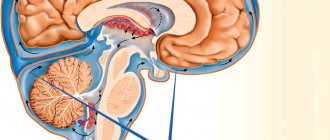
If excess fluid accumulates in a person’s brain, which prevents the organ from functioning normally, it is called dropsy, or hydrocephalus of the brain. Excess fluid increases pressure on the brain structures, pressing them against the skull. In the absence of timely diagnosis and qualified treatment, the patient may die.
The success of treatment depends on the degree of damage, severity of the process, symptoms and concomitant pathologies. The disease can be congenital or acquired.
Types of dropsy
The classification of hydrocephalus of the brain is quite complex, with blurred diagnostic boundaries. Until recently, this disease belonged exclusively to children, but today it has been proven that it is possible to develop dropsy in adults.
Clinical manifestations of dropsy are divided into groups:
- The mixed form is severe, the volume of fluid increases inside and outside the brain. The prognosis is unfavorable. Violations cause epileptic seizures, convulsions, and paralysis of the limbs.
- Atrophic hydrocephalus of the head develops against the background of traumatic brain injury. The ventricles increase symmetrically, the volume of gray and white matter decreases. A month after the injury, changes become noticeable. This is a natural reaction of the body. The prognosis of the post-traumatic form of the disease is unfavorable.
- Hydrocephalus vicarious - the ventricles become enlarged, but the anatomical structure of the brain does not change. The prognosis is favorable if detected at an early stage. In the vast majority of cases, the development of the disease can be stopped and the situation stabilized.
- Hypotrophic hydrocephalus develops as a reaction to a malnutrition of the brain, when soft tissues lack nutrients. A person has a headache and vestibular functions are impaired. The condition is aggravated by nausea and vomiting.
- The compensatory form appears when the acute stage of the disease has passed. The volume of fluid in the ventricles stabilizes, but their volume remains increased. There is no treatment.
- Non-occlusive form - changes do not cause hypertension. The nature of the disorders is not clear, the inflow and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid remains at the same level, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is within acceptable limits.
- Partial form - an increase in fluid volume causes neurological changes. A characteristic symptom of the disease is epileptic seizures.
- Discirculatory hydrocephalus - a lack of cerebral circulation is diagnosed, often accompanied by atrophic processes.
Whatever the etiology, dropsy remains a dangerous disease, the consequence of which is disruption of brain function, deterioration of thinking ability and perception of information. It is important to identify the disease at an early stage and stop its development.
Signs of the disease
The symptoms of the disease are dictated mainly by reduced perfusion of brain tissue, overstretching of groups of nerve fibers (conducting pathways) due to increased ICP.
- In acute pathogenesis, weak microcirculation (hypoperfusion) leads mainly only to functional disorders of intracranial metabolism. This is
a change in energy metabolism, a reduction in the level of creatine phosphate and ATP, an increase in the concentration of lactic acid and inorganic salts of phosphoric acids. The acute clinical picture is reversible. - The long-term existence of hypoperfusion causes irreversible transformations at the structural level. These are
defects in the vascular endothelium and disruption of the BBB, axonal damage (destruction of axons, up to their complete disappearance). Dropsy of prolonged duration ultimately causes brain atrophy. - The morphology of signs in hydrocephalus in combination with high intracranial pressure is characterized, first of all, by atrophy of the substance of the brain and periventricular edema. There is also damage to the vascular mesenchyme, disruption of brain homeostasis, axonal lesions, and in rare cases, neuronal death. These signs are combined with the clinical picture of the primary pathology that provoked hydrocephalic syndrome.
The symptomatic complex characteristic of hydrocephalus in early childhood includes such distinctive features as:
- increased head size;
- frequent regurgitation;
- restless behavior of the child;
- bulging of a large fontanel;
- divergence of cranial sutures;
- the severity of the venous pattern on the scalp;
- delayed psychomotor development, less often physical;
- throwing the head back;
- “setting sun” syndrome (Graefe);
- congestive optic disc;
- paraplegia of the lower extremities (in severe, advanced conditions).
In adults and older children, the clinical picture depends on the rate of progression of hydrocephalus. In the acute form of the disease, combined with high ICP, the following are observed:
- a bursting and pressing headache that spreads to the orbits of the eyes (one of the features is the peak of pain in the morning after a night's sleep, and then, during the day, the severity of the pain syndrome decreases);
- nausea, which usually accompanies morning headaches (vomiting often occurs in the morning, after which a person notices an improvement in the condition);
- visual disturbances usually include blurred vision, blurred vision, double vision and a burning sensation in the eyes;
- fatigue, drowsiness, lethargy;
- convulsive phenomena (like an epileptic seizure);
- when the brain stem is compressed due to dislocation of brain structures - oculomotor disorders, forced head position syndrome, clouding of consciousness (up to a coma), respiratory failure.
Hydrocele of the brain in the chronic stage manifests itself:
- signs of dementia (dementia), emotional instability;
- apraxia of walking, more often it manifests itself with a shaky and uncertain gait, disproportionately large steps (being in a lying position, patients often do not experience difficulties in imitating walking and twisting a “bicycle” with their legs);
- decreased muscle strength, sometimes patients complain of pain in the neck;
- severe imbalance (in the final stages), which is expressed by a person’s inability to move and sit independently;
- partial or complete loss of sensitivity (not always!):
- urinary and/or fecal incontinence (with a massive lesion).
The pathology is dangerous due to its life-threatening complications! In no case should you ignore an urgent visit to the doctor if one or more symptoms from the lists provided are identified. Timely visit to the hospital for the purpose of diagnosis and receiving adequate medical care increases the chances of a favorable prognosis, including complete recovery.
On average, out of 10 patients who do not receive treatment at the right time, 6-7 people die soon (this also applies to children). Those who did not undergo therapy but survived are doomed to disability with neurological disorders, mental and physical disabilities with a tendency to progress.
Reasons for the development of pathology
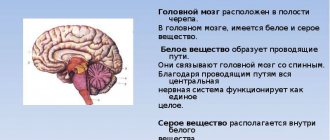
The human brain consists of soft tissues located in the skull. To protect against damage, cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the cavity - the liquid fills the internal ventricles and grooves. When a person is healthy, the inflow and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is balanced. The performance of its functions does not affect the patient’s health. If disturbances occur due to the development of tumors, injuries and infections, intracranial pressure increases and the process of cerebrospinal fluid movement is disrupted, causing changes in brain function and neurological manifestations.
Hydrocephalus can develop due to a stroke or tumor development.
Classification of pathology by form
Hydrocephalic syndrome is classified according to localization, pathogenesis, fluid pressure level, and flow rate.
The localization of the outbreak comes in three varieties:
- internal - cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in excess in the lateral ventricles;
- external - overconcentration of cerebrospinal fluid is determined in the subarachnoid space;
- mixed - simultaneous accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles and subarachnoid space.
Based on the pathogenesis, GM hydrocephalus can be:
- occlusive (closed) – the most dangerous form, resulting from blockage (occlusion) of the cerebrospinal fluid passages by a tumor, hematoma, or post-inflammatory adhesions;
- communicating (open) - with this pathogenesis, there is a disruption of resorption processes due to damage to the structures involved in the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous system.
Based on the CBF pressure indicator, they are distinguished:
- hypertensive hydrocephalus – the level of intracranial pressure is increased;
- normotensive – ICP remains within normal limits;
- hypotensive – the pressure inside the skull is reduced.
Hydrocephalus is diagnosed based on the rate of progression:
- acute - from the appearance of the first signs to the phase of severe clinical decompensation it takes no more than 72 hours;
- subacute – develops within 30 days;
- chronic - formation occurs at a slow pace, over months and even years (more common in open forms).
In ICD-10, hydrocephalus is assigned a general code of G91. Each form has its own alphanumeric symbol: communicating - G91.0; occlusal – G91.1; normotensive – G91.2; post-traumatic unspecified – G91.3; another type – G91.8; hydrocephalus of unspecified origin – G91.9.
How does dropsy manifest itself?
With moderate development of the process, minor neurological disorders appear. You can't ignore:
- Nausea;
- Headache;
- Vomiting;
- Deterioration of vision;
- Changes in the appearance of the eyeballs;
- Problems with the vestibular system;
- Mental abnormalities.
The open external form has manifestations similar to mental disorders. If the diagnosis is made incorrectly, the patient will be treated in a psychiatric clinic, and the underlying disease will go unnoticed. To make a correct diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes additional tests:
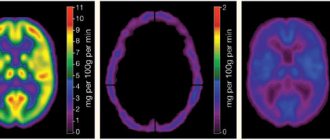
- MRI of the brain is clear - the results of tomographic diagnostics will show the localization of the pathology and the catalyst for the disorders (infants may be prescribed neurosonography instead of MRI);
- puncture - children are tested using general anesthesia;
- fundus examination.
At the initial stages of the development of the process, an accurate diagnosis can only be made using instrumental methods.
Diagnosis of dropsy of the brain
Clinical manifestations are so specific that they allow a neurology specialist to suspect hydrocephalus already during the initial examination of the patient. Despite this, the diagnosis of pathology always involves differentiating hydrocephalic syndrome from other possible diseases that have similar symptoms.
To differentiate, as well as establish the localization, degree and form of hydrocephalus, the etiological factor of its development, according to the doctor’s decision, the leading visual diagnostic tools are prescribed in a certain combination:
- magnetic resonance imaging (the most informative);
- conventional or multislice CT;
- echoencephalography (shows the level of ICP);
- neurosonography (done on infants through an open large fontanel to determine ICP);
- radiography (more of a backup method, sometimes recommended for assessing the condition of the skull bones).
If cerebral vascular pathology is suspected, the patient is examined using MR angiography. Dropsy of infectious origin additionally involves performing a PCR analysis to identify the type of infection. All patients are prescribed ophthalmological examinations, including examination of the fundus with an ophthalmoscope, eye perimetry, and visometry.
What is the danger of the disease?
The consequences of dropsy largely depend on the age at which the disorders occurred and the development of complications:
- Infants experience high excitability, sleep disturbances, and increased muscle tone. The most severe manifestation is developmental delay and mental deviations.
- Preschoolers show aggression, stutter, develop strabismus, and experience developmental delays.
- School-age children experience memory loss and headaches. The learning process is difficult.
- In adults, epilepsy, increased excitability, and hallucinations appear.
The danger of the disease in adulthood is the development of mental disorders, motor functions and motor skills. If urgent measures are not taken, the patient becomes disabled.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus in adults
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose hydrocephalus using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These methods make it possible to determine the size and shape of the ventricles, brain cisterns, and subarachnoid space. If doctors at a neurology clinic detect early signs of hydrocephalus on an MRI, they prescribe medication to stop the progression of the disease. X-ray of the cisterns at the base of the brain allows us to clarify the type of hydrocephalus and assess the direction of the cerebrospinal fluid flow.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use the following methods for diagnosing atrophic hydrocephalus:
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography, which allows you to determine the size and shape of the cisterns of the brain, ventricles and subarachnoid space;
- radiography of the tanks, with the help of which the type of hydrocephalus is clarified and the direction of the cerebrospinal fluid flow is determined;
- diagnostic test spinal puncture with collection of 40-55 ml of cerebrospinal fluid, accompanied by a short-term improvement in the patient’s condition;
- ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels to determine the state of arterial and venous blood flow.
After analyzing the results of a comprehensive study, individual treatment is prescribed. The tactics for managing patients with severe hydrocephalus are developed at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. Neurosurgeons determine indications for surgical intervention.
A trial diagnostic lumbar puncture with removal of 30-50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out to diagnose the disease. After the procedure, the patient’s condition temporarily improves due to the restoration of blood supply to ischemic brain tissue against the background of a decrease in intracranial pressure. In acute hydrocephalus, lumbar puncture is not performed due to the high risk of brainstem herniation and the development of dislocation syndrome.
To clarify the diagnosis, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe craniography, ultrasound, and angiography. The results of the examination are discussed at a meeting of the expert council, where tactics for managing a patient with hydrocephalus are developed.
How to treat dropsy?
This brain pathology is practically incurable. Existing medications are designed only to slow down the process.
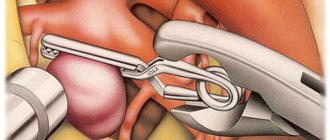
The most effective treatment method today is surgical, when the patient undergoes bypass surgery or endoscopic surgery.
Massage plays an important role in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Dropsy helps to increase muscle tone, and stroking and rubbing movements have a relaxing effect, helping to restore motor functions.
Another type of treatment, manual therapy, is used as an addition to the use of medications. Manual influence is aimed at activating the human body’s own reserves. The use of manual therapy for secondary dropsy is especially effective.
Recommendations for the use of treatment methods are given by a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Treatment of hydrocephalus
In the case of congenital hydrocephalus, treatment is carried out mainly through surgery. Its goal is to eliminate the cause that impedes the outflow of fluid. Surgical treatment is also used in the presence of a tumor process in the brain, intracranial hematoma, or abscess. If the cause cannot be eliminated, then shunting is performed (a system for cerebrospinal fluid drainage is applied to another area where nothing will interfere with its absorption).
For acquired hydrocephalus, treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of its occurrence. Diuretics are prescribed as drugs to alleviate the patient's condition.
Sources:
- Bogadelnik I.V. Hydrocephalus in children / I.V. Almshouse [and others] // Child’s health. — 2011.
- Zamyshlyaev P.S. Hydrocephalic syndrome. Pathomorphology. Prevalence in the Republic of Mordovia / P.S. Zamyshlyaev [and others] // Pulse. - 2015. - T. 17. - No. 2. - P. 65-67.
Diet
The patient's nutrition should be aimed at improving the water-salt balance. Foods that cause fluid accumulation should be excluded from the diet. Instead, vegetables and fruits, steamed meat, and cereals are introduced into the menu.
It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, exercise with moderate exercise, and walk a lot. Following these recommendations will help maintain the patient's mental and mental fitness.
Dropsy is a serious disease that does not go away on its own. The patient requires qualified specialist assistance for life. The disease is in an advanced stage and cannot be treated.
Classification of the disease
There are three main forms of pathology:
- occlusive hydrocephalus, or internal, is a condition in which fluid does not flow from the ventricles, while the space around the brain is compressed;
- non-occlusive hydrocephalus, or external, - fluid can enter from the ventricles into the space between the brain and its membranes, while they expand and compress the nervous tissue from the outside;
- mixed hydrocephalus is a combination of several blocks of cerebrospinal fluid outflow pathways.
External replacement hydrocephalus is a severe form in which the substance of the cerebral cortex atrophies, and excess fluid takes its place. A synonym for this condition is atrophic hydrocephalus.
The disease is also divided depending on its causes into post-traumatic, post-infectious and post-hemorrhagic forms. Hydrocephalus can be progressive (active) or chronic (compensated). It is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure.
Which doctor should I contact?
Hydrops is treated by neurosurgeons. When you contact the RAS clinic in Moscow, you will be provided with qualified, effective assistance: they will conduct an examination, prescribe tests, make a diagnosis, and determine an effective treatment strategy.
If any symptoms of neurological diseases appear, you must immediately make an appointment with a neurologist to prevent the situation from worsening. We invite you to a consultation with a neurologist in Moscow at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Registration can be made by phone or using the feedback form on the website.
Endoscopic operations
Endoscopic surgical techniques are used in the treatment of occlusive hydrocephalus, among them:
- ventriculocisternostomy;
- ventricular cystocisternostomy;
- ventriculoplasty of the aqueduct of Sylvius;
- septostomy;
- etiotropic endoscopy (getting rid of the causative factor - removal of a tumor, cyst, hematoma, etc.).
In 90% of cases, the method of endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy is used. The purpose of this operation is perforation of the bottom of the third ventricle of the brain under endoscopic control through a miniature trepanation window. The anastomosis created during the endoscopic procedure allows you to restore the natural path of outflow of cerebrospinal fluid between the third ventricle and the basal cisterns of the brain.
Endoscopy of any kind is a more gentle tactic of neurosurgery; it does not require the implantation of foreign bodies into the body and is less likely to cause postoperative consequences. Despite the promising characteristics of endoscopic methods, in some cases it is impossible to do without shunting or the use of open microsurgery.
Modern neurosurgery technologies have been honed to perfection in the Czech Republic; brain surgery in this country is a leading field of medicine. Neurosurgical care in clinics in the Czech Republic is no worse than in Germany and Israel, but the price is much lower (about 2 times). People with this diagnosis are operated on here at the most exemplary level, and upon completion of the full course of rehabilitation they are discharged with excellent and good results.
Prevention and consequences of hydrocephalus
The prognosis for this disease is difficult to determine. It largely depends on how early treatment is started and the extent of irreversible brain damage.
The consequences of hydrocephalus include delayed physical and mental development. However, with the right rehabilitation program, many children with this diagnosis can lead normal lives with minor limitations.
With a progressive form of pathology, the prognosis is unfavorable.
On the other hand, even bypass surgery is not always accompanied by complete recovery. The factors on which this depends have not been fully established.
Therefore, disease prevention is important:
- if necessary, genetic counseling for expectant mothers;
- protection against infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- prevention of traumatic brain and birth injuries;
- vaccination against pneumococcus, which protects against meningitis;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases causing hydrocephalus in adults.