Hospitalization and treatment under the compulsory medical insurance quota. More details after viewing the pictures.
- Aneurysm clipping
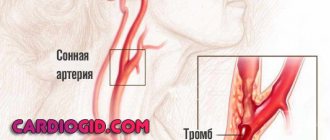
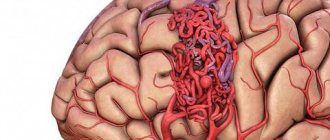
A cerebral aneurysm is a local protrusion of the arterial walls. The disease often occurs without symptoms. As the brain aneurysm grows, a significant thinning of the walls of the formation occurs, which can lead to its rupture and the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
Depending on the shape, a cerebral aneurysm can be spindle-shaped or saccular. The exact type of disease can only be determined during a comprehensive diagnosis. Saccular aneurysm is much more common.
Symptoms of cerebral aneurysm
A small protrusion of blood vessels (less than 11-12 cm) has virtually no symptoms. The patient experiences discomfort only when the protrusion of the cerebral arteries has increased in size.
| Type of intervention | Price |
| Endovascular embolization of cerebral aneurysm | 450,000 - 600,000 rub. |
Medium (12-26 mm) and large (from 26 mm) aneurysms are characterized by a number of symptoms.
Among them:
- deterioration of hearing and vision,
- pupil dilation,
- partial numbness of the facial muscles.
Pronounced symptoms of brain damage appear when an aneurysm ruptures.
The patient experiences:
- nausea,
- acute pain in the temples, occipital and frontal parts of the head.
Often the patient cannot speak or swallow. When an aneurysm ruptures, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted and vital functions of the body are lost. In addition, spasms and convulsions occur. The patient may fall into a coma. These symptoms are also associated with brain damage.
Important!
Treatment of an aneurysm through surgery should not be delayed. It should be understood that the pathology is very dangerous. The patient can die at any minute. It is extremely difficult to save him, especially if there is no way to quickly get medical help.
If you are diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm, you should immediately contact a specialist for treatment.
Risk group. Danger of aneurysm
An aneurysm is a disease of the arteries of the brain that is found in various people, regardless of age.
The risk group includes:
- smoking,
- alcohol abusers,
- patients with hypertension, hereditary vascular pathologies.
The insidiousness of an aneurysm is that in the early stages the symptoms of brain damage are almost invisible. It is not easy to notice them, especially for a constantly busy person. At the same time, a relatively small number of people undergo comprehensive examinations of the brain and blood vessels.
Many patients do not pay attention to headaches and nausea. Usually these conditions are associated with chronic fatigue and age.
Important! 25% of patients suffering from protrusion of the wall of a cerebral vessel die.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Causes of the disease
An aneurysm is a dangerous condition that primarily requires surgical treatment. Otherwise, complications will not be avoided. Experts believe that the disease is a consequence of developmental abnormalities that disrupt the structure of the vascular wall. Often, a cerebral aneurysm is combined with connective tissue dysplasia, polycystic kidney disease, and vascular disorders. The acquired form of the disease can be a consequence of traumatic brain injury. Also, a cerebral aneurysm occurs against the background of atherosclerosis and hypertension.
The vascular wall defect itself occurs gradually. Against the background of degenerative processes, tissue damage or underdevelopment, the area loses its former elasticity. Under the pressure of blood flow, the vascular wall begins to bulge. This is how a brain aneurysm forms. Most often, the formation occurs in the place where the arteries branch and there is the strongest pressure on the vessel wall.
Treatment of pathology
Emergency treatment for patients with a ruptured brain aneurysm includes restoring deteriorating breathing and reducing intracranial pressure.
There are 2 main treatment options.
They allow you to fasten the intracranial protrusion of cerebral vessels.
- Surgical clipping.
- Endovascular embolization.
If possible, treatment is given within the first 24 hours after bleeding to close the ruptured aneurysm and reduce the risk of recurrences that affect the blood vessels.
Let's consider the features of both methods.
Surgical clipping
The goal of the intervention is to apply a special clip to the neck of the aneurysm. This allows you to exclude it from the general bloodstream without blocking a normal vessel. If the aneurysm cannot be clipped, alternative techniques are used (wrapping, tripping, etc.).
Important! The operation to clip the cerebral vessels is performed with craniotomy. Microsurgical techniques are used to carry out the intervention. This allows you to free the aneurysm (its neck) from the feeding vessels. Complications after surgery arise from a previous rupture. Eliminating all its consequences is not so easy. When treating unruptured aneurysms, complications occur less frequently (in 4-10% of cases).
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Possible complications
Complications during aneurysm clipping are no more than 8%. However, a certain risk still exists, so the patient should be carefully informed about all possible consequences. The consequences can range from minor to serious and even life-threatening.
In the first case, after the operation, the patient’s memory, speech, attention are impaired, motor disorders develop, and intense headaches occur.
In the latter case, complications are caused by the development of postoperative vascular spasm, leading to ischemia and pulmonary edema. Despite the severity of these conditions, all of them can be corrected by appropriate therapy in the intensive care unit (antioxidants, neuroprotectors, mannitol, etc.).
With endovascular intervention, the wall of a vessel or aneurysm may be perforated by a balloon or coil, as well as thromboembolic complications, which can cause death.
Prevention of complications is a technically correct surgical intervention, as well as continuous monitoring of the patient in the early postoperative period.
Embolization
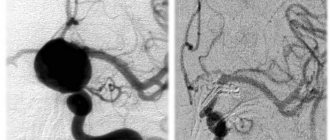
This technique has become widespread in the last 15 years. It allows you to exclude the damaged vessel from the cerebral circulatory system without opening the skull. A special catheter is inserted through one of the veins or arteries. It moves through the circulatory system until it reaches the aneurysm. After this, using special instruments, the vessel is disconnected from blood circulation.
Embolization is the least traumatic way to eliminate aneurysms. That is why it has become widespread. Efficiency and advantages of treating cerebral aneurysm using modern endovascular techniques Embolization is a method that has proven to be highly effective.
That is why it is often used to disconnect a cerebral vessel from the circulatory system when:
- Inaccessibility of the aneurysm.
- Risk of serious complications with direct intervention.
- Carrying out operations on elderly people.
- Treatment of patients in serious condition.
Intervention is also prescribed when the aneurysm cannot be clipped.
Over the past few years, a large number of interventions have been performed. Moreover, surgery on cerebral vessels was prescribed even for gigantic aneurysms. The majority of patients did not require a long stay in the intensive care unit and were discharged from the clinic within 2-3 days.
There was no damage to any major healthy cerebral vessel. Thanks to this, patients were able to lead a normal life and did not experience any restrictions.
In some patients, the aneurysm was not completely excluded from the bloodstream during one intervention. In this case, another operation was performed. Repeated intervention on the cerebral vessels did not lead to a worsening of the patient's condition.
Main advantages of the method
- Low probability of need for repeated interventions. The operation is performed a second time in approximately 1 case out of 300.
- Possibilities for intervention to stop a cerebral vessel in patients who are contraindicated for extensive surgical clipping.
- Short duration of the procedure. Usually the operation takes no more than 2-3 hours.
- Opportunities for full recovery of health. An aneurysm will not bother you.
5. Immediate improvement. After intervention on a cerebral vessel, patients recover as quickly as possible. Moreover, embolization of cerebral vessels does not prevent them from leading a normal life.
General information. Diagnostics
Surgical treatment of arterial aneurysms of cerebral vessels has been one of the main and most important areas of work of the institute’s vascular department for several decades. This is due to the fact that there are no conservative treatment methods for this pathology, and surgical interventions on aneurysms remain among the most complex neurosurgical operations. Despite numerous studies aimed at developing methods for preventing the rupture of aneurysms and treating complications of aneurysmal hemorrhages, arterial aneurysms of the cerebral vessels are still a disease with a high probability of death or permanent disability: in the absence of surgical care, up to 70% of patients die in the first year from onset illness, 25% of survivors remain disabled. The prevalence of arterial aneurysms in the population is quite high - at least 0.6% (about 600 people per 100,000 population). The incidence of SAH due to ruptured aneurysms is 10–15 cases per 100,000 population per year. Thus, in Russia, about 18,000 patients with aneurysmal SAH require hospitalization annually. The emergence of new diagnostic capabilities has led to an increase in the detection of asymptomatic aneurysms, which has further increased the number of patients seeking medical help.
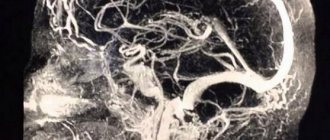
| CT angiography mode |
Over a more than 40-year period, the institute has performed about 5,000 direct surgical interventions and more than 700 endovascular operations for arterial aneurysms. The number of patients admitted annually for surgical intervention has increased from 100 patients in the 70s–80s to 300 or more today. Constant analysis of this clinical material in dissertations, detailing the principles of treatment depending on the timing after hemorrhage, size, location, anatomical features of aneurysms, their number in one person, and the age of patients, led to the creation of separate areas in the surgery of cerebral aneurysms. The most important role in the surgical treatment of aneurysms is played by methods of diagnosing the disease. Currently, diagnosis of aneurysms can be performed using direct angiography, MRI and SCT angiography. The results of these three methods can be presented in a volumetric image (3D reconstruction). SCT-AG can currently be considered the method of choice in identifying the cause of SAH. A special role in examining a patient in the acute period of SAH is played by methods for diagnosing vasospasm. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCUSDG), inferior to neuroimaging methods in sensitivity and specificity, allows one to assess the dynamics of vasospasm, since the non-invasiveness of the method makes it possible to conduct multiple studies. CT and MRI in various modes in patients with aneurysms are indispensable in the diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of such complications of SAH and surgery as intracerebral hematomas, intraventricular hemorrhages, cerebral edema and ischemia, acute and delayed hydrocephalus.
| Aneurysm clipping |
While remaining unchanged in its fundamental principles, cerebral aneurysm surgery is constantly evolving. The current stage of treatment of arterial aneurysms at the institute can be characterized as a stage of strictly differentiated and individualized treatment, performed taking into account all the features of the course of the disease, the morpho-functional characteristics of aneurysms, the patient’s condition and other factors. The basis of the ideology of aneurysm surgery is the integration and complementarity of microsurgical and endovascular methods. In microsurgical treatment of aneurysms, the main operation is clipping the aneurysm neck with a self-clamping clip. Depending on the anatomical and topographical features of the aneurysm, clips of various sizes and configurations are used. In recent years, the institute has developed and implemented a number of surgical and diagnostic methods that have improved the quality of exclusion of more complex aneurysms: intravascular aspiration of blood, intraoperative Doppler ultrasound, flowmetry, fluorescein angiography. The main advantages of the endovascular method of treating aneurysms are the ability to completely exclude the aneurysm from the bloodstream in the absence of surgical brain injury and the ability to exclude aneurysms that are difficult to reach or inaccessible for direct surgical intervention. These advantages are primarily important in patients in the acute period of hemorrhage, with aneurysms of the paraclinoid part of the ICA and the vertebrobasilar region. The preferred method for endovascular exclusion of aneurysms should be considered reconstructive operations—occlusion of the aneurysm cavity while maintaining the lumen of the supporting vessel. To switch off aneurysms, the technique of occluding the aneurysm with detachable microcoils is currently used.