| For a pregnant woman, the heartbeat of her unborn baby is a very important indicator and moral support. This knock can indicate whether the child is healthy or not. Of course, the mother will not understand this on her own, but doctors will identify pathologies if they are present. |
- Timing of detection of fetal heart rate
- Causes of fetal heart rhythm disturbances
- Why is the fetal heartbeat determined?
- Methods for listening to the fetal heartbeat
- Determining the sex of the baby by heartbeat
- How can you hear your child’s heartbeat?
Timing of detection of fetal heart rate
In the first months of gestation, the heart of the unborn child can already be heard.
With the help of ultrasound diagnostics, specialists hear the heart in the 5th week of gestation. Even earlier (at the 3rd or 4th week), the fetal heart rate can be heard by being diagnosed with a vaginal sensor. It is at these dates that you can hear the heart of your unborn child for the first time. With the period of gestation and with the activity of the fetus, the heart rate also changes. 110-130 beats per minute are recorded at 6-8 weeks. A maximum of 190 beats is heard at 8-11 weeks of gestation, and 140-160 beats can be heard starting from the 11th week of conception. The gynecologist must assess what phase the child’s activity is in when determining the heart rate, the time of the procedure, whether the unborn baby has any illnesses, and whether his mother has certain pathologies.
Obstetric stethoscope or phonendoscope
On the one hand, this method is available to everyone: you can buy this tube at any pharmacy for little money. On the other hand, it is not easy to count heartbeats using this tool at home. For this you need an assistant, because you can’t do it alone. At the same time, he must have skills that he most often does not have. Moreover, you need to listen to tones at certain points. Correctly counting the number of beats will be interfered with by extraneous noises (mother’s heartbeat, contraction of the muscles of the intestinal walls and other sounds), which you need to learn to distinguish from the fetal heartbeat.
Before 25 weeks, it is unlikely to be possible to hear the heart of an unborn child at home.
Causes of fetal heart rhythm disturbances
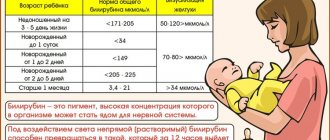
The reasons can be very different. If the heart rate is less than 80 beats/min, in the first weeks this may indicate that the pregnancy may be terminated. If the period is less than 4 weeks, then the heart rate may be less than 120 beats/min, this will not be a pathology. From the 12th week to the last day of gestation, a heart rate less than 120 beats/min may indicate compression of the umbilical cord or lack of air (chronic) in the fetus. The same heart rate during childbirth indicates that the baby is in a state of acute hypoxia, or that the umbilical cord is compressed by the mother’s muscles during contractions.
A fetal heart rate of 170 beats per minute in rare cases may indicate a dysfunction of the placenta, but in general this is a variant of the norm. At the 12th week and later, an increased fetal heart rate indicates chronic hypoxia, or may occur in response to the stress of the expectant mother. The reasons for increased heart rate during childbirth are similar to those described above.
If the tones are heard muffled, the doctor makes efforts to listen to the fetal heart rate, this may indicate the following:
- the child has cardiovascular system defects
- the mother is obese (significantly overweight)
- ultrasound sensor is outdated
- pregnancy is too early
Muffled tones, starting from the 12th week of gestation and until the last day of gestation, may have the following cause:
- defects of the cardiovascular system in a baby
- the fetus is positioned so that its heart is difficult to listen to
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios
- anterior placenta previa
- fetoplacental insufficiency
- obesity in the expectant mother
If the doctor cannot listen to the fetal heart sounds, do not be alarmed ahead of time. Again, the reason may be an old ultrasound sensor. But this may also indicate more serious problems, including an incipient abortion or a frozen pregnancy (the fetus stops developing and dies in the mother’s belly). The absence of fetal heart rate starting from the 12th week indicates that antenatal fetal death has occurred, or the doctor is using an old sensor, or listening to heart sounds incorrectly. During childbirth, the reasons are similar to the last two mentioned.
What problems are diagnosed using cardiotocography?
Cardiotocography is an additional examination method. Therefore, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based only on its results. However, with the help of CTG it is possible to detect the development of various fetal pathologies, including the following disorders:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- hypoxia;
- pressing or entwining the umbilical cord.
If CTG reveals abnormalities in the condition of the fetus, additional ultrasound and Doppler sonography are performed.
Why is the fetal heartbeat determined?
- to establish the fact of pregnancy
When a woman sees a positive result on a home pregnancy test, she should go to the gynecologist. He does an ultrasound to confirm or refute the test result. From the third week, as already noted, you can hear the heartbeat of the embryo. If at the first appointment you are told that there is no fertilized egg in the uterus, or that the embryo’s heartbeat cannot be heard, do not panic! After a week, most likely, your baby's heart will be sufficiently formed and the doctor will hear its beating.
In some cases, a return visit to the gynecologist reveals deformation of the ovum and lack of heart rate. Then the doctor speaks about a frozen pregnancy. Need a medical abortion. The doctor prescribes hormone-based medications. You can try to conceive again 3-6 months after an abortion for medical reasons.
- to assess the condition of the unborn baby
All environmental and maternal health factors affect the baby's heart. Heart rate depends on:
- the percentage of oxygen in the air that the mother is breathing at the moment
- fetal activity
- baby's sleep
- physical activity pregnancy
- mother's illnesses
- the stress that the mother is currently experiencing
But when exposed to these factors, the baby’s heartbeat changes temporarily. If the heart rate is not normal for a long time, the doctor may suspect that the baby is not getting enough blood. A diagnosis of fetoplacental insufficiency is made. It is almost always chronic. Sometimes the condition requires emergency delivery.
- to monitor the condition of the child during childbirth
Childbirth is a difficult stage in a baby’s life. There is a lack of oxygen; it is compressed as it passes through the mother’s birth canal. Basically, babies' hearts can withstand this stress. But in some cases there are emergency conditions, and the child will not survive without the help of qualified doctors. During the birth process, it is customary to check the baby’s heart rate after each contraction, otherwise you may miss the moment when acute hypoxia begins, which is life-threatening for the baby.
How is CHT performed?
To obtain accurate data during cardiotocography, a woman must be in the correct position: half-sitting or lying on her left side. If the expectant mother lies on her right side, the uterus may press on the inferior vena cava, which will lead to complications.
Before starting the examination, the doctor listens to the pregnant woman’s belly with a stethoscope and finds the point where the baby’s heartbeat can best be heard. It depends on how the baby turned in the womb. It is best to perform CTG within 2-3 hours after the patient has eaten. To avoid obtaining erroneous data, cardiotocography should not be done earlier than an hour after intravenous administration of glucose to the expectant mother.
Methods for listening to the fetal heartbeat
- Ultrasound (ultrasound)
With the help of ultrasound, you can not only hear the baby’s heart, but also see what condition the placenta is in, what size the fetus is, etc. The gynecologist-obstetrician pays special attention to the fetal heart rate if the pregnant woman has developmental defects or children born her in the past, had malformations of the heart and blood vessels.
- Auscultation
To implement this method, an obstetric stethoscope is needed. Relevant only from the 18th or even 20th week of gestation. But this method is not always easy to implement. In these cases, auscultation is difficult (and sometimes impossible):
- oligohydramnios
- polyhydramnios
- location of the placenta along the anterior wall of the uterus
- maternal obesity
- Cardiotocography (CTG)
The method helps to identify hypoxia and provide the necessary treatment. When measuring heart rate using this method, heartbeats are recorded on a special film. The activity of the uterus is also determined, which is very important during the birth process. The procedure usually takes about an hour, sometimes a little less. This duration is explained by the fact that the baby can sleep for some period, and then wakes up. This affects heart rate and indicators that are recorded during CTG.
Sometimes the doctor decides that the sensors should remain on the woman’s stomach for 24 hours. The first time cardiotocography is performed after the 32nd week of gestation. An earlier date is not advisable. In 9 months you need to undergo CTG 2 times. The procedure is absolutely safe for the fetus and the mother herself. What will be recorded on the tape will not be understood by the average person. The doctor must decipher it, taking into account the data of tests and ultrasound diagnostics.
CTG norms:
- Heart rate 120-160 beats per minute
- the fetal heartbeat does not become less frequent, or is recorded very rarely
- When the fetus moves, the heart rate increases
These three factors are important to determine the PSP index, which should be less than 1.
CTG may show abnormalities when:
- lack of oxygen baby
- pressing the umbilical cord to the fetal head or bones (but then changes will be recorded for a short period of time)
- sensors incorrectly attached to the mother's belly
- Echocardiography
This is another method of listening to the baby's heartbeat. The method is relevant for the 18th – 28th week of gestation if the doctor suspects that the child’s heart is not forming quite correctly. Echocardiography shows the structure of the heart and blood flow.
Determining the sex of a child by ultrasound
Modern medicine can determine the gender of the unborn child during a routine ultrasound during the 17-20th week of pregnancy - ultrasound of the second trimester.
This study is absolutely safe for the baby, but it is worth noting that its main goal is not to determine the gender of the fetus, but to monitor development and track changes in condition. In most cases, the gynecologist sees who will be born - a girl or a boy, but even the latest equipment can malfunction - at the right moment the baby may not be in the mood and turn his butt to the doctor and parents. In this case, if you really want to clarify the issue, the examination can be repeated in a couple of weeks.
How can you hear your child’s heartbeat?
You don't have to go to a gynecologist to hear your child's heart. The first way to listen to your heart rate is with a stethoscope . It can be bought at a pharmacy at a low price. But you will need help. Before the 25th week of gestation, people without appropriate medical education can almost never hear the fetal heart. You can repeat listening with a stethoscope every week. It is important to remember that the sounds of the fetus moving can be confused with the beating of its heart, as well as with the sounds of processes that occur in the mother’s abdomen.
The second way to hear the baby’s heart yourself is fetal doppler . This is an ultrasound detector that you can buy yourself. It does not record data on tape, but you will hear the baby's heartbeat. The method is relevant from the 8th and later weeks of gestation. Duration of the procedure: maximum 10 minutes. The device is expensive, so not all pregnant women can afford it.
Third way: put your ear to the pregnant woman's belly . But this is only relevant after the 30th week of gestation. But if a woman is overweight, this method will not work. If the fetus is head down, it is better to listen to its heart below the pregnant woman's navel.
If you tend to worry about little things and independently diagnose yourself and your child, it is better to entrust listening to the fetal heartbeat and determining the norm to doctors. Enjoy motherhood and be in harmony with yourself.
Cheap methods for determining the sex of a child: what is the reliability?
The content of the article
Not so long ago, the mystery of the sex of the unborn child remained a mystery until the moment of its birth. Our grandmothers used folk methods in solving this issue, from studying the shape of a pregnant woman’s belly to analyzing her taste preferences. Japanese and Chinese conception tables and signs relating to the appearance and behavior of a pregnant woman were used.
But already in those days, gynecologists preferred to trust the laws of anatomy, and knew how to determine the sex of a baby by its heartbeat. This technique is still used today, although it has been established that its reliability does not exceed 70%. Is this not enough? Any other folk methods of determining sex give a probability of 50%, i.e. absolutely useless - guessed right - wrong.
Methods for assessing the “adequacy” of fetal movements
Counting the number of movements
The easiest way to assess fetal movements is to count the number of movements by the pregnant woman herself. Self-assessment methods are very easy to use, do not require additional equipment or the presence of a doctor, and are easily reproduced by any woman. Their disadvantages are that each woman has different thresholds of susceptibility.
"Count to Ten"
The most common method for assessing fetal movements is called “count to ten” . It can be performed after 28 weeks of pregnancy, when the fetus is mature enough for active movements. Its essence lies in the fact that the expectant mother counts the movements of the fetus over a 12-hour period of time, for example from 9 am to 9 pm. The time when the pregnant woman detects the tenth movement is recorded on a tablet. If the fetus makes less than 10 movements in 12 hours, this is a reason to consult a doctor for further examination.
Sadowski method
In the evening after dinner (approximately from 19 to 23 hours), the woman lies on her left side and counts the movements of the fetus. At the same time, everything is counted, even the smallest movements. If 10 or more movements are noted within an hour, this indicates that the baby is moving quite actively and feels well. If the fetus moved less than 10 times in an hour, then the movements are counted over the next hour. The evening time for this assessment method was not chosen by chance. It is in the evening hours, especially after dinner and the associated increase in glucose, that the greatest activity of the fetus is observed. If the number of fetal movements during this test is less than 10 in two hours, this should be considered as a sign of a violation of its condition and additional research should be carried out.
For an obstetrician-gynecologist, fetal movements are also an important diagnostic criterion for certain deviations in the course of pregnancy from the norm. Too active, violent, painful movement of the fetus or weak, infrequent movements may indicate its unfavorable condition.
Dopplerography
This is a type of ultrasound examination. With its help, the state of the child’s cardiac activity is determined and the patency of the umbilical cord vessels is assessed. This diagnostic method gives significant results. A qualified specialist determines the presence of hypoxia, detects entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord and identifies abnormalities in the functioning of the placenta.
No preliminary preparation is required to conduct the study. Most ultrasound machines are equipped with a Doppler function. The procedure is absolutely painless. It lasts 15 minutes. The study is prescribed to women in the third semester of pregnancy.
The accuracy of detecting disorders using Doppler sonography is 70%. The absence of problems in a specific period of time does not exclude the development of complications in later stages.
Amnioscopy
This is a visual method with which amniotic fluid is examined. It is carried out in several cases: post-term pregnancy, suspected intrauterine death of the child and prolonged labor in which the amniotic sac has not burst.
Amnioscopy is performed at a stage of pregnancy exceeding 36 weeks. During the study, the doctor evaluates the amount and color of amniotic fluid. The presence of foreign impurities is also determined. The results obtained are sent to an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Fetal monitoring using an amnioscope can detect serious abnormalities. To conduct the study, preliminary preparation is required. Amnioscopy is carried out with the consent of the woman, informed about possible complications. The probability of miscarriage or onset of premature labor after the study is 0.5%.
Heart formation
The development of the child takes place under the careful supervision of gynecologists. The normal course of the process is indicated by the fetal heartbeat. This is one of the most important indicators by which one can judge how the formation of the body of the future person is progressing. This is due to the fact that many anomalies and pathologies of the child’s body occur during the period of intrauterine development. Their early detection will help specialists decide on treatment therapy.
The heart is one of the main human organs. Not only the formation of the baby’s entire body, but also his life depends on how normally it develops.
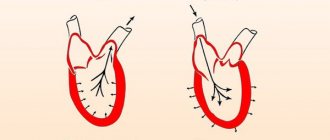
The fetal heart is formed from mesoderm approximately 3 weeks after conception. The primary heart tube bends and lengthens, acquiring a sigmoid shape. At the end of the 5th week, its separation by the primary interatrial septum is observed. It is in it that a hole is formed, which subsequently transforms into a specific hole called an open oval window. And at the end of the 7th week, a second interatrial septum already exists in the heart. During this period, the development of the heart valve system also occurs as a result of reformation.
During this period of fetal development, a valve is formed from the remnants of the primary interatrial septum, which after birth will close the foramen ovale. In addition, the valve is directly involved in the distribution of the child’s blood flow.
Blood under fairly high pressure is directed from the right to the left atrium. This direction of blood flow is due to the fact that the pressure in the right atrium is much higher than in the left.
One of the walls of the left atrium serves as a base for the development of a septum that separates the two cardiac ventricles of the small heart. And in its upper part a small hole is formed, which over time transforms into a connecting membrane.
At the same time, two horizontal folds develop, creating a septum after joining, which will subsequently separate the aorta from the pulmonary trunk. After this, the development of the four sections of the heart from the endocardial protrusions begins.
By the end of the 10th week after conception, the fetus has already fully formed 4 parts of the heart, as well as the placenta, which directly provides placental blood circulation to the fetus.
In order for the fetal heart to develop and form according to the norm, the expectant mother must not only lead a healthy lifestyle, but also fully follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist. The health of her child depends on it.
- How to listen to the fetal heartbeat at home
Features of the future baby's heart
Many mothers are interested in how long it takes to hear their baby’s heartbeat. Somewhere around 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, a heart rudiment forms in the embryo. Initially, it is a hollow tube, which within a week begins to pulsate. Already at week 9, four chambers appear in the organ.
Since in the mother's womb the fetus receives oxygen and nutrients through the umbilical cord, there is a patent ductus arteriosus in its vessels between the aorta and the pulmonary trunk, and in the heart there is a hole between the atria (open oval window). They should close after birth.
Electronic fetal monitoring
This is an advanced technique with which serious complications are determined: cerebral palsy, intrauterine death, cardiac dysfunction. Fetal monitoring is carried out as follows: the woman in labor, lying on her back, has belts with sensors placed on her stomach. One device records the fetal heartbeat, and the second - the duration and intensity of uterine contractions. Sensors are connected to the monitor.
In some cases (for example, serious danger to the fetus), an internal examination is used. Its essence is as follows: the electrode is inserted through the cervix and placed on the baby’s head. With such an examination, the doctor receives the exact data necessary to assess the current situation. Internal monitoring is used after rupture of membranes. The cervix should also be dilated (at least 1 cm).
External electronic monitoring lasts about half an hour. Innovative devices are used in clinics. For example, these could be Avalon fetal monitors. This is technological equipment with the best characteristics. It is distinguished by functionality, long service life, and ease of use.
Fetal monitoring is an advanced technology used in medical institutions equipped with the latest technology. Therefore, we need to take a closer look at its features and advantages.