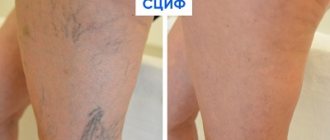
Rheovasography is a method for studying arterial and venous blood flow in the upper and lower extremities using a rheograph apparatus.
The procedure is painless and comfortable and takes 10–15 minutes. Two pairs of electrodes are placed on the limbs - above and below along the blood vessels. The electrical resistance between these areas is measured. The data is processed by a computer program and decrypted by a doctor.
Electrical resistance depends on the degree of blood filling of the vessels, their expansion or narrowing. The stronger the blood flow, the lower this indicator. An increase in resistance indicates difficulty in blood flow. Based on the nature of the diagram, the angiologist judges the characteristics of the arterial supply and venous outflow in the extremities.
Indications for the procedure
Rheovasography of the lower extremities can be prescribed for the following symptoms:
- Numbness of the legs.
- Cramps.
- Change in skin color of the lower extremities.
- Loss of sensation.
- Edema.
This diagnostic procedure is mandatory for diseases such as:
- Atherosclerosis.
- Thrombophlebitis.
- Rheumatic diseases.
- Diabetes.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Blockage of the bloodstream.
- Obliterating endarteritis, etc.
Indications for rheovasography of the lower extremities
Often, rheovasography of the lower extremities is performed after injuries. Reasons for prescribing diagnostics may be:
- Numbness;
- Convulsions;
- Pain;
- Constant feeling of coldness in the legs;
- Change in skin color;
- Phlebeurysm;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Peripheral autonomic failure;
- Impaired peripheral blood supply as a result of diabetes mellitus;
- Thrombophlebitis and other problems of the venous system.
Rheovasography of the legs is also performed if deep vein thrombosis is suspected.
A little information about the rheograph
The device is based on a generator that generates current. Using a special attachment, measurements are converted into graphic form.
Using appropriate electrodes attached to certain areas of the body, a rheogram is recorded.
What is rheography? At the beginning of the procedure, an electrophoresis-treated napkin is placed on the patient’s skin, through which the electrode reacts better with the body.
The skin is first wiped with medical alcohol; the presence of a fatty layer worsens the result of the process.
Central rheography
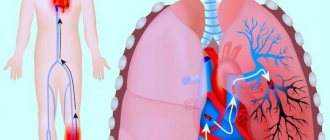
Varieties of rheography cover a huge number of proposals. But the central variation is consistently in high demand, as it is aimed at accurately assessing the condition of the heart.
The manipulation is based on the study of blood flow coming from the pulmonary artery and aorta. It is these two large vessels that allow you to familiarize yourself in detail with the health of the cardiac region.
Taking into account the blood flow of the lung and right ventricle, it is possible to evaluate the contractile function of the heart muscle.
Normal values in clinical practice are as follows:
- flat ascending part;
- round top with a small depression;
- round top with wave;
- smooth descent.
Carrying out central rheography involves dividing rheograms into certain types, depending on the data obtained:
- hypervolemic;
- hypovolemic;
- hypertensive.
The first version indicates an increased volume of incoming blood. The main indicators indicating such a deviation cover a high and at the same time peaked curve with a steep downward part.
Hypovolemic conditions are no less dangerous, but not all patients know what it is.
The scenario involves a reduced volume of blood flow, which is visible on visualization due to:
- decreasing the height of the curve;
- serifs on the ascending part;
- flat top;
- gently descending parts.
No less dangerous are the biophysical manifestations of the hypertensive subtype. This will indicate increased pressure recorded in the lungs. In the image, deviations can be recognized due to the steep rise of the curve, as well as the gentle descent and round top.
Limitations of the rheovasography method of the lower extremities
Unlike duplex scanning, which does not require any preparation or special conditions, rheovasography of the lower extremities requires compliance with a number of conditions and careful attention to external factors.
The rheovasography schedule of the lower extremities may be inaccurate in the presence of heart failure, vein occlusion (vein obstruction), or local thrombosis. Also, these rheograms are distorted when exposed to external factors: the presence of pressing force (tight bandage or plaster on the leg, tight, tight clothing), low temperature in the office, patient mobility during the examination.
For rheovasography of the legs to be informative, a number of conditions must be met.
- A day or more before, stop taking any vascular medications that can affect blood circulation;
- Two hours before the test, smoking patients should quit nicotine;
- Immediately before rheovasography of the lower extremities, the patient should rest for approximately 15 minutes;
- During vein diagnostics, the patient should remain as still as possible, unless the doctor asks otherwise.
Review of central rheography
During the procedure, the work of the heart muscle is assessed by diagnosing the aortic blood flow and pulmonary artery. In particular, the contractile function of the heart and its general condition are determined as the ventricles fill with blood.
The rheography of the pulmonary artery is considered normal if there is an ascending gentle section, the apex has a rounded smooth shape with a small additional depression, followed by a smooth descent.
Rheographs of various types show rheograms that differ in types during the examination:
- Hypertensive - high pressure is noted in the pulmonary vessels, the curve on the tape shows a steep rise and a similar descent, the top is round.
- Hypervolemic - indicates blood flow with increased volume; the tape shows a sharp, high curve with a very gentle slope.
- Hypovolemic - the amount of blood flow is greatly underestimated, the curve shows a decreasing height, a flat top, while the descending section descends gradually.
In addition, when performing rheography, it is possible to assess the state of blood circulation in nearby organs to the surface of the body: kidneys (rheonephrography) and liver (rheohepatography).
This study during physical stress, taking into account the performance of “stress tests,” helps to establish changes in blood flow.
Results and interpretation of the rheogram
To obtain the most correct analysis that determines the general condition of the blood flow.
To do this, several sinusoidal curves are performed that display the blood circulation in the arteries.
As for the smooth descent in the image, it is a reflection of the blood flow of the veins.
The resulting recording is deciphered by a diagnostician who studies the shape of the sinusoidal curves, the similarity between them, and analyzes the number and presence of additional curves that are displayed in the descending phase.
For example, if a person has arrhythmia and vegetative dystonia, the curves running together will differ in shape.
In addition to estimating the parameters of the curves, the specialist carries out certain calculations taking into account special formulas. The result is a calculation of the rheographic index taking into account a certain established interval.
If there is an exit beyond the boundaries of the designated zone, one can claim pathology.
When reading the rheogram, the doctor takes into account the time period during which the pulse wave propagated, the frequency-amplitude value, and the venous outflow in a coefficient ratio.
Indications for rheovasography
The technique makes it possible to identify many vascular pathologies and assess the risks of their development. Among the diseases:
- obliterating atherosclerosis;
- varicose veins;
- vascular occlusion;
- Raynaud's disease;
- impaired blood supply to the extremities after injury;
- diabetic, alcoholic or toxic angiopathy;
- differential diagnosis with polyneuropathies;
- peripheral vegetative-vascular insufficiency;
- thrombophlebitis.
It is necessary to do a study if the following symptoms occur:
- numbness or pain in the arms and legs;
- swelling of the limbs;
- coldness of the feet and hands compared to the overlying areas of the body;
- cramps in legs, arms;
- change in skin color to pale or purple-bluish;
- weakness in the limbs during physical activity.
The patient lies on the couch during the examination. An ECG is recorded simultaneously with the rheovasogram.
Rheovasography – carrying out
The procedure helps to explore different areas of the body.
So, during rheovasography, the vessels passing through the limbs are visible. These are the veins of the arms, namely the hand and shoulder, forearm, on the legs - the vessels of the lower legs, feet, thighs.
The procedure uses tape or rectangular electrodes. One of them is fixed at the beginning of the area under study, the other at the end.
The result is a wave in the form of an ascending section, with a rounded crown at the top, followed by a steep descent.
Based on the results of rheography, obliterating endarteritis is accurately diagnosed, in which the structure of the arteries in the legs and feet changes greatly.
This pathology is often called “smoker’s foot.”
During rheography, problems with peripheral vessels are detected, in which stenosis, decreased tone, elasticity, and blockage are observed.
What the procedure will show
Having figured out what the essence of the diagnostic method is, people begin to be interested in how they can independently decipher the result they receive. But without the proper knowledge, this is quite problematic, because for most people, a rheogram is some kind of mathematical graph, and the impedance of biological tissues does not mean anything at all.
The basis of the picture is based on two aspects:
- sinusoids, which are presented as a steep rise, which describes arterial blood flow;
- a smooth descent, which is a reflection of the venous blood flow.
But not only this makes it possible to assess the condition of the vascular network in terms of volumes and other features of the incoming blood. It will be necessary to take into account many curves and use additional calculations, where Kedrov’s formula plays an important role.
The diagnostician will definitely take into account the regularity of the verified curve, which implies similarity between several curves. The shape and the number of secondary curves that are in a descending phase are also taken into account.
For example, it is worth analyzing the indicators characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia or arrhythmia. The presented ailments will be indicated by adjacent curves with different shapes.
Next, a special index is calculated, which must fit into the average statistical interval. Falling out of it threatens with suspicion of serious pathologies.
The following values specifically help identify diseases:
- level of venous outflow;
- amplitude-frequency indicator;
- measurements of the time interval for pulse wave propagation.
An experienced doctor will take into account various functional tests in order to get a detailed picture of what is happening.
Preparatory measures
Performing rheography involves preparation similar to the procedure for recording an electrocardiogram.
Beforehand, the patient is not allowed to smoke or consume large quantities of caffeine-containing products.
If you are taking any medications, it is recommended to stop therapy one day before.
This point is especially important in the case of medications that change the blood circulation process.
Immediately before the examination, the person takes a sitting or lying position, relaxes as much as possible, nervousness is unacceptable.
About the impact of the procedure
The technique does not harm health, there is no damage, there is no outside interference in the operation of internal systems.
There is no damage to the tissues or skin through which the current is passed, because it is characterized by insignificant regularity and magnitude.
Despite this, the study is highly sensitive.
Rheography allows you to assess cardiac function, evaluate the blood flow system and identify deviations in its functioning. It helps to diagnose the pathological process in the vascular system as accurately as possible.