A stroke is a sudden disruption in the circulatory system of the brain, which leads to damage to various parts of the brain that lose functionality.
Along with the blood, the supply of oxygen to the brain stops. This leads to disruption of cell nutrition.
The short answer to the question of how long people live after a stroke depends on the type of brain stroke, as well as how serious the consequences are - with ischemic, mortality in the first 72 hours is no more than 15%; for hemorrhagic – no more than 35%; the most dangerous is subarachnoid hemorrhage - survival rate in the first 72 hours is about 50%. Details are below.
What's happened
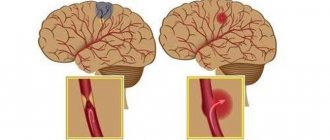
A stroke is a sudden disruption of the normal blood supply to the brain.
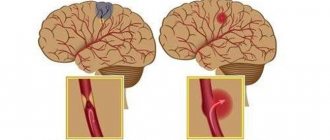
Based on the nature of the disorders, there are two main types of stroke: ischemic (often called cerebral infarction) and hemorrhagic (including subarachnoid hemorrhage). This article will talk about ischemic stroke, which is 4 times more common than hemorrhagic stroke. The word “ischemic” literally means that there is not enough blood flowing to one or another organ - with such a stroke, blood does not flow to the brain due to blockage or severe narrowing of the main arteries. As a result, brain tissue cells die.
Treatment
Cerebral infarction is treated with drug therapy, which includes anticoagulants and drugs for high blood pressure.
The patient is also prescribed treatment for concomitant diseases.
Hemorrhagic stroke is most often treated with surgery. Open craniotomy can relieve the patient of a hematoma, which poses a mortal threat. After the operation, the patient is prescribed drug therapy.
Causes and prevention of ischemic strokes
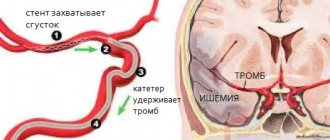
Most often, the cause of a cerebral infarction is the movement of a blood clot through an artery and clogging it in a narrow place. A thrombus is a blood clot that is primarily made up of platelets. With normal vascular patency, platelets are responsible for blood clotting, but with atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques form, narrowing the lumen of the artery, because of this, the usual blood flow is disrupted, side turbulence is formed, and platelets stick together into clots. Also, the cause of the formation of a blood clot can be an increased level of sugar in the blood: when it occurs, microtraumas form in the walls of the artery due to an increase in blood density, which also disrupts normal blood flow.
The cause of a cerebral infarction can also be a narrowing of the lumen of a large artery by more than half. You can read more about this using the example of carotid artery stenosis (note: link to article). When an artery narrows, the blood supply to the brain does not completely stop, so a person often experiences a so-called minor stroke. A minor stroke is similar in symptoms to a regular stroke. Although the degree of damage is much less, this condition requires immediate medical attention: further deterioration of the condition of the arteries can lead to a stroke with all its consequences.
A person cannot influence the movement of a blood clot through the vessels, but everyone can pay attention to a number of risk factors, eliminate them if possible, in order to prevent the formation of a blood clot and minimize the risk of ischemic stroke.
- It is important to undergo a course of treatment and periodically check your condition with a doctor if you have a chronic disease, such as diabetes mellitus, confirmed atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, or various disorders of the heart and blood vessels.
- Experts strongly recommend giving up tobacco and alcohol.
- It is advisable to maintain an active, mobile lifestyle.
- You need to monitor your diet and avoid a strong imbalance towards fats and fast carbohydrates.
The above points are effective measures to prevent not only stroke, but also many other diseases, proven through numerous studies.
But there are also risk factors that we cannot influence. Among them are old age (over 60 years old) and heredity (if immediate relatives suffered a stroke, or they were found to have serious vascular disorders).
How long do they live after a stroke: statistics in detail
The life expectancy of a person after a stroke is highly individual. In 20% of cases, a person’s death occurs instantly.
Studies have shown that in the first 30 days the mortality rate is 30-40%; after the first year after a stroke, approximately 50% of patients die.
The repeated process of cerebral circulatory disturbance increases the possibility of death. Often, if a patient has a first stroke, he can live up to 10 years, but with a second attack on the brain, life expectancy is no more than 3 years.
The reason for such a high mortality rate after a second stroke is that after the first attack, lesions remain in the brain.
Dependence on age and gender
With hemorrhage before 40 years of age, the death rate is 15%, after 50 years of age – 45% of cases.
Women have a higher mortality rate than men – 39% versus 29%.
It is several times more difficult for newborns and people aged 65 years and above to survive a stroke. This is due to age-related factors in blood vessels and their walls, which cannot recover quickly. In newborns, the cells have not yet formed. Such wall problems lead to:
- inflammation of the cranial nerves;
- damage to the vascular system;
- hemorrhage.
Lesion size
This is the main aspect that affects how long a person can live after a stroke. Tissues susceptible to necrosis take a long time to recover.
The larger the affected area, the worse the prognosis.
How consequences affect the outcome
If after a stroke the patient begins to develop concomitant pathologies (paralysis, numbness or impaired psychological functions), then life expectancy decreases several times.
In addition, these consequences create the preconditions for the occurrence of bedsores. Bedsores form irreparable processes in the blood circulation of the whole body. Mental disorders require round-the-clock care for the patient, since he is not able to soberly assess the situation and take medications on time.
Life expectancy without movement
A person who is immobilized after an attack does not have the necessary desire for long-term recovery. Because of this psychological feature, a person does not strive to adhere to all norms and procedures, which is why muscle endurance decreases, fibers lose tone, and blood flow in the limbs is disrupted.
This ultimately leads to blood clots and tissue necrosis, which poison the blood.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
Almost never a cerebral infarction is asymptomatic. You may have already come across actively distributed reminders on the timely recognition of a stroke: after all, it is very important to call an ambulance and provide medical assistance to the patient as early as possible - the earlier assistance is provided, the less brain damage.
The main symptoms of ischemic stroke are:
- dizziness,
- loss of orientation in space,
- vomit,
- convulsions,
- impaired coordination, speech, vision, writing, reading, swallowing,
- inability to move individual limbs and/or perform simple manipulations such as raising two arms at the same time, brushing teeth, or turning pages of a book.
The symptoms are extremely varied. They depend primarily on which particular part of the brain was deprived of blood supply - then exactly the function for which this part is responsible will be disrupted.
At the same time, all the symptoms do not appear; you may notice one or more - and this is a good reason to immediately call an ambulance.
Recovery forecasts
Doctors' forecasts directly depend on what symptoms the patient has. The most favorable prognosis is for those patients whose symptoms are not pronounced, motor activity is preserved and speech is not impaired.
Poor prognosis. Doctors are hesitant to allow patients to fully recover if they experience the following symptoms:
- Speech impairment.
- Breathing problems.
- Low blood pressure.
- Fluctuations in body temperature.
Uncertain forecast:
- Swallowing dysfunction.
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Dizziness.
- Eye movement disorder.
It is worth noting that the prognosis for the patient also depends on his age and physical condition. The younger the patient, and the fewer concomitant diseases he has, the greater the chance of recovery. Also of particular importance for the subsequent condition of a patient who has suffered a cerebral infarction is the speed of hospitalization. The sooner a person is taken to the hospital, the greater the chance doctors have to prevent extensive pathological changes in the stem cells.
Diagnosis of stroke
Diagnosis of a stroke is quite complex, because to identify the cause and assess brain damage, and therefore the consequences of a stroke, the doctor will need a large amount of data.
To visualize the condition of the brain vessels, CT or MRI can be used, depending on the situation. A fairly informative study on the state of blood flow will be angiography - an X-ray examination using a contrast agent injected into the vessels.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe blood and urine tests; test for glucose and cholesterol levels; conduct an ultrasound examination.
Rehabilitation
The patient’s rehabilitation plan must be developed individually by the attending physician. Rehabilitation is needed primarily to alleviate the symptoms of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life. For speech disorders, classes with a speech therapist are recommended; patients with swallowing problems need to learn special techniques to learn how to swallow soft food; those with paralysis of the limbs are prescribed special massages and exercises.
For effective rehabilitation, the participation of the patient's relatives is very important. Close people can provide invaluable assistance in restoring the patient’s health. The patient needs constant care, support and understanding.
If relatives strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the chances of partial or complete recovery greatly increase.
Often, even small progress takes quite a long time. If you are faced with such a disease in your family, the main thing is not to give up. For example, the motor ability of the limbs is restored within a year, while other disorders can take even longer to be treated. Most often, a person will never be able to return to a full life, but there is a chance that he will be able to take care of himself.
What are the requirements for the patient's regimen?
At home, control over the patient’s regimen falls entirely on loved ones. A local therapist or a home visit to a neurologist can help with advice. They won't be able to come every day, so it's better to write questions in advance so you don't forget to find out.
One of the relatives must be present at the patient’s place of residence at all times. If all relatives work and cannot afford alternate vacations, then you will have to hire a nurse. You should first ask about her work experience and characteristics.
While the patient is on bed rest, he needs the following:
- hygienic measures to prevent bedsores;
- sleep organization;
- special nutrition;
- establishing contact with impaired speech;
- daily massage;
- conducting passive and active physical exercises.
For treatment, it is important to create a positive attitude in the patient.
You should talk to the patient, tell the news, read books and newspapers. It is necessary to protect the patient from unpleasant news and emotional squabbles in the family. There are special exercises to restore speech. You can consult a speech therapist about them.
A separate article is devoted to this problem on our website.
The room where the patient is located should be ventilated several times a day. Heat and cold are equally contraindicated. Every 2.5 hours you need to change your position in bed, turn from one side to the other. This process is well combined with minimal passive warm-up of limbs paralyzed by stroke and massage, rubbing the skin with camphor alcohol, straightening and changing bed linen.
Blood pressure should be monitored three times a day. Sharp fluctuations contribute to repeated cerebral ischemia, so in such cases you should call a doctor and change the dose of medications taken.
How to restore swallowing?
Patients themselves associate swallowing problems with sensitivity on only one side of the mouth, the lips. Therefore, they cannot fully swallow food, choking and coughing.
Training will help restore sensitivity to the required level by doing the following exercises:
- imitation of the swallowing process with an empty mouth;
- yawning, opening your mouth wide;
- gargling with plain water;
- coughing;
- the patient puffs out his cheeks and holds the condition for a few seconds;
- pronouncing the long sound “i” while simultaneously tapping the larynx with your fingers.
Features of therapy
Complex therapy for right-sided stroke is divided into correction of the acute period and rehabilitation. During the acute period, if there is a risk of severe consequences, surgical intervention may be required. The patient remains in the intensive care unit throughout the acute period. Treatment of right-sided stroke of any origin is carried out in several areas:
- basic: for ischemia - thrombolytics, disaggregants, anticoagulants (thrombolysis with a recombined type plasminogen activator is most effective), for hemorrhage - emergency hemostatic and vasoconstrictor agents;
- hypotensive: drugs that lower blood pressure relieve compression of nerves, remove tissue pastiness (Betalok, Stugeron, Triampur);
- normalizing cerebral blood flow: drugs with vasoactive and antiplatelet properties (Trental, Cavinton, Eufillin);
- neuroprotective: restore connections between neurons (Cellex);
- antioxidant: detoxify tissues, remove free radicals, renew cells (Vitamin E, C, Lycopene).
In the acute phase, it is important to control breathing, heart rate, and body temperature. Treatment is most effective during the first three, maximum five hours after the attack. Within a day, irreversible processes occur in neurons.
Classification
Ischemic stroke can be a consequence of one or another disease of the cardiovascular system. There are several pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke. The TOAST (Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment) classification, which is most widely used, distinguishes the following types of ischemic stroke:
- cardioembolic - ischemic stroke caused by arrhythmia, valvular heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- atherothrombotic - ischemic stroke that occurred due to atherosclerosis of the large arteries, which resulted in arterio-arterial embolism;
- lacunar - ischemic stroke caused by occlusion of small arteries;
- ischemic stroke associated with other, more rare causes: blood hypercoagulation, arterial wall dissection, non-atherosclerotic vasculopathies;
- ischemic stroke of unknown origin - a stroke with an unknown cause or with the presence of two or more possible causes, when it is not possible to establish an accurate diagnosis.
In addition, a minor stroke is distinguished when the existing symptoms regress during the first three weeks of the disease.
There are also several periods of ischemic stroke:
- The most acute period is the first 3 days. Of these, the first three hours were defined as a “therapeutic window”, when it is possible to use thrombolytic drugs for systemic administration. In case of regression of symptoms during the first day, a transient ischemic attack is diagnosed;
- acute period - up to 4 weeks;
- early recovery period - up to six months;
- late recovery period - up to 2 years;
- period of residual effects - after 2 years.
What exercises can you do?
Physical education classes begin with simple exercises. After successful completion, they move on to more complex ones. Healthy limbs need to be developed to increase support on them. A paralyzed arm or leg must “perform” passive flexion and extension until it “learns” to work more or less fully again.
You should start training in bed in a lying position
Feet recommended:
- climb up;
- bend and straighten your knees;
- twist your feet in both directions.
After about 2 weeks, you can perform the exercises while standing:
- walk slowly in place;
- lift the bent knee forward, move it to the side.
The squat is performed when the patient has fully restored the ability to stand upright and move around while maintaining balance.
Warming up the arms begins with flexion and extension of the elbows, hands, and fingers. To develop small movements with your fingers, you can use gaming techniques:
- mosaic,
- laying out cards,
- puzzles,
- fingering the rosary.
Hand movements are more finely organized by the brain, so recovery will require more effort
A patient after such a serious illness as a stroke must again learn to use a spoon and fork, or a door key. You should not pay attention to the methods of grasping an object; the patient himself chooses the most convenient option.
Some experts recommend tying a healthy arm to the body for five hours and trying to get by with one sore limb. This is necessary to create an emergency situation for the brain and force it to quickly return functions to the paralyzed arm.
Is it possible to use traditional medicine?
Folk remedies are not decisive in the recovery period. All medications are prescribed and discontinued by a doctor. Auxiliary traditional methods must be agreed with the doctor. They are used without limiting therapy and other recommendations.
You should not be fooled by advertisements that claim “the growth of new nerve cells.” This is a complete bluff. Scientists are indeed conducting experiments on the use of stem cells for patients with strokes, increasing the activity of the opposite hemisphere. And the effect of decoctions and herbal tinctures is based on lowering cholesterol and supporting the immune system.
These properties have:
- garlic-lemon tincture;
- various recipes from pine cones;
- onion ointment.
What to prepare for welcoming a patient from the hospital?
The conditions for home treatment of a patient with a stroke should first of all provide for his safety and ease of mastering movements.
The bathroom, toilet, and bedside area must have grab bars or other devices that allow the patient to sit down and stand up without assistance.
- You should remove unnecessary things, boxes, carpets, wires from home appliances from the paths of movement. They increase the risk of falling.
- Some patients lose their sense of temperature and can get burned by too hot water. This will require installing thermometers in the bathroom.
- At first, it is better to use a tray or a small portable table for the patient’s food; it will be difficult to be in a common kitchen or dining room.
The purchase of a wheelchair can be postponed for six months, when the prospects for rehabilitation measures become clear. During this period, the patient may begin to walk independently.
If watching television programs is of great interest to the victim, then he will need a remote switch.
Prevention
Disease prevention measures include timely treatment of all diseases that can cause cerebral infarction. First of all, the risk group includes patients with atherosclerosis and hypertension. Also, people suffering from diabetes and having a hereditary predisposition to cardiovascular diseases should pay special attention to their health.
A brain stroke is a pathology that does not go away without a trace. Everyone who is at risk should remember that a healthy lifestyle can protect them from death or disability. Treatment of diseases such as hypertension, atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus must be timely. A stroke comes suddenly, and if you don't take care of yourself, the consequences can be dire. At the first signs of diseases that can cause a stroke, you need to consult a doctor and reconsider your lifestyle.
What to do in the period from three months to six months?
After 3 months of successful recovery, the patient adapts to his condition and moves independently with the help of a stick. After 6 months, he learns to climb steps and carry light bags. Goes shopping in the store, walks, uses transport.
It is necessary to equip the patient with a telephone with quick access and put a note in his pocket indicating personal information, address and contact telephone number of relatives. These measures will add confidence to the patient and reassure the family.
Physical exercises can be performed with light dumbbells, pedaling on a simulator
During this period, it is already possible to gain lost muscle mass.
If the training of the patient’s right hand does not allow writing, then attention should be paid to mastering this function with the left hand.
Pathogenesis
A certain sequence of molecular biochemical changes in the brain substance, caused by acute focal cerebral ischemia, can lead to tissue damage, resulting in cell death (cerebral infarction). The nature of the changes depends on the level of decrease in cerebral blood flow, the duration of this decrease and the sensitivity of the brain substance to ischemia. The degree of reversibility of tissue changes at each stage of the pathological process is determined by the level of decrease in cerebral blood flow and its duration in combination with factors that determine the sensitivity of the brain to hypoxic damage.
The term “infarction core” refers to a zone of irreversible damage, and the term “ischemic penumbra” (penumbra) refers to a zone of reversible ischemic damage. The duration of the penumbra's existence is the most important point, since over time, reversible changes become irreversible. The oligemic zone is a zone in which a balance is maintained between tissue needs and the processes that provide these needs, despite the decrease in cerebral blood flow. It is capable of existing for an indefinitely long time without passing into the core of the infarction, therefore it is not classified as a penumbra.