01.11.2017
Interesting
Bogacheva Sharofat Bairovna
The brain is a “mystical” organ that can fill us with incredible sensations, show us our own “movie”, dreams, accumulate experience and wisdom that allows us to think. This is an organ that controls and regulates the functioning of the entire organism as a whole and each organ and system separately; providing the balance, protection, and compensatory reactions to disturbances necessary for our body. This small organ, weighing about 1400–1500 g (2% of body weight), has incredible abilities that have not yet been fully studied.
What does the brain need? Working without rest day and night, he is in dire need of oxygen (the brain consumes 20% of all oxygen entering the body) and nutrients, without which he cannot live even for a few minutes. It is a known fact that oxygen reserves are not created in the brain, and there are no substances that can nourish it under anaerobic (in the absence of oxygen) conditions. That is, the nerve cells of the brain constantly need oxygen, glucose and “cleaning” (cleansing of cell waste products).
Excursion into physiology
The uninterrupted supply of substances necessary for the nerve cells of the brain and the cleansing of waste are carried out by the cerebral circulatory system, where arterial blood carries oxygen and nutrition to the brain, and venous blood removes toxins and metabolic products.
The vessels of the brain have a unique, perfect structure that ideally regulates blood flow, ensuring its stability. They are designed in such a way that with an increased flow of blood into large vessels, the strong pulse impulse of the blood coming from the heart is weakened due to numerous bends (siphons) of the vessels along the vascular bed, which contribute to the pressure drop and smoothing of the pulsating blood flow. Due to complex regulatory mechanisms, when total blood pressure increases, the pressure in the brain remains stable for a long time. Regulatory systems allow blood flow to be redistributed from parts of the brain with less load to areas with increased brain activity.
The brain has an autonomous regulatory system, which allows it to be in a healthy functional state and control the processes of continuous adaptation of the body to constantly changing conditions of the external and internal environment. In a state of functional rest, the brain receives 750 ml of blood per minute, which is 15% of cardiac output. In children, blood flow activity is 50–55% higher, and in elderly people it is 20% lower than in adults.
It should be noted that the gray matter of the brain (cell bodies of neurons) is supplied with blood more intensively than the white matter (conducting pathways), which is due to greater cell activity. Thus, during intense mental work, local blood flow in the cerebral cortex can increase 2–3 times compared to the resting state.
The brain has the richest capillary network. Nerve cells are not only intertwined, but also penetrated by capillaries. The vessels of the brain are connected to each other by collaterals (“bridges”). Arterial collateral circulation of the brain, important for maintaining normal blood flow, plays a particularly significant role in compensating for circulatory disorders when one of the cerebral arteries is blocked.
With a high intensity of blood flow in the vessels of the brain, the blood pressure in them is maintained relatively constant. A complex chain of regulatory mechanisms protects the brain from a drop in blood pressure and hypoxia (decreased oxygen). Along the path of blood flow to the brain, there are many sensitive cells (pressoreceptors, chemoreceptors) that can respond to blood pressure and regulate heart rhythm and vascular tone.
The activity of the vasomotor centers of the brain is associated not only with nervous and humoral regulation mechanisms, but also with the autonomic regulation system, which allows, despite significant fluctuations in total blood pressure, to maintain cerebral blood flow at a constant level.
Thus, cerebral circulation is provided with complex regulatory mechanisms that make it possible to maintain a constant supply of the substances it needs.
With excessive blood supply to the brain, excessive hydration (fluid accumulation) may occur, followed by the development of edema and damage to vital centers that are incompatible with life. The cause of excess blood supply can be, for example, an increase in systemic blood pressure to 160–170 mm Hg. Art. and higher.
In the problem of impaired blood supply to the brain, much attention is paid to arteries. But venous circulation is no less important. The veins carry out the removal of waste substances (toxins) with the blood - that is, cleansing the brain. Thanks to these vessels, constant intracranial pressure is maintained.
Violation of the venous outflow leads to stagnation of blood and accumulation of fluid in the brain, causes hydrocephalus with compression of the brain centers, and contributes to the occurrence of phlebitis and thrombophlebitis.
There is one more feature of the cerebral veins that must be taken into account. The wall of a venous vessel in the brain does not have a valve apparatus, unlike, for example, the veins of the extremities (valves help withstand loads by moving blood upward and preventing it from moving in the opposite direction). Therefore, venous blood in the vessels of the brain passes freely in both directions, depending on the pressure that arises. This creates a danger of rapid spread of infection from the sinuses and eye sockets, which is facilitated by the atomic structure of the nose and its paranasal sinuses, located in close proximity to the brain. When coughing, venous pressure increases, reverse venous flow, congestion, and brain hypoxia become possible. There are known cases of loss of consciousness during a coughing attack in the presence of a chronic respiratory tract disease and in young children when they “go into a fit” of coughing during illness and crying and screaming until they cough.
It becomes clear why long-term respiratory problems, accompanied by constant swelling and coughing, can cause cerebrovascular accidents. Because they not only cause brain hypoxia, but also disrupt venous outflow and, being a constant source of infection, contribute to its penetration into the brain.
An ophthalmologist, for example, can observe manifestations of congestion in the brain (dilated, blood-filled vessels of the fundus). But this is also visible to the naked eye: red, puffy eyes after sleep (due to drinking alcohol the night before, overeating at night, lack of sleep) are a symptom of congestion in the brain.
After a brief excursion into physiology, it becomes clear that the reasons for the deterioration of cerebral circulation may be associated with disturbances in the flow of blood to the brain and the outflow of blood from the brain.
How does the microcirculation system work?
The vessels providing peripheral blood flow include:
- Small arteries and arterioles;
- Capillaries;
- Venules and small veins;
- Arteriovenular anastomoses;
- Lymphatic vessels.
Venules, arterioles, capillaries and anastomoses between them constitute the main link of microcirculation, ensuring metabolic processes. Vascular resistance, and therefore blood pressure, is maintained by small arteries, arterioles and precapillary sphincters. The exchange occurs in capillaries and post-capillary venules, and the capacitive part of the blood flow consists of venules and small veins, which contain the largest amount of all human blood.
The connection between the arterial and venous parts of the systemic blood flow is carried out by special anastomoses (shunts), which are activated in case of trouble. Through anastomoses, blood flows from the arterioles directly into the venules, and the microcirculation does not receive enough of it. This mechanism forms the basis for the centralization of blood circulation, necessary for redirecting blood to vital organs (brain, myocardium, kidneys), which is clearly manifested in shock.
Arterioles are small precursor vessels to capillaries. Their peculiarity is the presence of smooth muscle cells in the walls, due to which the vessels are able to contract and relax, changing the diameter of the lumen. Changes in arteriolar diameter can occur both locally and throughout the body. Arterioles provide total peripheral resistance, which determines blood pressure levels.
Capillaries continue into venules , through which blood flows out from the microvasculature. The muscular layer of their walls is much less developed than in the arterioles, therefore the wall of these vessels is thinner and is not able to react with a strong spasm under pathological conditions, but the process of expansion and stagnation here occurs easier and faster.
The intermediate link between the arteriole and venule is the capillary - the thinnest vessel of the human body, which carries out the metabolic role. Transport of substances into tissues and back into capillaries is possible thanks to the single-layer wall of the latter, which consists only of endothelium and can have many pores and fenestrae (in the liver, bone marrow, lymphatic tissue).
The work of peripheral circulation is regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems and depends on the action of vasoactive metabolites and other chemicals. In response to stimulation of sympathetic nerve fibers, microcirculatory vessels constrict due to the action of adrenaline and similar metabolites. Vasodilators (histamine) have the opposite effect.
The expansion of the peripheral vascular network occurs under the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system, the main neurotransmitter in this case is acetylcholine. In addition to nervous regulation, the humoral mechanism plays a major role in vasodilation. Thus, hyperkalemia, excess sodium and magnesium, accumulation of acidic metabolic products (acidosis), inflammatory mediators (histamine, bradykinin) provoke a sharp expansion of the vascular network, while catecholamines (adrenaline), the hormone vasopressin, angiotensin and other substances form vasospasm with a decrease microvasculature capacity.
Humoral mechanisms are realized more slowly than the direct influence on the vascular walls from the nerve fibers. In addition, the venous bed responds better to nervous regulation than the resistive arterial bed.
What happens when blood pressure rises?
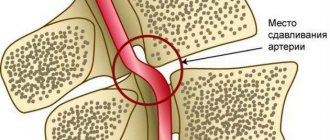
At first, vascular tone is slowly disrupted. Over time, if elevated blood pressure (BP) persists, minor cerebral hemorrhages and strokes may occur.
As a result of a constant increase in blood pressure during hypertension, plasma (part of the blood without formed elements) is released, which ultimately leads to the destruction of the walls of blood vessels.
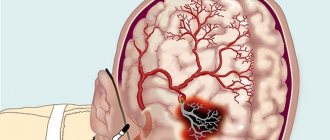
How does this happen? A specific protein (hyaline-like substance, similar in structure to cartilage) is deposited on the walls of blood vessels, which leads to the development of hyalinosis. The vessels become like glass tubes, lose their elasticity and ability to hold blood pressure. In addition, the permeability of the vascular wall increases, and blood can freely pass through it, soaking the nerve fibers (diapedetic bleeding). The result of such transformations can be the formation of microaneurysms and rupture of the vessel with hemorrhage and blood entering the white medulla. The resulting swelling and hematomas lead to further hemorrhages (hemorrhagic stroke).
Atherosclerosis that accompanies hypertension, or exists without it (which is rare), contributes to cerebral ischemia - insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen to the tissues (except for atherosclerotic plaques that narrow the lumen of the arteries, the blood itself can be thick and viscous).
Acute circulatory disorders are strokes (hemorrhagic and ischemic). But it all starts with transient cerebrovascular accidents against the background of hypertension and atherosclerosis, as well as obesity, diabetes mellitus, and respiratory diseases that often accompany them.
Manifestations of microcirculation disorders
Symptoms of peripheral circulatory disorders depend on the type of pathology, the nature of the course, the speed of development and the compensatory capabilities of the body. The symptoms of the pathology are extremely diverse and there is no particular point in trying to systematize it, because ischemia in the nervous tissue and legs will manifest itself differently, while thrombus formation in the vessels of the microcirculation of the kidneys and acute venous congestion in them can occur very similarly.
Common to all peripheral circulatory disorders:
- Possibility of acute or chronic course;
- The development of necrosis, hemorrhages, edema and, as a consequence, pain and disruption of the organ in case of acute microcirculation disturbance;
- The predominance of ischemic-dystrophic changes, atrophy and sclerosis in chronic conditions.
hyperemia (plethora)
Arterial hyperemia is characterized by redness of a tissue area, an increase in its temperature and size due to edema. As a rule, pathological arterial plethora is also accompanied by pain. These processes can be clearly observed during inflammation in visible areas of the body. When internal organs are damaged with symptoms of hyperemia, patients usually feel pain, and other symptoms are associated with the disease that occurs with this type of peripheral circulatory disorder.
Venous stagnation is accompanied by:
- Cyanosis (blueness) of the skin, mucous membranes;
- In the zone of venous hyperemia, the temperature decreases (the limbs become cold, but not the internal organs);
- An increase in the volume of a limb or internal organ due to edema;
- Pain, a feeling of fullness, itching on the skin, possible formation of trophic ulcers;
- Internal organs: lungs - the appearance of wheezing, possible cough and congestive pneumonia, liver - increase in size, heaviness in the hypochondrium, dyspepsia, brain - headaches, impaired memory and intelligence.
leg ischemia
Ischemia (anemia) can occur in acute or chronic form. Ischemic changes in the extremities are accompanied by pain, rapid fatigue during exercise, a feeling of coldness, crawling “goosebumps”, the skin becomes pale, and the development of trophic disorders, including ulcers, is possible.
In the brain, ischemia underlies discirculatory encephalopathy with corresponding neurological and psychiatric symptoms, and acute ischemia, turning into necrosis, is the basis of cerebral infarction (stroke) with paresis and paralysis.
Ischemia of the renal cortex, as well as thrombus formation in the microvasculature of the organ, contribute to epithelial necrosis and the development of acute renal failure. Chronic venous stasis or prolonged ischemia provoke sclerotic and atrophic changes with a possible outcome in chronic insufficiency.
Symptoms of cerebrovascular accident
When a lesion forms in the brain with impaired blood supply, the patient may experience numbness in half of the body (on the side opposite to the lesion) and part of the face around the lips; short-term paresis of the limbs or other parts of the body and face is possible. Speech is impaired and an epileptic seizure may occur.
If there is a circulatory disorder, depending on the location of the lesion, the legs and arms may become weak, the head may become dizzy, the patient may have difficulty swallowing and pronouncing sounds, photopsia (appearance of luminous spots, sparks, etc. in the eyes) or diplopia (doubling of visible objects) may occur. . The person loses orientation and has memory lapses.
Signs of impaired cerebral circulation due to hypertension are manifested in the following: the head and eyeballs begin to hurt very much, the person experiences drowsiness, he experiences stuffiness in the ears (like on an airplane during takeoff or landing) and attacks of nausea. The face turns red and sweating increases.
Unlike strokes, all these symptoms, which are called “transient attacks,” disappear within 24 hours.
Chronic cerebrovascular accident (CVA), unlike acute forms, develops gradually. There are three stages of the disease:
- At the first stage, the symptoms are vague. They are more like chronic fatigue syndrome. A person quickly gets tired, becomes hot-tempered and absent-minded, and forgets some minor points. His sleep is disturbed, his mood often changes, his head hurts and he feels dizzy.
- At the second stage, chronic cerebrovascular accident is accompanied by significant memory deterioration, and minor motor dysfunctions develop, causing unsteadiness in gait. There is a constant noise in my head. A person perceives information poorly, having difficulty concentrating his attention on it. Becomes irritable and unconfident, loses intelligence, reacts inadequately to criticism, and often becomes depressed. He gradually degrades as a person and adapts poorly socially. He constantly feels dizzy and has a headache. He always wants to sleep. Performance is significantly reduced.
- In the third stage, all symptoms intensify. Personality degradation turns into dementia, memory suffers. Having left home alone, such a person will never find his way back. Motor functions are impaired, which manifests itself in hand tremors and stiffness of movements. Speech impairment and uncoordinated movements are noticeable.
Treatment of pathology of peripheral circulation
The nature of treatment for peripheral circulatory disorders depends on the cause of the pathology and the changes that accompany it. In case of obstruction of microcirculatory vessels, it is important to restore blood flow as quickly as possible by:
- Fibrinolytic therapy (alteplase, streptokinase);
- Thrombolysis (heparin);
- Administration of antihypoxants (ascorbic acid), protease inhibitors (contrical, trasylol), antiplatelet agents (aspirin), anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin, fraxiparin), antispasmodics.
In the case of systemic disorders caused by heart failure, the underlying disease is treated, and additional drugs are prescribed to improve microcirculation in the tissues. Shock with blood shunting requires intensive care in an intensive care unit.
Drugs to improve peripheral circulation include:
- Angioprotectors and agents that improve blood rheology - dipyridamole, pentoxifylline, flexital (dipyridamole is often prescribed even to pregnant women with circulatory pathology in the placenta), ascorutin;
- Low molecular weight dextrans - rheopolyglucin, rheomacrodex - reduce blood viscosity by increasing plasma volume;
- Prostaglandins - increase the speed of blood flow and the intensity of microcirculation, have an angioprotective effect, somewhat expand the vascular lumen, while reducing the total peripheral resistance (vasaprostan);
- Calcium channel blockers - improve microcirculation, have a neuroprotective effect, regulate blood pressure - cinnarizine, stugeron, norvasc, nimotop, etc.;
- Vasodilators - promote vasodilation, facilitating blood flow in small vessels, have an antiplatelet, neuroprotective effect, increase tissue resistance to hypoxia - drotaverine, halidor, cavinton, aminophylline;
- Ganglioblockers - cause vasodilation and reduce blood pressure - dimecoline, pachycarpine, pentamine;
- Bioflavonoids - improve rheological parameters and elasticity of red blood cells - troxevasin, venoruton;
- α-adrenergic blockers - dilate the blood vessels of internal organs, reduce vascular resistance and improve blood flow - sermion, prazosin, pyrroxan and others;
- Herbal preparations - obtained from plant extracts, they act more slowly than synthetic drugs, are used for impaired blood flow in the brain, legs - ginkgo biloba, tanakan, bilobil.
Treatment of microcirculation disorders requires an integrated approach and the participation of a specialist; self-medication in this case is unacceptable. In case of serious disorders of peripheral blood flow, you should not rely on traditional methods, but it is better to consult a doctor - a therapist, cardiologist, hemostasiologist, phlebologist, neurologist who deals with vascular pathology of various organs.
Consequences of cerebrovascular accidents
Disability is a sad result of acute and in many cases chronic cerebrovascular accident.
Acute cerebrovascular accident has serious consequences. In most cases, a person who has suffered a stroke becomes completely helpless. He cannot eat, perform hygiene procedures, dress, etc. on his own. Such people have a completely impaired ability to think. They lose track of time and have absolutely no orientation in space.
Some people retain the ability to move. But many people, after a cerebrovascular accident, remain bedridden forever. Many of them maintain a clear mind, understand what is happening around them, but are speechless and cannot express their desires and feelings in words.