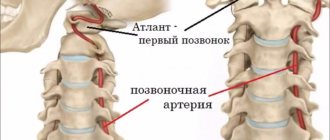
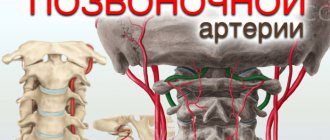
It is in the intracranial segment that pathological narrowing of the vertebral arteries is most often observed. The diameter of these great vessels is uneven along the entire length and ranges from the smallest value - 2 mm, to a lumen of 4.5 mm. The normal diameter of the PA usually ranges from 3.5 to 4 mm.
Hypoplasia of the vertebral artery is considered to be its critical narrowing of up to two millimeters. Congenital breakage or complete absence of one of the branches is also possible - this pathology is called aplasia.
- Incorrect position of the fetus in the womb, due to which it is exposed to unwanted mechanical stress.
- Carrying a pregnancy to term under negative conditions that negatively affect the development of the embryo: maternal use of alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- finding the future woman in labor in a hazardous environment (working in a chemical production facility, living in a gas-polluted or radioactive area);
- infectious pathologies, injuries, medication, intoxication, poisoning during pregnancy.
Barre-Lieu syndrome
A classic sign of a malnutrition of the occipital lobe of the brain. Gives headache, nausea, and rarely vomiting.
Orientation in space also decreases, pathological fatigue and fatigue are detected.
Insomnia, depressive mood, constant depression, apathy and reluctance to do anything.
Hypoplasia of the vertebral artery: what is it?
One of the most common pathologies of the vertebral arteries is their hypoplasia, that is, underdevelopment. This anomaly manifests itself as a significant narrowing of the lumen of the vessel (it becomes less than 2 mm). The left vertebral artery is affected more often than the right. Hypoplasia occurs in utero - this is a congenital pathology. Various factors can provoke the appearance of the disease in question:
- Bad habits of the expectant mother.
- A woman's use of dangerous drugs in early pregnancy.
- Intrauterine infection of the embryo.
- Effect of radiation on pregnant women.
It is also worth noting that quite often hypoplasia is found in children who do not have a history of any of the listed factors.
Treatment methods
To treat hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries, methods of conservative therapy and surgical treatment are used.
To treat hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries, methods of conservative therapy and surgical treatment are used.
- What is hypoplasia of the right or left vertebral arteries, how to treat this disease?
Diagnosis of hypoplasia of the vertebral artery of the brain
With hypoplasia of the vertebral artery of the brain, typical clinical symptoms are present, which are a direct indication for a number of clinical studies. Typically diagnosis includes:
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- MRI of brain structures;
- duplex scanning of cerebral blood vessels;
- angiography with the introduction of a contrast agent.
It is worth paying attention to the following negative manifestations of the disease:
Diagnostics
Depending on the preliminary diagnosis, the specialist prescribes a proper diagnostic regimen.
The process of diagnosing pathologies takes place in several stages:
- Face-to-face consultation with a survey of the patient regarding current complaints, duration and severity of symptoms, the presence of direct provoking factors;
- Study of anamnesis (personal and family);
- Laboratory tests for the presence of atherosclerosis (lipid profile with calculation of the atherogenic coefficient, biochemical blood test, determination of proteins in blood serum, etc., at the discretion of the specialist);
- Magnetic resonance or classical angiography;
- Ultrasound Dopplerography (Doppler ultrasound).
The latest study is considered the most informative. It allows you to determine:
- The speed and intensity of blood flow in the vessels;
- Places that prevent the movement of arterial blood to the brain;
- The presence of atherosclerotic lesions;
- The presence of detachments, dilations, occlusions, stenosis of the vessel;
- The presence of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques, their size and shape;
- Deformations of the vessel (tortuosity, loops, protrusions, bends);
- Dimensions of the lumen of the affected vessel;
- Condition of the vascular walls (elasticity, mobility, firmness);
- Modifications of the arterial wall.
When a pathology is detected, the specialist prescribes comprehensive treatment to the patient.
Right vertebral artery
According to statistics, hypoplasia of the right vertebral artery occurs once in every tenth person, that is, it affects 10 people out of 100.
Narrowing of the right VA in most cases is also a congenital pathology. This form of the pathological process is also accompanied by impaired blood supply, however, ischemia and blood stagnation in this case occur less frequently.
Doctors call concomitant diseases of the circulatory system and blood vessels the main danger factor for PPA hypoplasia. If hypoplasia of the vertebral artery on the right is accompanied, for example, by vascular atherosclerosis, the development of the second disease and associated degenerative changes in the head will proceed many times faster than if the disease developed independently.
The severity of the pathological process largely depends on how extensive it is. The disease can affect the posterior communicating artery, cover all 4 segments (segments of the artery are not involved in the pathological process immediately, but one at a time), etc. In cases where the pathology takes on a severe course, is complicated by other diseases, affects the vertebrobasilar system and concerns vertebral artery, the patient may experience decreased sensitivity in certain areas of the body. This is a clear sign of circulatory problems in the corresponding area of the brain; in such situations, immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination.