Our clinic is unique for Russia, as we use revolutionary methods of restoring blood flow, including microsurgical, endovascular and plastic surgeries. We manage to save more than 95% of limbs in patients with critical ischemia.
Critical leg ischemia is an emergency condition that requires immediate measures to improve blood supply. If the blood supply is not improved, then amputation of the limb is the only method that can save the patient from suffering and death. The danger of critical ischemia is that blood, through clogged vessels, very poorly fills the lower parts of the legs and causes their gradual death. Insufficient blood circulation does not allow the necessary medications to be delivered to the tissues of the foot and toes, which reduces the possibilities of therapy.
Anesthesia
An exhausted person needs a break from suffering. Without such rest it is impossible to continue treatment. The body simply cannot withstand any active methods. Long-term epidural anesthesia relieves pain best. A thin catheter is installed in the back, into which a painkiller is injected as needed. Anesthesia allows you to lay the patient horizontally and somewhat eliminate the swelling of the limb, and conduct the necessary studies.
Narcotic analgesics (tramadol, promedol, morphine) do not have a sufficient analgesic effect, but they allow you to dull the sensations and fall asleep. The downside is the development of tolerance and drug dependence. In some surgical departments, the use of drugs and their subsequent withdrawal can persuade the patient to amputate. Non-narcotic analgesics and sleeping pills have a very weak effect on pain, do not counteract the development of depression, and contribute to the development of acute psychosis after restoration of blood flow.
Neurostimulation is an effect on the sensitive bundles of the spinal cord using a special electrical device. Good and long-term pain relief without the administration of drugs. Allows pain relief for patients who refuse surgery. The downside is that gangrene continues, and the price for the device is about $30,000.
Stages of development and clinical picture
- Against the background of inflammatory and diabetic lesions of blood vessels, a gradual narrowing of their lumens occurs and subsequent blockage by blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques. In this regard, the nutrition of the lower extremities is significantly impaired.
- First, the body tries to compensate for the deficiency of nutrients and oxygen by activating the work of smaller bypass vessels. It is this process that entails the development of the first alarming symptoms - acute pain in the legs and intermittent claudication when covering a distance of no more than 30-35 m.
- Next, stagnant edematous phenomena occur, which further disrupt blood and lymph flow, squeezing the arteries. The nerve endings become inflamed, aggravating the already severe pain syndrome. Now it is characteristic of the patient and in a state of complete rest, even sleep.
- With the inevitable failure of compensation, the peak of critical ischemia occurs. If emergency medical intervention does not occur at this moment, tissue necrosis (death) begins. A gangrenous limb should be amputated, otherwise death is inevitable.
Symptoms of ischemia of the lower extremities are quite specific:
· Acute pain in the muscle tissue of the leg at rest;
· Intermittent claudication (forced stoppage of movement due to severe pain in the calf muscles);
· Deficiency of blood supply to the legs, accompanied by numbness, cooling and tingling;
· Formation of trophic ulcers, mainly in the area of the feet and toes;
· Presence of necrotic (dead) tissues;
· Blackening or bluish discoloration of the skin at the affected sites;
· Signs of decomposition of the tissues of the fingers or feet;
· Gangrene.
The pain syndrome is so intense that it cannot be relieved with conventional painkillers. During the active progression of the pathology, patients manage to relieve pain by changing body position and lowering their legs. Some patients sleep with their limbs down from the bed. In this case, the outflow of venous blood is disrupted, it accumulates in the tissues and puts more pressure on the vessels, which provokes the accelerated appearance of ulcers and necrosis.
Intermittent claudication is another obvious clinical manifestation of this pathology. It is characterized by acute pain in the calf muscles when walking short distances. An acute attack forces the patient to stop for a break, after which the pain gradually recedes. A similar sign can be noted after traveling a kilometer distance, and this is already a good reason to contact a specialist, since “painless” distances are quickly reduced due to the progression of the disease.
Considering the extremely dangerous consequences of critical ischemia of the lower extremities, if any symptom appears, you should urgently contact an angiologist or phlebologist.
Improving collateral blood flow
- Prostaglandins
Discovering all possible bypass routes to the blood supply. For this purpose, prostaglandin preparations (alprostan, vazaprostan) have proven themselves best. They are used in the form of long-term 3-5 hour intravenous infusions. The use of prostaglandins can sometimes reduce critical ischemia and save the limb. Physiotherapy (magnetic field, laser) serves the same purposes. These patients can be treated with conservative therapy for no longer than two weeks. If there is no effect, then resolve the issue with revascularization.
- Improving blood flow
It is necessary to examine the coagulation and anticoagulation system, blood viscosity, cholesterol, fat and protein content, and other indicators. It is necessary to eliminate the identified violations as much as possible. For this purpose, intravenous infusions of various drugs rheopolyglucin, dextrans, and trental are used. Increasing the oxygen content in the blood Hyperbaric oxygenation (a chamber with increased oxygen pressure) is used. The principle is simple - as pressure increases, the solubility of oxygen in the blood increases; more oxygen in the blood means more is released into the tissue. Infusions of perftoran, artificial blood that stimulates the release of oxygen into tissues, can be used.
- Stimulation of new vessel growth – Neovasculgen
To date, genetic drugs aimed at stimulating vascular growth have proven ineffective. Neovasculgen, the most advertised and expensive drug, was tested in our clinic, but we did not observe any effect in patients with critical ischemia. The basis of the treatment of chronic ischemia is to improve blood circulation in the lower leg and foot. The hope for drug treatment, including the use of prostaglandins (vasaprostan, ilomedil, alprostan), did not materialize, since the drugs do not reach the tissues due to serious damage to small vessels. Another therapeutic method that was of interest to surgeons and their patients was the Neovasculgen gene therapy complex. The drug is a virus-like particle that carries a gene that enhances the growth of small blood vessels. We used this drug in our clinic in patients with complex vascular pathology, but did not notice a noticeable effect. These patients required vascular surgery, and some even required amputation.
Causes and risk factors
The main causes of critical ischemia of the lower extremities are:
- Obliterating atherosclerosis - vascular lumens are blocked by cholesterol (atherosclerotic) plaques;
- Thrombosis - an artery is blocked by a blood clot (thrombus) at the site of its initial formation or subsequent movement (embolism);
- Endarteritis – the inflammatory process persists, provoking vasospasm;
- Thrombangiitis, or Buerger's disease - inflammation occurs that affects arteries and veins of small and large caliber;
- Diabetic angiopathy (vascular damage caused by decompensated diabetes mellitus);
- Mechanical injuries of large arteries.
Prevention
These measures help stop the progression of the disease and restore full functional activity of the body.
In addition to constantly taking medications, patients need to exercise. Walking, cycling, swimming will be useful.
It is important to follow a diet limiting fatty foods, fried, smoked, spicy foods, coffee, alcohol, and sugar. Lean meat and fish, vegetables, fruits, herbs, cereals, bread and pasta made from durum wheat will be beneficial.
Once every six months, patients need to undergo physiotherapy and massage sessions.
Therapeutic measures
Scientific research in the field of medicine has not yet been able to definitively resolve the issue of therapy when ischemia occurs. But the main rule has been formulated - treatment of the disease must be long-term, complex and continuous. It is necessary to increase the speed of blood flow through the vessels, to prevent atherosclerotic deposits and thrombus formation.
For this purpose, patients with ischemia are advised to quit smoking, follow a proper diet, treat concomitant diseases and lead a healthy lifestyle. Physical therapy is very useful.
The following drugs are recommended for therapeutic treatment:
- disaggregants - “Curantil”, “Trombo ACC”;
- antioxidants - "Dibikor";
- fibrinolytics - “Streptokinase”, “Fibrinolysin”;
- antispasmodics - “No-shpa”.
To correct lipid metabolism in case of ischemia, it is necessary to take drugs that improve microcirculation (Cavinton, Trental). Physiotherapy - magnetic therapy, dynamic currents, regional barotherapy - will be of great benefit.
Important! Initial degrees of ischemia are very treatable, so timely diagnosis is very important. Only a specialist should deal with these issues
Self-diagnosis and self-medication can provoke the opposite effect and cause a rapid deterioration of the condition.
Need for surgery
Surgical treatment of ischemia is aimed at removing plaques and blood clots from the lumen of the arteries. The need for such therapy is dictated by the need to expand the lumen of blood vessels and restore normal blood flow for complete blood supply to tissues and organs.
The decision on the conduct and extent of surgical intervention is made by the vascular surgeon after conducting all the necessary studies.
Surgical methods for treating ischemia include balloon angioplasty, endarterectomy and bypass surgery followed by prosthetics.
Timely surgery allows you to save your legs in 90% of all cases of the disease. If intervention is refused if indicated, limb loss is inevitable.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease depends on the stage of ischemia at which the initial visit to the hospital occurred, the duration of CCI, the extent of vessel damage, the height of occlusion, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies.
If you go to a medical facility in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable.
Attention! The development of CLI is an unfavorable prognostic sign and in most cases requires limb amputation.
Acute ischemia of the lower extremities
Acute ischemia usually develops as a result of thrombosis of the arteries supplying blood to the leg. The most common cause is the formation of blood clots in the cavities of the heart due to arrhythmia. A blood clot can break off and travel through the bloodstream into an artery, thereby disrupting the blood supply to the leg. Arterial thrombosis can also be caused by alcohol abuse, thrombophilia, atherosclerosis, and so on.
Symptoms
The patient feels pain, numbness, coldness, movements are impaired, the patient cannot move his leg, the leg becomes “not normal.” Symptoms occur abruptly and progress very quickly. If timely medical care is not provided, gangrene develops.
Treatment
In case of acute ischemia, emergency surgery is required - thrombectomy. A special device, a thrombus extractor, removes the blood clot from the artery and restores blood supply to the leg. The ideal time to perform the operation is less than 6 hours from the onset of the disease. If you have the above complaints, immediately call an ambulance.
Therapeutic measures
Scientific research in the field of medicine has not yet been able to definitively resolve the issue of therapy when ischemia occurs. But the main rule has been formulated - treatment of the disease must be long-term, complex and continuous. It is necessary to increase the speed of blood flow through the vessels, to prevent atherosclerotic deposits and thrombus formation.
For this purpose, patients with ischemia are advised to quit smoking, follow a proper diet, treat concomitant diseases and lead a healthy lifestyle. Physical therapy is very useful.
The following drugs are recommended for therapeutic treatment:
- disaggregants - “Curantil”, “Trombo ACC”;
- antioxidants - "Dibikor";
- fibrinolytics - “Streptokinase”, “Fibrinolysin”;
- antispasmodics - “No-shpa”.
To correct lipid metabolism in case of ischemia, it is necessary to take drugs that improve microcirculation (Cavinton, Trental). Physiotherapy - magnetic therapy, dynamic currents, regional barotherapy - will be of great benefit.
Need for surgery
Surgical treatment of ischemia is aimed at removing plaques and blood clots from the lumen of the arteries. The need for such therapy is dictated by the need to expand the lumen of blood vessels and restore normal blood flow for complete blood supply to tissues and organs.
The decision on the conduct and extent of surgical intervention is made by the vascular surgeon after conducting all the necessary studies.
Surgical methods for treating ischemia include balloon angioplasty, endarterectomy and bypass surgery followed by prosthetics.
Timely surgery allows you to save your legs in 90% of all cases of the disease. If intervention is refused if indicated, limb loss is inevitable.
Diagnostics
To identify critical leg ischemia, the doctor examines the patient and analyzes his complaints. When examining the lower extremities, the following signs are revealed:
- skin changes;
- significant weakening or complete absence of pulsation;
- intermittent claudication.
The following methods are used as physical tests:
- ankle-brachial index - the ratio of pressure values on the ankle and shoulder is established (with vasoconstriction it decreases, and with stiffness of the vascular walls it increases);
- treadmill marching test - used to determine the distance after which pain occurs.
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of damage to leg tissue and deterioration of blood circulation, the following studies are carried out:
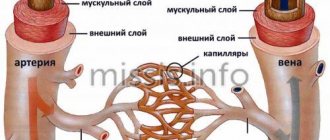
- Doppler ultrasound – visualizes the condition of the vascular walls and the quality of blood flow;
- CT and MRI - allow you to accurately determine the degree of tissue damage, study the condition of the vascular walls and the quality of blood flow;
- electrothermometry and capillary oscillography - assess the patency of blood vessels;
- arteriography and capillarography - carried out to monitor the dynamics of pathology;
- blood tests - carried out to identify the causes of atherosclerosis and determine the indicators of the blood coagulation system.
Staged course
- The initial stage is characterized by a minimum of symptoms: the unreasonable occurrence of fatigue in the legs with little physical activity (walking up to 1 km), the appearance of stabbing sensations and chilliness in the feet, the skin is cold and pale to the touch.
- At subsequent stages, more intense manifestations occur:
- pain in the legs with the inability to move at the usual speed (“intermittent claudication”), which occurs after covering a distance of 200 m;
- pallor of the skin of the legs, hair loss, decreased elasticity of the skin, and trophic lesions appear.
Chronic ischemia with severe vascular occlusion leads to:
- pain at rest or with minimal physical activity (inability to overcome 25 m);
- muscle transformations (atrophic phenomena and weakness);
- the appearance of cracks due to minor injuries, ulcers, in the nail plates of the toes - inflammatory processes (felons).
When the lumen is blocked in the upper parts of the abdominal aorta, there are necessarily signs of ischemia of the pelvic organs (disorder of stool, urination, dysfunction of the genital organs).
- Vascular ischemia of the lower extremities
Classification
The classification of ischemic lesions of the lower extremities with the formation of a sudden decrease in the vascular lumen (occlusion) provides for the level of blockage.
- Abdominoaortic obstruction:
- high (above the arteries of the kidneys).
- average;
- low (behind the mesenteric artery, which arises from the aorta).
- Blockage of arterial vessels of the lower extremities:
- high;
- low.
Taking into account the intensity of clogging manifestations, the following forms are provided:
- acute;
- chronic;
- critical.
Of great importance is the division of the pathological process according to the degree of hypoxia - I-IV degrees.
Treatment
In the first stages, the disease is treated very simply - the patient undergoes regular examinations and takes preventive measures. Blood clotting medications are taken to prevent a sudden blockage of an artery by a blood clot - medications containing acetylsalicylic acid are used, such as Aspirin, Anopyrin, Godasal, or drugs containing clopidogrel, such as Plavix, Trombex, Zilt.
In addition, medications are prescribed to lower cholesterol levels and medications to lower blood pressure. Therapeutic assistance consists of angiography, which shows the narrowing of the blood vessels and allows them to be enlarged by angioplasty. However, vascular surgical interventions are also possible. In advanced stages of the disease, lower limb amputation is often the main treatment option.