A blood test is the first test that is prescribed during a preventive examination or in the presence of various complaints for patients of any age. Deviation of individual indicators from the norm may indicate a certain disease or be a consequence of a pathological or physiological process. One of the important blood indicators is ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Its increase may indicate the presence of inflammation.
ESR is usually determined during a general or abbreviated blood test, and not as an independent study. In most cases, the analysis is used to detect inflammation of various types at an early stage. To make an accurate diagnosis, one analysis is usually not enough. Diagnosis usually involves a comprehensive examination.
General information
Determination of ESR is required if acute inflammation or cancer is suspected. The test is also used to diagnose infectious diseases and evaluate the effectiveness of their treatment.
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
analysis data are generally not used in preventive screening programs. It is prescribed only if indicated. Short-term abnormalities in red blood cell counts may indicate the presence of disease, but are often explained by physiological processes. They return to normal without special treatment. Therefore, a violation of ESR when other blood parameters are normal in most cases does not signal the presence of a disease. If necessary, the patient is under the supervision of a doctor and after a certain time the test is repeated to make sure there is no pathology.
What does ESR show in the blood in adults?
Red blood cells are the main cells of the bloodstream and have the ability to “stick together” with other components of the biological fluid - globulins, albumins, etc. When pathogenic microorganisms (mainly bacterial in nature), remnants of damaged cells of internal organs, etc. penetrate into the blood, these particles also “stick together” with red blood cells, making them heavier and the rate of their sedimentation increases.
Thus, the study concludes: if the ESR value in a blood test is normal, then there are no inflammatory processes in the body, and if the indicator is exceeded or decreased, an extended diagnosis should be carried out to determine the etiology of the inflammatory process.
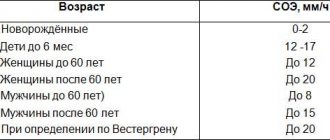
The indicator also has its own characteristics - its parameters depend on the age of the patient.
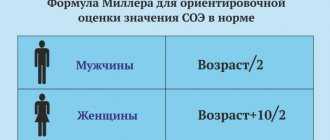
Determining the normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate makes it possible to identify inflammatory processes in men at the earliest, asymptomatic stages, and this increases the chances of quick and successful treatment. Such an analysis is usually carried out for preventive purposes, for early diagnosis, as well as to evaluate the therapy being carried out - if the ESR level returns to age-related norms, it means that the treatment is producing positive results.
Based on the results of the examination, the ESR level may be normal, increased or decreased. In the first case, we can say that the man is healthy; in the other case, we can look for a disease that led to deterioration in health or establish the physiological causes of such deviations (stress, overwork, a vegetarian diet and etc.).
ESR: norm and pathology
Reference values are differentiated by age and gender of patients. There is a special norm for pregnant women. For the age category up to 10 years, the reference ESR values are 0-10 mm/hour. At the age of 10-50 years, the norm for women is 0-20 mm/hour, and for male patients 0-15 mm/hour. For people over 50, the reference values for men are 0-20 mm/hour, and for women the norm is up to 30 mm/hour. An increase in indicators during pregnancy is usually explained by physiological processes. In infants, ESR values are low. As they grow older, they gradually increase in size.
It is important to remember that deviations from the generally accepted norm do not always indicate the presence of a disease. They may be explained by the individual characteristics of the patient. When interpreting test results, the doctor takes into account the patient's medical history, clinical picture and a number of other factors.
Calculation of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Table of contents
- Rules for preparing for the test
- What can affect the result?
- Analysis result
- Additional Research
- Which doctors refer you for the study?
- MEDSI cares about its patients
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a test that evaluates the rate at which blood separates into red blood cells and plasma.
The rate of separation is mainly determined by the ability of them to stick together. Biological material: capillary blood (for children only), venous blood.
Taking the test is recommended:
When diagnosing pathologies caused by chronic or acute inflammation, autoimmune conditions and oncological processes.
The study is performed when:
- Diagnosis and monitoring of infectious, inflammatory, autoimmune and oncological diseases
- Conducting preventive examinations (together with CBC (general blood count), leukocyte count examination, etc.)
Rules for preparing for the test
- Food.
You should not eat for 2-3 hours before taking blood. You are allowed to drink clean still water - Loads.
Excluded 30 minutes before blood sampling - Alcohol.
Excluded the day before the examination - Smoking.
Excluded 30 minutes before the test - Medications.
The day before blood collection, take it only in consultation with your doctor.
What can affect the result?
In women, ESR increases during menstruation and pregnancy.
The following also helps to increase the indicator:
- vitamin A
- oral contraceptives
- theophylline
A decrease in ESR can be caused by:
- administration of albumin
- taking corticosteroids
It is important to keep in mind that only a doctor who is aware of the medications the patient is taking and his condition can correctly interpret the diagnostic results. Therefore, in many cases, it is important to consult a doctor for advice before taking the test. The test result is also assessed by the doctor in comparison with the clinical picture.
If necessary, the specialist will refer you for other examinations. Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, an accurate diagnosis will be made.
We recommend that you consult a doctor or undergo a Checkup (a complete examination program).
To clarify the specifics of the test or make an appointment at the clinic, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500. A specialist will answer your questions and select the optimal time to visit. Registration and payment for services is also possible through the SmartMed application.
Analysis result
| Floor | Age | Reference values |
| Male | Up to 15 years | 2 – 20 mm/h |
| From 15 to 50 years | 2 – 15 mm/h | |
| Over 50 years old | 2 – 20 mm/h | |
| Female | Up to 50 years | 2 – 20 mm/h |
| Over 50 years old | 2 – 30 mm/h |
The reasons for increased ESR include:
- Infectious diseases (mainly bacterial)
- Common inflammatory diseases
- Connective tissue diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease)
- Oncological diseases: myeloma, Hodgkin's disease, cancer of various localizations
- Myocardial infarction
- Anemia
- Injuries and burns
- Amyloidosis
The reasons for a decrease in ESR include:
- Diseases that are accompanied by changes in the shape of red blood cells (hereditary spherocytosis, sickle cell anemia)
- Polycythemia
Additional Research
ESR is not a specific test, that is, the analysis can be prescribed by a doctor in conjunction with other studies. Additionally, the patient may be referred for the following tests:
- C-reactive protein
- Rheumatoid factor
- General blood analysis
Which doctors refer you for the study?
A general practitioner, hematologist, oncologist, or infectious disease specialist can refer you for diagnostics.
MEDSI cares about its patients
- You will be treated by experienced doctors and other medical personnel.
Specialists from MEDSI clinics carry out competent collection of biological material and its qualitative examination - The research is carried out using high-precision, expert-class equipment.
It reduces the risk of errors - We have the capabilities to conduct a comprehensive survey.
At the clinic you can take an ESR test and undergo other tests. This will allow you to obtain a comprehensive clinical picture of pathological conditions. - Comfortable conditions for collecting biomaterial.
We made sure there were no queues or discomfort during the procedure, even for young children and elderly patients - Opportunities for pre-registration of appointments with a doctor
- All our clinics have created comfortable conditions for taking the test.
To make an appointment with a doctor, to clarify the conditions for taking an erythrocyte sedimentation rate test (its cost, etc.), call +7 (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer all questions and suggest the optimal time to visit the clinic. Recording is also possible through the SmartMed application.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
A deviation of ESR from reference values may indicate pathology, but sometimes a change in indicators is caused by a physiological process and indicates the onset of the disease. For example, a decrease in indicators is observed in vegetarians, with prolonged fasting, and significant dehydration. Increased rates are typical for women during menstruation, pregnant women, and the elderly.
An increase in ESR may indicate the presence of diseases such as infections, inflammation, pathologies of the endocrine system, kidneys, liver, etc. A low ESR allows one to suspect circulatory disorders, genetic diseases, and epilepsy. Also, a decrease in indicators can be observed in a number of other pathologies. To make an accurate diagnosis, the results of one analysis are not enough; a comprehensive examination is required. It should be remembered that only a doctor can correctly interpret the test results.
What does increased ESR in the blood mean in men?
It is impossible to establish the exact pathology only based on ESR data in men, but its importance increases in diseases:
- musculoskeletal system (arthritis, rheumatism);
- endocrine system (hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus);
- respiratory organs (tuberculosis);
- myocardial infarction;
- paraproteinemias;
- hyperfibrinogenemia;
- injuries and fractures;
- burn injuries;
- infectious, viral (rare) and bacterial etiology;
- autoimmune nature;
- injuries (burns, fractures);
- oncological processes.
Thus, a significant excess of the norm in patients with malignant tumors indicates the development of the terminal stage of the disease and the formation of metastases. The indicator values also increase sharply in case of severe viral infections - bacterial complications of influenza, purulent sinusitis, otitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, etc. And with hepatitis C, the ESR rate increases abruptly - during the initial diagnosis it can be normal, but after a few days it can reach a level of 100 mm/h.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment that would bring the study results into line with healthy parameters. To reduce the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, you will need to establish the correct diagnosis and undergo a course of appropriate treatment. What therapy will be depends on the detected pathology and existing chronic diseases.
Normal ESR in men occurs only in absolute health, but in most patients there are minor deviations up or down. If the changes are not critical and other parameters of the biological fluid are normal, the patient is recommended to undergo a repeat study in two to three weeks.
False parameter changes
An increase or decrease in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in representatives of the stronger sex can also be caused by physiological reasons not related to dysfunction of internal organs. Thus, the ESR level may increase if you are allergic to medications or food.
A false decrease is observed when:
- fasting;
- refusal of animal products (vegetarianism);
- treatment with glucocorticosteroids.
If in adult men the ESR level in the blood drops to 10 mm/h and below, this indicates the absence of inflammatory processes in the body.
How to prepare for analysis
To eliminate errors in the results, the patient needs to properly prepare for the collection of biomaterial. For this analysis, the rules are not complicated: take it on an empty stomach, i.e. 8-12 hours after the last meal, and inform the laboratory assistant about all medications taken, because they may affect the final outcome of the study.
You should also stop drinking alcohol for 2-3 days. One hour before blood collection, you should not smoke. You should also limit physical activity and avoid emotional stress.
It is allowed to drink still water on the eve of the study (teas, juices, coffee, etc. are excluded).
Read further: Is it possible to drink alcohol before donating blood for analysis?
Diagnostics
The ESR norm is determined in two ways (Panchenkova, Westergren), but their essence is the same: biological fluid is mixed with an anticoagulant, a substance that prevents its clotting. And then they are left to separate the red blood cells from the plasma. The difference lies in the accuracy of the data obtained.
Panchenkov method
The study requires capillary blood obtained by puncturing the fingers on the hand, and a special pipette - a glass tube with a scale from 0 to 100. Biological fluid (1 part) is mixed with anticoagulants (4 parts), placed vertically and left for 60 minutes. The mark on the scale that appears after an hour, which separates plasma and red blood cells, is the desired result.
This technique has not received wide recognition in Europe and is used most often in Russia and the countries of the post-Soviet space. The sensitivity of the method is inferior to the Westergren analysis.
Westergren method
It is he who is approved by the World Health Organization, because... during the study, a more accurate scale is used, already 200 divisions located exactly 1 millimeter from each other. The second difference is that the technique is carried out by examining blood obtained from the cubital vein.
Otherwise, the research procedure is the same as Panchenko’s method: biological fluid is mixed with an anticoagulant and left for 1 hour. Afterwards, the data corresponding to the scale between the translucent plasma and the formed precipitate is noted.