- Home >
- Directory >
- Interpretation of ultrasound of the heart
Has your doctor prescribed an ultrasound of your heart?
Or is the echocardiography already over, and the results are in your hands? In order not to miss the pathology, do not try to interpret the ultrasound of the heart yourself. Don’t risk your health, take the protocol to a specialist! If you are interested in what parameters and how the survey results are assessed, refer to this article!
"The heart is on the left"
– The top of the organ and 2/3 of its parts are on the left, but 1/3 is behind the sternum in the middle.
Often people claim that they are stabbed in the heart and grab their left side. It is important to understand here: classic heart pain is pain, as a rule, precisely behind the sternum. Pain on the left side can also be cardiac. But they are burning, pressing. Therefore, if you have a stabbing sensation on the left side, the cause may not be cardiological at all. Answer: myth
How is cardiac ultrasound interpreted?
- Competent ultrasound doctors with many years of experience
- Expert device with high resolution
- All types of ultrasound (ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs, ultrasound of blood vessels, ultrasound of the heart, ultrasound of the joints)
Conclusion during the study.
Burning to disc
Sign up for an ultrasound
Prices for ultrasound
Echo-CG interpretation occurs by comparing normal indicators with the indicators of the study. What are these indicators:
- Myocardial mass
- Volume and dimensions of the left and right ventricles
- Wall thickness of the left and right ventricle
- Aortic diameter
- Thickness of the interventricular septum
It seems simple, but in reality everything turns out to be much more complicated. For competent decoding, it is necessary to know the individual characteristics of the patient, his medical history and many other factors. Therefore, to interpret echocardiography, contact a specialist!
“Body weight has no effect on heart function”
- How it influences!
After all, this organ circulates blood throughout the body. And the more a person weighs, the more his heart muscle is exhausted. Although thin people can have problems, dystrophy is one of them. Body weight should be normal. There is a special formula that can be used to estimate the degree of correspondence between a person’s mass and his height. To do this, you need to divide your weight by your height squared. If the resulting figure ranges from 19 to 25, this is a good indicator. Answer: myth
Normal ultrasound of the heart
Here are some of the indicators that are taken into account when assessing results:
- Myocardial mass: men - 130-180 g; women - 90-140 g.
- Left ventricle size: At rest - 5.7 cm in men, 4.6 cm in women)
- During contraction – 4.3 cm in men, 3.1 cm in women)
Interpreting the results of a cardiac ultrasound is a serious process that requires the doctor to have fundamental knowledge of human anatomy. Only a specialist can competently assess deviations and understand whether it is worth sounding the alarm. You may need additional examinations.
Take care of your health! Trust the decryption to professionals!
If you have any questions, ask our specialist!
Ask a Question
“Heart disease occurs only in older people”
– Of course, older people are more susceptible to such diseases: the body ages, loses its former shape and “engine”.
But, unfortunately, young guys and small children often turn to cardiologists with problems. Complaints arise for various reasons. This could be physical or emotional stress, or a previous infection that caused complications. The cause of the disease can also be heredity. It happens that a person leads a healthy lifestyle: eats right, plays sports, does not have bad habits, but from his parents he inherited, for example, incorrect cholesterol metabolism. In this case, problems cannot be avoided. Answer: myth
Ultrasound of the heart in Moscow
The most competent interpretation of a heart ultrasound may not bring results if a poor-quality diagnosis was carried out: this can happen if you were examined using outdated equipment, and the protocol was drawn up by an inexperienced, unqualified doctor.
Don't risk your health! Contact a trusted clinic! The Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center is your confidence in the quality of diagnostics! Experienced doctors with many years of experience, an expert-class ultrasound scanner and affordable prices are at your service!
Sign up for an interpretation of cardiac ultrasound at the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center near the Baumanskaya metro station (see map) by phone: 8 (495) 127-03-71 or leave a request on the website.
Baumanskaya metro station (see map) 8
leave a request on the website
“During physical and emotional stress, the heart pumps more blood than at rest”
– At rest, the heart pumps about 4.5–5 liters of blood per minute.
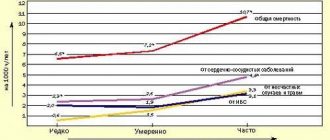
But with physical stress, the figure can increase two to three times, sometimes reaching one hundred liters. Let's say an athlete is running a cross-country race. In order for a person to cope with a difficult task, his heart needs to provide the muscles with energy, fill the body with glucose and oxygen. With emotional stress, the situation is even more serious, because our emotions are adrenaline, that is, acceleration. Acute stress, such as the loss of a loved one, increases the risk of heart disease by 21 times, and chronic stress increases the risk by 50 times. Answer: true
Introductory part
Before heart surgery, a person has many questions. Some of them we ask the doctor, and some we cannot even formulate. When we understand what is happening to our body and what we can do to restore health, it is easier for us to endure all procedures.
Acquired heart valve defects
- these are diseases that are based on morphological and/or functional disorders of the valve apparatus (valve leaflets, annulus fibrosus, chordae, papillary muscles), developed as a result of acute or chronic diseases and injuries, disrupting the function of the valves and causing changes in intracardiac hemodynamics.
Valve defects can be congenital or acquired.
Congenital defects occur when the structures of the heart are formed incorrectly during intrauterine development; sometimes they do not make themselves felt until adulthood. Acquired defects arise due to rheumatism, infection, metabolic disorders (when calcium is deposited in the valves), trauma and other reasons.
The main types of heart valve defects:
- mitral stenosis
- mitral valve insufficiency
- mitral valve prolapse
- aortic stenosis
- aortic valve insufficiency
- tricuspid stenosis
- tricupidal insufficiency
The normal functioning of the heart largely depends on the functioning of its valve apparatus.
Obstacles to the passage of blood cause overload, hypertrophy and expansion of the structures above the valve. Obstructed heart function disrupts the nutrition of the hypertrophied myocardium and leads to heart failure.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Etiology of stenosis
and combined rheumatic disease,
insufficiency
- usually rheumatic, rarely septic, atherosclerotic, traumatic, syphilitic.
Stenosis is formed as a result of cicatricial fusion or cicatricial rigidity of the valve leaflets and subvalvular structures; valve insufficiency - due to their destruction, damage or scar deformation.
Failure
valve damage occurs due to destruction or damage to its valve flaps. Valve insufficiency is characterized by incomplete closure of the leaflets and occurs as a result of their wrinkling, shortening, perforation or expansion of the fibrous valve ring, deformation or separation of the chordae and papillary muscles. In some cases, valve insufficiency develops as a result of dysfunction of the valve apparatus, in particular the papillary muscles.
Often stenosis and insufficiency develop on one valve (the so-called combined defect
).
In addition, there are cases when the defects affect two or more valves - this is called combined
heart disease.
Affected valves form an obstacle to the passage of blood - anatomical in case of stenosis, dynamic in case of insufficiency. The latter is that although some of the blood passes through the hole, it returns back in the next phase of the cardiac cycle.
A “parasitic” volume is added to the effective volume, performing a pendulum-like movement on both sides of the affected valve. Significant valvular insufficiency is complicated by relative stenosis (due to increased blood volume). Obstruction to the passage of blood leads to overload, hypertrophy and expansion of the overlying chambers of the heart.
The expansion is more significant with valve insufficiency, when the overlying chamber is stretched by additional blood. With stenosis of the atrioventricular orifice, the filling of the underlying chamber is reduced (left ventricle with mitral stenosis, right ventricle with tricuspid stenosis); There is no hypertrophy or expansion of the ventricle.
With valve insufficiency, the filling of the corresponding ventricle is increased, the ventricle is dilated and hypertrophied. Difficulty in the functioning of the heart due to improper functioning of the valve and degeneration of the hypertrophied myocardium leads to the development of heart failure.
to the top of the page
“In children and adults, the heart beats at different frequencies”
– In children under five years of age, the heart makes about 120 beats per minute, while in adults the optimal frequency is from 55 to 70 beats.
Your heart rate may increase. It also depends on the state of the autonomic nervous system, temperature, and physical fitness. A trained person’s “engine” will run slower than someone who does not exercise. Answer: true
Diagnosis of heart valve diseases
After listening to the symptoms you describe and examining your medical record, the doctor will measure your pulse and blood pressure and listen to your heart using a stethoscope.
If your doctor suspects that you have a heart disease, he may ask you to undergo a series of special diagnostic tests that will help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
One of these research methods is a non-invasive method, i.e. which does not require any internal intervention.
Another type of research is invasive: with the help of instruments inserted into the body, which, as a rule, causes only minor inconvenience to the patient.
Chest X-ray
This test allows the doctor to obtain valuable information about the size of the heart, heart chambers and the condition of the lungs.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An electrocardiogram monitors the electrical current passing through the heart and stimulates the chambers to contract. An ECG is especially useful in diagnosing abnormal heart rhythms and rates.
These studies also show muscle enlargement or damage, and the presence of congestion on one side or another of the heart.
Echocardiogram (EchoCG)
This test is carried out using a “small” microphone placed on the surface of the chest, which emits high-frequency sound waves.
Sound waves are reflected back (hence the term "echo") from each layer of the heart wall and valves and then displayed on a monitor screen. The “echo” image from different points allows you to see a cross-section of the heart at the moment of its operation.
During the echo, the speed of blood flow is also recorded, the direction of blood movement is monitored: is the blood moving in the normal forward direction or is there a reverse movement (as in the case of valve insufficiency).
A narrowed (or stenotic) valve causes increased blood flow. The degree of valve stenosis is in many cases accurately determined by the increased blood flow velocity.
This test will not only show how the heart valves work, it will also provide useful and comprehensive information about the size of the heart chambers, as well as the thickness and function of the heart muscle.
Cardiac catheterization and angiogram
These tests are done by inserting a thin, hollow tube (catheter) through a vein or artery in the arm or groin area and into the chambers of the heart, using X-rays.
During catheterization, the pressure in the chambers of the heart is measured and the volume of blood in the bloodstream is determined.
Angiography consists of the injection of a radiopaque contrast agent, which is visible using X-rays and allows you to evaluate the work of the heart in pumping blood, the function of the valve and the patency of the arteries (coronary) that supply blood to the heart muscle.
Despite the fact that similar studies have been routinely carried out before, it is not at all necessary that they are needed in your case if the information obtained by echocardiography is complete and accurate.
In many cases, the only invasive test required before surgery is a coronary angiogram if it is determined that the patency of one or more arteries is impaired.
If there are blockages in the coronary arteries, the doctor will usually perform bypass surgery at the same time as heart valve surgery.
to the top of the page
Heart valve surgery
Often heart defects do not manifest themselves for a long time, because the heart adapts to working under overload. In the case where the heart defect is “moderate” and does not lead to serious overload of the heart, in some cases they are limited to observation or drug therapy. But when the defect is severe, it must be treated surgically.
The following operations are performed on heart valves: reconstruction or complete replacement of a damaged valve.
Heart valve reconstruction
Sometimes during surgery it is possible to preserve the valve flaps and only correct their shape. This procedure is called valve repair.
.
Sometimes the shape of the valve can be restored by strengthening its base with threads, or by sewing a special ring to the base, while the valve’s own flaps are preserved. This procedure is called annuloplasty.
, it is possible only for the mitral and tricuspid valves.
Valve reconstruction can largely restore its function. For severe heart valve damage, valve replacement surgery may be the only treatment option. The results of these operations exceed the effect of drug therapy. Today, heart valve surgery can be performed on patients of any age group.
Access for operations on the aortic valve or on several valves simultaneously is made through an incision in the center of the sternum. When performing operations on the mitral valve, it is possible to use the “keyhole technique,” when surgical access is made through a small incision in the projection of the mitral valve: on the side and below the chest.
When it is impossible to save the leaflets of the native valve, or if they are preserved, there is a high probability of the defect returning and repeated surgery, the native valve is excised and implanted in its place
artificial
valve prosthesis
.
The most commonly performed surgeries are mitral valve reconstruction. In this case, the own valve is preserved - this is very important.
, Ross surgery is performed to treat aortic disease.
. The damaged aortic valve is replaced with the patient's own pulmonary valve, which is similar in structure, and an artificial prosthesis is implanted instead of the excised pulmonary valve.
When the aortic valve and aortic wall are damaged, it may be necessary to replace the ascending aorta with a valve-containing aortic graft
(sometimes called a conduit). In this case, not only the aortic valve is replaced, but also the adjacent ascending aorta.
Your attending physician will inform you about the possibility of reconstructive surgery on the heart valve in your case. In some cases, the question of the possibility of valve reconstruction is decided during the operation: if reconstruction is not possible, then an operation is performed to replace the damaged valve.