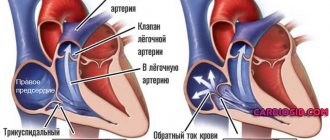
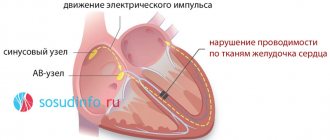
Impaired conduction function (blockade) of the heart is a slowdown or complete cessation of the conduction of impulses through any part of the conduction system.
In this case, there is a violation of the sequence, speed and strength of excitation and contraction of the heart, or there is no contraction of a certain area of the heart.
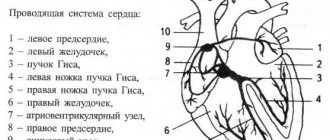
Based on the degree of conduction disturbance in an element of the conduction system of the heart, the following are distinguished:
- incomplete (partial) blockade – impulse conduction is slowed down;
- complete blockade - there is no impulse conduction.
Causes of heart failure
The lecture of every expert in the field of cardiology begins with cardiac arrhythmia and conduction disorders. First of all, it is important to analyze the reasons for the development of the pathological condition. There are the following unfavorable factors that provoke the disease:
- Cardiological (ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, congenital and acquired heart defects, myocardial abnormalities, prolapses);
- Pharmacological influence (taking glycosides, antiarrhythmic drugs, diuretics, sympatholytics);
- Electrolyte type failure (hyperglycemia, hypercalcemia, etc.);
- Toxic substances (smoking, drug, alcohol addiction, poisoning with one’s own hormonal substances).
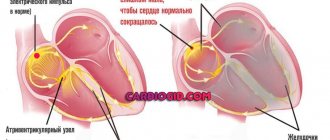
AV block (atrioventricular block) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of AV block depends on its degree and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In the case of 1st degree AV block, treatment of the underlying pathology that provoked the development of the block is indicated. All patients with this degree of conduction impairment should be monitored to ensure its progression. If intoxication with digitalis preparations (digoxin, strophanthin, corglycon) is detected, they should be discontinued. With increased tone of the parasympathetic nervous system, atropine must be prescribed. Ajmaline, quinidine, procainamide, beta-blockers and potassium should be avoided due to the risk of increasing the degree of AV block [2].
Second degree AV block (primarily type I) in the absence of symptoms and signs of acute cardiac pathology usually does not require active treatment, since there are no objective signs of circulatory disorders.
Special drug treatment is necessary for second degree AV block with slow heart function, causing circulatory disorders and various symptoms. Pharmacotherapy is also indicated in all cases of acute myocardial infarction. Treatment begins with the administration of atropine and isoprenaline, which increase the conduction of impulses in the His bundle. The exception is cases when, due to a very rare rhythm and impaired blood supply, urgent placement of an artificial pacemaker is necessary. Treatment with these drugs is carried out only by a doctor.
To determine treatment tactics, complete AV block can be divided into three groups:
1. Complete AV block without symptoms . No treatment required. This form occurs in a small group of people with congenital or acquired at a young age AV block with a ventricular contraction rate of 50-60 beats per minute. These patients should be monitored, visit a cardiologist and have an ECG done once every 6 months. If your condition worsens and complaints appear, you should definitely consult a doctor. If the ventricles contract less than 40 times per minute and the QRS complexes become wider, a permanent pacemaker should be installed, even in the absence of symptoms. This will help prevent sudden cardiac death.
2. Complete AV block with impaired circulation in the brain or heart . When cerebral circulation is impaired, fainting occurs. The main method of treatment is the installation of a pacemaker. Most doctors consider even a single faint to be an indication for its installation, since each attack may be the last and lead to the death of the patient. Drug therapy is carried out if the pacemaker is ineffective or during preparation for its use. The most suitable drugs are sympathomimetics - orciprenaline (alupent), isoprenaline (isoproterenol, proternol, saventrin). They cannot eliminate complete AV block, but they can increase the automaticity of the replacement ventricular center and maintain the ventricular contraction rate within 50-60 beats per minute. The dosage of the drug is selected individually for different periods of treatment.
Impaired cardiac circulation is associated with heart failure. If fainting is not observed, complete AV block is treated with digitalis and saluretics. To increase the frequency of ventricular contractions and minute volume, long-term therapy with isoprenaline, orciprenaline or ephedrine is indicated. If drug treatment does not improve heart failure, a pacemaker may be necessary.
3. Complete AV block of acute, transient form in case of fresh myocardial infarction, intoxication with cardiac glycosides, myocarditis, after heart surgery. Corticosteroids are an effective treatment for such blockade. They accelerate the resorption of edema and stop the process of inflammation in the area of the AV system. Hydrocortisone is administered intravenously, or prednisolone in tablet form is used.
The role of saluretics in the treatment of complete AV block is still being clarified. By influencing the excretion of salt from the body, they reduce the level of potassium in the serum by 1 mEq/L. This may improve AV conduction, increase the number of ventricular contractions, and stop or reduce the frequency of syncope. It is necessary to take saluretics for a long time, be sure to monitor the level of potassium in the blood.
Types of cardiac conduction disorders
Arrhythmias are divided into the following categories:
- Impaired automaticity (sinus arrhythmia, tachycardia, bradycardia);
- Heart rhythm disturbances (ventricular extrasystole, paroxysmal tachycardia, sick sinus syndrome);
- Failure in the conduction program (increase or decrease in blockade);
- Mixed species.
Considering exactly where the failure occurs, heart rhythm disturbances are divided into atrial (supraventricular) and ventricular. Tachycardia is a heart rhythm disorder that is manifested by an increase in heart rate (more than 90 beats/min). Bradycardia is the opposite condition when the heart rate decreases to 55 beats or less.
What does normal conductivity depend on?
Studies have shown that for blockade to appear in the conduction system of the heart, damage to 1 mm of the atrioventricular communication is sufficient. The normal spread of excitation depends on:
- the content of parasympathetic and sympathetic mediators of the nervous system in the blood (acetylcholine slows down conduction in all parts, norepinephrine speeds up);
- ischemia of the myocardial zone along which the conduction pathways pass, it causes a direct block or indirect through a change in the acid-base balance in the affected area (creates a local zone of acidosis) of the heart;
- level of adrenal hormones (glucocorticoids, catecholamines);
- concentration of potassium in the blood (with hyperkalemia, conduction slows down, hypokalemia accelerates the speed of impulse transmission along the extra- and intraventricular pathways.
Symptoms
Considering each specific heart rhythm disorder, the symptoms should also be studied taking into account a certain deviation. Common complaints made by patients:
- Feeling of a hard or fast beating heart;
- Headache;
- Discomfort behind the sternum;
- Fainting;
- Blueness of the nasolabial triangle;
- Pale dermal tissue;
- Severe shortness of breath;
- Inexplicable feeling of anxiety;
- Partial or complete disorientation in space and time.
With tachycardia, the child feels a “heavy heart”, he is too overexcited against the background of general weakness, and there is a strong feeling of chest compression. With bradycardia, patients are more prone to fainting. Severe dizziness, severe cephalalgia, the patient's skin becomes sticky from cold sweat.
What can cause conduction problems?
The causes of conduction disturbances may be:
- general diseases accompanied by changes in metabolism (endocrine pathology, systemic collagenosis);
- local damage to the conduction system by zones of ischemia, inflammation, cardiosclerosis, myocardial stretching with hypertrophy of individual areas.
After scarring of the necrosis zone, myofibrils and conductive cells are gradually replaced by areas of cardiosclerosis
An inflammatory reaction (myocarditis) most often occurs when:
- acute infectious diseases of a viral and bacterial nature (influenza, ARVI, diphtheria in children, rheumatic attacks after tonsillitis);
- autoallergic processes against the background of vasculitis involving the coronary vessels;
- productive granulomatous inflammation.
The ischemic zone, caused by insufficient blood supply to the conducting fibers, depends on thrombus formation in both the right and left branches of the coronary artery. Sometimes the possible localization of a heart attack is judged by the appearance of intraventricular blockade.
Pathology is observed in acute heart attack and chronic coronary insufficiency.
Heart defects cause deformation of the heart chambers, overstretching and hypertrophy. Therefore, conduction disorders are not uncommon in children with congenital changes in the structure of the chambers and valve apparatus.
The development of left ventricular hypertrophy with hypertension and cardiomyopathy also leads to interruption of the ventricular impulse propagation pathways. In these cases, the degree of blockade indicates the severity of the lesion.
Diagnostic measures
The arrhythmia may disappear on its own. Minor disturbances in heart rhythm and conduction do not require emergency care. If failures occur too often and bother the patient for a long time, you should immediately seek help.
Diagnosis of heart rhythm and conduction disorders is based on the use of the following diagnostic techniques:
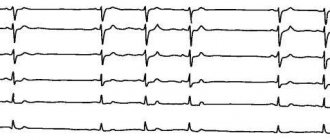
- Electrocardiography is the main way to thoroughly study the characteristics of the heart rhythm;
- ECG monitoring – recording of heart function for 24 hours on magnetic media;
- Echocadiography is used as an additional diagnostic method.
Diagnostics
- analysis of life history (past diseases and operations, bad habits, lifestyle, level of work and living) and heredity (presence of heart disease in close relatives);
- Indicators of general and biochemical analysis of blood and urine, analysis of hormonal status (hormone levels) - can identify extracardiac (not related to heart disease) causes of the blockade;
- Electrocardiography (ECG) data – allows you to identify changes characteristic of each type of blockade;
- Indicators of daily ECG monitoring (Holter monitoring) - a diagnostic procedure that involves the patient wearing a portable ECG device throughout the day. At the same time, a diary is kept in which all the patient’s actions are recorded (getting up, eating, physical activity, emotional anxiety, deterioration in health, going to bed, waking up at night). ECG and diary data are compared, thus identifying intermittent cardiac conduction disturbances (associated with physical activity, food intake, stress, or night blockades);
- Echocardiography data - EchoCG (ultrasound examination of the heart) - allows you to identify cardiac causes of blockades (heart disease leading to impaired cardiac conduction);
- The results of stress tests - recording an ECG during and after physical activity (squats, walking on a treadmill or exercising on an exercise bike) - allow you to identify blockade that occurs during physical activity, determine the heart's response to stress, and exclude myocardial ischemia (insufficient blood supply and oxygen starvation of the heart). muscles);
Heart rhythm disturbances: treatment of arrhythmia
Treatment of most types of arrhythmias is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that provoked the occurrence of systematic failures. Some conduction and rhythm disorders can be eliminated by adhering to a healthy lifestyle: eating right, giving up any strong alcoholic drinks and nicotine, playing sports, avoiding stress and psycho-emotional tension.
If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe medication. For patients with tachycardia, topical pharmacological products from the group of beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, cardiac glycosides. To generally stabilize the patient’s emotional state, sedatives are prescribed.
In some cases, patients are indicated for surgical intervention. The pacemaker is a pacemaker and helps to correct the functioning of the organ in such serious conditions as AV blockade, severe bradycardia that is not amenable to medication, and sick sinus syndrome. The treatment regimen is always selected strictly individually, taking into account the characteristics and needs of each patient.
Treatment of heart rhythm disorders
Our specialists, having made a diagnosis, try to prescribe the most effective and at the same time gentle treatment. Often, in order for cardiac conduction disorders to disappear, more attention must be paid to correcting nutrition and lifestyle, and medications become only an auxiliary tool.
In addition, if arrhythmia is detected, the diagnosis should include all possible directions - sometimes it is necessary to correct the functioning of the thyroid gland to eliminate problems. In the event that the problem is at the very heart, we are ready to provide any assistance, including prompt assistance.
Our specialists also monitor patients after treatment - if they need preventive, advisory care or checking their pacemaker.
Features of intraventricular conduction disorders
Intraventricular conduction changes are divided into:
- monofascicular (single bundle branch) - depending on the specific location of the right leg, left anterior or posterior branches;
- bifascicular (two branches) - a common left trunk, a combination of the right leg with one of the left branches;
- trifascicular - 2 left branches and the right one are blocked;
- aborization - concerns the extensive terminal ropes of Purkinje fibers, is regarded as unfavorable in the prognosis of myocardial damage;
- focal or local - characterized by limited manifestation in single ECG leads, does not apply to everyone, the shape of the ventricular complex is not similar to other types of blockades.
In terms of frequency, damage to the left leg and its branches comes first. This correlates with the most common ischemia of the left coronary artery. Identified in elderly patients with severe atherosclerosis.