Some people sometimes have a question: how to deceive an ECG? Moreover, some want to achieve a good conclusion in order to get a job, while others, on the contrary, want to make things worse so as not to serve in the army. There are other reasons that prompt a person to deliberately deceive not only the doctor, but also the diagnostic apparatus. Naturally, if you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the procedure, then the results obtained can be distorted, but will this help achieve your goal? And is it possible to simulate angina pectoris, arrhythmia, RGC syndrome and other diseases on an ECG?
Indications for the procedure
The examination is carried out only with a referral from a cardiologist. A visit to the doctor can be either planned or in case of complaints about heart function.
Frequent symptoms of impaired heart function include conditions such as:
- Compressive pain in the chest, as well as in the region of the heart, which radiates to the shoulder blade;
- Rapid pulse, which causes dizziness and increased heart rate;
- Shortness of breath with minor exertion;
- Periodic fainting;
- Dry barking cough;
- Swelling of the lower extremities.
Particular attention is paid to patients who have suffered a stroke, have congenital heart abnormalities or rheumatism.
Specialists conduct an examination and give a referral to see a doctor if they find:
- extraneous noise in the work of the heart muscle;
- with low or high blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
The following categories of citizens are subject to mandatory examinations, namely:
- Persons with congenital or acquired heart disease;
- Athletes who have a serious load on their heart function;
- Patients undergoing examination before surgery;
- Women who are pregnant.
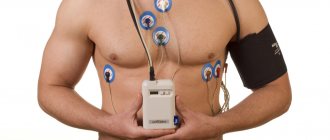
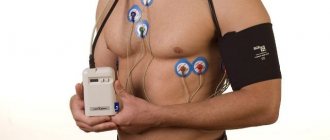
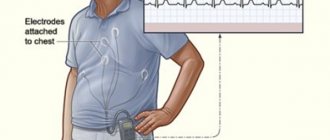
Holter
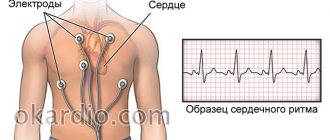
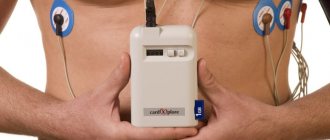
A holter is attached to the patient, most often on a belt, in a special case and electrodes are applied.
Doctors often use the phrase “hang a holter” or “do a holter,” meaning that the device will be used for 24 hours, on an outpatient basis, in the patient’s usual living conditions - at home, at work, during night sleep. Patients are asked not to wet the device, but otherwise lead their usual lifestyle.
This process of taking readings is called Holter monitoring, named after the American research scientist Norman J. Holter, who first used this technique in 1961.
Why do you need a holter?
It would seem, why do you need a Holter if you can just go to the doctor and take an ECG? Often, people with heart health problems experience the following situation: they have complaints, but they arise when it is not possible to immediately see a doctor - in the evening, at night, during some events.
The next day the person goes to the clinic, an ECG is taken, but no abnormalities are found.
Why might this happen? Because a standard electrocardiogram is a record, like a “snapshot,” that records cardiac activity over a short period of time.
A regular ECG records only a few myocardial contractions: from three to twenty, depending on the cardiograph used for this purpose.
Whereas the heart contracts about 100 thousand times per day! Holter records an ECG throughout the day, and not a single heartbeat during this period will go unnoticed by the device, because the electrocardiogram is recorded continuously. Holter makes available for analysis that information about the patient's heart health that cannot be obtained during a short visit to the doctor, and this is the most important diagnostic value of this device.
Then the holter is removed from the patient, and with the help of a special computer program that processes the data obtained, all types of heart rhythm disturbances, painless and painful attacks of myocardial ischemia, etc. are identified and analyzed.
Holter is a device that allows both accurate diagnosis of heart disease and helps to treat cardiovascular diseases - hypertension, atherosclerosis, heart attack, myocarditis - much more effectively.
24-hour monitoring, which Holter proposed, is a procedure that identifies almost all possible cardiac abnormalities that appear during the day, which cannot be done using other methods of cardiac diagnostics currently used.
Holter monitoring is a simple and safe procedure. In order to carry it out, two visits to the doctor will be required. On the first visit, the holter is programmed and installed on the patient; this procedure takes no more than a quarter of an hour. In a day, the holter will need to be removed and its records analyzed.
These actions usually take the doctor about half an hour or an hour - in more complex cases. Modern clinics often offer Holter monitoring at the patient’s home: all necessary visits are made by the doctor himself.
This is certainly very convenient, especially if the study is required by an elderly, sedentary person.
How to deceive Holter?
Very often, patients of military age try to deceive the holter by running tirelessly up the stairs and bringing themselves to complete exhaustion, imitating tachycardia. But I hasten to disappoint those who came here in the hope of learning how to deceive Holter - Meditech 24-hour blood pressure and ECG monitors are equipped with special sensors that, together with an experienced doctor, always recognize malingerers.
When is a halter needed?
Holter monitoring may be indicated for a patient if:
- there are complaints resulting from heart rhythm disturbances (palpitations, dizziness, loss of consciousness);
- diagnosis of coronary heart disease is required;
- it is necessary to preventively monitor patients with threatening ischemia and arrhythmias;
- it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment;
- “white coat” hypertension is present;
- arterial hypertension has been detected for the first time, and the heart needs to be examined in order to decide whether to begin drug therapy;
- the fact of chronic constitutional hypotension was revealed;
- Moderate to severe hypertension, resistant to previous treatment, was diagnosed.
In addition, it is advisable to use a Holter if the patient has congenital heart defects, both unoperated and operated, or if he has suffered a myocardial infarction; to evaluate the performance of a pacemaker; in all cases of acute and chronic heart failure. A Holter monitoring procedure would be useful for people who are overweight (obese) or have diseases of the endocrine system.
How to prepare for Holter monitoring?
If the patient is to wear a halter, then during the 24 hours during which the study will be carried out, he must live his normal life - work, relax, meet people, and perform his usual physical activities.
Some doctors, when installing a holter for their patients, ask them to keep an activity diary during the 24-hour examination. This diary should record everything that affects cardiac activity: sleep, medication, movements, etc. This is not always necessary.
Firstly, because constant attention to the process on the part of the patient can affect the reliability of the result (the person will only think about what the Holter shows in the event of one or another action).
And, secondly, a modern holter can have a built-in sensor that records the patient’s physical activity, from which it is possible to determine at what moment the patient was sleeping and at what point, for example, he was running in the park. During the analysis, these points are clarified.
Modern Holter records not only an electrocardiogram, but also performs actigraphy (this is the recording of the patient’s physical activity) and monitors blood pressure.
The software, which is used to analyze the parameters recorded by Holter, allows you to effectively and quickly identify both heart rhythm disturbances and obtain a clear picture of how the autonomic nervous system regulates the functioning of the heart.
During Holter monitoring, no special actions need to be taken. You just need to remember that a holter is a complex, expensive electronic device, and your attitude towards it should be appropriate. This means:
- The halter should not be wetted - take a bath, shower, or swim in open water with it;
- Do not expose the holter to low or high temperatures (for example, do not go to the bathhouse on the day of the test);
- The device must be protected from shock and vibration. It is advisable to avoid contact with aggressive household chemicals, especially those containing acids, during Holter monitoring.
In addition, heavy, prolonged physical activity is very undesirable, since, firstly, it can distort the results of the study, and secondly, due to increased sweat, the electrodes may come off.
A patient wearing a halter is advised not to be near transformer booths or powerful power lines. And also come close to working electrical household and medical equipment.
During the examination, it is better to give preference to cotton underwear and avoid wearing clothes made of synthetic and silk fabrics, which can accumulate static electricity.
Holter is a medical device with which 24-hour monitoring of heart activity is carried out - an important and serious study, the relevance of which is undeniable these days.
Source: https://formed.ru/glossary/holter/
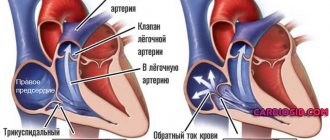
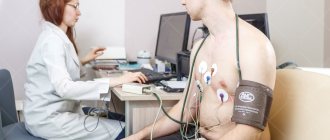
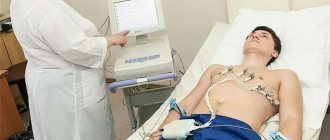
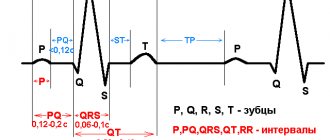
What is electrocardiography and the features of its implementation?
The principle of this examination method is based on recording electronic pulses of the heart that occur during myocardial contraction. The pulses that have arisen are read by the cardiograph, displaying them in the form of a graphic curve on special paper.
Order of conduct:
- Before the procedure, all jewelry should be removed;
- Expose the chest, ankles and hands;
- Lie horizontally and relax;
- Before applying the electrodes, the nurse should treat exposed skin with a cotton pad, which is moistened with water for better conductivity of the impulses.
- Afterwards, 4 electrodes of different colors are applied to the limbs in a certain sequence;
- They are fixed on the chest using suction cups. The number of the latter should be 6 pieces;
- The electrodes are connected to the device, then they are registered.
A cardiogram is necessary when detecting any heart disease; it is also prescribed during a preventive examination.
Using this examination, you can identify such disturbances in the functioning of the heart as:
- Heart rhythm disturbances, for example, tachycardia, arrhythmia, extrasystole;
- Impulse conduction disorder, for example, antiventricular block;
- Myocardial nutritional disorders, for example, heart attack, ischemia;
- Congenital or acquired diseases, for example, disorders in the structure of the fibrous ring, valves, chord;
- Myocardial thickening, for example, atrial ventricular hypertrophy.
Persons who have reached the age of 40 years old must undergo an ECG every year. This will help to identify violations in time at the initial stage.
This study is quite informative, however, despite this, to clarify the diagnosis it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the heart.
The study is very effective and indicative, but despite this, to clarify the condition of the myocardium, it is necessary to resort to ultrasound diagnostics of the heart.
Pros of the procedure
Among the undeniable advantages are the painlessness of the procedure, safety, and the ability to obtain reliable data. In addition, another advantage is that the procedure does not take much time.
Also, the procedure has no contraindications, and due to the mobility of the device, diagnostics can be carried out outside the clinic.
Disadvantages of the procedure:
The disadvantages of the procedure include the following:
- short recording;
- inability to record heart murmurs;
- impossibility of diagnosing heart defects and various tumors;
- To obtain reliable data, the procedure should be carried out at rest or under load.
What is cardiac ultrasound?
Diagnosing the heart using ultrasound is a fairly new method used in cardiology, called echocardiography. The procedure is performed using a special device - an electrocardiograph, which regenerates ultrasound, the rays of which penetrate through the chest, determining the condition of the soft tissues and the thickness of the myocardium. This technique is absolutely safe for the patient. In addition, it has high information content and reliability of the results. The procedure is necessary for:
- determination of congenital pathology in children.
- identifying any diseases in adults;
- confirmation of the diagnosis of heart attack;
- thrombosis detection;
- detecting tumors in the breast;
- monitoring the state of the myocardium.
An ultrasound of the heart must be performed in cases where a person has abnormalities in the functioning of the heart that cannot be determined using an ECG or the diagnosis needs to be confirmed.
Ultrasound can reveal:
- Hidden heart defects;
- Enlargement and compaction of the myocardium;
- Accumulation of fluid in the heart;
- Pathological changes in the contractility of the organ;
- Establishing the speed and nature of blood movement through the aortas and chambers of the organ;
The disadvantage of the procedure is the inability to detect disturbances in the passage of electrical impulses.
This diagnosis allows you to identify even minor disturbances in the functioning of the heart that cannot be determined using an ECG.
Pros of the procedure
The advantages of ECG and ultrasound are very similar. Ultrasound diagnostics is also highly informative, painless, and harmless to the patient. The procedure does not require any special preparation. Using this method, you can assess the state of heart health, as well as track genodynamics.
In addition, the advantages of the procedure also include the fact that during the procedure the specialist can listen to how the heart beats. This allows you to determine whether there are extraneous noises in the heart. And due to the echogenicity of tissues and organs, a tumor can be noticed in time.
Cons of the procedure
The disadvantages of this procedure include:
- low resolution;
- limited image clarity;
- a lot of interference.
It should be mentioned that another disadvantage is the need to perform special training when it comes to diagnosing diseases of the abdominal organs.
How to slope along a halter
What and how to do so that the examination shows unimportant results. I have my examination today at 2 p.m.
00 as far as I understand, if on the issue of Holter extrasystoles, then drink coffee and run like crazy, if on the issue of bradycardia and blockades, then drink valerian and other sedatives and lie on the couch all day and massage either the left or right carotid artery, hold your breath, strain, etc. Google carotid techniques and what should doctors write on the paper? Here is my diagnosis.
So the first option suits me, I need to load myself up, right? Spend the day actively. If something is there, it will manifest itself, if not, you will not be able to cause it with anything.
Many diseases of the cardiovascular system occur latently in the initial stages and make themselves felt when a serious pathology develops and a threat to life and health arises.
To avoid serious consequences, if you suspect any heart disease, you need to conduct a full examination. Today, there are many effective diagnostic methods, one of them is ABPM (24-hour blood pressure monitoring).
- What it is?
- Holter ECG and ABPM simultaneously
- ABPM during pregnancy
- How is the examination carried out?
- On what part of the body is the device placed?
- Where to do the procedure?
- Decoding the results
- How to deceive ABPM
| Restoring blood pressure at home |
| How to reduce high diastolic pressure? |
Foods that increase blood pressure Normal blood pressure in a child Systolic pressure is high and diastolic pressure is low: reasons
What it is?
The essence of the method for studying the state of the cardiovascular system is to constantly measure blood pressure and its fluctuations throughout the day. Measurements are carried out using a device - a sphygmomanometer.
A typical blood pressure measurement with a blood pressure monitor, which can be done only a few times, usually does not provide a complete picture of a person's health. A person’s blood pressure levels constantly fluctuate - this depends on many factors: physical activity, the person’s emotional state, and taking various medications.
ABPM allows you to take into account all possible daily fluctuations in blood pressure - measurements and their recording are carried out continuously throughout the day. Based on the average blood pressure per day and the nature of fluctuations, it is possible to determine whether a person has any pathologies of the cardiovascular system, whether treatment and further examinations are needed.
Undergoing a medical procedure may be indicated in many cases. ABPM is usually prescribed for the following reasons:
- Diagnosis of arterial hypertension (high blood pressure). ABPM is used for various borderline conditions and doubts in making the correct diagnosis. This technique is also required if elevated blood pressure is detected against the background of various neurological disorders, or with heart failure.
- Diagnosis of arterial hypotension (low blood pressure), as well as various disorders associated with the manifestation of low blood pressure.
- Control of drug intervention. Daily monitoring helps to better understand how effective the intervention is and whether it is possible to select a more suitable drug. ABPM helps to monitor the dynamics of changes in various diseases and therapy.
ABPM is often prescribed if you need to assess the state of the cardiovascular system as objectively as possible in a short period of time. For example, this is often required when determining fitness or unfitness for military service. Making many cardiac diagnoses can take a long time, and 24-hour monitoring can speed up this process.
ECG using the Holter method is a daily electrocardiogram, when heart rhythm readings are also recorded continuously.
This technique is required for many diseases; it can also be prescribed to a healthy person for sleep disorders and many other conditions.
The advantages of the examination are the same: constantly monitoring changes allows you to get the most complete picture of the health of the cardiovascular system.
Sometimes ECG and ABPM are combined and performed simultaneously. Tracking all changes in heart rhythm simultaneously with the dynamics of blood pressure provides enough information for a specialist to determine the final diagnosis for many conditions where single measurements are not enough.
This study can be performed during pregnancy if there is a suspicion of a pathological increase in blood pressure. Carrying a child is not included in the list of contraindications to this diagnostic method.
Blood pressure dynamics are checked throughout the day using a special device. The device records the blood pressure level constantly, every fifteen minutes or half an hour - there are different methods and device settings.
You will have to wear the device on yourself throughout the day. It is worth noting that this usually does not cause any particular difficulties. The subject is required to spend the day as he normally spends it. It is important to track the dynamics of changes that are constantly present in the norm.
A device for measuring blood pressure throughout the day - a sphygmomanometer - consists of a conventional cuff, which is usually attached to the shoulder, and the device itself. The cuff functions like a regular blood pressure monitor - periodically inflating and then deflating. The device is usually attached to the belt.
The device should be worn without removing it for the entire specified measurement time. Usually one day is allotted for this; in rare cases, measurements last forty-eight hours.
If the end time of the study falls on the weekend or any other time when the site where the study was started is closed, the 24-hour blood pressure monitor should be removed and turned off independently.
Also, during measurements, an activity diary is usually kept. It should describe what the subject is doing and indicate the exact time. This will help specialists analyze the device readings after the examination. For example, if a person was engaged in physical activity, an increase in blood pressure during this period will be considered normal and not a deviation.
Also, subjects are usually asked to follow the following rules so that the measurement results are as reliable as possible:
- It is imperative to monitor the position of the cuff. It should be two fingers above the elbow. If it slips down or becomes unfastened, it should definitely be corrected. Some devices do not record at all if the cuff is not in the correct position.
- Before starting the next measurement, it is advised to prepare and stop during it, if it begins while walking, playing sports, or other vigorous activity. Instruments usually beep before and after measurement. If there is no signal or cannot be heard, you can determine the start of the measurement by the inflating cuff.
- The tube that connects the device itself and the cuff should not be twisted or compressed.
- If the next measurement causes severe discomfort, it should be stopped. This is usually done using the stop button on the monitor. The next measurement will be as scheduled.
- If any disturbances in the operation of the device are noticeable, the air does not come out of the cuff completely, the monitor shows a malfunction, the device can be removed and turned off, after which you need to take it back to the specialist. You may need to perform the procedure again with a working device.
- If the result is not displayed on the monitor and the time is not marked on it, this indicates that the batteries are discharged and no further measurements will be taken.
- Do not expose the device to liquids or high temperatures. If for some reason you need to remove the cuff, the device must be turned off. If measurements are taken while the cuff is not on the arm, it may burst.
After all measurements have been taken and the study time has ended, the ABPM device and the activity diary must be taken back to the doctor. You should then wait until the study transcripts are ready.
Such diagnostics can be carried out free of charge upon referral from a cardiologist with suspicion of any disease or disorder related to the level of blood pressure.
If there is no referral, you should contact specialists yourself. ABPM can be performed in various clinics and private cardiologists. The average cost of an examination is from 2000 rubles.
After the diagnosis is completed, the results are analyzed, after which the conclusion is given to the patient. It usually contains all the data on lower and upper blood pressure for the entire measurement time, taking into account differences and other factors. To a person without special education, most of the information will mean almost nothing, so with a transcript you should immediately contact a cardiologist.
The result of the study may be alarming if the subject was assigned to the group of so-called “non-dippers” - people with an insufficient degree of reduction in blood pressure at night. This can be an extremely negative sign.
So which study is better: ECG or ultrasound of the heart?
Ultrasound and ECG are two diagnostic methods that are used in cardiology to diagnose problems in the functioning of the heart muscle. Based on the results, the specialist assesses the degree of damage to the organ and selects the most appropriate treatment method.
The data obtained from both studies have equally high information content, but the results of the ultrasound examination provide a more meaningful picture. That is why, before conducting any examination, you should visit a cardiologist, who, based on the patient’s complaints, will be able to determine the most appropriate examination method. In most cases, an ECG is considered the primary procedure, because it allows you to get a general picture of the condition of the heart muscle. If the cardiologist does not like the resulting picture, then he can prescribe a more accurate procedure, namely an ultrasound.
Both methods are independent of each other and it is not possible to determine which one is better, because both of them must be completed periodically if there are complaints about the work of the body. Thus, timely detection of heart disease will help to avoid more serious consequences.
Who should not conduct
There are absolute and relative contraindications to performing ECG stress tests.
Absolute:
- the first 2 days of acute myocardial infarction;
- unstable heartbeat without prior drug treatment;
- pronounced signs of aortic stenosis;
- acute pulmonary embolism;
- acute pericarditis and myocarditis;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm, occurring in an acute form.
Relative:
- aneurysm of blood vessels or heart;
- hypertension with systolic blood pressure above 200 and diastolic blood pressure above 110 mmHg. Art.;
- tachyarrhythmia of unknown origin;
- bradyarrhythmia with pronounced symptoms;
- heart block;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- severe heart rhythm problems, fainting;
- mental or physical disorders that prevent adequate physical activity;
- electrolyte disturbances;
- joint diseases;
- severe anemia;
- endocrine diseases;
- severe obesity.
Testing is not recommended in case of fever, acute thrombophlebitis, or recent stroke. However, relative contraindications are neglected if the significance of the diagnostic results outweighs the risks.
During the procedure, the patient is constantly under the supervision of a specialist. If during the examination a severe arrhythmia, sharp chest pain, increased blood pressure, dizziness, darkening of the eyes occur, or your health deteriorates significantly, the testing is stopped immediately.