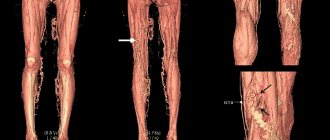
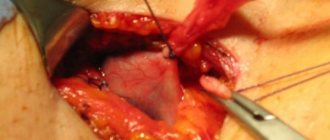
Varicose veins of the lower extremities are the most common vascular pathology. Its spread is explained by the modern sedentary lifestyle. Bad habits, excess weight, sedentary work and hereditary predisposition are the main factors in the development of varicose veins. Modern medicine offers an effective solution to this problem. Thanks to phlebectomy - surgery on the veins of the legs - it is possible to completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease, restore blood circulation in the lower extremities and return to a normal lifestyle.
Phlebectomy (venectomy) is an operation to remove varicose veins, which is performed in cases where other methods of treating varicose veins have proven ineffective. The main goal of this method is to normalize blood flow, as well as reduce the risk of developing thrombosis, bleeding and trophic ulcers in patients with advanced stages of varicose veins. Phlebectomy is safe and effective.
Combined phlebectomy is the most common surgical method for treating varicose veins. It involves the removal of pathologically altered veins using special instruments and a variety of surgical techniques. During the operation, only the saphenous veins are removed, which do not disrupt the functioning of the human circulatory system.
You can undergo modern diagnostics and innovative treatment for varicose veins of the lower extremities at the Yusupov Hospital, where a full range of phlebological services is provided. Phlebologists at the Yusupov Hospital are fluent in all modern methods of eliminating varicose veins.
Description of the disease
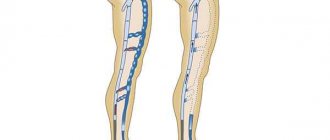
Varicose veins in the legs are a common disease in which gross changes in the walls of the veins occur and the development of functional insufficiency of the valve apparatus. As a result, a circulatory disorder occurs, which is accompanied by corresponding clinical symptoms.
Women are more likely to develop CVD than men. This is due to cyclical changes in the concentration of hormones in the body. Due to this, the elasticity of the vein walls increases and the valve apparatus loosens. Among the main causes of varicose veins of the lower extremities are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- prolonged standing or sitting;
- lack of physical activity;
- regular weight lifting;
- long-term use of estrogen-containing drugs;
- age over 30 years.
Symptoms of varicose veins in the legs are heaviness, a feeling of fullness, itching or burning. An aching, pulling, throbbing pain appears in the lower extremities. The most typical localization of pain is the calf muscles. Symptoms of varicose veins worsen after standing for a long time. A decrease in the severity of clinical signs is observed when walking, lying horizontally, and wearing compression garments. Depending on the severity of the condition, cramps may occur at night.
When examining the lower extremities, visible tortuous veins of a bluish color are determined. Many people mistakenly mistake spider veins for the initial manifestations of varicose veins of the lower extremities. This symptom is characteristic of various vascular pathologies. Therefore, when a clinical sign appears, it is recommended to consult a doctor to make a correct diagnosis.
If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, the course of varicose veins becomes severe. As a result of prolonged circulatory disturbances, trophic changes occur in the affected area. Early signs of ulcer development are hyperpigmented areas. Next, the pathological process spreads to the subcutaneous fat. Compacted areas appear. In addition to the formation of trophic ulcers, severe swelling of the lower extremities occurs. The appearance of the above symptoms requires consulting a doctor. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out all types of diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins and its complications. For this purpose, the latest equipment and modern materials are used.
Make an appointment
Other phlebectomy methods
There is also a set of methods used in the surgical treatment of varicose veins, which are conventionally called “vein-saving”.
These methods are aimed at restoring the functions of the valve apparatus and preventing the further development of varicose veins.
To do this, various synthetic cuffs or fascia are used, which are fixed around non-functioning valves and segments of venous lines that need treatment.
Unfortunately, vein-sparing operations do not have a pronounced effect in the long term.
Thus, the 5-year relapse rate of the disease exceeds 50%. [/td]
Kinds
The following types of surgical removal of veins of the lower extremities are distinguished:
- Crossectomy. The operation to remove varicose veins on the legs involves ligating the place where the superficial vein joins the deep one in the upper thigh. Scars from surgery may not be noticeable. Surgical access is performed in the area of the inguinal folds.
- Stripping. Removal of the affected veins is carried out using a special probe. The surgical intervention consists of making several punctures at both ends of the vessel. After stripping, relapses occur in 30% of cases.
- Safenectomy. During surgery, large venous trunks are removed.
- Phlebectomy with sclerosis. The essence of the operation to remove varicose veins is the introduction of a special substance that leads to their dissolution.
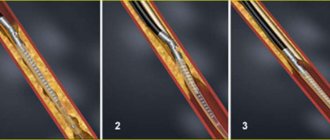
- Laser phlebectomy. It differs from the classic version of surgical intervention in that a low-frequency laser is used to remove the affected veins. Thanks to its action, coagulation and adhesion of the inner lining of the veins occurs. Over time, the walls of the vessel collapse. In a similar way, it is excluded from the general blood flow system.
- Miniphlebectomy. It is used for lesions of small caliber veins. Using pinpoint punctures, vessels are removed. After this surgical intervention, relapses occur extremely rarely.
Alternative techniques (INNOVATION IN PHLEBOLOGY)
The most modern achievements of phlebology are innovative techniques:
- radiofrequency vein obliteration (medicaltechnologies VNUS Closure)
- endovasal laser obliteration (EVLO), performed using a radial light guide.
- foam-form sclerotherapy (or so-called foam sclerotherapy).
Also considered the gold standard for the treatment of varicose veins is:
All these methods are significantly superior to the surgical method of treating varicose veins.
Indications
The main indications for phlebectomy of the veins of the lower extremities include:
- Varicose veins. This is the most common reason for phlebectomy. The pathology affects the subcutaneous and deep veins and contributes to circulatory disorders. In the initial stages, it is possible to use medications. In more severe stages of the disease, surgery is prescribed.
- Thrombophlebitis of superficial veins. The operation is performed for acute or chronic forms of pathology. The disease leads to the lumen of the vessel being blocked by the resulting clot. As a result, an obstruction occurs in the path of blood flow with subsequent circulatory disorders. In cases where medications do not help resolve the clot, surgical intervention is performed.
- Trophic ulcers. The disease can affect the skin and soft tissues. An indication for emergency vein removal surgery is the occurrence of heavy bleeding from the affected areas.
- Venous insufficiency. Pathologically, the process affects the valves of blood vessels. As a result, there is a disruption in the outflow of blood, which leads to stagnation. Phlebectomy is the most appropriate surgical option for this condition.
Postoperative period
After surgery, an elastic bandage or elastic stocking is placed on the limb to provide uniform compression. The legs are given an elevated position. It is recommended to take venotonic drugs. You are allowed to walk the very next day. Early activity and compression therapy make it possible to normalize venous outflow and prevent thrombus formation.
To perform phlebectomy, the Scientific and Practical Center for Surgery uses high-tech devices and modern techniques. Surgeons at our center pay special attention to the aesthetic side of the issue, so the incisions made are minimal and do not leave scars.
Contraindications
Despite the large number of advantages and indications for use, phlebectomy has some limitations. These include:
- Acute viral or infectious diseases. Such conditions increase the possibility of developing postoperative complications in the form of sepsis.
- Severe hypertension, uncontrolled by medications.
- Chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation.
- Pregnancy period. An absolute contraindication is the second half of gestation. This is due to the fact that any intervention can provoke the development of spontaneous abortion.
- The presence of inflammatory diseases in the lower extremities. These conditions can trigger the spread of inflammation to other organs and tissues.
- Age over 65 years. With age, surgical interventions are more difficult to tolerate. This is due to the presence of a sufficient number of concomitant pathologies. Phlebectomy of veins can lead to exacerbation of chronic diseases, which will negatively affect the course of the recovery period.
Some of the listed contraindications are temporary. This means that after removing the restrictions, the surgical intervention can be carried out in full. Depending on the severity of the condition and the type of affected vessel, the doctor selects a phlebectomy technique that will be most effective in each specific case.
What do we offer today instead of classical surgical treatment of varicose veins?
Everything changed about 20 years ago with the advent of the first successful attempts at endovasal thermoobliteration. This was a significant technological breakthrough that radically changed phlebology. The initial clinical experience with the use of thermoobliteration was on the verge of a medical experiment. Any innovative technology goes through this stage. During that period of the first steps and development of the thermoobliteration technique, one could talk about its competition with classical surgery.
Laser radial light guide
After the appearance of radial light guides for laser coagulation in 2008, there could no longer be any talk of a significant opposition between combined phlebectomy (in any form) and endovasal thermoobliteration. What are the benefits of endovascular varicose vein surgery:
- Fine manipulation control via ultrasound imaging
- Minimally invasive, only skin punctures.
- Mild anesthesia in the form of local tumescent anesthesia.
- Full outpatient service for all procedures.
- Good patient tolerance of both the manipulation and the postoperative period.
Preparation
Phlebectomy, like any other surgical intervention, requires special preparation. In a similar way, the body’s readiness for the upcoming surgical treatment is checked. The main tests required for passing include:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood parameters;
- analysis for HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis;
- blood type and Rh factor;
- coagulogram;
- fluorography;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities.
After completing the research, it is necessary to obtain a conclusion from the therapist that there are no contraindications for surgery. Next, a referral to an anesthesiologist is given. After interviewing and examining the patient, the doctor selects the most appropriate anesthesia. Hospitalization to the hospital is carried out one day before the planned date of surgery.
Make an appointment
Progress of the operation
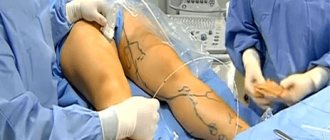
Phlebectomy of the veins of the lower extremities is performed under local anesthesia. In rare cases, general anesthesia is used. As a rule, it is prescribed when removing large trunks. To ensure maximum muscle relaxation, the patient is asked to take a supine position.
- After the patient is positioned on the operating table, the operated area is freed from clothing.
- Next, markings are made to determine the location of the operated vein. This stage is necessary to accurately establish the insertion site for medical instruments.
- Carrying out local anesthesia. The injected drug begins to act within a few minutes. This can be understood by the presence of a characteristic pattern along the course of the vessel.
- Antiseptic treatment of the surgical field. A necessary measure to reduce the risk of infectious complications in the postoperative period.
- Performing punctures through which the affected vein will be removed. Special hooks are used for this. The distance between punctures is selected individually depending on the severity of pathological changes.
- Inserting the probe and hooks through the holes made. With their help, the vessel is removed. Bleeding that occurs during surgery is eliminated by tamponade with one's own tissues.
- The final stage of the operation is suturing followed by repeated antiseptic treatment.
The duration of the operation to remove leg veins is determined individually. On average, surgery lasts about two hours. For several days after phlebectomy, the patient must remain in bed and be under the supervision of doctors. Compliance with medical recommendations in the postoperative period speeds up the duration of rehabilitation.
Complications
The success of surgical treatment of varicose veins depends on many factors: the age of the patient, the degree of advanced disease, concomitant diseases, etc. Depending on this, complications may arise after phlebectomy. The most common negative consequences of phlebectomy include:
- Bleeding. In the postoperative period, light bleeding from surgical wounds may occur during the first 24 hours. The reason for this is small cutaneous and subcutaneous vessels. The complication is nonspecific and is associated with errors in the surgeon’s operative technique. In some cases, bleeding may be associated with the use of anticoagulants (blood thinners). If the bleeding does not stop, revision of the wound (unraveling of sutures in the operating room) may be required.
- Hemorrhages and hematomas. The source of hemorrhage and the appearance of a hematoma after phlebectomy are small vessels that break during surgery. Hemorrhages are the soaking of blood into the skin and subcutaneous tissue (hemorrhages) or the accumulation of blood in cavities (hematoma) and are a natural complication of traumatic phlebectomy. Prevention of this complication is the use of modern low-traumatic methods of vein removal (intussusception stripping, cryostripping, miniphlebectomy), careful hemostasis both during surgery (manual compression) and after surgery (elastic bandaging and compression hosiery). Typically, hemorrhages and bruises after phlebectomy resolve on their own within 7-10 days, leaving behind slight pigmentation for up to 1-2 months.
- Infectious and inflammatory complications, such as inflammatory infiltrates (indurations) and wound suppuration. In case of development, removal of sutures and open wound management with local use of antimicrobial agents is indicated. Seals after phlebectomy are much more common (up to 15% of all phlebectomies) and represent an infectious inflammation without purulent fusion of tissue. Most often, the infiltrate forms in the area of maximum trauma and blood accumulation (hematoma infection). To treat infiltrates, antibacterial therapy and local use of anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents are used.
- Lymphorrhea (leakage of lymph through the surgical wound) and lymphocele (formation of a cavity filled with lymph in the surgical area) are the result of damage to lymphatic vessels and nodes due to rough handling of tissues. Lymphorrhea is treated conservatively. Lymphocele requires emptying by puncture or opening a wound. The main method of prevention is careful adherence to surgical technique and careful handling of tissues.
- Impaired skin sensitivity: decreased sensitivity on the inner surface of the leg and foot (hypoesthesia) or the appearance of unpleasant sensations such as crawling (paresthesia) is associated with damage to the nerves passing in close proximity to the trunks of the saphenous veins. This is observed when using traumatic methods of safenectomy. The method of prevention is careful handling of tissues.
- Thrombosis and embolism. Thrombosis of the deep veins of the leg, as well as the development of thrombophlebitis after phlebectomy, is extremely rare, which is associated with mandatory elastic compression after surgery and early activation of the patient.
Rehabilitation
The postoperative period after phlebectomy of the veins of the lower extremities takes on average about 6 months. Rehabilitation begins when the patient is transferred from the operating room to the ward. The patient is under the supervision of doctors for 7-14 days. This is necessary for timely provision of medical care in case of early complications. The timing of suture removal depends on their location. If the incision was made in the groin area, the sutures are removed after 7 days, if under the knee, then after 11-12 days.
To reduce the risk of blood clots, patients are advised to wear compression stockings or elastic bandaging for 1 month after surgery. Before removing the sutures, it is forbidden to wet the operated area. The length of time to wear compression garments or bandages is determined individually. The duration is influenced by the severity of the condition and the volume of surgical intervention. On average, bandages and stockings can be removed at night and a full bath or shower can be taken 1 month after surgery. For the next 2-3 months, you must wear compression garments during the day. During this period, it is strictly forbidden to visit the bathhouse, sauna, or overheat or overcool.
In order to provide adequate pain relief in the postoperative period, analgesics and phlebotonics are prescribed. For the first few days of recovery after phlebectomy, antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are prescribed. With their help, thrombosis is prevented, the risk of which increases in the early period of rehabilitation after phlebectomy on the leg.
The occurrence of hot flashes in the legs and a tingling sensation is an expected reaction of the body in the first days after phlebectomy of the veins of the lower extremities. These symptoms are associated with the accumulation of blood and the formation of edema. After a few days, clinical signs should subside. In the event of an increase in body temperature, increased pain or the appearance of other pathological symptoms, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
After returning home, doctors advise following the following recommendations, which will speed up the postoperative period after phlebectomy:
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- visiting the pool, cycling and walking in the fresh air are allowed;
- it is important to choose comfortable shoes;
- try to change your body position every 30 minutes: sitting or standing;
- while in a horizontal position, try to raise your legs a little higher;
- avoid drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- Avoid eating fatty, spicy, salty and spicy foods;
- adhere to a rational and balanced diet.
Your daily diet includes foods rich in fiber, healthy vitamins and minerals. They are found in fresh vegetables, fruits, and herbs. In addition, you must adhere to the drinking regime. It is recommended to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day.
Make an appointment
Physiotherapy
Strict bed rest is observed only while in the hospital. On average, this time lasts about 1-2 weeks. Next, it is recommended to gradually expand physical activity. To do this, it is necessary to perform extension and flexion of the legs at the knee joints, rotation in the shins and feet. These exercises help prevent the development of congestion in the lower extremities.
Starting from the second day of hospital stay, the patient is assigned to perform a specially designed complex of therapeutic physical training. It includes the following exercises:
- lying on your back, simulating cycling;
- lifting and lowering straight or bent legs;
- bending and drawing the knees to the chest;
- rotation in the ankle joint;
- performing the scissors exercise;
- alternate walking on heels and toes.
Regular adherence to medical recommendations will significantly reduce the risk of developing postoperative complications. In addition to exercise therapy, the patient will benefit from a massage course. Thanks to it, blood circulation is normalized and the possibility of thrombosis is minimized. In addition, exercise therapy combined with massage relieves swelling and pain. In the future, physical therapy may be prescribed to speed up the recovery period. It helps activate regeneration processes. As a result, the healing of sutures is accelerated and scarring is prevented. Magnetic therapy and ultra-high frequency therapy are prescribed as methods of physiotherapeutic treatment during the recovery period after phlebectomy.
Products for external use
For the purpose of pain relief, relieving the severity of edema syndrome and inflammation after phlebectomy, special ointments, creams or gels are recommended. They are selected by the doctor on an individual basis. Products for external use are used in the presence of postoperative compactions or hematomas. As a result of the use of these medications, the recovery period is accelerated, formations in the area of the surgical field are resolved. The recommended frequency of use of medications is 2-3 times a day. It is important to remember that the presence of open lesions in the skin area is a contraindication for the use of products for external use.
Advantages of innovative techniques:
- Painless and comfortable procedures. New techniques are carried out in a comfortable atmosphere for the patient, using minimally invasive techniques, using local anesthesia if necessary. Therefore, they do not cause any discomfort or pain either during the procedures or after them;
- Minimally invasive. To carry out the procedures, only a small puncture is required, which does not leave any scars or scars;
- High efficiency. The results of RFA, EVLO or sclerotherapy are impressive with their high efficiency - a persistent therapeutic effect and the absence of relapses;
- Speed of procedures. The total time for the procedures is 20-30 minutes (no more than 1 hour);
- Outpatient mode. Modern methods do not require a hospital stay, are carried out on an outpatient basis, and do not require any special rehabilitation program;
- Carrying out manipulations without loss of ability to work. Literally immediately after the procedure, the patient is allowed (and even strongly recommended) to exercise – walking. That is, you can return to your usual lifestyle on the day of the treatment;
- No need for long-term rehabilitation. The post-procedure period only requires wearing compression stockings for a short time (up to two weeks);
- Excellent cosmetic effect. There are no scars, cuts or scars left on the skin at the site of exposure;
- Wide range of indications. Innovative techniques treat different stages of venous pathologies - from ordinary spider veins to large-diameter varicose veins.